前言
MyBatis拦截器可以做的工作:SQL修改,分页操作,数据过滤,SQL执行时间性能监控等。
1. 基础介绍
1.1. 核心对象
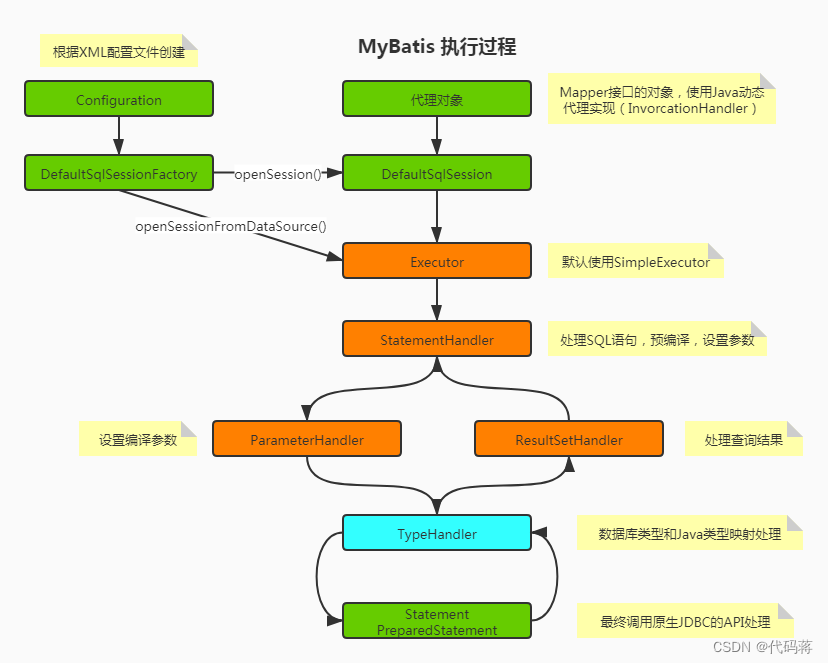
从MyBatis代码实现的角度来看,MyBatis的主要的核心部件有以下几个:
·Configuration:初始化基础配置,比如MyBatis的别名等,一些重要的类型对象,如插件,映射器,ObjectFactory和typeHandler对象,MyBatis所有的配置信息都维持在Configuration对象之中。
·SqlSessionFactory:SqlSession工厂。
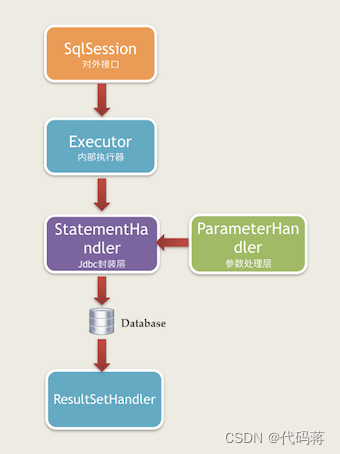
·SqlSession:作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要的数据库增删改查功能。
·Executor:MyBatis的内部执行器,它负责调用StatementHandler操作数据库,并把结果集通过ResultSetHandler进行自动映射,另外,它还处理二级缓存的操作。
·StatementHandler:MyBatis直接在数据库执行SQL脚本的对象。另外它也实现了MyBatis的一级缓存。
·ParameterHandler:负责将用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement所需要的参数。是MyBatis实现SQL入参设置的对象。
·ResultSetHandler:负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合。是MyBatis把ResultSet集合映射成POJO的接口对象。
·TypeHandler:负责Java数据类型和JDBC数据类型之间的映射和转换。
·MappedStatement:MappedStatement维护了一条<select|update|delete|insert>节点的封装。
·SqlSource :负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回。
·BoundSql:表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息。
1.2. 执行过程
2. 实现步骤
1.写一个实现org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor接口的拦截器类,并实现其中的方法。
2.添加@Intercepts注解,写上需要拦截的对象和方法,以及方法参数。
3.Spring项目注意添加@Component注解即可,使其成为Spring管理的一个Bean。
2.1. 添加注解
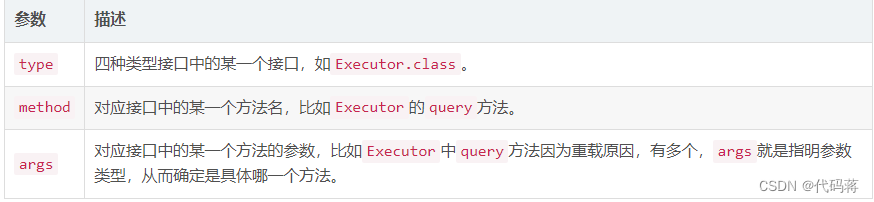
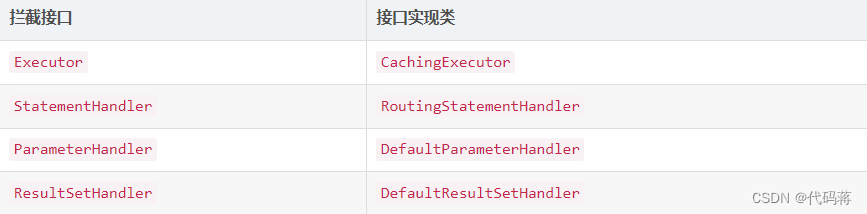
MyBatis拦截器默认可以拦截的类型只有四种,即四种接口类型Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler。对于我们的自定义拦截器必须使用MyBatis提供的@Intercepts注解来指明我们要拦截的是四种类型中的哪一种接口。
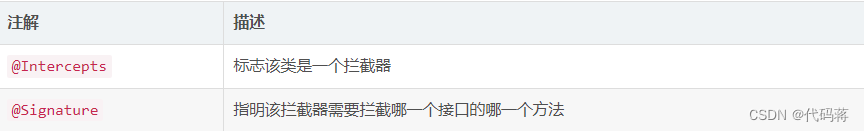
@Signature注解的参数:
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class, Integer.class}),
@Signature(type = ParameterHandler.class, method = "setParameters", args = {PreparedStatement.class}),
@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class})
})
2.1.1. type
MyBatis拦截器默认会按顺序拦截以下的四个接口中的所有方法:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor //拦截执行器方法
org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler //拦截SQL语法构建处理
org.apache.ibatis.executor.parameter.ParameterHandler //拦截参数处理
org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.ResultSetHandler //拦截结果集处理
具体是拦截这四个接口对应的实现类:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor
org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler
org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler
2.1.2. method
这个可以根据MyBatis源码了解下。
2.1.3. args
根据参数类型区分重载的方法。
2.2. 方法实现
2.2.1. intercept
进行拦截的时候要执行的方法。该方法参数Invocation类中有三个字段:
private final Object target;
private final Method method;
private final Object[] args;
可通过这三个字段分别获取下面的信息:
Object target = invocation.getTarget();//被代理对象
Method method = invocation.getMethod();//代理方法
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();//方法参数
2.2.2. plugin
插件用于封装目标对象的,通过该方法我们可以返回目标对象本身,也可以返回一个它的代理,可以决定是否要进行拦截进而决定要返回一个什么样的目标对象,官方提供了示例:return Plugin.wrap(target, this);,可以在这个方法中提前进行拦截对象类型判断,提高性能:
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
//只对要拦截的对象生成代理
if(target instanceof StatementHandler){
//调用插件
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
return target;
}
MyBatis拦截器用到责任链模式+动态代理+反射机制;
所有可能被拦截的处理类都会生成一个代理类,如果有N个拦截器,就会有N个代理,层层生成动态代理是比较耗性能的。而且虽然能指定插件拦截的位置,但这个是在执行方法时利用反射动态判断的,初始化的时候就是简单的把拦截器插入到了所有可以拦截的地方。所以尽量不要编写不必要的拦截器。另外我们可以在调用插件的地方添加判断,只要是当前拦截器拦截的对象才进行调用,否则直接返回目标对象本身,这样可以减少反射判断的次数,提高性能。
2.2.3. setProperties
如果我们拦截器需要用到一些变量参数,而且这个参数是支持可配置的,类似Spring中的@Value("${}")从application.properties文件获取自定义变量属性,这个时候我们就可以使用这个方法。
(1)在application.properties文件中添加配置:
mybatis.config-location=classpath:mybatis-config.xml
(2)在resources目录下添加mybatis-config.xml配置文件,并添加插件和属性配置。添加完需要注意去掉自定义MyBatis拦截器上的@Component注解,否则该拦截器相当于注册了两个,会执行两遍拦截方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.example.demo.mapper.plugin.MyPlugin">
<property name="key1" value="value1"/>
<property name="key2" value="value2"/>
<property name="key3" value="value3"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>
(3)在拦截器插件的setProperties方法中进行。这些自定义属性参数会在项目启动的时候被加载。
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("key1=" + properties.getProperty("key1"));
System.out.println("key2=" + properties.getProperty("key2"));
System.out.println("key3=" + properties.getProperty("key3"));
}
3. 代码示例
package com.example.demo.mapper.plugin;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})
})
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
Properties properties = null;
/**
* 拦截方法逻辑
* 这里主要是通过反射去获取要执行的SQL相关信息,然后进行操作
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object target = invocation.getTarget();//被代理对象
Method method = invocation.getMethod();//代理方法
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();//方法参数
// do something ...... 方法拦截前执行代码块
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// do something .......方法拦截后执行代码块
return result;
}
/**
* 生成MyBatis拦截器代理对象
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
if(target instanceof StatementHandler){
//调用插件
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
return target;
}
/**
* 设置插件属性(直接通过Spring的方式获取属性,所以这个方法一般也用不到)
* 项目启动的时候数据就会被加载
*/
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
//赋值成员变量,在其他方法使用。
this.properties = properties;
}
}