💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
💥1 概述
来源:

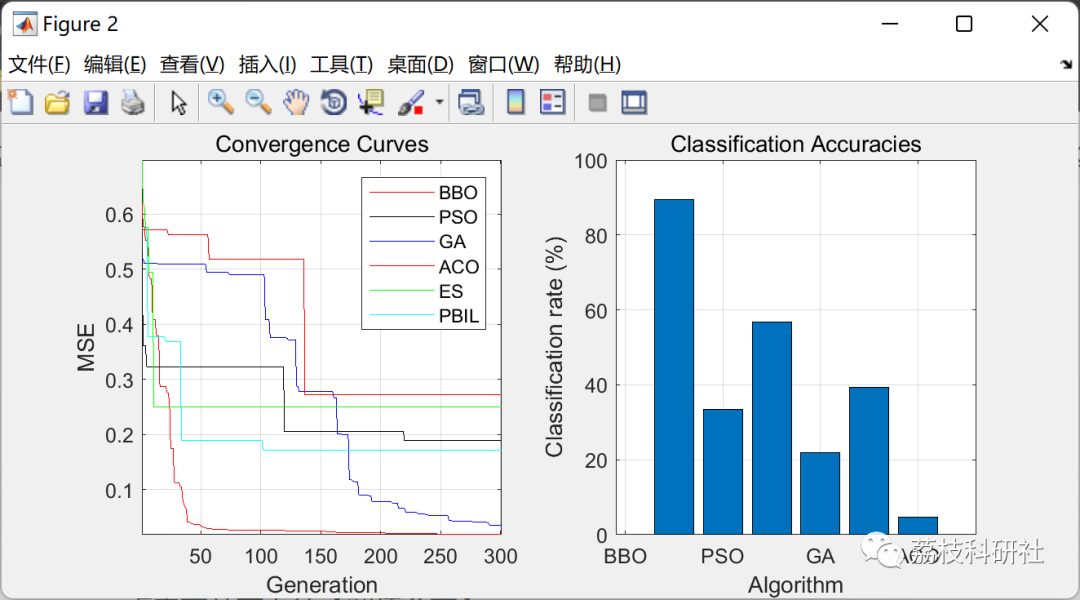
多层感知器(MLP)作为使用最广泛的神经网络(NN)之一,已被应用于许多实际问题。MLP 需要针对特定应用程序进行培训,经常会遇到局部最小值、收敛速度和初始化敏感性问题。本文建议使用最近开发的基于生物地理学的优化(BBO)算法来训练MLP以减少这些问题。为了研究BBO在训练MLP中的效率,使用了五个分类数据集以及六个函数近似数据集。将结果与5种著名的启发式算法反向传播(BP)和极限学习机(ELM)在局部最小值的捕获、结果精度和收敛率方面进行了比较。结果表明,利用BBO训练MLP明显优于目前的启发式学习算法和BP。此外,结果表明,与ELM相比,BBO能够提供非常有竞争力的结果。
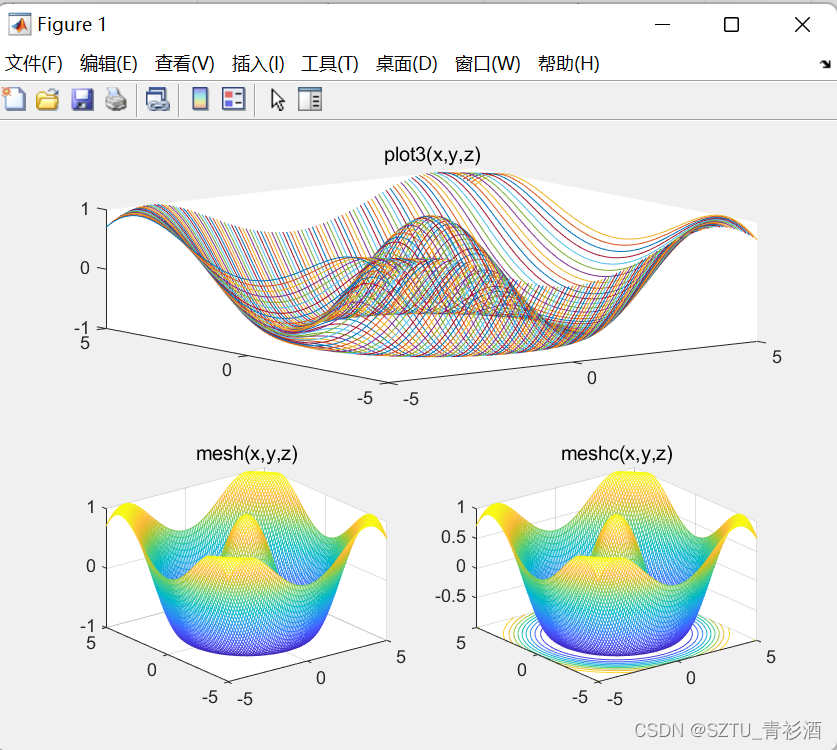
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
[1]Seyedali Mirjalili (2022). Biogeography-Based Optimizer (BBO) for training Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) .
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.038
部分代码:
function [MinCost,Best] = ACO(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag)
% Ant colony optimization algorithm for optimizing a general function.
% INPUTS: ProblemFunction is the handle of the function that returns
% the handles of the initialization, cost, and feasibility functions.
% DisplayFlag says whether or not to display information during iterations and plot results.
if ~exist('DisplayFlag', 'var')
DisplayFlag = true;
end
[OPTIONS, MinCost, AvgCost, InitFunction, CostFunction, FeasibleFunction, ...
MaxParValue, MinParValue, Population] = Init(DisplayFlag, ProblemFunction);
Keep = 2; % elitism parameter: how many of the best individuals to keep from one generation to the next
% ACO parameter initialization
tau0 = 1e-6; % initial pheromone value, between 0 and 0.5
Q = 20; % pheromonone update constant, between 0 and 100
q0 = 1; % exploration constant, between 0 and 1
rhog = 0.9; % global pheromone decay rate, between 0 and 1
rhol = 0.5; % local pheromone decay rate, between 0 and 1
alpha = 1; % pheromone sensitivity, between 1 and 5
beta = 5; % visibility sensitivity, between 0 and 15
tau = tau0 * ones(MaxParValue-MinParValue+1, 1); % initial pheromone values
p = zeros(size(tau)); % allocate array for probabilities
% Begin the optimization loop
for GenIndex = 1 : OPTIONS.Maxgen
% pheromone decay
tau = (1 - rhog) * tau;
% Use each solution to update the pheromone for each parameter value
for k = 1 : OPTIONS.popsize
Cost = Population(k).cost;
Chrom = Population(k).chrom;
for i = 1 : length(Chrom)
j = Chrom(i);
j=floor(j);
if (Cost == 0)
tau(j-MinParValue+1) = max(tau);
else
tau(j-MinParValue+1) = tau(j-MinParValue+1) + Q / Cost;
end
end
end
% Use the probabilities to generate new solutions
for k = Keep+1 : OPTIONS.popsize
for j = 1 : OPTIONS.numVar
% Generate probabilities based on pheromone amounts
p = tau .^ alpha;
p = p / sum(p);
[Maxp, Maxpindex] = max(p);
if rand < q0
Select_index = Maxpindex;
else
SelectProb = p(1);
Select_index = 1;
RandomNumber = rand;
while SelectProb < RandomNumber
Select_index = Select_index + 1;
if Select_index >= MaxParValue - MinParValue + 1
break;
end
SelectProb = SelectProb + p(Select_index);
end
end
Population(k).chrom(j) = MinParValue + Select_index - 1;
% local pheromone update
tau(Select_index) = (1 - rhol) * tau(Select_index) + rhol * tau0;
end
end
% Make sure the population does not have duplicates.
Population = ClearDups(Population, MaxParValue, MinParValue);
% Make sure each individual is legal.
Population = FeasibleFunction(OPTIONS, Population);
% Calculate cost
Population = CostFunction(OPTIONS, Population);
% Sort from best to worst
Population = PopSort(Population);
% Compute the average cost of the valid individuals
[AverageCost, nLegal] = ComputeAveCost(Population);
% Display info to screen
MinCost = [MinCost Population(1).cost];
AvgCost = [AvgCost AverageCost];
if DisplayFlag
disp(['The best and mean of Generation # ', num2str(GenIndex), ' are ',...
num2str(MinCost(end)), ' and ', num2str(AvgCost(end))]);
end
end
Best=Conclude(DisplayFlag, OPTIONS, Population, nLegal, MinCost);
return;
![[附源码]java毕业设计网络学习平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/82b4474d2d1d412b81f592f72cda1f9b.png)