手撸俄罗斯方块(四)——渲染与交互
如何渲染游戏界面
我们知道,当我们看到页面先呈现图像时,实际上看到的是一张图片,多张图片按照一定的刷新频率进行切换,则变成了动态的视频。当刷新频率超过24Hz时,人眼不会察觉到卡顿情况。
因此,一个简单的方案呼之欲出,我们只需要按照1000 / 24 = 41.7ms的时间间隔整体刷新一下频率即可。

对于俄罗斯方块而言,从上到下,我们可以将整个操作界面分为如下区域:
-
外框区域: 包括外框的颜色和整体的背景,以及外框的样式;
-
分数区域: 用于显示分数;
-
当前图形: 显示当前正在移动的方块;
-
下一图形: 显示接下来要出现的方块;
-
游戏状态: 显示当前游戏的状态,如: 游戏暂停;
-
已填充图形: 显示已填充的图形;
我们有两种方式进行处理:
-
每次刷新时重新渲染所有部分。该方法处理逻辑简单,清空全局区域,渲染有效区域。
-
每次刷新时仅渲染更新区域。该方法能减少页面整体重绘,提交渲染效率,但相对来说处理复杂,控制逻辑较多。
但是,有些场景却无法使用局部刷新,如控制台渲染。
下面我分别以控制台渲染和DOM渲染为例,分别讲述如何实现渲染。
控制台渲染
按照上文描述,我们将渲染过程进行了抽象,包括了首次渲染和更新渲染,如下:
import { Canvas } from '@shushanfx/teris-core';
class ConsoleCanvas extends Canvas {
render(): void {
}
update(): void {
}
}
对于控制台而言,每次更新实际上也是渲染全部区域,因此我们可以定义update为:
class ConsoleCanvas extends Canvas {
update(): void {
this.render();
}
}
那么接下来的问题就是如何实现render方法。
render实现
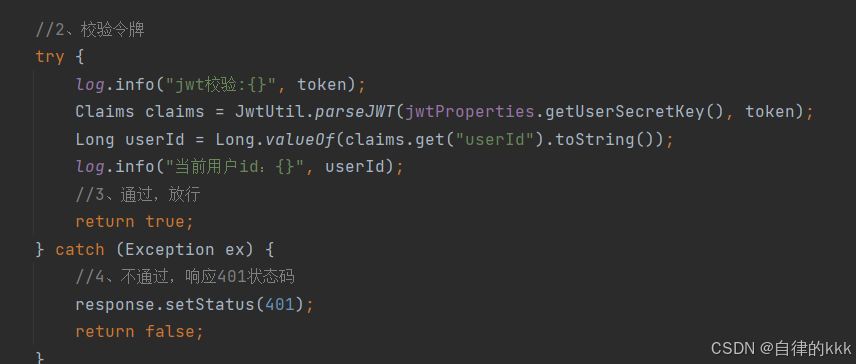
render为全局渲染,在渲染之前需要首先清除控制台。我们可以使用如下代码表示渲染逻辑:
render() {
const printArray = [];
// 1. 清空可视区域
console.clear();
// 2. array填充
// ...
// 3. 打印array
print(printArray);
}
array的填充
将整个渲染区域分解成一个个字符,多个字符组合组装成画面。这个是控制台游戏的特点。
我们俄罗斯方块游戏的特点:
-
第一行显示为外边框的上边框;
-
第二行显示为分数;
-
第三行为内边框的上边框;
-
游戏核心区域渲染,包括填充方块、下一个方块、游戏帮助、游戏状态等字符;
-
内边框的下边框;
-
外边框的下边框。
-
渲染外边框的上边框时:
const outLine1 = this.getOutterLine(
this.leftTopChar +
this.createChar(xSize + 2 + this.rightWidth, this.horizonalChar) +
this.rightTopChar
);
printArray.push(outLine1);
包括leftTopChar、horizonalChar、rightTopChar。
- 渲染分数:
// 2. 渲染score
const scoreText = this.theme.scoreTemplate(score);
const scoreConsoleChar = ConsoleChar.create(scoreText);
this.theme.scoreStyle(scoreConsoleChar);
// 计算左侧需要补充的空格
const leftSpace = this.rightWidth - scoreText.length - 3;
// 右侧需要补充的空格
const rightSpace = 3;
let scoreLine =
this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar) +
this.createChar(xSize + 2 + leftSpace) +
scoreConsoleChar.ch +
this.createChar(rightSpace) +
this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar);
printArray.push(scoreLine);
- 1~3行,用于生成score的文本和样式,后续在
theme中会描述。 - 5行,计算左侧补充的空格数
- 7行,右侧补充的空格数
- 添加scoreLine,包括verticalChar,左侧空格,分数,右侧空格,verticalChar。
- 渲染内边框的上边框
// 3. 渲染内边框的上边框
let line1 =
this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar) +
this.getInnerLine(this.leftTopChar);
for (let x = 0; x < xSize; x++) {
const oneBlockItem = current?.points.find(item => item.x === x);
if (oneBlockItem) {
line1 += this.getInnerLine(bold(this.horizonalChar))
} else {
line1 += this.getInnerLine(this.horizonalChar)
}
}
line1 +=
this.getInnerLine(this.rightTopChar) +
this.createChar(this.rightWidth) +
this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar);
printArray.push(line1);
内边框包括,verticalChar,leftTopChar、horizonalChar、空格和verticalChar。
- 核心区域渲染
游戏核心区域主要是一些方块,包括当前方块currentBlock,下一个方块nextBlock,已经落地的方块以及左右边框。
基本思路为:
4.1. 对于游戏区域,按照xSize x ySize维度,遍历每个点
* 如果当前点存在points(已经固定的点)中,则渲染固定点;
* 如果当前点包含在currentBlock中,则渲染当前活动的block。
* 否则渲染空点
```javascript
for (let y = 0; y < ySize; y++) {
let rowLength = 2;
let row = this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar)
+ this.getInnerLine(this.verticalChar);
for (let x = 0; x < xSize; x++) {
const point = stage.points[y][x];
const currentPoint = current
? current?.points.find((p) => p.x === x && p.y === y)
: null;
if (currentPoint || !point.isEmpty) {
let consoleChar = new ConsoleChar(this.blockChar);
this.theme.blockPointStyle(consoleChar, currentPoint || point);
row += consoleChar.ch;
} else {
row += " ";
}
}
rowLength += xSize;
row += this.getInnerLine(this.verticalChar);
rowLength += 1;
// 渲染其他点位
// 扣除末尾的结束符号
const leftLength = outLength - rowLength - 1;
if (leftLength > 0) {
row += new Array(leftLength).fill(" ").join("");
}
row += this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar);
printArray.push(row);
}
```
从上述代码来看,渲染逻辑很简单,先是渲染左侧外边框`verticalChar`、内边框`verticalChar`,之后渲染具体的方块,即如果方块包含在currentBlock或者不为空,则渲染方块,否则渲染空字符。之后,渲染内边框`verticalChar`,补充空格和外边框`verticalChar`。
4.2. 渲染nextBlock
从游戏区第一行开始,我们需要渲染`nextBlock`部分,因此实现逻辑如下:
```javascript
// drawNext
if (y >= 0 && y <= 4) {
row += this.createChar(1);
rowLength += 1;
if (next) {
let xStart = 0;
let xEnd = 0;
next.points.forEach((point) => {
if (xStart === 0 || point.x < xStart) {
xStart = point.x;
}
if (xEnd === 0 || point.x > xEnd) {
xEnd = point.x;
}
});
for (let x = xStart; x <= xEnd; x++) {
const point = next.points.find((p) => p.x === x && p.y === y);
let consoleChar: ConsoleChar | null = point
? new ConsoleChar(this.blockChar)
: null;
if (point) {
this.theme.nextPointStyle(consoleChar, point);
}
row += consoleChar ? consoleChar.ch : " ";
rowLength += 1;
}
}
}
```
需要说名的是`nextBlock`的x坐标并不是从0开始,需要先找到x坐标的最小值和最大值,然后再依次渲染对应的行。
比如Block T,如果形状如下:
```javascript
// 口
// 口口
// 口
```
那么,`xStart`和`xEnd`的差值为1。y只有0-2是有效的行,其余均渲染为空格。
4.3. 渲染游戏状态
第7行,渲染游戏状态
```javascript
else if (y === 6) {
const { status } = game;
if (status === GameStatus.PAUSE) {
row += this.createChar(1) + this.getStatusLine("游戏暂停");
rowLength += 5;
} else if (status === GameStatus.OVER) {
row += this.createChar(1) + this.getStatusLine("游戏结束");
rowLength += 5;
} else if (status === GameStatus.STOP) {
row += this.createChar(1) + this.getStatusLine("游戏停止");
rowLength += 5;
}
}
```
4.4. 渲染游戏帮助
从第9行开始,渲染游戏的帮助信息:
```javascript
else if (y >= 8) {
const messsage = this.createChar(1) + this.getHelpMessage(y - 8);
row += messsage;
rowLength += messsage.length;
}
```
- 渲染内边框的下边框
let line2 =
this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar) +
this.getInnerLine(this.leftBottomChar);
for (let x = 0; x < xSize; x++) {
const oneBlockItem = current?.points.find(item => item.x === x);
if (oneBlockItem) {
line2 += this.getInnerLine(bold(this.horizonalChar))
} else {
line2 += this.getInnerLine(this.horizonalChar)
}
}
line2 += this.getInnerLine(this.rightBottomChar) +
this.createChar(this.rightWidth) +
this.getOutterLine(this.verticalChar);
printArray.push(line2);
逻辑与渲染内边框的上边类似。
- 渲染外边框的下边框
const outLine2 = this.getOutterLine(
this.leftBottomChar +
this.createChar(xSize + 2 + this.rightWidth, this.horizonalChar) +
this.rightBottomChar
);
printArray.push(outLine2);
小结
本章主要讲述如何将游戏数据渲染成画面,以及渲染的一些通用的原理。渲染的本质是绘图,即告诉显示器如何绘制图像,通过不停的更新绘图实现动态的交互的效果。
详细内容可以关注在git上查看: https://github.com/shushanfx/tetris
也可以关注我的git账号: https://github.com/shushanfx
接下来我将从如下几个方面来阐述:
- 手撸俄罗斯方块——游戏主题