Design Patterns for Reuse and Maintainability
(面向可复用性和可维护性的设计模式)
Open-Closed Principle (OCP) ——对扩展的开放,对修改已有代码的封
Why reusable design patterns
A design…
…enables flexibility to change (reusability)…minimizes the introduction of new problems when fixing old ones (maintainability)…allows the delivery of more functionality after an initial delivery (extensibility).
除了类本身,设计模式更强调多 个类/对象之间的关系和交互过程—比接口/类复用的粒度更大.
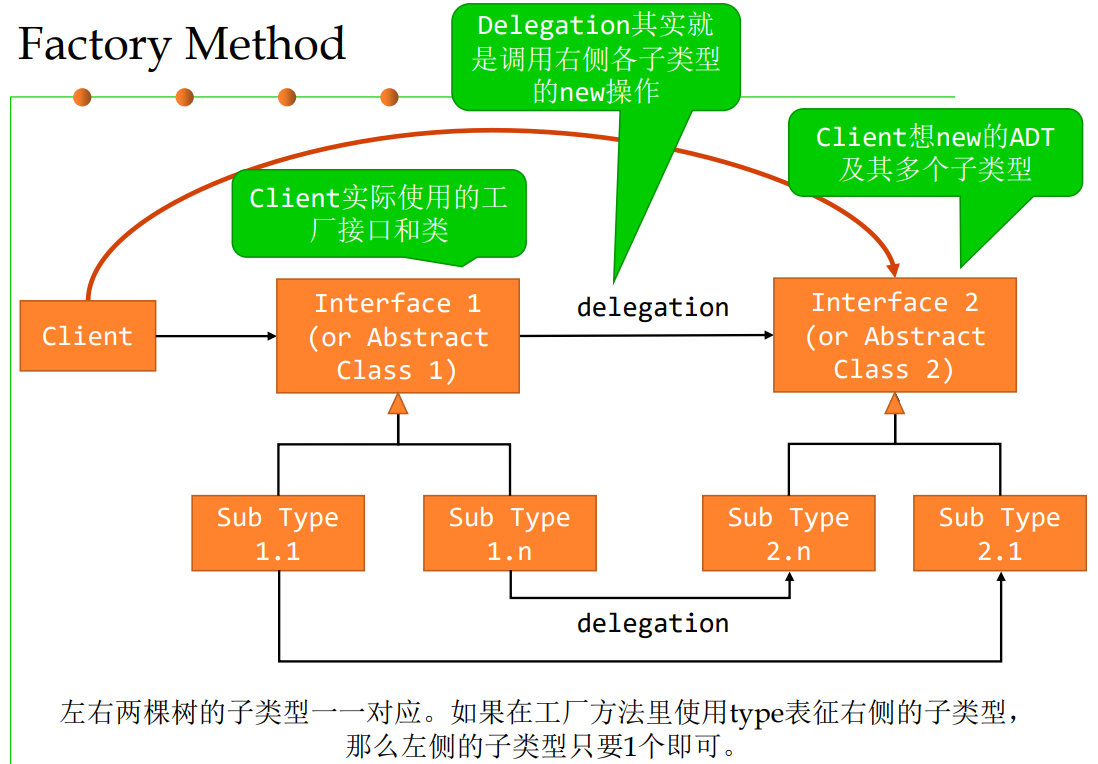
1 🍉Creational patterns
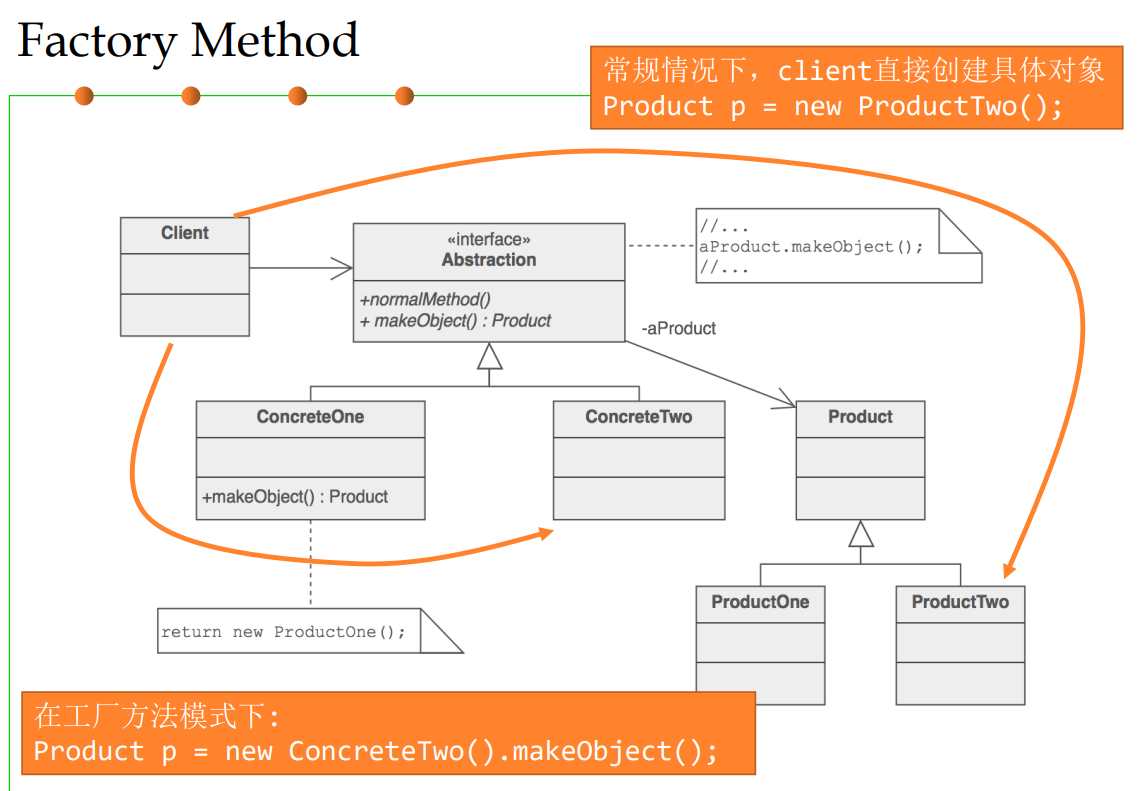
Factory Method pattern(工厂方法)
Also known as “Virtual Constructor”(虚拟构造器)
- 当client不知道要创建哪个具体类的实例,或者不想在client代码中指明要具体 创建的实例时,用工厂方法。
- 定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让其子类来决定实例化哪一个类,从而使一个 类的实例化延迟到其子类。
// Abstract product
public interface Trace{
// turn om and off debugging
public void setDebug(boolean debug);
// write out aa debug message
public void debug(String message);
// write out an error message
public void error(String message);
}
// Concrete product 1
public class FileTrace implements Trace{...}
// Concrete product 1
public class SystemTrace implements Trace{...}
工厂方法来创建实例
interface TraceFactory {
public Trace getTrace();
public Trace getTrace(String type);
void otherOperation(){};
}
public class Factory1 implements TraceFactory {
public Trace getTrace() {
return new SystemTrace();
}
}
// 根据类型决定创建哪个具体产品
public class Factory2 implements TraceFactory {
public getTrace(String type) { // public static getTrace(String type);
if(type.equals(“file”)
return new FileTrace();
else if (type.equals(“system”)
return new SystemTrace();
}
}
Trace log1 = new Factory1().getTrace(); // TraceFactory2.getTrace(“system”)
log1.setDebug(true);
log1.debug( "entering log" );
Trace log2 = new Factory2().getTrace("system");
log2.setDebug(false);
log2.debug("...");
2 🍈Structural patterns
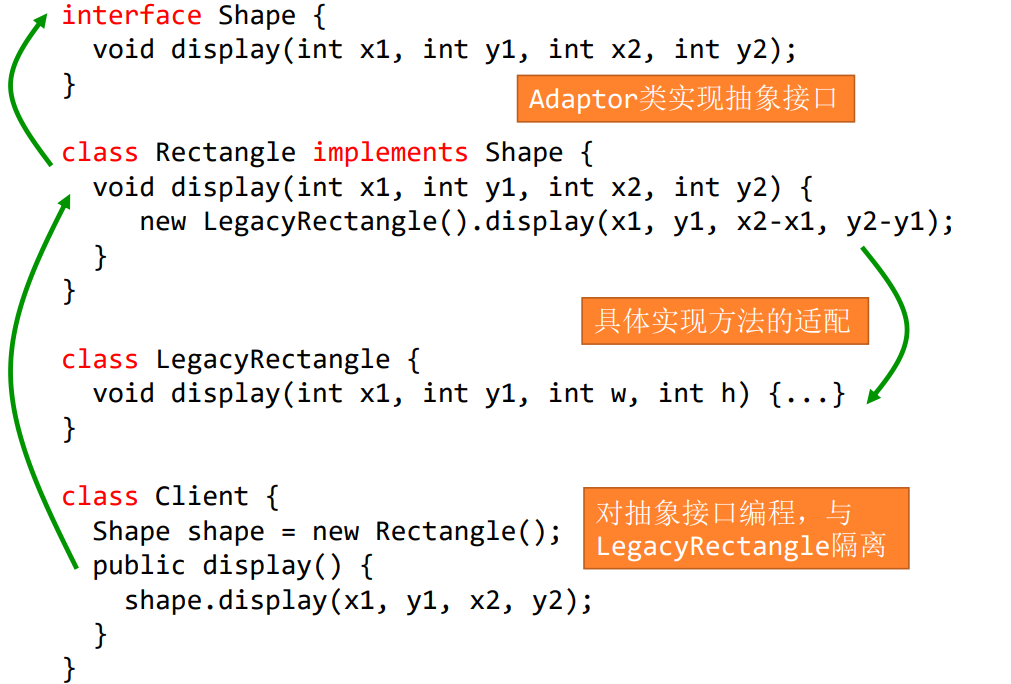
2.1 Adapter适配器模式
Convert the interface of a class into another interface that clients expect to get.
将某个类/接口转换为client期望的其他形式
A LegacyRectangle 组件的 display() 方法希望接收 接收 "x、y、w、h "参数。但客户希望传递 "左上方 x 和 y "以及 "右下方 ”x 和 y”。这种不协调可以通过添加额外的间接层(即适配器对象)来解决。
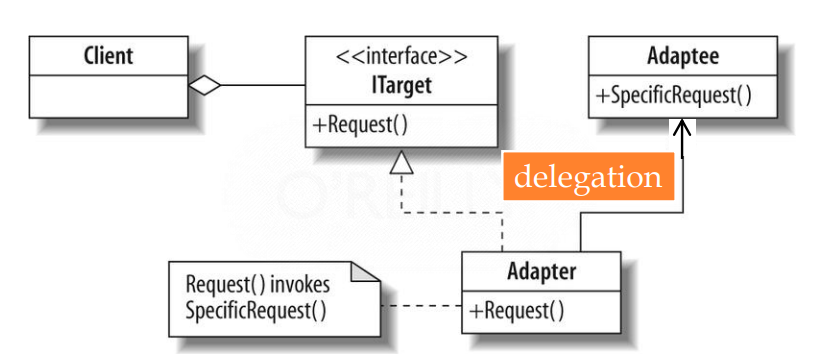
没有适配器
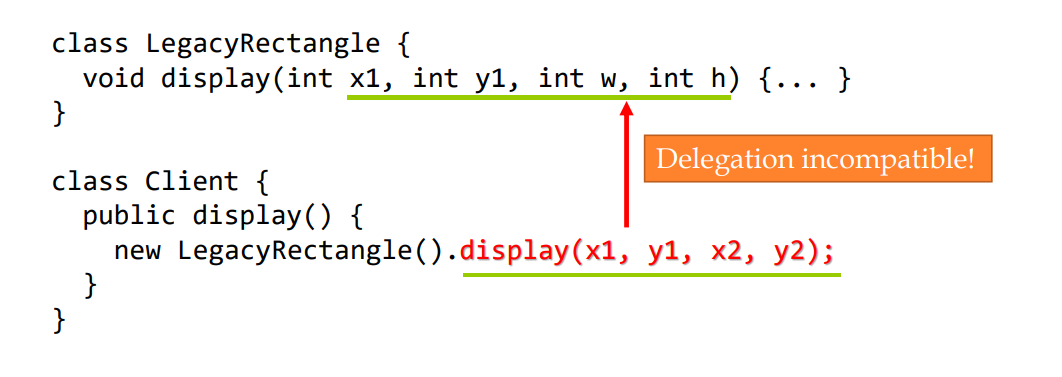
有适配器
2.2 Decorator(装饰器模式)
对每一个特性构造子类,通过委派机制增加到对象上
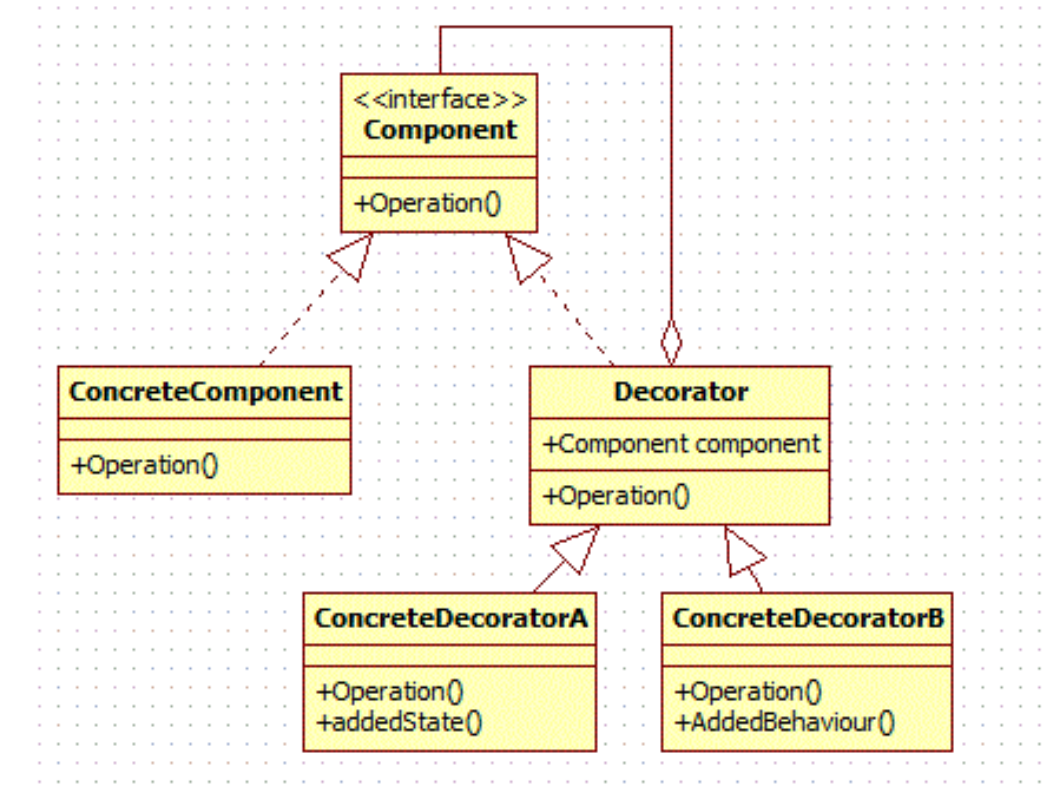
继承与装饰器的区别
- 目的:继承主要用于实现代码重用和扩展功能,而装饰器主要用于在不修改原有类代码的情况下动态地添加新功能或修改其行为。
- 耦合性:继承可能导致较高的耦合性,因为子类与父类紧密相关;而装饰器与原始类之间的耦合度较低,因为它们之间是通过接口或抽象类进行交互的。
- 灵活性:装饰器比继承更灵活,因为它们可以在运行时动态地添加或删除功能,而不需要修改原始类的代码。
- 扩展性:虽然继承也支持扩展功能,但装饰器提供了一种更灵活、更可维护的方式来扩展类的功能。
- 使用场景:当需要在多个类之间共享一些公共功能时,可以使用继承;当需要在不修改原始类代码的情况下动态地添加新功能或修改其行为时,可以使用装饰器。
An example
以下是一个使用装饰器设计模式的具体例子,这个例子展示如何为一个简单的咖啡类添加不同的“调料”或“装饰”,比如加奶或加糖。
首先,我们定义一个Coffee接口,它有一个getCost()方法和一个getDescription()方法:
public interface Coffee {
double getCost();
String getDescription();
}
然后,我们创建一个实现了Coffee接口的简单咖啡类SimpleCoffee:
public class SimpleCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 2.0;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "Simple Coffee";
}
}
接下来,我们定义一个装饰器基类CoffeeDecorator,它也实现了Coffee接口,并持有一个Coffee对象的引用:
public abstract class CoffeeDecorator implements Coffee {
protected Coffee coffee;
public CoffeeDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
this.coffee = coffee;
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return coffee.getCost();
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return coffee.getDescription();
}
}
现在,我们可以创建具体的装饰器类,比如MilkDecorator(加奶的装饰器)和SugarDecorator(加糖的装饰器):
public class MilkDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
public MilkDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 0.5; // 假设加奶增加0.5元
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + ", Milk";
}
}
public class SugarDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
public SugarDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 0.3; // 假设加糖增加0.3元
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + ", Sugar";
}
}
最后,我们创建一个客户端类来测试这些装饰器:
public class CoffeeShop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coffee coffee = new SimpleCoffee();
System.out.println("Cost: " + coffee.getCost() + ", Description: " + coffee.getDescription());
coffee = new MilkDecorator(coffee);
System.out.println("Cost: " + coffee.getCost() + ", Description: " + coffee.getDescription());
coffee = new SugarDecorator(coffee);
System.out.println("Cost: " + coffee.getCost() + ", Description: " + coffee.getDescription());
// 也可以先加糖再加奶
Coffee anotherCoffee = new SimpleCoffee();
anotherCoffee = new SugarDecorator(anotherCoffee);
anotherCoffee = new MilkDecorator(anotherCoffee);
System.out.println("Cost: " + anotherCoffee.getCost() + ", Description: " + anotherCoffee.getDescription());
}
}
运行CoffeeShop的main方法,你将看到不同装饰器对咖啡成本和描述的影响。这就是装饰器设计模式的一个具体实现,它允许我们在运行时动态地给对象添加新的责任(比如加奶或加糖),同时保持代码的灵活性和可扩展性。
3 🍌Behavioral patterns
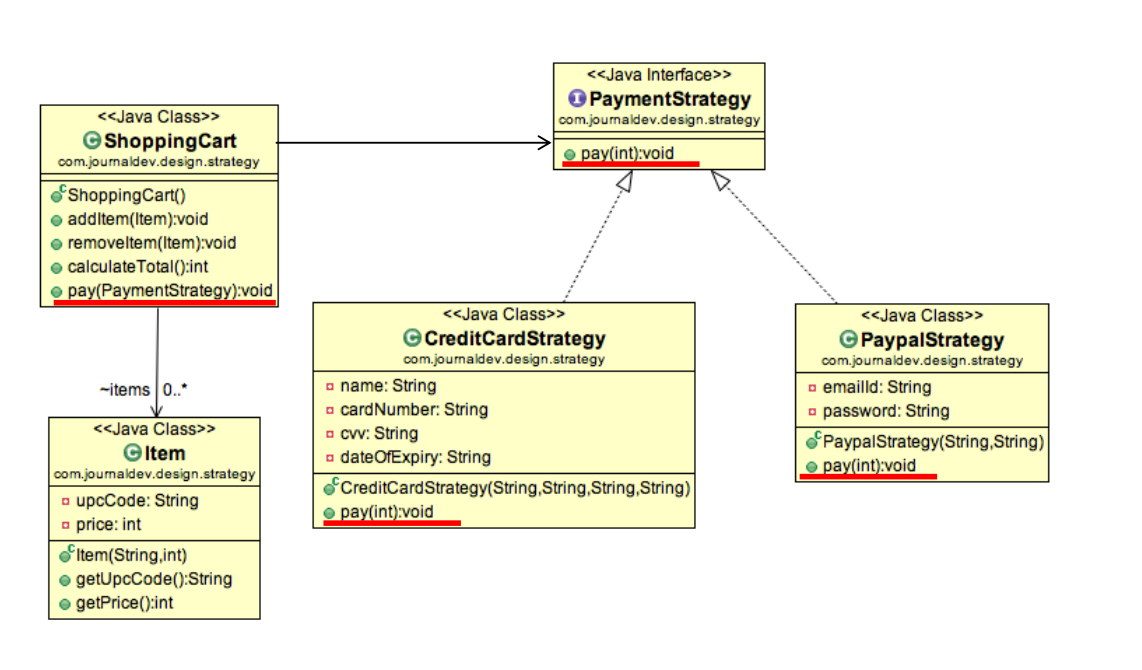
3.1 Strategy
有多种不同的算法来实现同一个任务,但需要client根据需要 动态切换算法,而不是写死在代码里
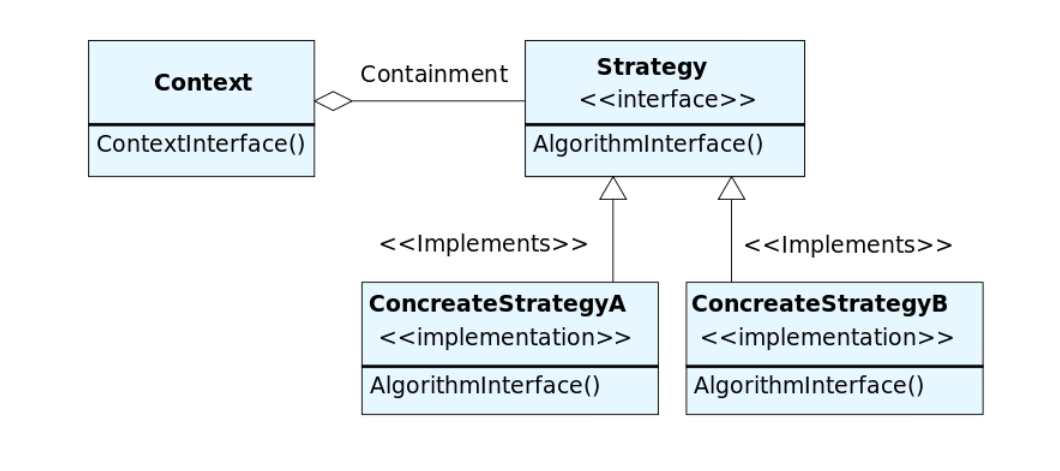
public interface PaymentStrategy {
public void pay(int amount);
}
public class CreditCardStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
private String name;
private String cardNumber;
private String cvv;
private String dateOfExpiry;
public CreditCardStrategy(String nm, String ccNum,
String cvv, String expiryDate){
this.name=nm;
this.cardNumber=ccNum;
this.cvv=cvv;
this.dateOfExpiry=expiryDate;
}
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
System.out.println(amount +" paid with credit card");
}
}
public class PaypalStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
private String emailId;
private String password;
public PaypalStrategy(String email, String pwd){
this.emailId=email;
this.password=pwd;
}
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
System.out.println(amount + " paid using Paypal.");
}
}
策略设计模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,使它们可以互相替换。策略模式使得算法可以独立于使用它的客户端变化。
在给出的代码中,我们可以看到以下组成部分:
- 策略接口 (
PaymentStrategy):
定义了一个支付策略的公共接口,即pay(int amount)方法。客户端代码将使用此接口与不同的支付策略交互,而无需知道它们的具体实现。 - 具体策略 (
CreditCardStrategy和PaypalStrategy):
这两个类分别实现了PaymentStrategy接口,提供了不同的支付算法实现。它们分别对应于使用信用卡和PayPal进行支付的逻辑。CreditCardStrategy类保存了信用卡的相关信息(如持卡人姓名、卡号、CVV和到期日期),但在pay方法中并没有使用这些信息,只是简单地打印了一条消息。在实际应用中,这些信息可能会被用来与信用卡处理系统交互以完成支付。PaypalStrategy类保存了PayPal账户的相关信息(如电子邮件和密码),但同样在pay方法中并没有使用这些信息,只是打印了一条消息。在实际应用中,这些信息可能会被用来与PayPal系统交互以完成支付。
- 客户端代码:
客户端代码通常会包含一个PaymentStrategy类型的变量,并使用它来执行支付操作。客户端代码可以通过在运行时动态地更改此变量的类型来选择不同的支付策略。
下面是一个简单的客户端代码示例,展示了如何使用这些策略:
public class PaymentClient {
private PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy;
public PaymentClient(PaymentStrategy strategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = strategy;
}
public void makePayment(int amount) {
paymentStrategy.pay(amount);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PaymentClient client = new PaymentClient(new CreditCardStrategy("John Doe", "1234567890123456", "123", "12/25"));
client.makePayment(100); // 100 paid with credit card
client = new PaymentClient(new PaypalStrategy("user@example.com", "password"));
client.makePayment(50); // 50 paid using Paypal.
}
}
在这个示例中,PaymentClient类封装了对支付策略的引用,并提供了makePayment方法来执行支付操作。通过向PaymentClient构造函数传入不同的PaymentStrategy对象,我们可以动态地更改其使用的支付策略。
3.2 Template Method
做事情的步骤一样,但具体方法不同;共性的步骤在抽象类内公共实现,差异化的步骤在各个子类中实现
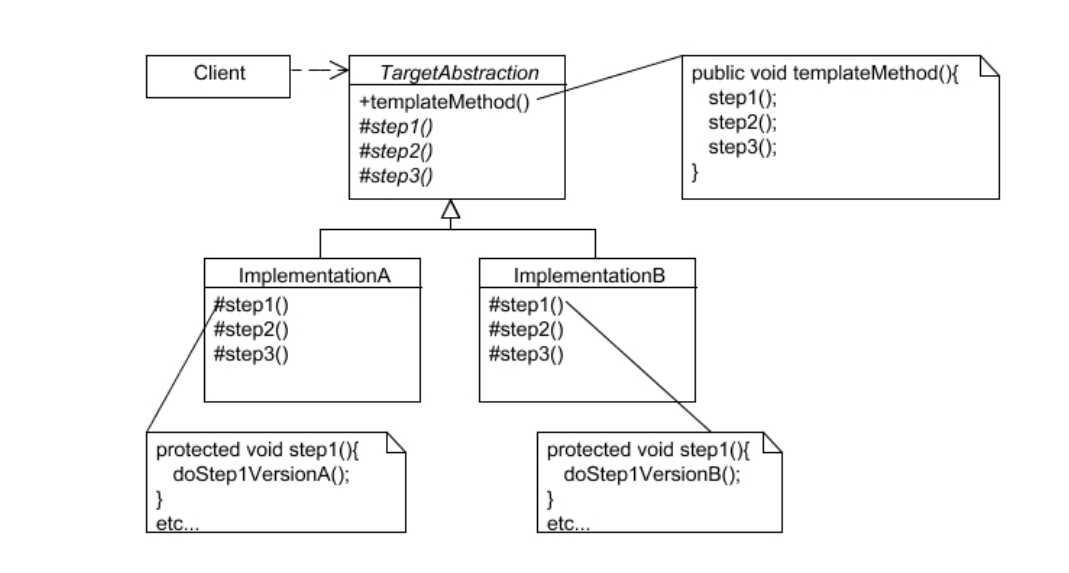
Template Method设计模式是一种行为设计模式,它在一个方法中定义了一个算法的骨架,并允许子类为一个或多个步骤提供实现。模板方法使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重新定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
public abstract class OrderProcessTemplate {
public boolean isGift;
public abstract void doSelect();
public abstract void doPayment();
public void giftWrap() {
System.out.println("Gift wrap done.");
}
public abstract void doDelivery();
public final void processOrder() {
doSelect();
doPayment();
if (isGift)
giftWrap();
doDelivery();
}
}
public class NetOrder extends OrderProcessTemplate {
@Override
public void doSelect() { … }
@Override
public void doPayment() { … }
@Override
public void doDelivery() { … }
}
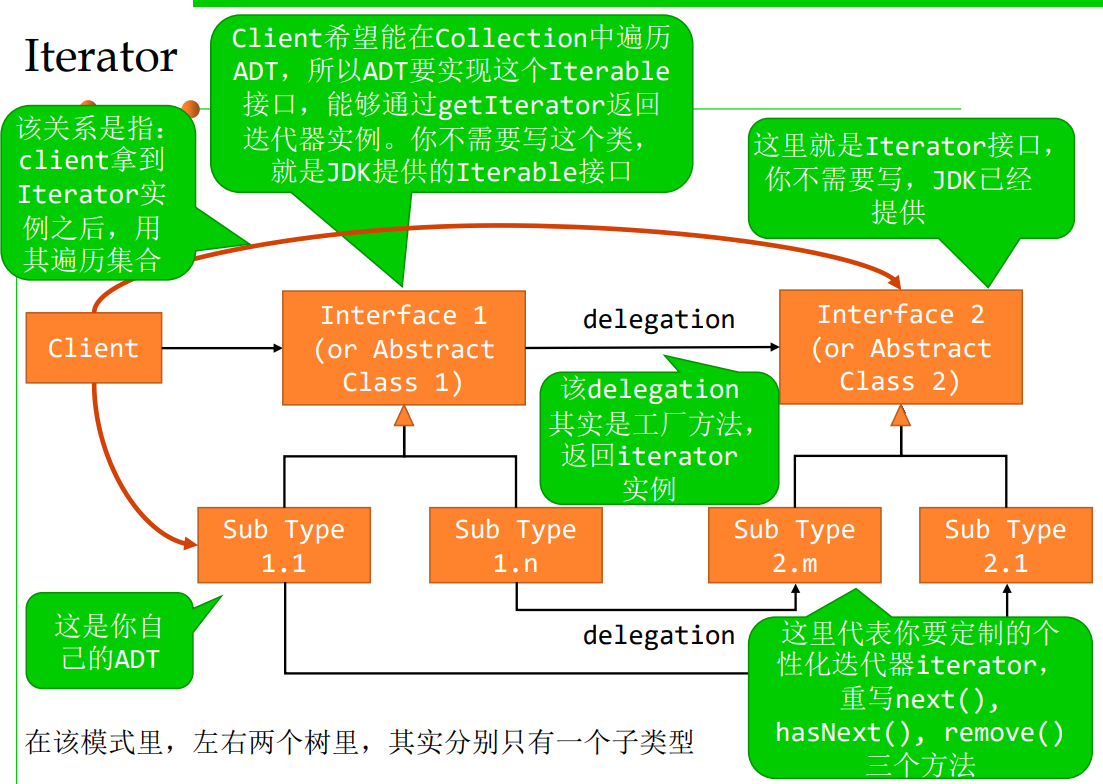
3.3 Iterator
客户端希望遍历被放入 容器/集合类的一组ADT对象,无需关心容器的具体类型
也就是说,不管对象被放进哪里,都应该提供同样的遍历方式
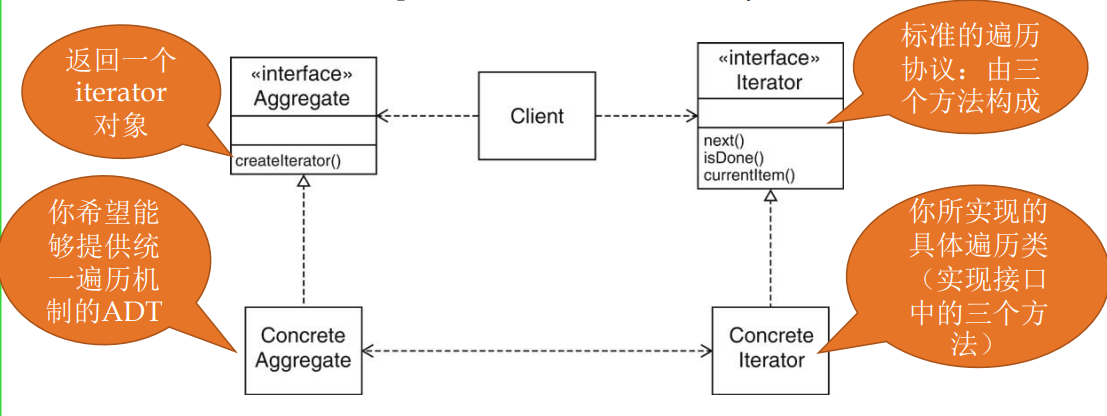
Iterable接口:实现该接口的集合对象是可迭代遍历的
public interface Iterable<T> {
...
Iterator<T> iterator();
}
Iterator接口:迭代器
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
void remove();
}
Iterator pattern:让自己的集合类实现Iterable接口,并实现自己的独特Iterator迭代器(hasNext, next, remove),允许客户端利用这个 迭代器进行显式或隐式的迭代遍历:

迭代器设计模式包含以下几个主要角色:
- 迭代器(Iterator):
- 定义一个访问聚合对象元素但不暴露其内部表示的接口。
- 提供遍历聚合对象的方法,如
hasNext()(检查是否还有下一个元素)和next()(获取下一个元素)。
- 具体迭代器(ConcreteIterator):
- 实现迭代器接口,并跟踪遍历中的当前位置。
- 使用聚合对象的内部表示法来遍历元素。
- 聚合(Aggregate):
- 定义创建迭代器对象的接口。
- 通常是包含一组元素的类,如列表、集合等。
- 具体聚合(ConcreteAggregate):
- 实现聚合接口,返回具体迭代器的实例。
- 在具体聚合中,通常包含存储元素的私有成员变量。
下面是一个简单的Java示例,展示了迭代器设计模式的基本用法:
// 聚合接口
interface Aggregate {
Iterator createIterator();
}
// 迭代器接口
interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
}
// 具体聚合(例如一个列表)
class MyList implements Aggregate {
private List<Object> elements = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加元素的方法
public void add(Object element) {
elements.add(element);
}
// 创建迭代器的方法
@Override
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new MyListIterator(this);
}
// 内部类:具体迭代器
private class MyListIterator implements Iterator {
private int currentIndex = 0;
private MyList list;
public MyListIterator(MyList list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return currentIndex < list.elements.size();
}
@Override
public Object next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return list.elements.get(currentIndex++);
}
}
}
// 客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyList list = new MyList();
list.add("Element 1");
list.add("Element 2");
list.add("Element 3");
Iterator iterator = list.createIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
显示的迭代
在这个示例中,MyList类实现了Aggregate接口,并提供了创建迭代器的方法。MyListIterator是MyList的内部类,实现了Iterator接口,并用于遍历MyList中的元素。客户端代码通过调用createIterator()方法获取迭代器,并使用迭代器遍历聚合对象中的元素。
An example of Iterator pattern
public class Pair<E> implements Iterable<E> {
private final E first, second;
public Pair(E f, E s) { first = f; second = s; }
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new PairIterator();
}
private class PairIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private boolean seenFirst = false, seenSecond = false;
public boolean hasNext() { return !seenSecond; }
public E next() {
if (!seenFirst) { seenFirst = true; return first; }
if (!seenSecond) { seenSecond = true; return second; }
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
}

尽管for-each循环在语法上看起来像是隐式迭代,但实际上它仍然依赖于Iterable接口和Iterator的实现来工作。在运行时,Java会调用iterable.iterator()来获取迭代器,并使用迭代器的hasNext()和next()方法来遍历元素。因此,虽然从语法上看似隐式,但从实现上看,迭代仍然是显式的。(for-each循环是Java提供的一种语法糖,用于简化对实现了Iterable<E>接口集合的遍历。)
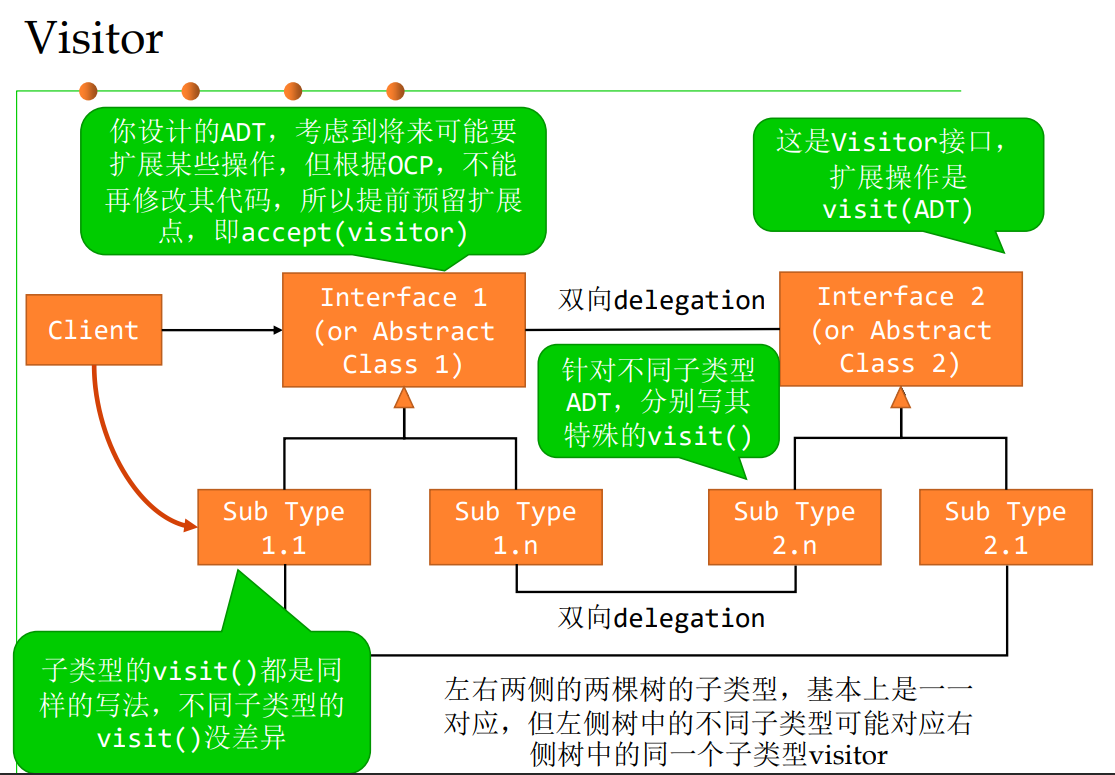
3.4 Visitor
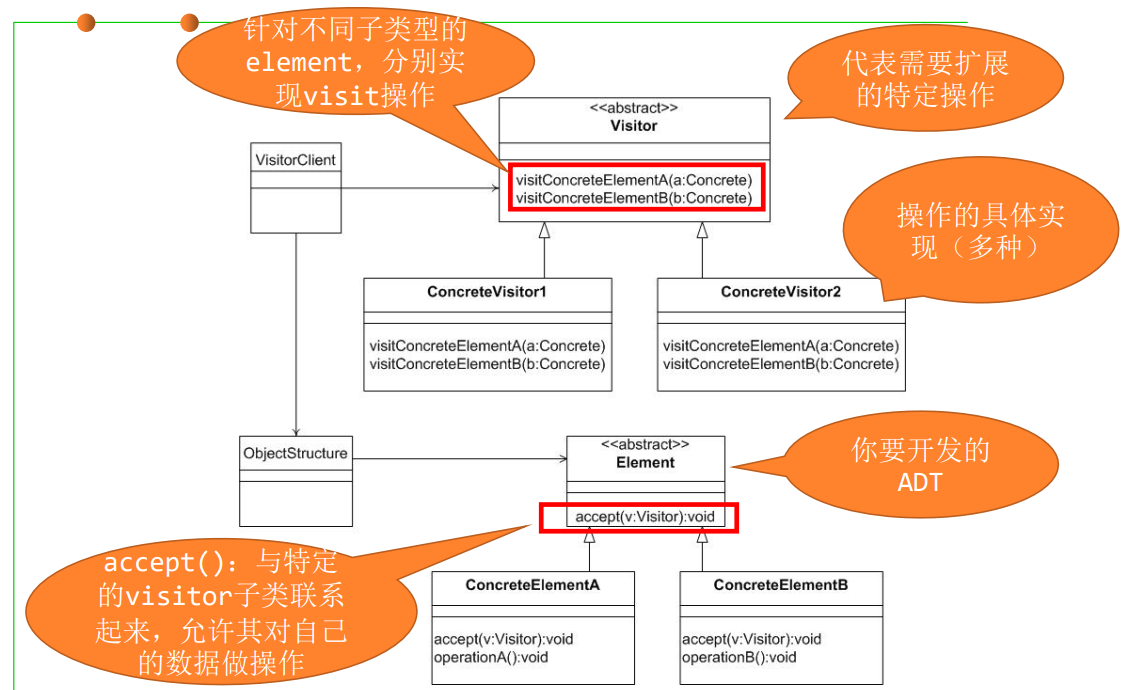
/* Abstract element interface (visitable) */
public interface ItemElement {
public int accept(ShoppingCartVisitor visitor);
}
/* Concrete element */
public class Book implements ItemElement{
private double price;
...
int accept(ShoppingCartVisitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
}
public class Fruit implements ItemElement{
private double weight;
...
int accept(ShoppingCartVisitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
}
代码展示了Visitor设计模式中的一部分,包括一个抽象元素接口(ItemElement)和两个具体的元素类(Book 和 Fruit)。这里我会逐一分析并解释代码。
抽象元素接口(ItemElement)
/* Abstract element interface (visitable) */
public interface ItemElement {
public int accept(ShoppingCartVisitor visitor);
}
- 接口定义:
ItemElement是一个接口,它定义了一个名为accept的方法,该方法接受一个类型为ShoppingCartVisitor的参数,并返回一个整数。这个接口表示可以被访问(或称为“可访问的”)的元素。 - 方法
accept:这个方法用于允许一个ShoppingCartVisitor对象“访问”当前的元素对象。accept方法中通常不会包含任何具体的业务逻辑,它只是调用传入的visitor对象的visit方法,并将当前对象(this)作为参数传递。
具体元素类
Book 类
/* Concrete element */
public class Book implements ItemElement{
private double price;
// ... 其他成员变量和方法 ...
int accept(ShoppingCartVisitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
}
- 类定义:
Book类实现了ItemElement接口,这意味着它必须提供accept方法的实现。 - 方法
accept:Book类的accept方法按照ItemElement接口的定义实现了对ShoppingCartVisitor的访问。当accept方法被调用时,它会将this(即当前的Book对象)传递给visitor对象的visit方法。 - 注意:
accept方法应该是public的,因为接口中的方法默认是public的。但是在您提供的Book类的定义中,accept方法是默认的包级私有访问权限(即没有显式地声明为public)。这会导致编译错误,因为子类必须实现接口中的所有方法,并且这些方法的访问级别必须与接口中定义的访问级别相匹配。
Fruit 类
public class Fruit implements ItemElement{
private double weight;
// ... 其他成员变量和方法 ...
int accept(ShoppingCartVisitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
}
- 类定义:
Fruit类同样实现了ItemElement接口,并且也需要提供一个accept方法的实现。 - 方法
accept:与Book类类似,Fruit类的accept方法也是将当前对象(this)传递给visitor对象的visit方法。 - 同样的问题:
accept方法也应该是public的,否则会导致编译错误。
总结
代码展示了Visitor设计模式的一部分,但是有几个地方需要注意:
accept方法的访问级别:在Book和Fruit类中,accept方法应该是public的,以便它们可以正确地实现ItemElement接口。ShoppingCartVisitor接口:虽然您没有提供ShoppingCartVisitor接口的定义,但根据代码中的使用,我们可以推测它应该定义了一个或多个visit方法,这些方法接受不同类型的ItemElement(例如Book和Fruit)作为参数。- 返回类型:
accept方法返回了一个整数。在Visitor模式中,这通常用于表示操作的结果或状态,但在某些情况下,该方法也可能返回void。 - 方法的实际业务逻辑:通常,在
accept方法内部不直接执行业务逻辑,而是在visitor的visit方法中执行。这样,您就可以在不修改元素类的情况下添加新的操作。
/* Abstract visitor interface */
public interface ShoppingCartVisitor {
int visit(Book book);
int visit(Fruit fruit);
}
public class ShoppingCartVisitorImpl implements ShoppingCartVisitor {
public int visit(Book book) {
int cost=0;
if(book.getPrice() > 50){
cost = book.getPrice()-5;
}else
cost = book.getPrice();
System.out.println("Book ISBN::"+book.getIsbnNumber() + " cost ="+cost);
return cost;
}
public int visit(Fruit fruit) {
int cost = fruit.getPricePerKg()*fruit.getWeight();
System.out.println(fruit.getName() + " cost = "+cost);
return cost;
}
}
4 🫐Commonality and Difference of Design Patterns
4.1 共性样式1
只使用“继承”,不使用“delegation” 核心思路:OCP/DIP 依赖反转,客户端只依赖“抽象”,不能 依赖于“具体” 发生变化时最好是“扩展”而不是“修改”
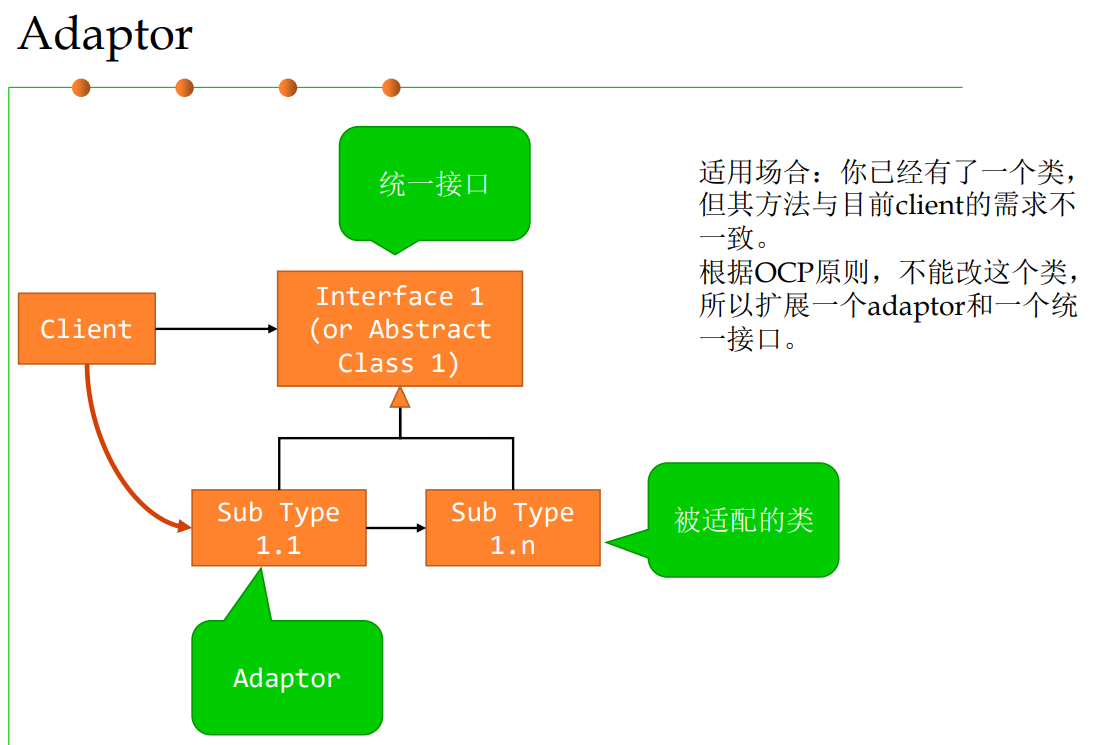
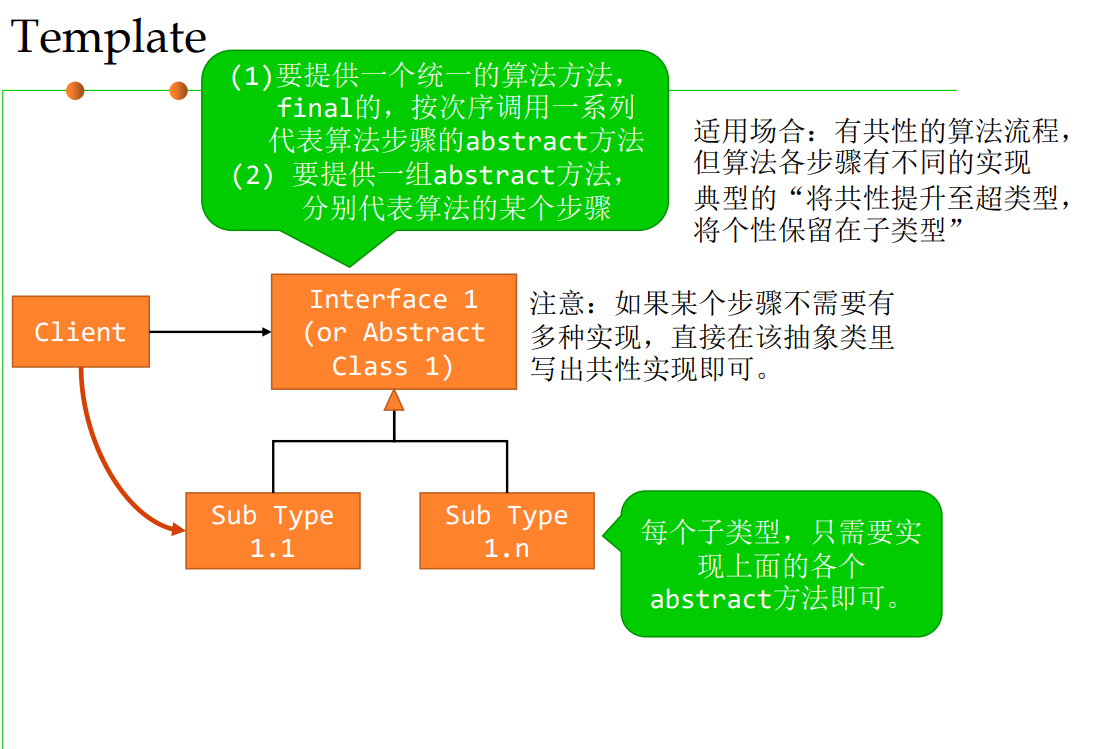
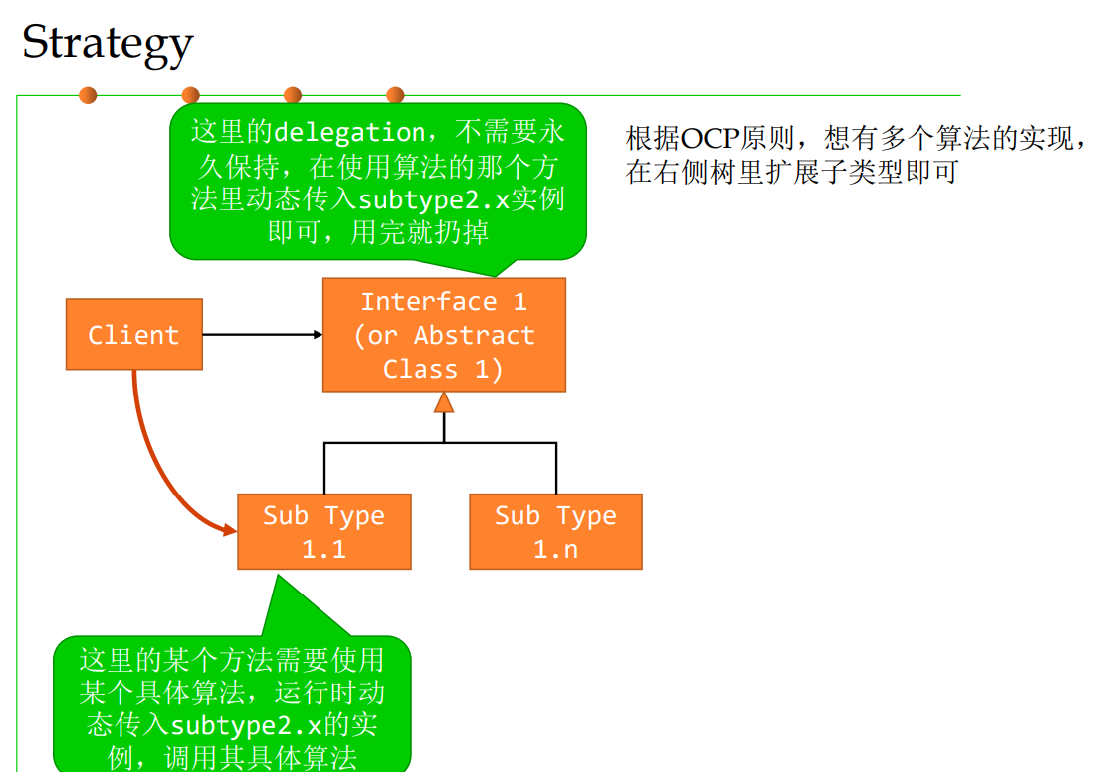
4.2 共性样式2
两棵“继承树”,两个层次的“delegation”