paper:LLA: Loss-aware Label Assignment for Dense Pedestrian Detection
code:https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/LLA
背景
标签分配由于对检测器的性能影响很大,在通用目标检测中得到了广泛的研究,但是密集行人检测中的标签分配关注很少。密集行人检测和一般目标检测主要有以下两点区别:
不同个体之间的姿态差别很大
人体区域可能会被他人严重遮挡
存在的问题
在anchor-based的模型中,利用anchor与GT之间的IoU进行标签分配是常用的方法,但对于姿态千变万化的行人检测,基于IoU大小得到的positive anchor可能不是最合适的,比如在下图中,绿色框为目标的GT box,红色框是基于IoU分配的postive anchor,可以看到虽然两者的IoU很大,但anchor box中只包含了很小部分的前景,显然不是最优选择。

在anchor-free的模型中,比如FCOS,如果一组anchor points落入GT box中心的一个正方形区域中,同时落在事先定义尺度区间中,则它们被指定为positive anchor points。在密集行人检测中,遮挡问题很常见,如果一个人被另一个人严重遮挡,这个人GT box的几何中心可能落在另一个人的身上,这将导致导致采样点的特征和目标不一致。
本文的创新点
基于以上两个问题,本文提出了一种新的标签分配方法Loss-aware Label Assignment(LLA),LLA首先计算每个anchor和每个GT之间的分类和回归损失,然后定义联合损失为分类损失和回归损失的加权和作为标签分配的指标,最后将与某一个GT联合损失最小的K个anchor作为该GT的正样本,未分配和任何GT的anchor作为负样本。LLA是基于这样一种观察:联合损失较小的anchor通常包含更丰富的语义信息,因此可以更好的表示对应的GT。
方法介绍
给定一张输入图片 \(M\),假设共有 \(J\) 个anchor和 \(I\) 个GT,在一次前向传播中,我们可以得到分类得分预测 \(S(\theta, M)\in \mathbb{R}^{J\times N}\),其中 \(N\) 是类别数,\(\theta\) 是模型权重参数,同时可以得到bounding box预测 \(B(\theta, M)\in \mathbb{R}^{J\times 4}\)。之前只计算每个anchor和其分配的GT之间损失的方法不同,LLA计算所有anchor和所有GT之间的损失,得到:
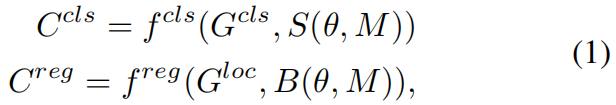
其中 \(C^{cls}\in \mathbb{R}^{I\times J}\),\(C^{reg}\in \mathbb{R}^{I\times J}\)。\(G^{cls}\) 和 \(G^{loc}\) 分别是GT的类别和边界框标注。\(f^{cls}\) 是binary cross entropy Loss或Focal Loss,\(f^{reg}\) 可以是任何回归损失比如Smooth L1、IoU、GIoU Loss。然后,按下式计算一个Cost Matrix
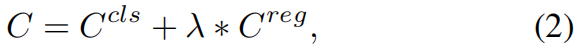
其中 \(C\in \mathbb{R}^{I\times J}\),\(C_{ij}\) 表示anchor \(a_{j}\) 和GT \(g_{i}\) 之间的联合损失,\(C_{ij}\) 越小,\(a_{j}\) 越有可能被分配给 \(g_{i}\)。因此,我们选择 \(C\) 中每行最小的 \(K\) 个值,并且将对应的anchor-GT对作为匹配的候选。但是,作者在实验中发现,在训练的初始阶段,由于模型的拟合不足,LLA很难得到稳定的分配结果。为了帮助模型更快收敛,作者添加了一个空间先验,即只有当 \(a_{j}\) 或 \(a_{j}\) 的中心点落入 \(g^{loc}_{i}\) 的范围中,才将 \(a_{j}\) 分配给 \(g_{i}\),基于此先验作者引入了 \(C^{inbox}\)
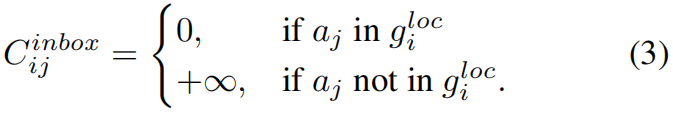
在具体实现中,\(+\infty \) 用一个大的正值比如102替代,Restricted Cost Matrix如下
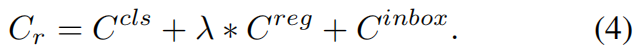
最后挑选 \(C\) 中最小的 \(K\) 个值,得到assignment matrix \(\pi _{ij}\in \left \{ 0,1 \right \} \)

注意,如果一个anchor被分配给了多个GT,选择联合损失最小的的那个GT。
实验结果
消融实验
Effect of LLA
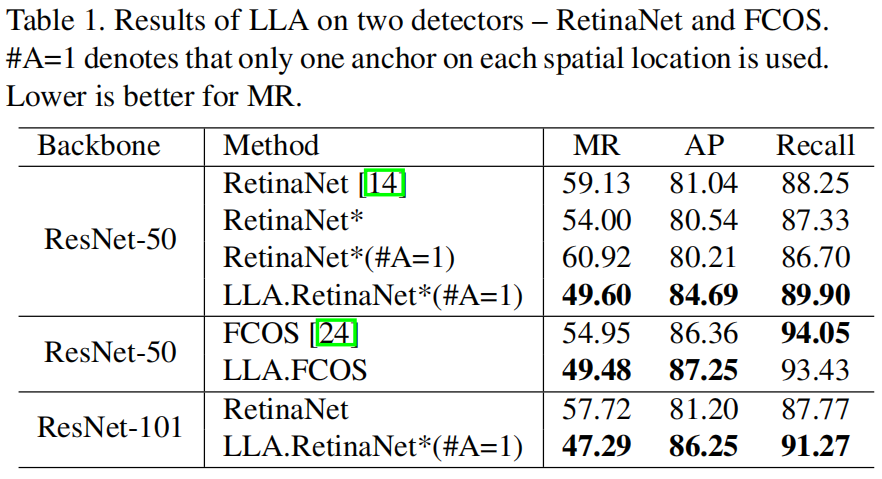
下表是将LLA应用到RetinaNet和FCOS上的结果对比,其中RetinaNet*是将原始RetinaNet中的Smooth L1 Loss换成了GIoU Loss,#A=1表示将原始RetinaNet中的anchor数量由9个减少为1个,MR是行人检测中的评价指标,越小越好。可以看出,将RetinaNet和FCOS原始的标签分配方法换成LLA后,性能都得到了提升
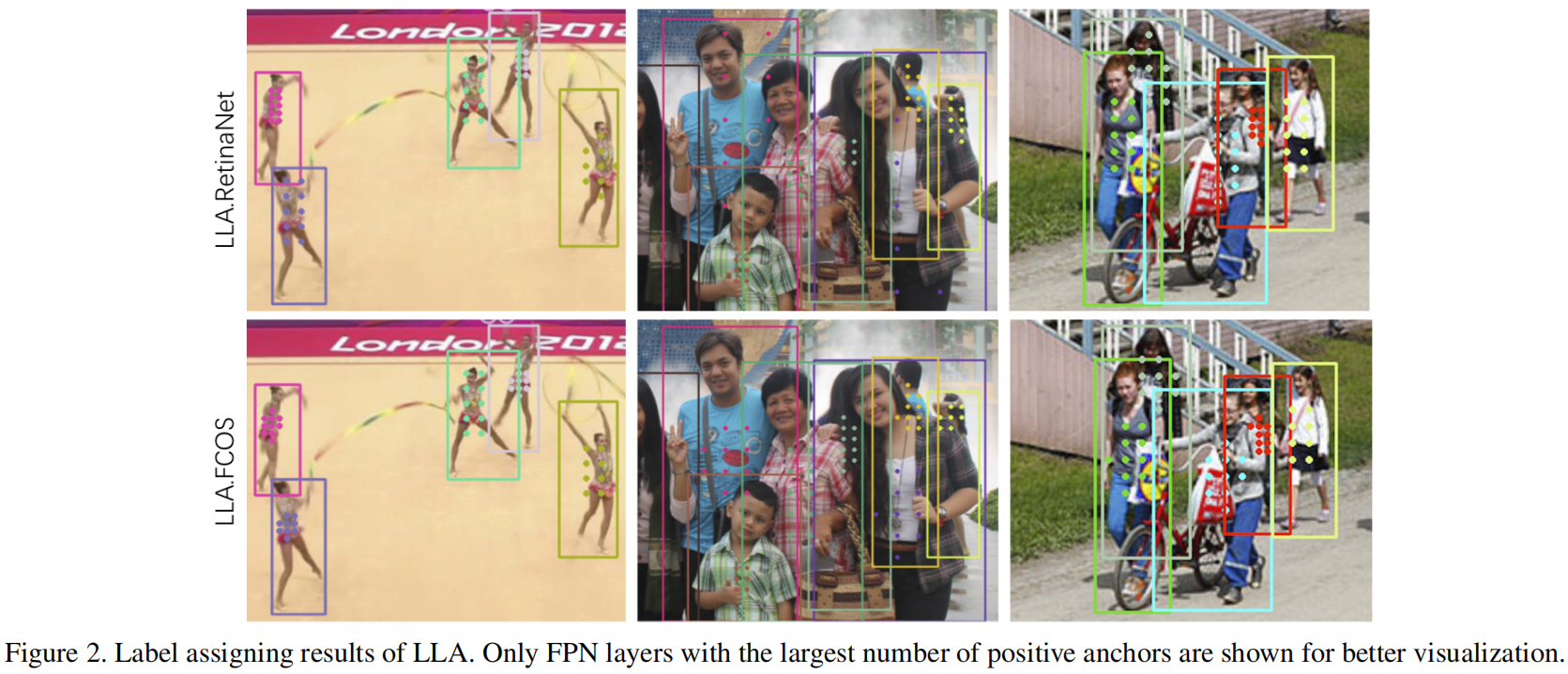
从下图第一列可以看出,不是均匀的分布在GT box中,LLA中分配positive anchor更紧凑的落在了前景目标上。从第二列和第三列可以看出,对于严重遮挡的人体,LLA分配的positive anchor更多的落在了可见区域如头部、肩膀等,并且离GT box的几何中心较远。

Analysis of Each Component in Restricted Cost Matrix
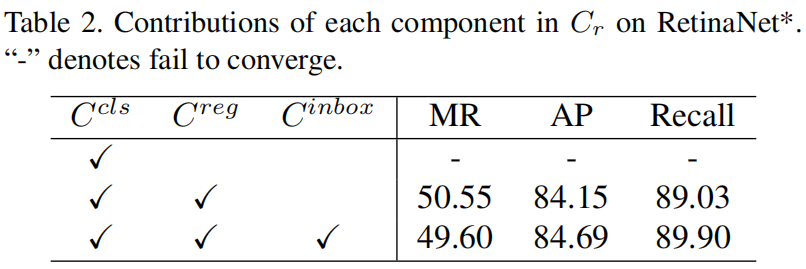
下表是Restricted Cost Matrix中的各项对最终精度的影响,可以看出,当只有 \(C^{cls}\) 时,这主要是因为 \(C^{cls}\) 无法帮助模型区分同一类别的不同实例,比如一个anchor可能在属于同一类别的多个实例的topk锚框列表中。当引入 \(C^{reg}\) 后模型性能已经超过了baseline,当引入 \(C^{inbox}\) 后,模型的性能得到了进一步提升。
Different Usage of IoU/GIoU Loss
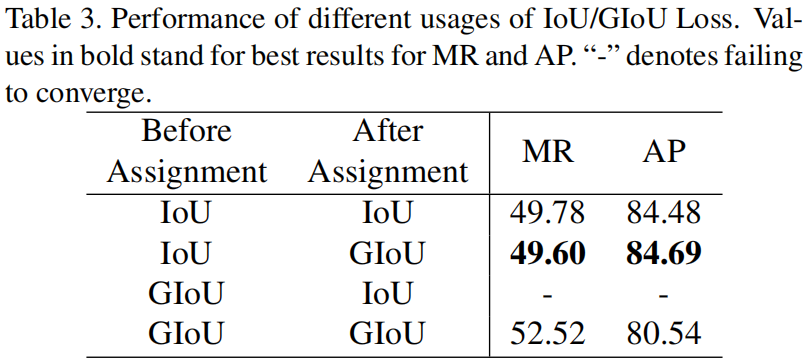
IoU在LLA中一共使用了两次,一次是在标签分配之前计算每一个anchor和每一个GT之间的回归损失,另一次是在标签分配后,计算anchor和对应GT之间的回归损失,作者选择的是IoU和GIoU,从下表可以看出,这种组合的精度最高。
Effect of K
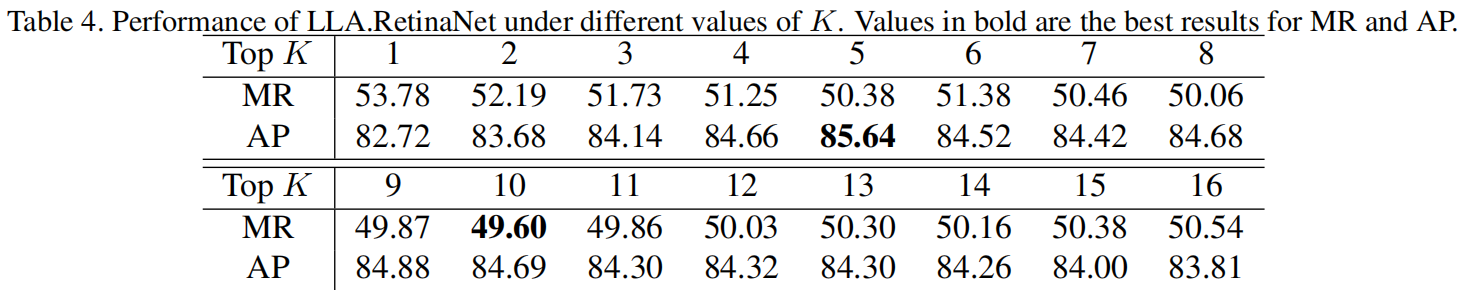
超参K是事先设定的为每个GT分配的positive anchor的数量,K太小会导致候选对象不足,K太多会导致引入过多低质量候选对象,从下表可以看出,K=10时,模型的MR最小。
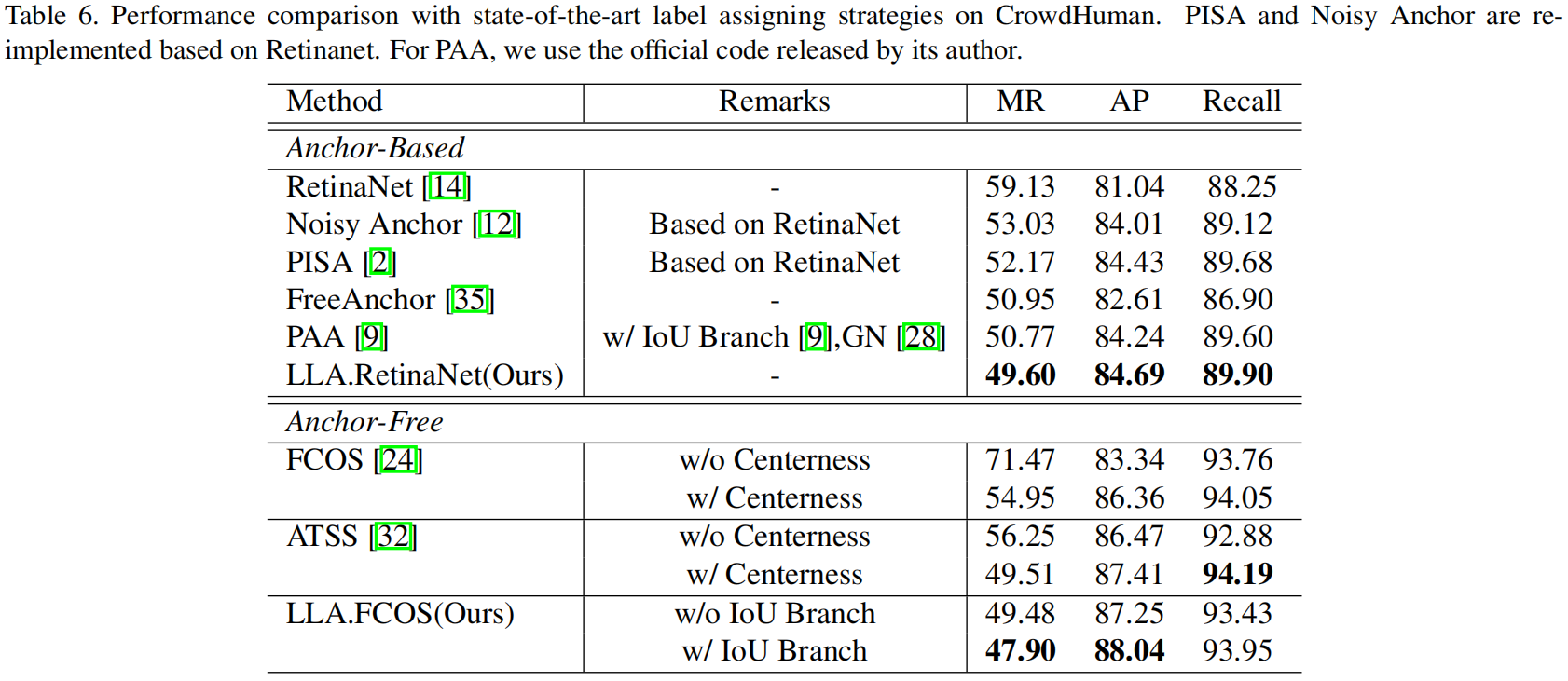
Comparison with SOTA
下表是LLA和其它一些sota label assgnment方法在CrowdHuman数据集上的精度对比,可以看到LLA得到了最好的性能表现。
代码解析
下面是官方的实现代码,加了一些注释。其中Line 284是计算restricted cost matrix的代码loss = loss_cls + self.reg_cost * loss_delta + 1e3 * (1 - is_in_boxes.float()),Line 292是挑选topk个联合损失最小的anchor作为正样本,Line 301是处理多个GT分配个同一个anchor的情况。
import logging
import math
from typing import List
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.distributed as dist
from cvpods.layers import ShapeSpec, batched_nms, cat
from cvpods.structures import Boxes, ImageList, Instances
from cvpods.utils import log_first_n
from cvpods.modeling.box_regression import Shift2BoxTransform
from cvpods.modeling.postprocessing import detector_postprocess
from cvpods.modeling.meta_arch.retinanet import permute_to_N_HWA_K
from cvpods.modeling.losses import sigmoid_focal_loss_jit, iou_loss
def permute_all_cls_and_box_to_N_HWA_K_and_concat(box_cls,
box_delta,
num_classes=80):
"""
Rearrange the tensor layout from the network output, i.e.:
list[Tensor]: #lvl tensors of shape (N, A x K, Hi, Wi)
to per-image predictions, i.e.:
Tensor: of shape (N x sum(Hi x Wi x A), K)
"""
# for each feature level, permute the outputs to make them be in the
# same format as the labels. Note that the labels are computed for
# all feature levels concatenated, so we keep the same representation
# for the objectness, the box_delta and the centerness
box_cls_flattened = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, num_classes) for x in box_cls]
box_delta_flattened = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, 4) for x in box_delta]
# concatenate on the first dimension (representing the feature levels), to
# take into account the way the labels were generated (with all feature maps
# being concatenated as well)
box_cls = cat(box_cls_flattened, dim=1).view(-1, num_classes)
box_delta = cat(box_delta_flattened, dim=1).view(-1, 4)
return box_cls, box_delta
@torch.no_grad()
def get_ious(inputs, targets, weight=None, box_mode="xyxy", loss_type="iou", reduction="none"):
"""
Compute iou loss of type ['iou', 'giou', 'linear_iou']
Args:
inputs (tensor): pred values
targets (tensor): target values
weight (tensor): loss weight
box_mode (str): 'xyxy' or 'ltrb', 'ltrb' is currently supported.
loss_type (str): 'giou' or 'iou' or 'linear_iou'
reduction (str): reduction manner
Returns:
loss (tensor): computed iou loss.
"""
if box_mode == "ltrb":
inputs = torch.cat((-inputs[..., :2], inputs[..., 2:]), dim=-1)
targets = torch.cat((-targets[..., :2], targets[..., 2:]), dim=-1)
elif box_mode != "xyxy":
raise NotImplementedError
eps = torch.finfo(torch.float32).eps
inputs_area = (inputs[..., 2] - inputs[..., 0]).clamp_(min=0) \
* (inputs[..., 3] - inputs[..., 1]).clamp_(min=0)
targets_area = (targets[..., 2] - targets[..., 0]).clamp_(min=0) \
* (targets[..., 3] - targets[..., 1]).clamp_(min=0)
w_intersect = (torch.min(inputs[..., 2], targets[..., 2])
- torch.max(inputs[..., 0], targets[..., 0])).clamp_(min=0)
h_intersect = (torch.min(inputs[..., 3], targets[..., 3])
- torch.max(inputs[..., 1], targets[..., 1])).clamp_(min=0)
area_intersect = w_intersect * h_intersect
area_union = targets_area + inputs_area - area_intersect
ious = area_intersect / area_union.clamp(min=eps)
return ious
class Scale(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, init_value=1.0):
super(Scale, self).__init__()
self.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor([init_value]))
def forward(self, input):
return input * self.scale
class FCOS(nn.Module):
"""
Implement FCOS (https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002).
"""
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
self.device = torch.device(cfg.MODEL.DEVICE)
# fmt: off
self.num_classes = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.NUM_CLASSES
self.in_features = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.IN_FEATURES
self.fpn_strides = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.FPN_STRIDES
# Loss parameters:
self.focal_loss_alpha = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.FOCAL_LOSS_ALPHA
self.focal_loss_gamma = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.FOCAL_LOSS_GAMMA
self.iou_loss_type = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.IOU_LOSS_TYPE
# Inference parameters:
self.score_threshold = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST
self.topk_candidates = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.TOPK_CANDIDATES_TEST
self.nms_threshold = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.NMS_THRESH_TEST
self.max_detections_per_image = cfg.TEST.DETECTIONS_PER_IMAGE
# LLA parameters:
self.topk = cfg.MODEL.LLA.TopK
self.reg_cost = cfg.MODEL.LLA.REG_COST
# fmt: on
self.backbone = cfg.build_backbone(
cfg, input_shape=ShapeSpec(channels=len(cfg.MODEL.PIXEL_MEAN)))
backbone_shape = self.backbone.output_shape()
feature_shapes = [backbone_shape[f] for f in self.in_features]
self.head = FCOSHead(cfg, feature_shapes)
self.shift_generator = cfg.build_shift_generator(cfg, feature_shapes)
# Matching and loss
self.shift2box_transform = Shift2BoxTransform(
weights=cfg.MODEL.FCOS.BBOX_REG_WEIGHTS)
self.object_sizes_of_interest = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.OBJECT_SIZES_OF_INTEREST
self.norm_sync = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.NORM_SYNC
pixel_mean = torch.Tensor(cfg.MODEL.PIXEL_MEAN).to(self.device).view(
3, 1, 1)
pixel_std = torch.Tensor(cfg.MODEL.PIXEL_STD).to(self.device).view(
3, 1, 1)
self.normalizer = lambda x: (x - pixel_mean) / pixel_std
self.to(self.device)
def forward(self, batched_inputs):
"""
Args:
batched_inputs: a list, batched outputs of :class:`DatasetMapper` .
Each item in the list contains the inputs for one image.
For now, each item in the list is a dict that contains:
* image: Tensor, image in (C, H, W) format.
* instances: Instances
Other information that's included in the original dicts, such as:
* "height", "width" (int): the output resolution of the model, used in inference.
See :meth:`postprocess` for details.
Returns:
dict[str: Tensor]:
mapping from a named loss to a tensor storing the loss. Used during training only.
"""
images = self.preprocess_image(batched_inputs)
if "instances" in batched_inputs[0]:
gt_instances = [
x["instances"].to(self.device) for x in batched_inputs
]
elif "targets" in batched_inputs[0]:
log_first_n(
logging.WARN,
"'targets' in the model inputs is now renamed to 'instances'!",
n=10)
gt_instances = [
x["targets"].to(self.device) for x in batched_inputs
]
else:
gt_instances = None
features = self.backbone(images.tensor) # (2,3,1088,800)
features = [features[f] for f in self.in_features] # ['p3', 'p4', 'p5', 'p6', 'p7']
# [(2,256,136,100),(2,256,68,50),(2,256,34,25),(2,256,17,13),(2,256,9,7)]
box_cls, box_delta, box_iou = self.head(features)
# [(2,20,136,100),(2,20,68,50),(2,20,34,25),(2,20,17,13),(2,20,9,7)]
# [(2,4,136,100),(2,4,68,50),(2,4,34,25),(2,4,17,13),(2,4,9,7)]
# [(2,1,136,100),(2,1,68,50),(2,1,34,25),(2,1,17,13),(2,1,9,7)]
shifts = self.shift_generator(features)
if self.training:
losses = self.get_lla_assignments_and_losses(
shifts, gt_instances, box_cls, box_delta, box_iou)
return losses
else:
results = self.inference(box_cls, box_delta, box_iou, shifts,
images)
processed_results = []
for results_per_image, input_per_image, image_size in zip(
results, batched_inputs, images.image_sizes):
height = input_per_image.get("height", image_size[0])
width = input_per_image.get("width", image_size[1])
r = detector_postprocess(results_per_image, height, width)
processed_results.append({"instances": r})
return processed_results
def get_lla_assignments_and_losses(self, shifts, targets, box_cls, box_delta, box_iou):
# shifts
# [[(13600,2),(3400,2),(850,2),(221,2),(63,2)],
# [(13600,2),(3400,2),(850,2),(221,2),(63,2)]]
# targets
# [Instances(num_instances=2, image_height=1085, image_width=800,
# fields=[gt_boxes = Boxes(tensor([[216.9492, 217.0000, 605.6497, 965.1979], [246.3277, 160.4896, 501.6949, 641.9583]], device='cuda:0')),
# gt_classes = tensor([12, 14], device='cuda:0'), ]),
# Instances(num_instances=2, image_height=1085, image_width=800,
# fields=[gt_boxes = Boxes(tensor([[216.9492, 217.0000, 605.6497, 965.1979], [246.3277, 160.4896, 501.6949, 641.9583]], device='cuda:0')),
# gt_classes = tensor([12, 14], device='cuda:0'), ])]
gt_classes = []
box_cls = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, self.num_classes) for x in box_cls]
# [(2,13600,20),(2,3400,20),(2,850,20),(2,221,20),(2,63,20)]
box_delta = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, 4) for x in box_delta]
# [(2,13600,4),(2,3400,4),(2,850,4),(2,221,4),(2,63,4)]
box_iou = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, 1) for x in box_iou]
# [(2,13600,1),(2,3400,1),(2,850,1),(2,221,1),(2,63,1)]
box_cls = torch.cat(box_cls, dim=1) # (2,18134,20)
box_delta = torch.cat(box_delta, dim=1) # (2,18134,4)
box_iou = torch.cat(box_iou, dim=1) # (2,18134,1)
losses_cls = []
losses_box_reg = []
losses_iou = []
num_fg = 0
for shifts_per_image, targets_per_image, box_cls_per_image, \
box_delta_per_image, box_iou_per_image in zip(
shifts, targets, box_cls, box_delta, box_iou):
shifts_over_all = torch.cat(shifts_per_image, dim=0) # (18134,2)
gt_boxes = targets_per_image.gt_boxes # (2,4)
gt_classes = targets_per_image.gt_classes # tensor([12, 14], device='cuda:0')
deltas = self.shift2box_transform.get_deltas(
shifts_over_all, gt_boxes.tensor.unsqueeze(1)) # anchor_point到gt四边的距离,(18134,2),(2,1,4) -> (2,18134,4)
is_in_boxes = deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.01 # (2,18134)
shape = (len(targets_per_image), len(shifts_over_all), -1) # (2, 18134, -1)
box_cls_per_image_unexpanded = box_cls_per_image # (18134,20)
box_delta_per_image_unexpanded = box_delta_per_image # (18134,4)
box_cls_per_image = box_cls_per_image.unsqueeze(0).expand(shape) # (2,18134,20)
tmp = F.one_hot(
torch.max(gt_classes, torch.zeros_like(gt_classes)), self.num_classes
)
gt_cls_per_image = F.one_hot(
torch.max(gt_classes, torch.zeros_like(gt_classes)), self.num_classes
).float().unsqueeze(1).expand(shape)
# tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
# device='cuda:0')
# (2,20) -> (2,18134,20)
with torch.no_grad():
loss_cls = sigmoid_focal_loss_jit(
box_cls_per_image,
gt_cls_per_image,
alpha=self.focal_loss_alpha,
gamma=self.focal_loss_gamma).sum(dim=-1) # (2,18134,20) -> (2,18134)
loss_cls_bg = sigmoid_focal_loss_jit(
box_cls_per_image_unexpanded,
torch.zeros_like(box_cls_per_image_unexpanded),
alpha=self.focal_loss_alpha,
gamma=self.focal_loss_gamma).sum(dim=-1) # (18134,20) -> (18134)
box_delta_per_image = box_delta_per_image.unsqueeze(0).expand(shape) # (18134,4) -> (2,18134,4)
gt_delta_per_image = self.shift2box_transform.get_deltas(
shifts_over_all, gt_boxes.tensor.unsqueeze(1)) # (2,18134,4)
loss_delta = iou_loss(
box_delta_per_image,
gt_delta_per_image,
box_mode="ltrb",
loss_type='iou') # (2,18134), 注意box_delta_per_image和gt_delta_per_image中每个anchor point点是对齐的
ious = get_ious(
box_delta_per_image,
gt_delta_per_image,
box_mode="ltrb",
loss_type='iou') # (2,18134)
loss = loss_cls + self.reg_cost * loss_delta + 1e3 * (1 - is_in_boxes.float()) # 1.5, (2,18134)
loss = torch.cat([loss, loss_cls_bg.unsqueeze(0)], dim=0) # (3,18134)
num_gt = loss.shape[0] - 1 # 2
num_anchor = loss.shape[1] # 18134
# Topk
matching_matrix = torch.zeros_like(loss) # (3,18134)
_, topk_idx = torch.topk(loss[:-1], k=self.topk, dim=1, largest=False) # 10, (2,10)
matching_matrix[torch.arange(num_gt).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1,
self.topk).view(-1), topk_idx.view(-1)] = 1.
# (2)->(2,1)->(2,10)->(20), (2,10)->(20)
# tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
# [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
# make sure one anchor with one gt
anchor_matched_gt = matching_matrix.sum(0) # (18134)
if (anchor_matched_gt > 1).sum() > 0: # 存在多个gt分配给同一个anchor的情况
loss_min, loss_argmin = torch.min(loss[:-1, anchor_matched_gt > 1], dim=0)
# (anchor_matched_gt > 1).shape=(18134), 对应位置为True/False,True表示有多个gt分配给了当前anchor
# loss[:-1, anchor_matched_gt > 1].shape = (2,7)
# torch.Size([7]),torch.Size([7])
# loss_argmin表示被分配多个gt的anchor和哪个gt的loss最小
# loss_argmin == tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], device='cuda:0'), 表示这个anchor都被分配了2个gt,且这7个anchor都与第2个gt的loss小
matching_matrix[:, anchor_matched_gt > 1] *= 0. # 把多个gt的对应位置全置0
matching_matrix[loss_argmin, anchor_matched_gt > 1] = 1. # 把loss最小的gt对应位置置1
anchor_matched_gt = matching_matrix.sum(0) # (18134), positive anchor对应位置为1
num_fg += matching_matrix.sum()
matching_matrix[-1] = 1. - anchor_matched_gt # assignment for Background
assigned_gt_inds = torch.argmax(matching_matrix, dim=0)
gt_cls_per_image_bg = gt_cls_per_image.new_zeros(
(gt_cls_per_image.size(1), gt_cls_per_image.size(2))).unsqueeze(0)
gt_cls_per_image_with_bg = torch.cat(
[gt_cls_per_image, gt_cls_per_image_bg], dim=0)
cls_target_per_image = gt_cls_per_image_with_bg[
assigned_gt_inds, torch.arange(num_anchor)]
# Dealing with Crowdhuman ignore label
gt_classes_ = torch.cat([gt_classes, gt_classes.new_zeros(1)])
anchor_cls_labels = gt_classes_[assigned_gt_inds]
valid_flag = anchor_cls_labels >= 0
pos_mask = assigned_gt_inds != len(targets_per_image) # get foreground mask
valid_fg = pos_mask & valid_flag
assigned_fg_inds = assigned_gt_inds[valid_fg]
range_fg = torch.arange(num_anchor)[valid_fg]
ious_fg = ious[assigned_fg_inds, range_fg]
anchor_loss_cls = sigmoid_focal_loss_jit(
box_cls_per_image_unexpanded[valid_flag],
cls_target_per_image[valid_flag],
alpha=self.focal_loss_alpha,
gamma=self.focal_loss_gamma).sum(dim=-1)
delta_target = gt_delta_per_image[assigned_fg_inds, range_fg]
anchor_loss_delta = 2. * iou_loss(
box_delta_per_image_unexpanded[valid_fg],
delta_target,
box_mode="ltrb",
loss_type=self.iou_loss_type)
anchor_loss_iou = 0.5 * F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
box_iou_per_image.squeeze(1)[valid_fg],
ious_fg,
reduction='none')
losses_cls.append(anchor_loss_cls.sum())
losses_box_reg.append(anchor_loss_delta.sum())
losses_iou.append(anchor_loss_iou.sum())
if self.norm_sync:
dist.all_reduce(num_fg)
num_fg = num_fg.float() / dist.get_world_size()
return {
'loss_cls': torch.stack(losses_cls).sum() / num_fg,
'loss_box_reg': torch.stack(losses_box_reg).sum() / num_fg,
'loss_iou': torch.stack(losses_iou).sum() / num_fg
}
def inference(self, box_cls, box_delta, box_iou, shifts, images):
"""
Arguments:
box_cls, box_delta, box_center: Same as the output of :meth:`FCOSHead.forward`
shifts (list[list[Tensor]): a list of #images elements. Each is a
list of #feature level tensor. The tensor contain shifts of this
image on the specific feature level.
images (ImageList): the input images
Returns:
results (List[Instances]): a list of #images elements.
"""
assert len(shifts) == len(images)
results = []
box_cls = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, self.num_classes) for x in box_cls]
box_delta = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, 4) for x in box_delta]
box_iou = [permute_to_N_HWA_K(x, 1) for x in box_iou]
# list[Tensor], one per level, each has shape (N, Hi x Wi, K or 4)
for img_idx, shifts_per_image in enumerate(shifts):
image_size = images.image_sizes[img_idx]
box_cls_per_image = [
box_cls_per_level[img_idx] for box_cls_per_level in box_cls
]
box_reg_per_image = [
box_reg_per_level[img_idx] for box_reg_per_level in box_delta
]
box_iou_per_image = [
box_iou_per_level[img_idx] for box_iou_per_level in box_iou
]
results_per_image = self.inference_single_image(
box_cls_per_image, box_reg_per_image, box_iou_per_image,
shifts_per_image, tuple(image_size))
results.append(results_per_image)
return results
def inference_single_image(self, box_cls, box_delta, box_iou, shifts,
image_size):
"""
Single-image inference. Return bounding-box detection results by thresholding
on scores and applying non-maximum suppression (NMS).
Arguments:
box_cls (list[Tensor]): list of #feature levels. Each entry contains
tensor of size (H x W, K)
box_delta (list[Tensor]): Same shape as 'box_cls' except that K becomes 4.
box_center (list[Tensor]): Same shape as 'box_cls' except that K becomes 1.
shifts (list[Tensor]): list of #feature levels. Each entry contains
a tensor, which contains all the shifts for that
image in that feature level.
image_size (tuple(H, W)): a tuple of the image height and width.
Returns:
Same as `inference`, but for only one image.
"""
boxes_all = []
scores_all = []
class_idxs_all = []
# Iterate over every feature level
for box_cls_i, box_reg_i, box_iou_i, shifts_i in zip(
box_cls, box_delta, box_iou, shifts):
# (HxWxK,)
box_cls_i = box_cls_i.flatten().sigmoid_()
# Keep top k top scoring indices only.
num_topk = min(self.topk_candidates, box_reg_i.size(0))
# torch.sort is actually faster than .topk (at least on GPUs)
predicted_prob, topk_idxs = box_cls_i.sort(descending=True)
predicted_prob = predicted_prob[:num_topk]
topk_idxs = topk_idxs[:num_topk]
# filter out the proposals with low confidence score
keep_idxs = predicted_prob > self.score_threshold
predicted_prob = predicted_prob[keep_idxs]
topk_idxs = topk_idxs[keep_idxs]
shift_idxs = topk_idxs // self.num_classes
classes_idxs = topk_idxs % self.num_classes
box_reg_i = box_reg_i[shift_idxs]
shifts_i = shifts_i[shift_idxs]
# predict boxes
predicted_boxes = self.shift2box_transform.apply_deltas(
box_reg_i, shifts_i)
box_iou_i = box_iou_i.flatten().sigmoid_()[shift_idxs]
predicted_prob = torch.sqrt(predicted_prob * box_iou_i)
boxes_all.append(predicted_boxes)
scores_all.append(predicted_prob)
class_idxs_all.append(classes_idxs)
boxes_all, scores_all, class_idxs_all = [
cat(x) for x in [boxes_all, scores_all, class_idxs_all]
]
keep = batched_nms(boxes_all, scores_all, class_idxs_all,
self.nms_threshold)
keep = keep[:self.max_detections_per_image]
result = Instances(image_size)
result.pred_boxes = Boxes(boxes_all[keep])
result.scores = scores_all[keep]
result.pred_classes = class_idxs_all[keep]
return result
def preprocess_image(self, batched_inputs):
"""
Normalize, pad and batch the input images.
"""
images = [x["image"].to(self.device) for x in batched_inputs]
images = [self.normalizer(x) for x in images]
images = ImageList.from_tensors(images,
self.backbone.size_divisibility)
return images
class FCOSHead(nn.Module):
"""
The head used in FCOS for object classification and box regression.
It has two subnets for the two tasks, with a common structure but separate parameters.
"""
def __init__(self, cfg, input_shape: List[ShapeSpec]):
super().__init__()
# fmt: off
in_channels = input_shape[0].channels
num_classes = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.NUM_CLASSES
num_convs = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.NUM_CONVS
prior_prob = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.PRIOR_PROB
self.fpn_strides = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.FPN_STRIDES
self.norm_reg_targets = cfg.MODEL.FCOS.NORM_REG_TARGETS
# fmt: on
cls_subnet = []
bbox_subnet = []
for _ in range(num_convs):
cls_subnet.append(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1))
cls_subnet.append(nn.GroupNorm(32, in_channels))
cls_subnet.append(nn.ReLU())
bbox_subnet.append(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1))
bbox_subnet.append(nn.GroupNorm(32, in_channels))
bbox_subnet.append(nn.ReLU())
self.cls_subnet = nn.Sequential(*cls_subnet)
self.bbox_subnet = nn.Sequential(*bbox_subnet)
self.cls_score = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
num_classes,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
self.bbox_pred = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
4,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
self.ious_pred = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
1,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
# Initialization
for modules in [
self.cls_subnet, self.bbox_subnet, self.cls_score,
self.bbox_pred, self.ious_pred
]:
for layer in modules.modules():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
torch.nn.init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, 0)
if isinstance(layer, nn.GroupNorm):
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.weight, 1)
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, 0)
# Use prior in model initialization to improve stability
bias_value = -math.log((1 - prior_prob) / prior_prob)
torch.nn.init.constant_(self.cls_score.bias, bias_value)
self.scales = nn.ModuleList(
[Scale(init_value=1.0) for _ in range(len(self.fpn_strides))])
def forward(self, features):
"""
Arguments:
features (list[Tensor]): FPN feature map tensors in high to low resolution.
Each tensor in the list correspond to different feature levels.
Returns:
logits (list[Tensor]): #lvl tensors, each has shape (N, K, Hi, Wi).
The tensor predicts the classification probability
at each spatial position for each of the K object classes.
bbox_reg (list[Tensor]): #lvl tensors, each has shape (N, 4, Hi, Wi).
The tensor predicts 4-vector (dl,dt,dr,db) box
regression values for every shift. These values are the
relative offset between the shift and the ground truth box.
centerness (list[Tensor]): #lvl tensors, each has shape (N, 1, Hi, Wi).
The tensor predicts the centerness at each spatial position.
"""
logits = []
bbox_reg = []
ious_pred = []
for l, feature in enumerate(features):
# (2,256,136,100)
cls_subnet = self.cls_subnet(feature) # (2,256,136,100)
bbox_subnet = self.bbox_subnet(feature) # (2,256,136,100)
logits.append(self.cls_score(cls_subnet)) # (2,20,136,100)
ious_pred.append(self.ious_pred(bbox_subnet)) # (2,1,136,100)
bbox_pred = self.scales[l](self.bbox_pred(bbox_subnet)) # (2,4,136,100)
if self.norm_reg_targets: # True
bbox_reg.append(F.relu(bbox_pred) * self.fpn_strides[l]) # [8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
else:
bbox_reg.append(torch.exp(bbox_pred))
# [(2,20,136,100),(2,20,68,50),(2,20,34,25),(2,20,17,13),(2,20,9,7)]
# [(2,4,136,100),(2,4,68,50),(2,4,34,25),(2,4,17,13),(2,4,9,7)]
# [(2,1,136,100),(2,1,68,50),(2,1,34,25),(2,1,17,13),(2,1,9,7)]
return logits, bbox_reg, ious_pred