路径规划——RRT算法
算法原理
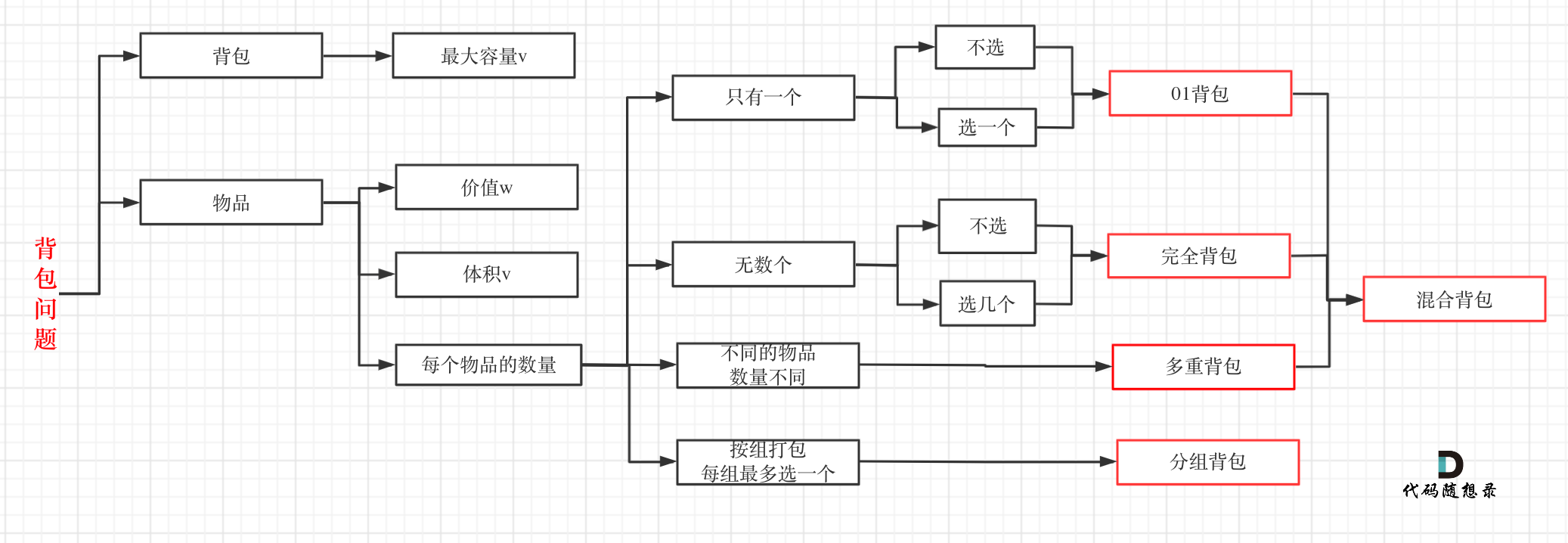
RRT算法的全称是快速扩展随机树算法(Rapidly Exploring Random Tree),它的思想是选取一个初始点作为根节点,通过随机采样,增加叶子节点的方式,生成一个随机扩展树,当随机树中的叶子节点包含了目标点或进入了目标区域,边可以在随机树中通过回溯的方式,找到这条从初始点到目标点的路径。
此算法的重点随机采样+步⻓限制+碰撞检测
算法流程:
1.初始化:以起点start为根节点,创建一棵树(通常用二叉树表示),树的根节点表示起始位置。
2.随机采样:在搜索空间中随机生成一个点x_rand。这个点可能在自由空间中,也可能在障碍物中。
3.寻找最近的节点:在当前的树中找到距离x_rand最近的节点x_near。
4.扩展树:从x_near沿着指向x_rand的方向移动一小步,生成一个新的节点x_new。如果x_new在自由空间中(即不与障碍物碰撞),则将x_new加入到树中,并将x_near和n_new用一条边连接。
5.检查目标:检查x_new是否在目标区域附近,这里的“附近”可以设置一个搜索距离来量化。如果是,则生成一条路径从起点到x_new,并结束算法。
6.迭代:重复步骤2~步骤5,直到找到目标点goal,或达到预设的迭代次数。
由于RRT采用随机采样的方法,RRT生成的路径通常不一定是最优路径,但可以通过多次运行RRT或结合其他优化算法来获得更优路径。

算法实现
import numpy as np
import random
import math
from itertools import combinations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import matplotlib.patches as patches
class RRT:
def __init__(self,start,goal,obstacles,board_size,max_try,max_dist,goal_sample_rate,env) -> None:
self.start = self.Node(start,None,0)
self.goal = self.Node(goal,None,0)
self.obstacles = obstacles
self.board_size = board_size
self.max_try = max_try # Number of iterations
self.max_dist = max_dist # Maximum sampling distance
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.env = env
self.inflation = 1
self.searched = []
class Node:
def __init__(self,position,parent,cost):
self.position = position
self.parent = parent
self.cost = cost
def run(self):
cost,path = self.plan()
self.visualize(cost,path)
def plan(self):
self.searched.append(self.start)
closed_list = {self.start.position: self.start}
# plan max_try times
for i in range(self.max_try):
node_rand = self.get_random_node()
# visited
if node_rand.position in closed_list:
continue
# Get the nearest neighbor node
node_near = self.get_nearest_neighbor(list(closed_list.values()),node_rand)
# Get the new node
node_new = self.get_new_node(node_rand,node_near)
if node_new:
closed_list[node_new.position] = node_new
self.searched.append(node_new)
dist = self.distance(node_new,self.goal)
# Found goal successfully
if dist <= self.max_dist and not self.isCollision(node_new,self.goal):
self.searched.append(self.goal)
self.goal.parent = node_new
self.goal.cost = node_new.cost + self.distance(self.goal,node_new)
closed_list[self.goal.position] = self.goal
cost, path= self.extractPath(closed_list)
print("Exploring {} nodes.".format(i))
return cost,path
return 0,None
def get_random_node(self) :
"""
Return a random node.
"""
if random.random()>self.goal_sample_rate:
node = self.Node(
(random.uniform(0,self.env.height),random.uniform(0,self.env.width)),None,0)
else:
node = self.Node(self.goal.position,None,0)
return node
def get_nearest_neighbor(self,node_list,node) -> Node:
"""
Return node that is nearest to 'node' in node_list
"""
dist = [self.distance(node, n) for n in node_list]
node_near = node_list[int(np.argmin(dist))]
return node_near
def get_new_node(self,node_rand,node_near):
"""
Return node found based on node_near and node_rand.
"""
dx = node_rand.position[0] - node_near.position[0]
dy = node_rand.position[1] - node_near.position[1]
dist = math.hypot(dx,dy)
theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)
d = min(self.max_dist,dist)
position = ((node_near.position[0]+d*math.cos(theta)),node_near.position[1]+d*math.sin(theta))
node_new = self.Node(position,node_near,node_near.cost+d)
if self.isCollision(node_new, node_near):
return None
return node_new
def isCollision(self,node1,node2):
"""
Judge collision from node1 to node2
"""
if self.isInObstacles(node1) or self.isInObstacles(node2):
return True
for rect in self.env.obs_rectangle:
if self.isInterRect(node1,node2,rect):
return True
for circle in self.env.obs_circle:
if self.isInterCircle(node1,node2,circle):
return True
return False
def distance(self,node1,node2):
dx = node2.position[0] - node1.position[0]
dy = node2.position[1] - node1.position[1]
return math.hypot(dx,dy)
def isInObstacles(self,node):
"""
Determine whether it is in obstacles or not.
"""
x,y = node.position[0],node.position[1]
for (ox,oy,w,h) in self.env.boundary:
if ox-self.inflation<x<ox+w+self.inflation and oy-self.inflation<y<oy+h+self.inflation:
return True
for (ox,oy,w,h) in self.env.obs_rectangle:
if ox-self.inflation<x<ox+w+self.inflation and oy-self.inflation<y<oy+h+self.inflation:
return True
for (ox,oy,r) in self.env.obs_circle:
if math.hypot(x-ox,y-oy)<=r+self.inflation:
return True
return False
def isInterRect(self,node1,node2,rect):
""""
Judge whether it will cross the rectangle when moving from node1 to node2
"""
ox,oy,w,h = rect
vertex = [[ox-self.inflation,oy-self.inflation],
[ox+w+self.inflation,oy-self.inflation],
[ox+w+self.inflation,oy+h+self.inflation],
[ox-self.inflation,oy+h+self.inflation]]
x1,y1 = node1.position
x2,y2 = node2.position
def cross(p1,p2,p3):
x1 = p2[0]-p1[0]
y1 = p2[1]-p1[1]
x2 = p3[0]-p1[0]
y2 = p3[1]-p1[0]
return x1*y2 - x2*y1
for v1,v2 in combinations(vertex,2):
if max(x1,x2) >= min(v1[0],v2[0]) and min(x1,x2)<=max(v1[0],v2[0]) and \
max(y1,y2) >= min(v1[1],v2[1]) and min(y1,y2) <= max(v1[1],v2[1]):
if cross(v1,v2,node1.position) * cross(v1,v2,node2.position)<=0 and \
cross(node1.position,node2.position,v1) * cross(node1.position,node2.position,v2):
return True
return False
def isInterCircle(self,node1,node2,circle):
"""
Judge whether it will cross the circle when moving from node1 to node2
"""
ox,oy,r = circle
dx = node2.position[0] - node1.position[0]
dy = node2.position[1] - node1.position[1]
# Projection
t = ((ox - node1.position[0]) * dx + (oy - node1.position[1]) * dy) / (dx * dx + dy * dy)
# The projection point is on line segment AB
if 0 <= t <= 1:
closest_x = node1.position[0] + t * dx
closest_y = node1.position[1] + t * dy
# Distance from center of the circle to line segment AB
distance = math.hypot(ox-closest_x,oy-closest_y)
return distance <= r+self.inflation
return False
def extractPath(self,closed_list):
""""
Extract the path based on the closed list.
"""
node = closed_list[self.goal.position]
path = [node.position]
cost = node.cost
while node != self.start:
parent = node.parent
node_parent = closed_list[parent.position]
node = node_parent
path.append(node.position)
return cost,path
def visualize(self, cost, path):
"""
Plot the map.
"""
....
结果图: