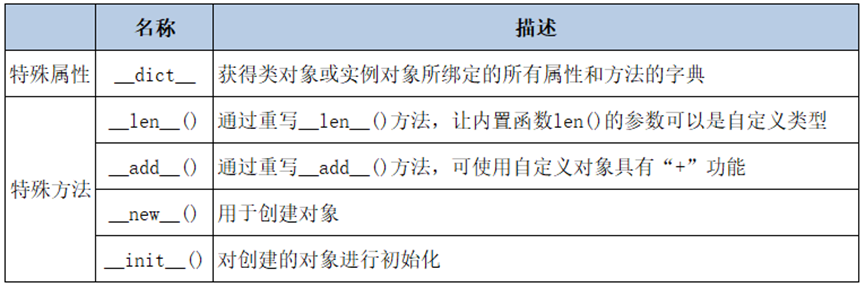
反射的概念
- 反射:Refelection,反射是Java的特征之一,允许运行中的Java程序获取自身信息,并可以操作类或者对象的内部属性
- 通过反射,可以在运行时获得程序或者程序中的每一个类型的成员活成成员的信息
- 程序中的对象一般都是在编译时就确定下来,Java反射机制可以动态地创建对象并且调用相关属性,这些对象的类型在编译时是未知的
- 也就是说 ,可以通过反射机制直接创建对象,即使这个对象类型在编译时是未知的
- Java反射提供下列功能:
- 在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
- 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
- 在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法,可以通过反射调用 private 方法
- 在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法
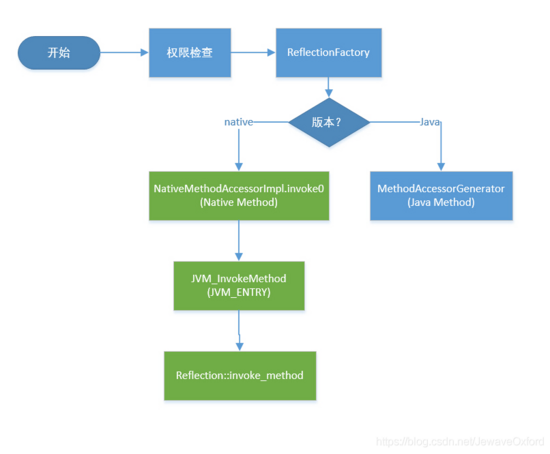
反射调用方法原理
- 首先Java通过字节码获取类的基本信息,其次通过Class#getMethod(“myMethod”)经过查找获取Method对象
- 接着通过Method#invoke调用方法, 此处包括Native版本和Java版本实现
- Native版本的invoke0()在HotSpot VM里是由JVM_InvokeMethod()支持
- JVM_InvokeMethod()中通过JNIHandles::resolve(method)解析方法的符号引用(个人理解, 详情参考R大博客)
- 拿到method_handle后, 即符号引用, 获取方法的返回类型等相关信息, 最后调用invoke()执行方法(个人理解, 详情参考R大博客)
- 含native版本以及Java版本, native版本初始化快, 但由于对JVM是黑盒, 因此无法内联等优化, 当超过15次时, 会自动转成Java版本, Java版本初始化慢, 但长时间执行效率更高, 可进行内联等优化
public final
class Method extends AccessibleObject implements GenericDeclaration, Member {
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
...
return methodAccessor.invoke(obj, args);
}
}
// methodAccessor通过ReflectionFactory实例化返回
public class ReflectionFactory {
public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method method) {
...
if (noInflation) {
return new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
} else {
NativeMethodAccessorImpl acc =
new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(method);
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl res =
new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(acc);
acc.setParent(res);
return res;
}
}
}
// native版本则是直接调用Reflection::invoke_method()
class NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
...
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold()) {
MethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
parent.setDelegate(acc);
}
return invoke0(method, obj, args);
}
...
private static native Object invoke0(Method m, Object obj, Object[] args);
}
// Java版本, 通过MethodAccessorGenerator生成MethodAccessor的实现类
public class GeneratedMethodAccessor1 extends MethodAccessorImpl {
...
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
...
try {
target.foo(arg0);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new InvocationTargetException(t);
}
}
}
Field
使用反射获取或者修改一个变量的值时,编译器不会进行自动装/拆箱
public class FieldTrouble extends BaseTestClass {
public Integer value;
public static void main(String[] args) {
FieldTrouble fieldTrouble = new FieldTrouble();
Class<? extends FieldTrouble> cls = fieldTrouble.getClass();
...
Field value = cls.getField("value");
// 抛java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
value.setInt(fieldTrouble, 23);
...
}
}
访问限制阻止我们修改 final 类型的变量, final变量通过反射修改需要调用Filed#setAccessible(true) 在使用反射修改某个对象的成员变量前你要明白,这样做会造成一定程度的性能开销,因为在反射时这样的操作需要引发许多额外操作,比如验证访问权限等。另外使用反射也会导致一些运行时的计算优化失效
Method
synthetic method合成方法
public class Foo {
private int get(){
return 1;
}
private class Bar {
private Bar() {
System.out.println(get());
}
}
}
...
// Synthetic (合成)方法是由编译器产生的、源代码中没有的方法。当内部类与外部类之前有互相访问 private 属性、方法时,编译器会在运行时为调用方创建一个 synthetic 方法。
static int access$000(Foo); //多出来的 synthetic 方法,为了在 Bar 中的这段代码 System.out.println(get());
varagrs方法
public void testVarargs(String... args) {
...
}
bride桥接方法, 为了兼容JDK 1.5版本以前的代码
反射慢的原因
- 运行时通过Class对象查找Method等对象
- 方法调用时, 编译器无法进行方法内联等优化
- 需要校验, 根据方法名和签名查找方法的符号引用等
反射优化
- 缓存, 避免多次加载
- 调用method#setAccessible(true)避免安全检查缓存
- 直接调用方法
反射的主要用途
- 反射最重要的用途就是开发各种通用框架
- 很多框架都是配置化的,通过 XML 文件配置 Bean
- 为了保证框架的通用性,需要根据配置文件加载不同的对象或者类,调用不同的方法
- 要运用反射,运行时动态加载需要加载的对象
- 示例:
- 在运用 Struts 2 框架的开发中会在 struts.xml 中配置 Action:
<action name="login"
class="org.ScZyhSoft.test.action.SimpleLoginAction"
method="execute">
<result>/shop/shop-index.jsp</result>
<result name="error">login.jsp</result>
</action>
123456
- 配置文件与 Action 建立映射关系
- 当 View 层发出请求时,请求会被 StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter 拦截
- StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter会动态地创建Action实例
- 请求 login.action
- StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter 会解析 struts.xml 文件
- 检索 action 中 name 为 login 的 Action
- 根据 class 属性创建 SimpleLoginAction 实例
- 使用 invoke 方法调用 execute 方法
- 反射是各种容器实现的核心
反射的运用
- 反射相关的类在 StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter 包
- 反射可以用于:
- 判断对象所属的类
- 获得class对象
- 构造任意一个对象
- 调用一个对象
- 九大预定义的Class对象:
- 基本的Java类型: boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, double
- 关键字void通过class属性的也表示为Class对象
- 包装类或者void类的静态TYPE字段:
- Integer.TYPE == int.class
- Integer.class == int.class
- 数组类型的Class实例对象:
- Class<String[]> clz = String[].class;
- 数组的Class对象如何比较是否相等:
- 数组的维数
- 数组的类型
- Class类中的 isArray() ,用来判断是否表示一个数组类型
invoke方法
- 在Java中很多方法都会调用 invoke 方法,很多异常的抛出多会定位到 invoke 方法:
java.lang.NullPointerException
at ......
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:497)
123456
invoke执行过程
- invoke 方法用来在运行时动态地调用某个实例的方法,实现如下:
@CallSensitive
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object ... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Refelection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor;
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
1234567891011121314
权限检查
-
AccessibleObject类是Field,Method和Constructor对象的基类:
-
提供将反射的对象标记为在使用时取消默认Java语言访问控制检查的能力
-
invoke方法会首先检查AccessibleObject的override属性的值:
-
override默认值为false:
-
表示需要权限调用规则,调用方法时需要检查权限
-
也可以使用 setAccessible() 设置为 true
-
override如果值为true:
-
表示忽略权限规则,调用方法时无需检查权限
-
也就是说,可以调用任意private方法,违反了封装
-
如果override属性为默认值false,则进行进一步的权限检查:
- 首先用 Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers) 方法检查方法是否为 public 1.1 如果是public方法的话,就跳过本步 1.2 如果不是public方法的话,就用Reflection.getCallerClass()方法获取调用这个方法的Class对象,这是一个 native 方法
@CallerSensitive
public static native Class<?> getCallerClass();
----------------------------------------------------------
- 在OpenJDK中可以找到getCallerClass方法的JNI入口-Reflection.c
JNIEXPORT jclass JNICALL Java_sun_reflect_Reflection_getCallerClass__
(JNIEnv *env, jclass unused)
{
return JVM_GetCallerClass(env, JVM_CALLER_DEPTH);
}
----------------------------------------------------------
- JVM_GetCallerClass的源码位于jvm.cpp中
VM_ENTRY(jclass, JVM_GetCallerClass(JNIEnv* env, int depth))
JVMWrapper("JVM_GetCallerClass");
// Pre-JDK 8 and early builds of JDK 8 don't have a CallerSensitive annotation; or
// sun.reflect.Reflection.getCallerClass with a depth parameter is provided
// temporarily for existing code to use until a replacement API is defined.
if (SystemDictionary::reflect_CallerSensitive_klass() == NULL || depth != JVM_CALLER_DEPTH) {
Klass* k = thread->security_get_caller_class(depth);
return (k == NULL) ? NULL : (jclass) JNIHandles::make_local(env, k->java_mirror());
}
// Getting the class of the caller frame.
//
// The call stack at this point looks something like this:
//
// [0] [ @CallerSensitive public sun.reflect.Reflection.getCallerClass ]
// [1] [ @CallerSensitive API.method ]
// [.] [ (skipped intermediate frames) ]
// [n] [ caller ]
vframeStream vfst(thread);
// Cf. LibraryCallKit::inline_native_Reflection_getCallerClass
for (int n = 0; !vfst.at_end(); vfst.security_next(), n++) {
Method* m = vfst.method();
assert(m != NULL, "sanity");
switch (n) {
case 0:
// This must only be called from Reflection.getCallerClass
if (m->intrinsic_id() != vmIntrinsics::_getCallerClass) {
THROW_MSG_NULL(vmSymbols::java_lang_InternalError(), "JVM_GetCallerClass must only be called from Reflection.getCallerClass");
}
// fall-through
case 1:
// Frame 0 and 1 must be caller sensitive.
if (!m->caller_sensitive()) {
THROW_MSG_NULL(vmSymbols::java_lang_InternalError(), err_msg("CallerSensitive annotation expected at frame %d", n));
}
break;
default:
if (!m->is_ignored_by_security_stack_walk()) {
// We have reached the desired frame; return the holder class.
return (jclass) JNIHandles::make_local(env, m->method_holder()->java_mirror());
}
break;
}
}
return NULL;
JVM_END
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263
- 获取 Class 对象 caller 后使用 checkAccess 方法进行一次快速的权限校验 ,checkAccess 方法实现如下:
volatile Object securityCheckCache;
void checkAccess(Class<?> caller, Class<?> clazz, Object obj, int modifiers) throws IllegalAccessException {
if(caller == clazz){ // 快速校验
return; // 权限通过校验
}
Object cache = securityCheckCache; // 读取volatile
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
if (obj != null && Modifier.isProtected(modifiers) && ((targetClass = obj.getClass()) != clazz)) { // 必须匹配caller,targetClass中的一个
if (cache instanceof Class[]) {
Class<?>[] cache2 = (Class<?>[]) cache;
if (cache2[1] == targetClass && cache[0] == caller) {
return; // 校验通过
}
}
} else if (cache == caller) {
return; // 校验通过
}
slowCheckMemberAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers, targetClass);
}
1234567891011121314151617181920
首先先执行一次快速校验,一旦 Class 正确则权限检查通过;如果未通过,则创建一个缓存,中间再进行检查
- 如果上面所有的权限检查都未通过,将会执行更详细的检查:
void slowCheckMemberAccess(Class<?> caller, Class<?> clazz, Object obj, int modifiers, Class<?> targetClass) throws IllegalAccessException {
Refelection.ensureMemberAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
// 如果成功,就更新缓存
Object cache = ((targetClass == clazz) ? caller : new Class<?>[] {caller, targetClass});
securityCheckCache = cache;
}
123456
用 Reflection.ensureMemberAccess 方法继续检查权限.若检查通过就更新缓存,这样下一次同一个类调用同一个方法时就不用执行权限检查了,这是一种简单的缓存机制
由于 JMM 的 happens-before 规则能够保证缓存初始化能够在写缓存之间发生,因此两个cache不需要声明为volatile
- 检查权限的工作到此结束.如果没有通过检查就会抛出异常,如果通过检查就会到下一步
调用MethodAccessor的invoke方法
-
Method.invoke() 不是自身实现反射调用逻辑,而是通过 sun.refelect.MethodAccessor 来处理
-
Method对象的基本构成:
-
每个 Java 方法有且只有一个 Method 对象作为 root, 相当于根对象,对用户不可见
-
当创建 Method 对象时,代码中获得的 Method 对象相当于其副本或者引用
-
root 对象持有一个 MethodAccessor 对象,所有获取到的 Method 对象都共享这一个 MethodAccessor 对象
-
必须保证 MethodAccessor 在内存中的可见性
-
root对象及其声明:
private volatile MethodAccessor methodAccessor;
/**
* For sharing of MethodAccessors. This branching structure is
* currently only two levels deep (i.e., one root Method and
* potentially many Method objects pointing to it.)
*
* If this branching structure would ever contain cycles, deadlocks can
* occur in annotation code.
*/
private Method root;
12345678910
- MethodAccessor:
/**
* This interface provides the declaration for
* java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(). Each Method object is
* configured with a (possibly dynamically-generated) class which
* implements this interface
*/
public interface MethodAccessor {
// Matches specification in {@link java.lang.reflect.Method}
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException;
}
12345678910
MethodAccessor是一个接口,定义了 invoke() 方法,通过 Usage 可以看出 MethodAccessor 的具体实现类:
- sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl
- sun.reflect.MethodAccessorImpl
- sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl
- 第一次调用 Java 方法对应的 Method 对象的 invoke() 方法之前,实现调用逻辑的 MethodAccess 对象还没有创建
- 第一次调用时,才开始创建 MethodAccessor 并更新为 root, 然后调用 MethodAccessor.invoke() 完成反射调用
/**
* NOTE that there is no synchronization used here.
* It is correct(though not efficient) to generate more than one MethodAccessor for a given Method.
* However, avoiding synchronization will probably make the implementation more scalable.
*/
private MethodAccessor acquireMethodAccessor() {
// First check to see if one has been created yet, and take it if so
MethodAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null)
tmp = root.getMethodAccessor();
if (tmp != null) {
methodAccessor = tmp;
} else {
tmp = reflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor(this);
setMethodAccessor(tmp);
}
return tmp;
}
12345678910111213141516171819
- methodAccessor 实例由 reflectionFactory 对象操控生成 ,reflectionFactory 是在 AccessibleObject 中声明的:
/**
* Reflection factory used by subclasses for creating field,
* method, and constructor accessors. Note that this is called very early in the bootstrapping process.
*/
static final ReflectionFactory reflectionFactory = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory.GetReflectionFactoryAction());
123456
- sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory 方法:
public class ReflectionFactory {
private static boolean initted = false;
private static Permission reflectionFactoryAccessPerm = new RuntimePermission("reflectionFactoryAccess");
private static ReflectionFactory soleInstance = new ReflectionFactory();
// Provides access to package-private mechanisms in java.lang.reflect
private static volatile LangReflectAccess langReflectAccess;
/**
* "Inflation" mechanism. Loading bytecodes to implement Method.invoke() and Constructor.
* newInstance() currently costs 3-4x more than an invocation via native code for the first invocation (though subsequent invocations have been benchmarked to be over 20x faster)
* Unfortunately this cost increases startup time for certain applications that use reflection intensively (but only once per class) to bootstrap themselves
* To avoid this penalty we reuse the existing JVM entry points for the first few invocations of Methods and Constructors and then switch to the bytecode-based implementations
*/
// Package-private to be accessible to NativeMethodAccessorImpl and NativeConstructorAccessorImpl
private static noInflation = false;
private static int inflationThreshold = 15;
// 生成MethodAccessor
public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method method) {
checkInitted();
if (noInflation && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return new MethodAccessorGenerator().generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
} else {
NativeMethodAccessorImpl acc = new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(method);
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl res = new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(acc);
acc.setParent(res);
return res;
}
}
/**
* We have to defer full initialization of this class until after the static initializer is run since java.lang.reflect
* Method's static initializer (more properly, that for java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject) causes this class's to be run, before the system properties are set up
*/
private static void checkInitted() {
if (initted) return;
AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
/**
* Tests to ensure the system properties table is fully initialized
* This is needed because reflection code is called very early in the initialization process (before command-line arguments have been parsed and therefore these user-settable properties installed
* We assume that if System.out is non-null then the System class has been fully initialized and that the bulk of the startup code has been run
*/
if (System.out == null) {
// java.lang.System not yet fully initialized
return null;
}
String val = System.getProperty("sun.reflect.noInflation");
if (val != null && val.equals("true")) {
noInflation = true;
}
val = System.getProperty("sun.reflect.inflationThreshold");
if (val != null) {
try {
inflationThreshold = Integer.parseInt(val);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to parse property sun.reflect.inflationThreshold", e);
}
}
initted = true;
return null;
}
});
}
}
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273
-
实际的MethodAccessor实现有两个版本,一个是Java版本,一个是native版本,两者各有特点:
-
初次启动时 Method.invoke() 和 Constructor.newInstance() 方法采用native方法要比Java方法快3-4倍
-
启动后 native 方法又要消耗额外的性能而慢于 Java 方法
-
Java实现的版本在初始化时需要较多时间,但长久来说性能较好
-
这是HotSpot的优化方式带来的性能特性:
-
跨越native边界会对优化有阻碍作用
-
为了尽可能地减少性能损耗,HotSpot JDK采用inflation方式:
-
Java方法在被反射调用时,开头若干次使用native版
-
等反射调用次数超过阈值时则生成一个专用的 MethodAccessor 实现类,生成其中的 invoke() 方法的字节码
-
以后对该Java方法的反射调用就会使用Java版本
-
ReflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor()生成MethodAccessor对象的逻辑:
-
native 版开始会会生成 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 和 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 两个对象
-
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl:
/* Delegates its invocation to another MethodAccessorImpl and can change its delegate at run time */
class DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private MethodAccessorImpl delegate;
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {
setDelegate(delegate);
}
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
return delegate.invoke(obj, args);
}
void setDelegate(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
}
123456789101112131415
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl对象是一个中间层,方便在 native 版与 Java 版的 MethodAccessor 之间进行切换
- native版MethodAccessor的Java方面的声明: sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl
/* Used only for the first few invocations of a Method; afterward,switches to bytecode-based implementation */
class NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private Method method;
private DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent;
private int numInvocations;
NativeMethodAccessorImpl(Method method) {
this.method = method;
}
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
/* We can't inflate methods belonging to vm-anonymous classes because that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't be found from the generated bytecode */
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold()
&& !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
parent.setDelegate(acc);
}
return invoke0(method, obj, args);
}
void setParent(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
private static native Object invoke0(Method m, Object obj, Object[] args);
}
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031
- 每次 NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke() 方法被调用时,程序调用计数器都会增加 1, 看看是否超过阈值
- 如果超过则调用 MethodAccessorGenerator.generateMethod() 来生成 Java 版的 MethodAccessor 的实现类
- 改变 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 所引用的 MethodAccessor 为 Java 版
- 经由 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke() 调用到的就是 Java 版的实现
invoke总结
以上就是Android开发中的invoke原理反射与原理;更多Android开发可以前往《Android核心技术手册》查看获取海量学习资料;里面内容包含Android开发中进阶技术30几个技术板块。
- invoke方法的过程:
- MagicAccessorImpl:
- 原本Java的安全机制使得不同类之间不是任意信息都可见,但JDK里面专门设了个 MagicAccessorImpl 标记类开了个后门来允许不同类之间信息可以互相访问,由JVM管理
/** <P> MagicAccessorImpl (named for parity with FieldAccessorImpl and
others, not because it actually implements an interface) is a
marker class in the hierarchy. All subclasses of this class are
"magically" granted access by the VM to otherwise inaccessible
fields and methods of other classes. It is used to hold the code
for dynamically-generated FieldAccessorImpl and MethodAccessorImpl
subclasses. (Use of the word "unsafe" was avoided in this class's
name to avoid confusion with {@link sun.misc.Unsafe}.) </P>
<P> The bug fix for 4486457 also necessitated disabling
verification for this class and all subclasses, as opposed to just
SerializationConstructorAccessorImpl and subclasses, to avoid
having to indicate to the VM which of these dynamically-generated
stub classes were known to be able to pass the verifier. </P>
<P> Do not change the name of this class without also changing the
VM's code. </P> */
class MagicAccessorImpl {
}
1234567891011121314151617
- @CallerSensitive注解
Summary: Improve the security of the JDK’s method-handle implementation by replacing the existing
hand-maintained list of caller-sensitive methods with a mechanism that accurately identifies
such methods and allows their callers to be discovered reliably.
/**
* A method annotated @CallerSensitive is sensitive to its calling class,
* via {@link sun.reflect.Reflection#getCallerClass Reflection.getCallerClass},
* or via some equivalent.
*
* @author John R. Rose
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({METHOD})
public @interface CallerSensitive {
}
1234567891011121314
-
用@CallerSensitive注解修饰的方法从一开始就知道具体调用此方法的对象
-
不用再经过一系列的检查就能确定具体调用此方法的对象
-
实际上是调用 sun.reflect.Reflection.getCallerClass 方法
-
Reflection类位于调用栈中的0帧位置
-
sun.reflect.Reflection.getCallerClass() 方法返回调用栈中从0帧开始的第x帧中的类实例
-
该方法提供的机制可用于确定调用者类,从而实现"感知调用者(Caller Sensitive)"的行为
-
即允许应用程序根据调用类或调用栈中的其它类来改变其自身的行为
反射注意点
- 反射会额外消耗系统资源,如果不需要动态地创建一个对象,就不要使用反射
- 反射调用方法时可以忽略权限检查.可能会破坏封装性而导致安全问题




![[Lua实战]Skynet-1.如何启动(linux环境启动)[开箱可用]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9ba41846f0a84d89ac5449bed97b462c.png)