Express是一个用于构建Web应用程序和API的JavaScript框架。它是基于Node.js平台的,并提供了一系列简化了常见Web开发任务的功能,如路由、中间件、模板引擎和数据库集成等。 是一个处理请求、响应的库
其可以通过use一个个中间件来处理请求和返回响应(洋葱模型),我们基于这些中间件能实现各种功能 ,但Express 只是一个处理请求的库,没有开发规范和组织架构的能力,会导致写出来的代码参差不齐 不同人写的代码会差距可能很大。
Express 的 洋葱模型: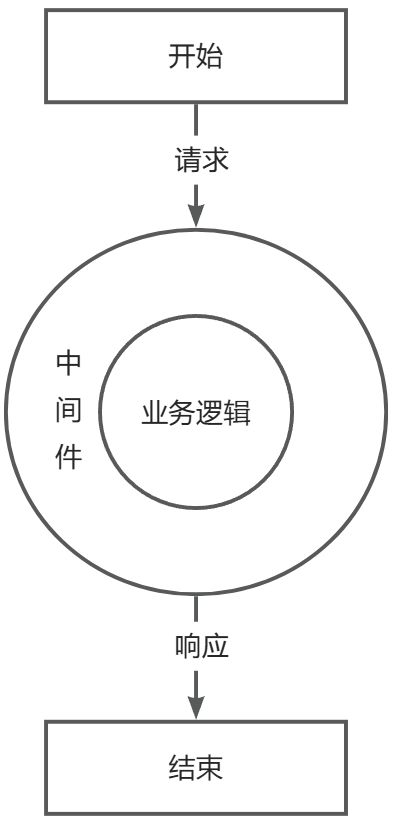
而Nest 提供了 IOC、AOP 等架构特性,有着规定的代码组织形式,且有很多很多开箱即用的方案。
用 Node 写一个 http 服务有三个层次:
第一层:直接使用 http、https 的模块
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.statusCode = 200;
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.end('Hello World\n');
});
server.listen(3000, '127.0.0.1', () => {
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:3000/');
});
第二层:使用 express、koa 这种库
使用 Express:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
});
使用 Koa:
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
});
第三层:使用 Nest 这种企业级框架
const { NestFactory } = require('@nestjs/core');
const { AppModule } = require('./app.module');
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3000);
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
}
bootstrap();
在 Nest 中,我们需要定义一个 AppModule,并在其中定义控制器和提供者:
const { Module, Controller, Get } = require('@nestjs/common');
@Controller()
class AppController {
@Get()
getHello() {
return 'Hello World!';
}
}
@Module({
controllers: [AppController],
})
class AppModule {}
module.exports = {
AppModule,
};
注意 Nest没有和 Express 进行强耦合 而是做了一层抽象,之后分别提供了 express 和 fastify 的实现,所以我们可以在Nest项目灵活的切换express和 fastify
下面是nest中 express和 fastify 的定义逻辑: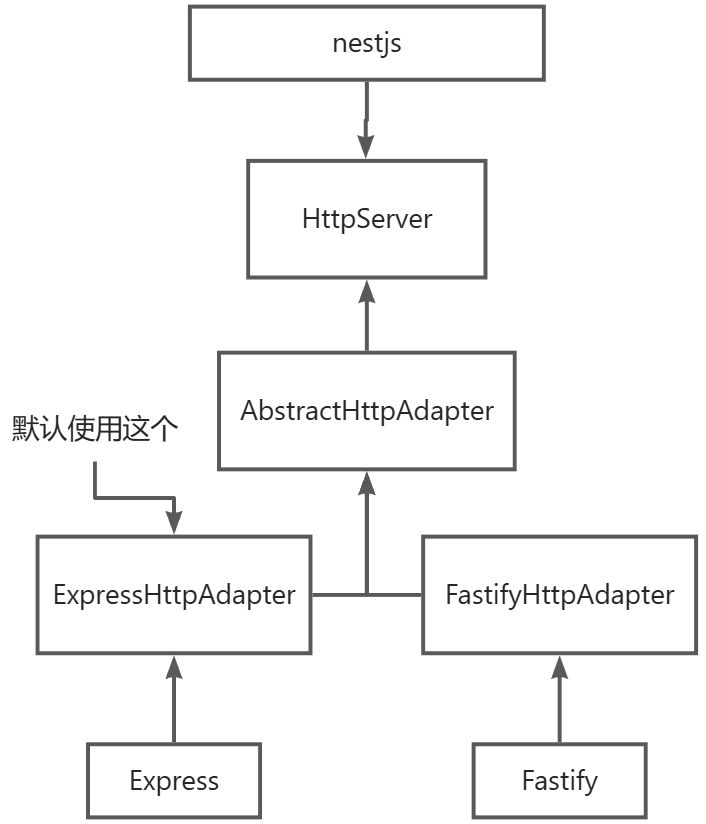
接下来我们创建一个项目来测试:
nest new fastify-test -p npm
启动项目:
pnpm run start:dev
访问 http://localhost:3000 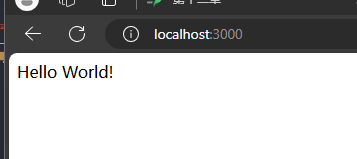
成功启动项目
_注意:我们创建的项目 默认是使用 _express
如果想切换使用 fastify 则需要安装 fastify 和 @nestjs/platform-fastify
npm install fastify @nestjs/platform-fastify
接着修改main.ts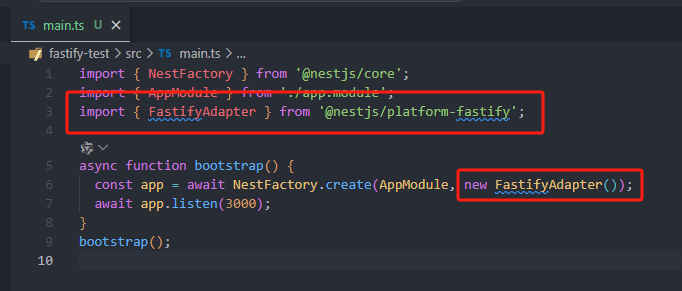
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { FastifyAdapter } from '@nestjs/platform-fastify';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule, new FastifyAdapter());
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
这样就成功切换到使用fastify 但是现在还有一个问题就是我们在使用app.xxx 的时候 没有fastify 相关的提示 使用NestFastifyApplication 之后就有提示方法: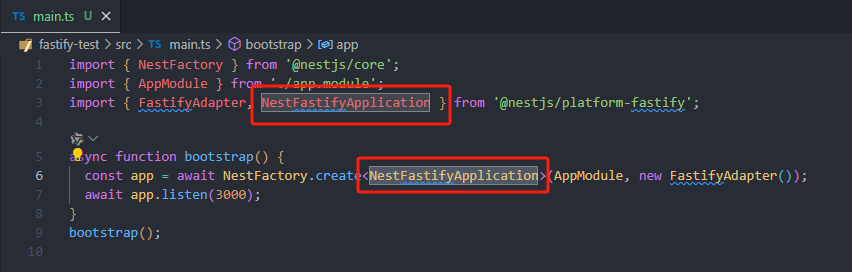
接着在controller 里可以注入 fastify 的 reqeust 和 reply 对象:
import { Controller, Get, Request, Response } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { FastifyReply, FastifyRequest } from 'fastify';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) { }
/**
* 处理HTTP GET请求并返回一个简单的欢迎信息。
*
* 此方法装饰了`@Get()`注解,表示它将响应HTTP GET请求。
* 它使用`@Request()`和`@Response()`注解来获取请求和响应对象,以便可以操作它们。
*
* @param request FastifyRequest - 表示当前HTTP请求的对象,包含请求的相关信息。
* @param reply FastifyReply - 表示当前HTTP响应的对象,允许设置响应头和发送响应体。
*/
@Get()
getHello(@Request() request: FastifyRequest, @Response() reply: FastifyReply): string {
// 设置响应头中的'url'字段为当前请求的URL,以便客户端可以获取请求的URL。
reply.header('url', request.url)
// 发送简单的'hello'字符串作为响应体。
reply.send('hello')
}
}
注意:如果使用@Response 注入响应对象 那不能使用return 返回响应内容 需要通过 reply.send 来返回内容
当然 如果改成下面的形式也可以直接return响应内容:
将@Response() 设置为 @Response({ passthrough: true })
import { Controller, Get, Request, Response } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { FastifyReply, FastifyRequest } from 'fastify';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) { }
/**
* 处理HTTP GET请求并返回一个简单的欢迎信息。
*
* 此方法装饰了`@Get()`注解,表示它将响应HTTP GET请求。
* 它使用`@Request()`和`@Response()`注解来获取请求和响应对象,以便可以操作它们。
*
* @param request FastifyRequest - 表示当前HTTP请求的对象,包含请求的相关信息。
* @param reply FastifyReply - 表示当前HTTP响应的对象,允许设置响应头和发送响应体。
* @returns string - 从appService获取的欢迎信息。
*/
@Get()
getHello(@Request() request: FastifyRequest, @Response({ passthrough: true }) reply: FastifyReply): string {
// 设置响应头中的'url'字段为当前请求的URL,以便客户端可以获取请求的URL。
reply.header('url', request.url)
// 调用appService的getHello方法并返回其结果,该结果通常是另一个欢迎信息。
return 'hello';
}
}
Nest 不强依赖 express 是因为可能后面会出跟好的http处理库 可以切换到更好用的。这样比较通用、灵活,有更强的扩展性