题目链接
对于f(n)=3f(n−1)+2f(n−2)+2这种式子,先将右边拥有的项竖着列出来,不包括系数,再将这个竖列的下一项写出来,然后将右边的每一项按照左边顺序的等式写出来,然后我们将等式右边只保留系数,那么这些系数就是我们需要的矩阵
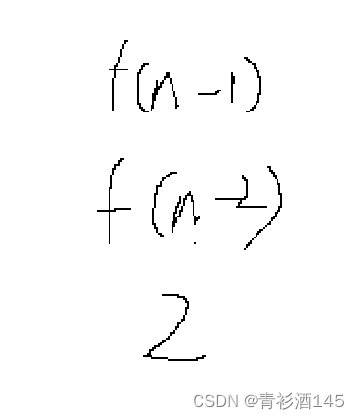
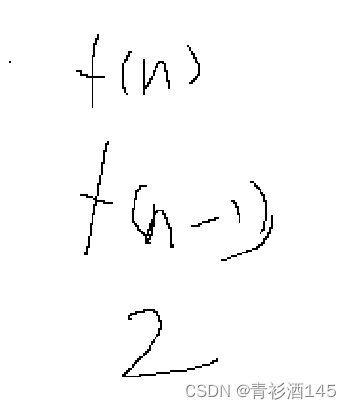
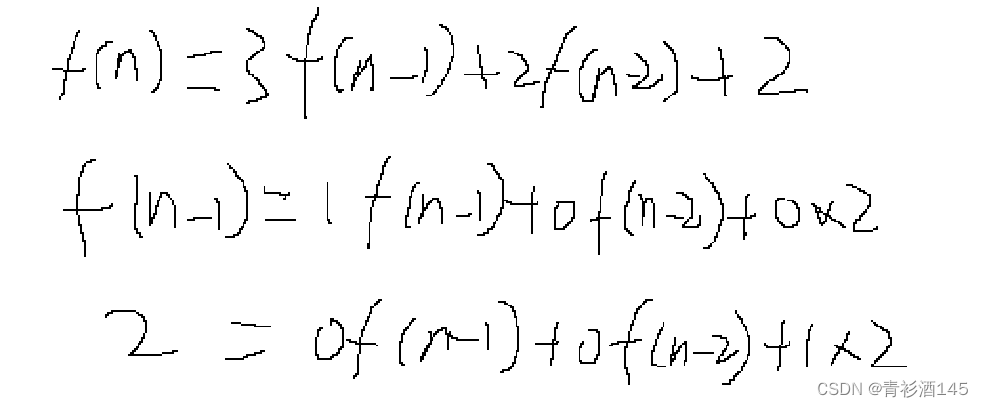

于是我们得到了系数矩阵,然后我们只需要求出系数矩阵的n-2次幂,最后再和第一项矩阵的乘积即可,也就是{f(2),f(1),2}(这是竖着的),也就是(1,1,2)。最后的左上角第一项就是答案f(n)。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=5e5+10;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
//#define int long long
//const ll P=2281701377;
const ll P=998244353;
const int mod=1e9+7;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int ll
struct node{
int n,m;
int a[5][5];
node(){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
}
node(int x){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
a[0][0]=a[1][1]=a[2][2]=x;
}
node operator *(const node &b){
node res;
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
res.a[i][j]=(res.a[i][j]+(ll)a[i][k]*b.a[k][j])%mod;
return res;
}
};
node qpow(node a,ll b){
node s(1);
while(b){
if(b&1) s=s*a;
a=a*a;
b>>=1;
}
return s;
}
int n;
void solve(){
cin>>n;
node q;
q.a[0][0]=q.a[1][0]=1,q.a[2][0]=2;
node a;
a.a[0][0]=3,a.a[0][1]=2,a.a[0][2]=1;
a.a[1][0]=a.a[2][2]=1;
if(n<=2)
cout<<1<<endl;
else{
ll m=n-2;
node t=qpow(a,m);
t=t*q;
cout<<t.a[0][0];
}
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
}题目链接
和上题一样,就是将n-2次改成n-1次,因为f(n)的下标可以到0了,也就是可以多乘一个系数矩阵。系数矩阵和第一项矩阵:
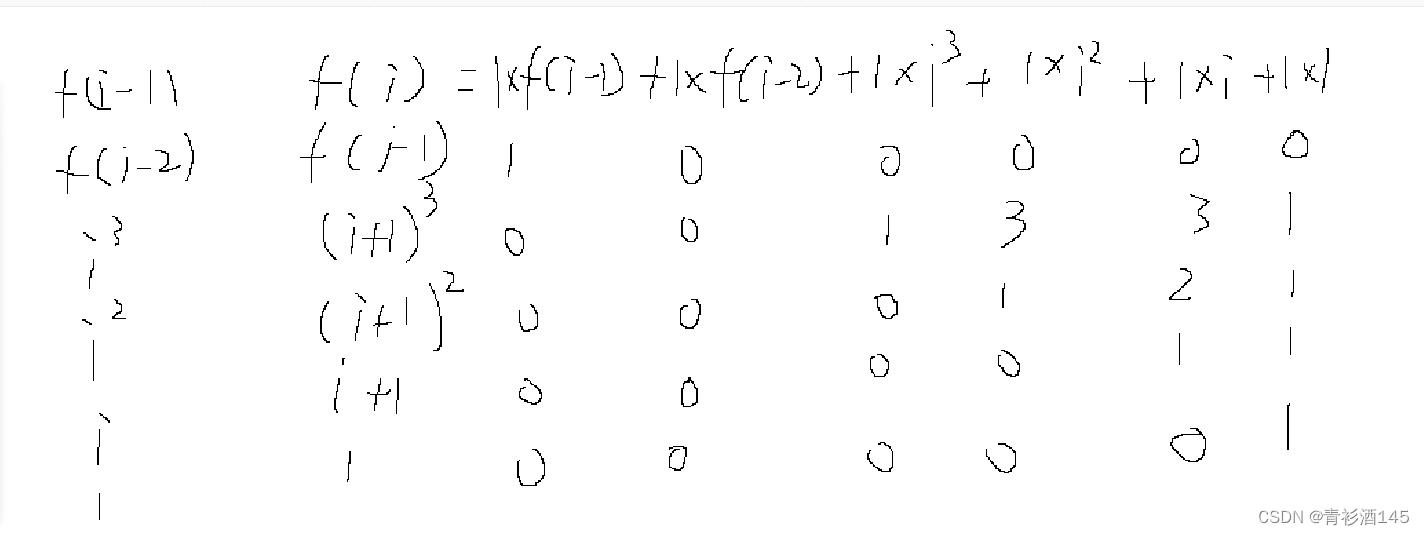

代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=5e5+10;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
//#define int long long
//const ll P=2281701377;
const ll P=998244353;
const int mod=1e9+7;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int ll
struct node{
int n,m;
int a[7][7];
node(){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
}
node(int x){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
a[i][i]=x;
}
node operator *(const node &b){
node res;
for(int k=0;k<6;k++)
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
for(int j=0;j<6;j++)
res.a[i][j]=(res.a[i][j]+(ll)a[i][k]*b.a[k][j])%mod;
return res;
}
};
node qpow(node a,ll b){
node s(1);
while(b){
if(b&1) s=s*a;
a=a*a;
b>>=1;
}
return s;
}
int n;
void solve(){
cin>>n;
node q;
q.a[0][0]=1,q.a[1][0]=0,q.a[2][0]=8,q.a[3][0]=4,q.a[4][0]=2,q.a[5][0]=1;
node a;
a.a[0][0]=a.a[0][1]=a.a[0][2]=a.a[0][3]=a.a[0][4]=a.a[0][5]=1;
a.a[1][0]=1;
a.a[2][2]=a.a[2][5]=1,a.a[2][3]=a.a[2][4]=3;
a.a[3][3]=a.a[3][5]=1,a.a[3][4]=2;
a.a[4][4]=a.a[4][5]=1;
a.a[5][5]=1;
if(n==0)
cout<<0<<endl;
else if(n==1)
cout<<1<<endl;
else{
ll m=n-1;
node t=qpow(a,m);
t=t*q;
cout<<t.a[0][0]<<endl;
}
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
}