一、定义与作用
Jitter Injection,即抖动注入,是一种在通信系统中人为地添加抖动的技术。该技术通过在发送端对数据包进行延迟和抖动调整,以实现对整个通信系统的时延和抖动的控制。其主要作用包括:
- 改善传输质量:通过调整数据包的时延和抖动,可以有效地降低误码率,提高数据传输的可靠性。
- 均衡网络负载:通过对不同的数据流进行不同程度的抖动注入,可以实现网络资源的合理分配,提高整体传输效率。
- 增强网络容错能力:Jitter Injection可以降低数据传输对网络状况的敏感性,增强网络在面对故障时的容错能力。
二、原理与实现方法
Jitter Injection的原理基于两种主要实现方法:
- 基于时延的Jitter Injection:
- 方法:主要通过调整数据包的发送时间来实现抖动注入。
- 控制:通常采用一定的时间分布,如均匀分布、指数分布等,来控制数据包的发送时延。
- 特点:简单易实现,但对网络负载的均衡效果较差。
- 基于误码的Jitter Injection:
- 方法:通过检测数据包的误码率,动态地调整数据包的时延和抖动。
- 调整:当检测到误码率较高时,会增加抖动注入量,以降低误码率;当误码率较低时,会减小抖动注入量,以提高传输效率。
三、应用
Jitter Injection在多个领域有广泛应用,包括:
- 数字通信系统:有效地解决数据包丢失、音频/视频同步等问题,提高通信质量。
- 网络视频通信:改善视频流的同步性,降低视频卡顿现象,提高用户体验。
Jitter is an important part of SerDes systems specification. You can include jitter parameters from the SerDes Designer app and from the Simulink® model. Including jitter impairment in your link and equalization design helps calculate the required eye margins. You can also perform trade-off between different equalization schemes based on total jitter contribution. You can export the jitter values to IBIS-AMI models.
The most common types of jitter are:
| Jitter Type | Description |
|---|---|
| DCD (duty cycle distortion) | Impairment from half and quarter rate clock misalignment. Also known as even-odd jitter. Duty cycle distortion is defined as the difference in symbol duration between one symbol and the next. The transmitter and receiver duty cycle distortions are half of the clock duty cycle distortion. |
| DJ (deterministic jitter) | Usually modeled as bounded uniform jitter. Also known as uncorrelated bounded high probability jitter. Deterministic jitter is defined as half of the peak-to-peak variation. |
| RJ (random jitter) | Gaussian process that models unbounded jitter events. Also known as uncorrelated unbounded Gaussian jitter. Random jitter is defined as the standard deviation of a white Gaussian phase noise process. |
| SJ (sinusoidal jitter) | Bounded periodic jitter that typically comes from power supply voltage variation. Sinusoidal jitter is defined as half of the peak-to-peak variation of sinusoidal phase noise amplitude. |
| Noise | Random voltage noise. IBIS-AMI 7.0 defines Gaussian noise and uniform noise impairments. Also known as additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). |
The expected simulation results vary depending on the type of jitter, injection site (transmitter or receiver), and analysis domain (statistical or time-domain). The SerDes Designer app only supports statistical or impulse-based analysis. To perform time-domain analysis, you must export the model to Simulink. The different types of jitter are injected into transmitter and receiver sites according to the IBIS-AMI specifications:

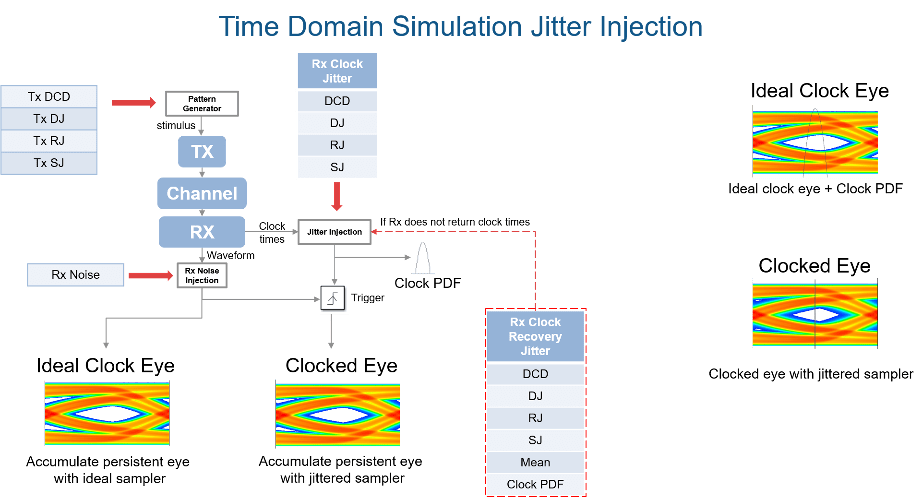
| Normal Mode | Statistical Analysis | Time Domain Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Transmitter jitter | Convolved with eye | Injected in stimulus |
| Receiver jitter | Convolved with clock PDF (probability density function) | Injected in clock times |
| Clock recovery jitter | Convolved with clock PDF | Injected in clock times if receiver does not return clock times |
四、优缺点分析
优点:
- 提高通信系统的性能。
- 均衡网络负载,提高传输效率。
- 增强网络容错能力。
缺点:
- 基于时延的Jitter Injection对网络负载的均衡效果较差。
- 实际应用中可能需要针对特定场景进行优化和调整。