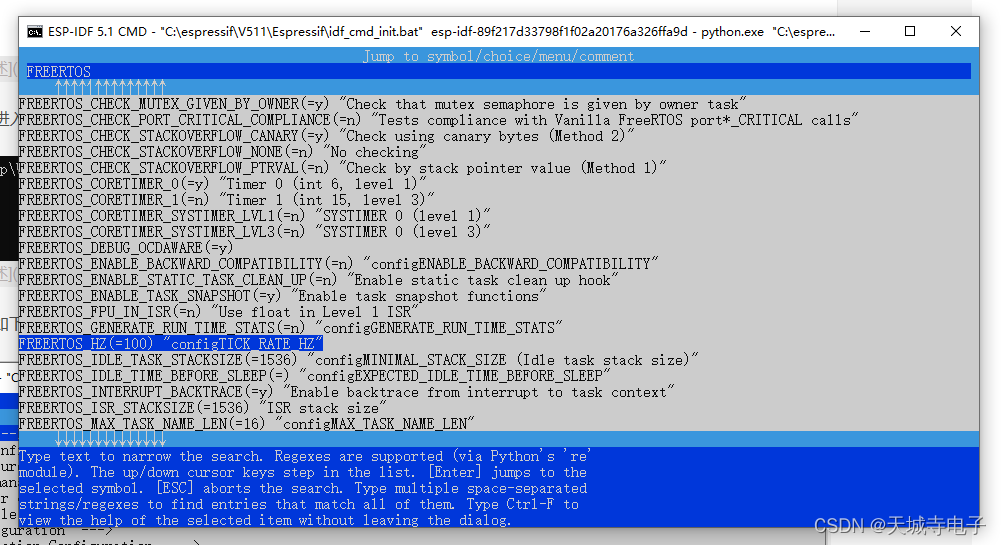
Vue 2 技术文档
Vue.js 是一款用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。与其他重量级框架不同的是,Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整合。而 Vue.js 2(以下简称 Vue 2)则是该框架的一个重要版本,提供了许多新的特性和改进。本文将详细介绍 Vue 2 的各项功能及其使用方法。
目录
- Vue 2 技术文档
- 1. Vue 2 的安装和基本使用
- 安装 Vue 2
- 创建 Vue 实例
- 2. 模板语法
- 插值
- 指令
- 计算属性
- 3. Vue 实例
- 实例属性与方法
- 生命周期钩子
- 4. 组件
- 定义与注册组件
- 组件通信
- 父子组件通信
- 5. 路由
- 安装 Vue Router
- 配置路由
- 动态路由匹配
- 6. 状态管理
- 安装 Vuex
- Vuex 基本使用
- 模块化
- 7. 过渡与动画
- 过渡类名
- 动画
- 8. HTTP 请求
- 使用 axios
- 在 Vue 组件中使用 HTTP 请求
- 9. 表单处理
- 基本表单处理
- 表单修饰符
- 10. 插件
- 使用插件
- 创建插件
- 11. 实践
- 代码结构
- 性能优化
1. Vue 2 的安装和基本使用
安装 Vue 2
Vue 2 提供了多种安装方式:
-
通过 CDN 引入:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2"></script> -
使用 npm 安装:
npm install vue@2 -
使用 Vue CLI 创建项目:
npm install -g @vue/cli vue create my-project cd my-project npm run serve
创建 Vue 实例
一个简单的 Vue 实例示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Vue 2 示例</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello, Vue 2!'
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个新的 Vue 实例,并将其挂载到 #app 元素上。data 对象中的 message 属性将显示在页面上。
2. 模板语法
插值
Vue 允许在模板中使用双花括号语法进行数据绑定:
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>
也可以在属性中使用:
<div id="app">
<span v-bind:title="message">
鼠标悬停几秒钟查看此处动态绑定的提示信息!
</span>
</div>
指令
指令(Directives)是带有 v- 前缀的特殊属性:
v-bind: 绑定属性v-if: 条件渲染v-for: 列表渲染v-on: 事件监听
示例:
<div id="app">
<p v-if="seen">现在你看到我了</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
seen: true
}
});
</script>
计算属性
计算属性是基于依赖进行缓存的属性:
<div id="app">
{{ reversedMessage }}
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello'
},
computed: {
reversedMessage: function() {
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
});
</script>
在这个示例中,reversedMessage 是一个计算属性,它基于 message 计算出一个反转字符串。
3. Vue 实例
实例属性与方法
Vue 实例有许多属性和方法,如 el、data、methods 等:
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button @click="reverseMessage">Reverse Message</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
},
methods: {
reverseMessage: function () {
this.message = this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
});
</script>
生命周期钩子
Vue 实例在生命周期内会触发一些钩子函数:
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
},
created: function () {
console.log('实例已创建');
},
mounted: function () {
console.log('实例已挂载');
},
updated: function () {
console.log('实例已更新');
},
destroyed: function () {
console.log('实例已销毁');
}
});
</script>
4. 组件
定义与注册组件
Vue 组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,通常我们可以通过 Vue.component 方法来全局注册一个组件:
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
});
new Vue({
el: '#app'
});
</script>
也可以通过 components 选项局部注册组件:
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script>
var myComponent = {
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
};
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component': myComponent
}
});
</script>
组件通信
父子组件通信
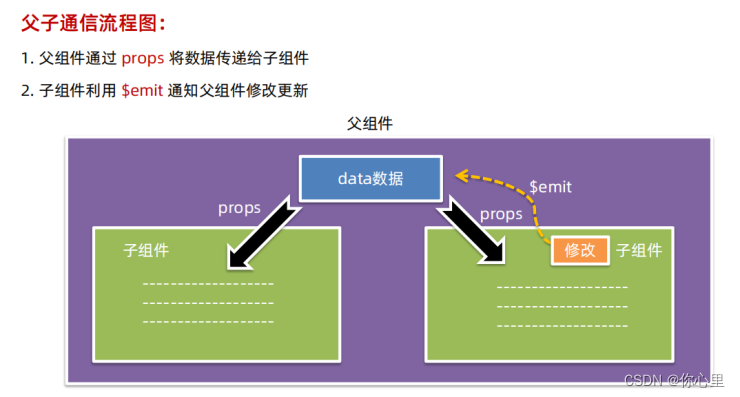
父组件通过 props 向子组件传递数据:
<div id="app">
<child message="Hello from parent"></child>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('child', {
props: ['message'],
template: '<div>{{ message }}</div>'
});
new Vue({
el: '#app'
});
</script>
子组件通过 $emit 向父组件发送事件:
<div id="app">
<button-counter @increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
<p>总计点击次数: {{ total }}</p>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('button-counter', {
template: '<button @click="incrementCounter">{{ counter }}</button>',
data: function () {
return {
counter: 0
}
},
methods: {
incrementCounter: function () {
this.counter += 1;
this.$emit('increment');
}
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
total: 0
},
methods: {
incrementTotal: function () {
this.total += 1;
}
}
});
</script>
5. 路由
Vue Router 是官方的路由管理器,用于构建单页面应用。
安装 Vue Router
npm install vue-router
配置路由
首先创建路由组件:
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script>
const Foo = { template: '<div>foo</div>' }
const Bar = { template: '<div>bar</div>' }
const routes = [
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', component: Bar }
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router
})
</script>
动态路由匹配
你可以在路由路径中使用动态参数:
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script>
const User = {
template: '<div>User {{ $route.params.id }}</div>'
}
const routes = [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User }
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
new
Vue({
el: '#app',
router
})
</script>
在这个示例中,/user/:id 路径中的 :id 是一个动态片段,$route.params.id 将会被当前的 id 值替换。
6. 状态管理
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用设计的状态管理模式。
安装 Vuex
npm install vuex
Vuex 基本使用
创建一个简单的 Vuex store:
<script>
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('increment')
}
}
})
</script>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="increment">Increment</button>
</div>
模块化
当应用变得复杂时,可以将 store 分割成模块:
<script>
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({ count: 0 }),
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.a.count
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('a/increment')
}
}
})
</script>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="increment">Increment</button>
</div>
7. 过渡与动画
Vue 提供了非常易用的过渡效果系统。
过渡类名
可以使用 transition 组件来为元素添加过渡效果:
<div id="app">
<button @click="show = !show">Toggle</button>
<transition name="fade">
<p v-if="show">Hello Vue!</p>
</transition>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
show: true
}
})
</script>
<style>
.fade-enter-active, .fade-leave-active {
transition: opacity 0.5s;
}
.fade-enter, .fade-leave-to /* .fade-leave-active in <2.1.8 */ {
opacity: 0;
}
</style>
动画
Vue 也支持使用 CSS 动画和第三方动画库,例如 Animate.css:
<div id="app">
<button @click="show = !show">Toggle</button>
<transition
name="bounce"
enter-active-class="animated bounceIn"
leave-active-class="animated bounceOut"
>
<p v-if="show">Hello Vue!</p>
</transition>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
show: true
}
})
</script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/animate.css/4.1.1/animate.min.css"/>
8. HTTP 请求
在 Vue 项目中,通常使用 axios 来进行 HTTP 请求。
使用 axios
首先安装 axios:
npm install axios
在 Vue 组件中使用 HTTP 请求
在 Vue 组件中使用 axios 进行 HTTP 请求:
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="post in posts" :key="post.id">{{ post.title }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
posts: []
},
created() {
axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts')
.then(response => {
this.posts = response.data
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error)
})
}
})
</script>
在这个示例中,我们在组件创建时发起 HTTP 请求,并将响应的数据绑定到组件的数据属性 posts 上。
9. 表单处理
Vue 2 提供了简单而强大的表单处理功能。
基本表单处理
使用 v-model 指令来创建双向数据绑定:
<div id="app">
<input v-model="message" placeholder="edit me">
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: ''
}
})
</script>
表单修饰符
Vue 提供了几个表单修饰符来简化表单处理:
.lazy: 取代input监听change事件。.number: 将用户输入自动转换为数值。.trim: 自动过滤用户输入的首尾空格。
示例:
<div id="app">
<input v-model.lazy="message" placeholder="edit me">
<input v-model.number="age" type="number" placeholder="age">
<input v-model.trim="name" placeholder="name">
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
<p>Age is: {{ age }}</p>
<p>Name is: {{ name }}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '',
age: null,
name: ''
}
})
</script>
10. 插件
Vue.js 的插件系统使得我们可以很方便地扩展 Vue 的功能。
使用插件
使用插件通常需要通过 Vue.use 方法来注册:
<script>
Vue.use(SomePlugin)
</script>
例如使用 Vue Router 插件:
<script>
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
</script>
创建插件
创建一个简单的插件:
MyPlugin.install = function (Vue, options) {
Vue.myGlobalMethod = function () {
console.log('MyPlugin global method')
}
Vue.directive('my-directive', {
bind(el, binding, vnode, oldVnode) {
el.textContent = binding.value
}
})
Vue.prototype.$myMethod = function (methodOptions) {
console.log('MyPlugin instance method')
}
}
Vue.use(MyPlugin)
11. 实践
代码结构
-
目录结构:合理的目录结构能提升项目的可维护性。
components: 存放 Vue 组件。views: 存放视图组件(页面级)。store: 存放 Vuex 状态管理相关文件。router: 存放路由配置文件。
-
组件划分:尽量保持组件的单一职责,一个组件只完成一项任务。
-
命名规范:遵循一致的命名规范,如组件命名使用 PascalCase。
性能优化
- 按需加载:使用路由懒加载和动态导入来减少初始加载时间。
- 长列表性能优化:使用
v-for渲染大量数据时,使用v-bind:key。 - 避免不必要的响应:使用
Object.freeze冻结数据,避免深层嵌套的数据对象变成响应式。 - 使用事件代理:在大量元素上绑定事件时,使用事件代理。