目录
- 模版方法模式
- 模版方法模式结构
- 模版方法模式适合应用场景
- 模版方法模式优缺点
- 练手题目
- 题目描述
- 输入描述
- 输出描述
- 题解
模版方法模式
模板方法模式是一种行为设计模式, 它在超类中定义了一个算法的框架, 允许子类在不修改结构的情况下重写算法的特定步骤。
类比真实世界中建造大量房屋。 标准房屋建造方案中可提供几个扩展点, 允许潜在房屋业主调整成品房屋的部分细节。
每个建造步骤 (例如打地基、 建造框架、 建造墙壁和安装水电管线等) 都能进行微调, 这使得成品房屋会略有不同。
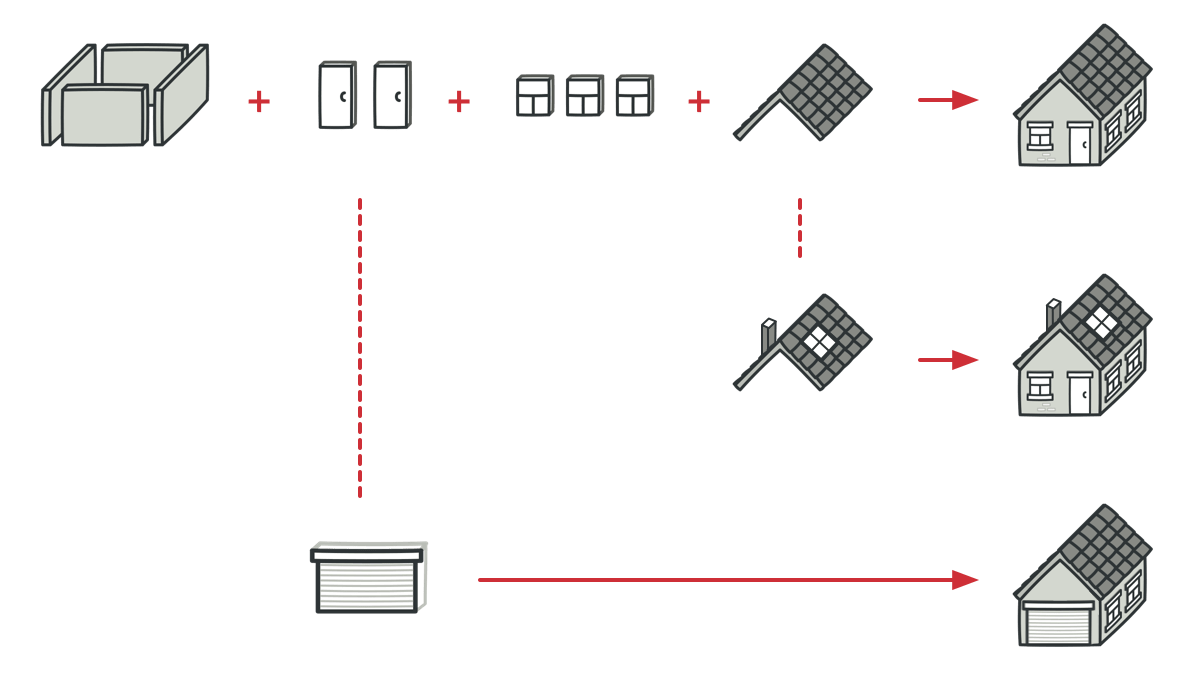
模版方法模式结构
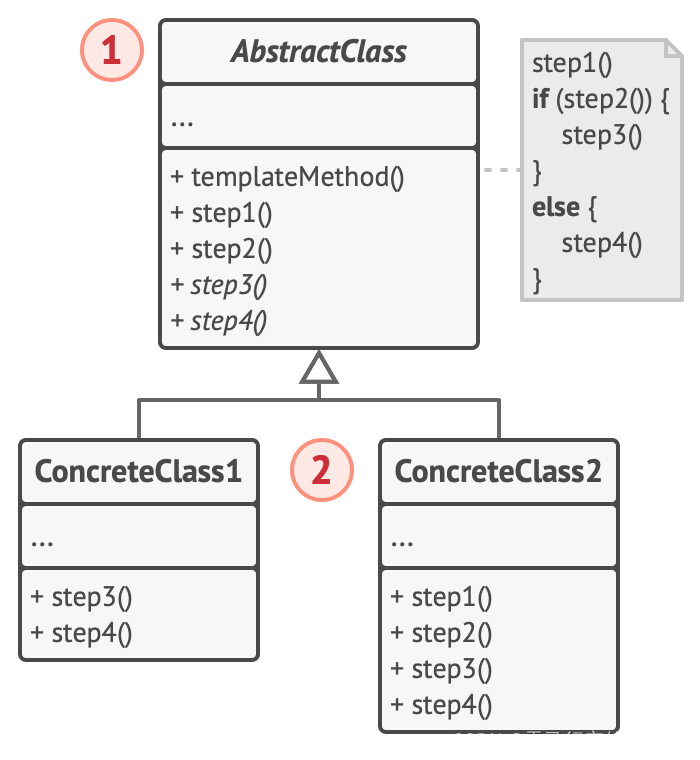
-
抽象类 (AbstractClass) 会声明作为算法步骤的方法, 以及依次调用它们的实际模板方法。 算法步骤可以被声明为
抽象类型, 也可以提供一些默认实现。 -
具体类 (ConcreteClass) 可以重写所有步骤, 但不能重写模板方法自身。
一般,模版方法都加上final关键字,不允许被覆写。
通用代码结构
//抽象类定义了一个模板方法,其中通常会包含某个由抽象原语操作调用组成的算法框架。
public abstract class AbstractClass{
//基本算法步骤
protected abstract void step1();
protected abstract void step2();
//模版方法
final public void templateMethod(){
//算法基本逻辑
this.step1();
this.step2();
...
}
}
// 具体类必须实现基类中的所有抽象操作,但是它们不能重写模板方法自身。
public class ConcreteClass1 extends AbstractClass{
//实现基本方法
protected abstract void step1(){
...
};
protected abstract void step2(){
....
};
}
public class ConcreteClass2 extends AbstractClass{
//实现基本方法
protected abstract void step1(){
...
};
protected abstract void step2(){
....
};
}
//客户端
public class Client{
public static void main(String[] args){
AbstractClass class1 = new ConcreteClass1();
AbstractClass class2 = new ConcreteClass2();
class1.templateMethod();
class2.templateMethod();
}
}
模版方法模式适合应用场景
-
当你只希望客户端扩展某个特定算法步骤,而不是整个算法或其结构时,可使用模板方法模式。
-
当多个类的算法除一些细微不同之外几乎完全一样时,你可使用该模式。但其后果就是,只要算法发生变化,你就可能需要修改所有的类。

**识别方法:**模版方法可以通过行为方法来识别,该方法已有一个在基类中定义的 “默认” 行为。
模版方法模式优缺点
模版方法模式的优点
-
你可仅允许客户端重写一个大型算法中的特定部分, 使得算法其他部分修改对其所造成的影响减小。
-
你可将重复代码提取到一个超类中。
模版方法模式的缺点
-
部分客户端可能会受到算法框架的限制。
-
通过子类抑制默认步骤实现可能会导致违反里氏替换原则。
-
模板方法中的步骤越多, 其维护工作就可能会越困难。
练手题目
题目描述
小明喜欢品尝不同类型的咖啡,她发现每种咖啡的制作过程有一些相同的步骤,他决定设计一个简单的咖啡制作系统,使用模板方法模式定义咖啡的制作过程。系统支持两种咖啡类型:美式咖啡(American Coffee)和拿铁(Latte)。
咖啡制作过程包括以下步骤:
研磨咖啡豆 Grinding coffee beans
冲泡咖啡 Brewing coffee
添加调料 Adding condiments
其中,美式咖啡和拿铁的调料添加方式略有不同, 拿铁在添加调料时需要添加牛奶Adding milk
输入描述
多行输入,每行包含一个数字,表示咖啡的选择(1 表示美式咖啡,2 表示拿铁)。
输出描述
根据每行输入,输出制作咖啡的过程,包括咖啡类型和各个制作步骤,末尾有一个空行。

题解
模版方法实现。
import java.util.Scanner;
// 抽象类,定义咖啡制作的基本步骤
abstract class CoffeeModel {
private String coffeeName;
// 构造函数,接受咖啡名称参数
public CoffeeModel(String coffeeName) {
this.coffeeName = coffeeName;
}
protected abstract void grind();
protected abstract void brew();
protected abstract void addCondiments();
// 添加其他调料可使用该类
public void addThings(){};
// 模板方法,定义咖啡制作的流程
public final void createCoffeeTemplate() {
System.out.println("Making " + coffeeName + ":");
grind();
brew();
//根据情况,是否调用添加更多调料
if (isAddThings()) {
addThings();
}
addCondiments();
System.out.println();
}
// 默认不添加其他调料。如牛奶等
public boolean isAddThings() {
return false;
}
}
//美式咖啡类实现
class CreateAmericanCoffee extends CoffeeModel {
public CreateAmericanCoffee() {
super("American Coffee");
}
@Override
protected void grind() {
System.out.println("Grinding coffee beans");
}
@Override
protected void brew() {
System.out.println("Brewing coffee");
}
@Override
protected void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding condiments");
}
// 美式咖啡默认不添加其他调料,如牛奶等
@Override
public boolean isAddThings() {
return false;
}
}
//拿铁类实现
class CreateLatte extends CoffeeModel {
private boolean addThingsFlag = true;
public CreateLatte() {
super("Latte");
}
@Override
protected void grind() {
System.out.println("Grinding coffee beans");
}
@Override
protected void brew() {
System.out.println("Brewing coffee");
}
@Override
protected void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding condiments");
}
//需要添加调料,牛奶
@Override
public void addThings(){
System.out.println("Adding milk");
}
// 拿铁默认添加牛奶
@Override
public boolean isAddThings() {
return this.addThingsFlag;
}
// 外部调用以改变是否添加牛奶的状态,钩子函数
public void setAddThingsFlag(boolean flag) {
this.addThingsFlag = flag;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in)) {
while (scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int input = scanner.nextInt();
CoffeeModel coffee;
switch (input) {
case 1:
coffee = new CreateAmericanCoffee();
break;
case 2:
coffee = new CreateLatte();
break;
default:
System.out.println("无效选择,请输入1或2");
continue;
}
coffee.createCoffeeTemplate();
}
}
}
}







![[数据集][目标检测]围栏破损检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式1196张1类别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/43e31971d466416a8f68dd061a8907e6.png)