学习了example中pose_graph_3d的部分,记录一下学习过程。
前言:
翻译一下readme里面的内容:
...
该示例还说明了如何将 Eigen 的几何模块与 Ceres 的自动微分功能结合使用。 为了表示方向,我们将使用 Eigen 的四元数,它使用 Hamiltonian 约定,但与 Ceres 的旋转表示相比具有不同的元素顺序。 具体来说,它们的区别在于标量分量 q_w 是第一个还是最后一个; Ceres 的四元数的元素顺序是 [q_w, q_x, q_y, q_z],而 Eigen 的四元数是 [q_x, q_y, q_z, q_w]。
该包定义了对 3 维位姿图优化问题进行建模所需的必要 Ceres 成本函数,以及构建和解决问题的二进制文件。 显示成本函数是为了指导目的,并且可以通过使用需要更长的时间来实现的分析导数来加速。
运行 ---------- 此包包含一个可执行文件 `pose_graph_3d`,它将读取问题定义文件。 此可执行文件可以处理任何使用 g2o 格式的 3D 问题定义,四元数用于方向表示。 为不同格式(如 TORO 或其他格式)实施新阅读器会相对简单。 `pose_graph_3d` 将打印 Ceres 求解器的完整摘要,然后将机器人的原始和优化姿势(分别为 `poses_original.txt` 和 `poses_optimized.txt`)输出到磁盘,格式如下:
pose_id x y z q_x q_y q_z q_w
pose_id x y z q_x q_y q_z q_w
pose_id x y z q_x q_y q_z q_w
其中 `pose_id` 是文件定义中对应的整数 ID。 请注意,文件将按 `pose_id` 的升序排序。
...
主要是对于ceres用于位姿优化的一个说明,对于ceres和eigen关于四元数定义还有costfunction的设置。然后对于g2o文件内容的说明。example里面没有找到g2o文件的data,最后在github里面翻到了,链接如下:
Datasets – Luca Carlone
一、pose_graph_3d_error_term.h部分的解析
pose_graph_3d将代价函数类的定义单独写了一个头文件pose_graph_3d_error_term.h。先对它进行学习。
翻译注释:
计算两个姿势的误差项,这两个姿势之间具有相对姿势测量值。 带hat的变量是测量值。 我们有两个位姿 x_a 和 x_b。 通过传感器测量,我们可以测量帧 B w.r.t 帧 A 的变换,表示为 t_ab_hat。 我们可以计算位姿的当前估计和测量之间的误差度量。
在这个公式中,我们选择将刚性变换表示为哈密顿四元数 q 和位置 p。 四元数顺序为 [x, y, z,w]。
估计的测量值是:t_ab = [ p_ab ] = [ R(q_a)^T * (p_b - p_a) ]
[ q_ab ]
[ q_a^{-1}* q_b ]
其中 ^{-1} 表示逆矩阵,R(q) 是四元数的旋转矩阵。 现在我们可以计算估计和测量转换之间的误差度量。 对于方向误差,我们将使用标准乘法误差,结果为:
error = [ p_ab - \hat{p}_ab ]
[ 2.0 * Vec(q_ab * \hat{q}_ab^{-1}) ]
其中 Vec(*) 返回四元数的向量(虚部)部分。 由于测量具有与其准确性相关的不确定性,我们将通过测量信息矩阵的平方根对误差进行加权:
residuals = I^{1/2) * error 其中 I 是信息矩阵,它是协方差的倒数。
下面对PoseGraph3dErrorTerm类进行解析。
private:
// The measurement for the position of B relative to A in the A frame.
const Pose3d t_ab_measured_;
// The square root of the measurement information matrix.
const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> sqrt_information_;有两个私有变量,
t_ab_measured_表示在A下,B相对于A的位姿。这里要看一下Pose3d的定义:
struct Pose3d {
Eigen::Vector3d p;
Eigen::Quaterniond q;
// The name of the data type in the g2o file format.
static std::string name() { return "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT"; }
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
};它包括一个数据类型是Eigen::Vector3d的p表示位置,一个数据类型是Eigen::Quaterniond的q表示旋转。然后还定义了一个name函数返回VERTEX_SE3:QUAT,是se3下的四元数。
sqrt_information_表示测量信息矩阵的平方根,它的数据类型是double,size是6*6。
然后是构造函数:
PoseGraph3dErrorTerm(const Pose3d& t_ab_measured,
const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>& sqrt_information)
: t_ab_measured_(t_ab_measured), sqrt_information_(sqrt_information) {}它将传入的两个参数分别赋值给两个私有变量。
接下来是关键的重载运算符operator():
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const p_a_ptr,
const T* const q_a_ptr,
const T* const p_b_ptr,
const T* const q_b_ptr,
T* residuals_ptr) const传入了5个参数,注意这里全部是相对于世界坐标系下的
p_a_ptr表示a点的位置;
q_a_ptr表示a点的旋转用四元数来表示;
p_b_ptr表示b点的位置;
q_b_ptr表示b点的旋转;
residuals_ptr是最后算的残差。
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1>> p_a(p_a_ptr);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaternion<T>> q_a(q_a_ptr);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1>> p_b(p_b_ptr);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaternion<T>> q_b(q_b_ptr);这里使用了eigen里面的映射函数主要是为了数据转换,将p_a_ptr等分别赋值给p_a等,方便之后的运算。
// Compute the relative transformation between the two frames.
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_a_inverse = q_a.conjugate();
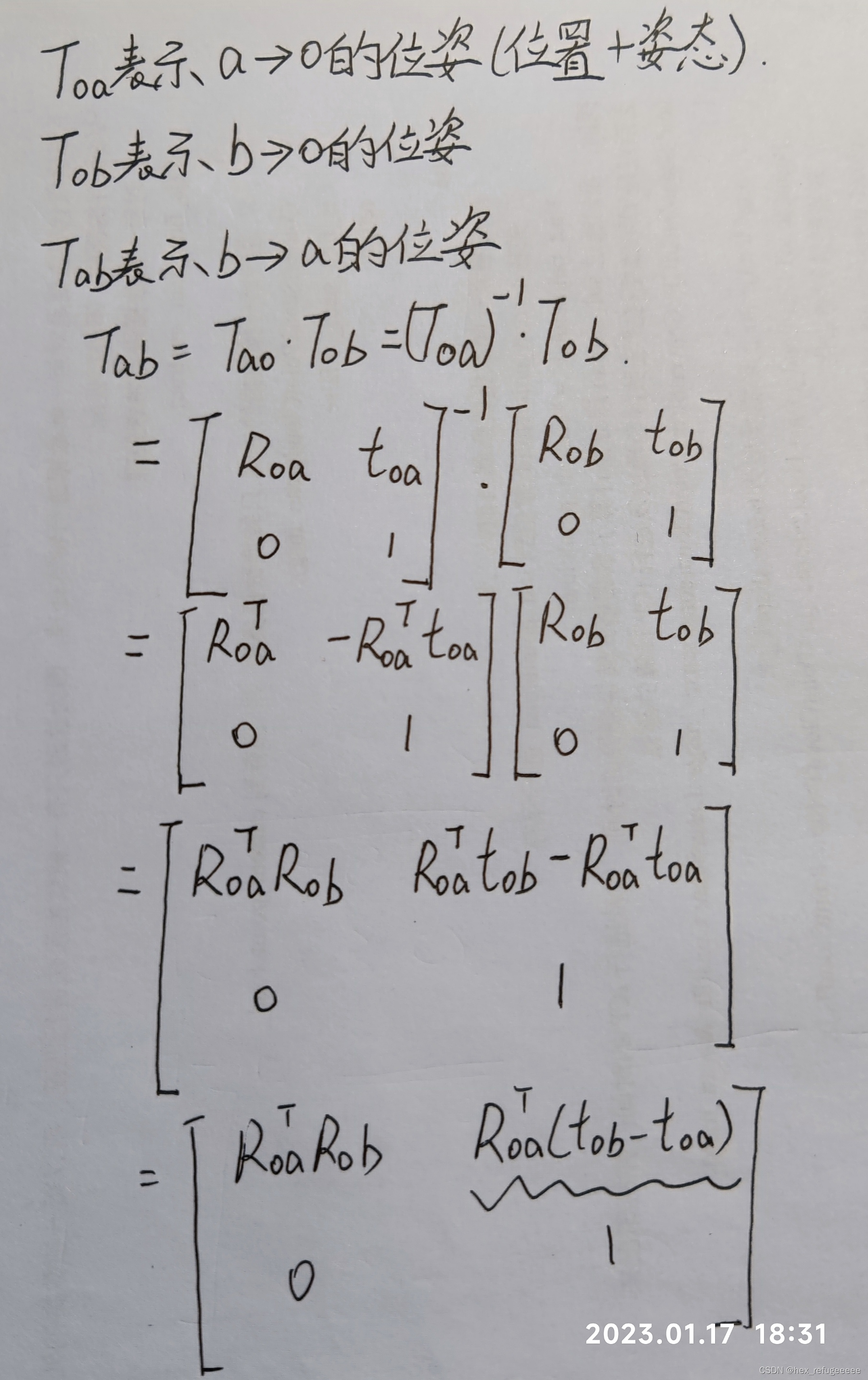
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_ab_estimated = q_a_inverse * q_b;计算a和b之间的位姿变换关系,q_a_inverse表示q_a的逆,使用conjugate函数来求。最后求出了q_ab_estimated表示从b变换到a的旋转矩阵。这里就相当于q_b是相对于世界坐标系下的旋转,q_a是相当于世界坐标系下的旋转。然后q_a_inverse * q_b就算出了b在a坐标系下的旋转。

公式推导如上图所示。
// Represent the displacement between the two frames in the A frame.
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> p_ab_estimated = q_a_inverse * (p_b - p_a);这是求出了从b到a的平移向量p_ab_estimated。同理p_b表示世界坐标系下b的位置,p_a表示世界坐标系下a的位置,然后p_ab_estimated就应该表示b点在a坐标系下平移向量。公式推导如下:
比较清晰明确。
// Compute the error between the two orientation estimates.
Eigen::Quaternion<T> delta_q =
t_ab_measured_.q.template cast<T>() * q_ab_estimated.conjugate();这部分是计算从b到a的旋转部分的测量值和估计值之间的差,这里运用了四元数的差来求旋转的角度差,这部分没有找到什么资料,在一篇博客里面看到了四元数的差,只给出了公式,但也没有给出推导的过程。
四元数的差、对数、指数、幂以及差值_Magic_Conch_Shell的博客-CSDN博客_四元数的差
// Compute the residuals.
// [ position ] [ delta_p ]
// [ orientation (3x1)] = [ 2 * delta_q(0:2) ]
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<T, 6, 1>> residuals(residuals_ptr);
residuals.template block<3, 1>(0, 0) =
p_ab_estimated - t_ab_measured_.p.template cast<T>();
residuals.template block<3, 1>(3, 0) = T(2.0) * delta_q.vec();这部分就是给6*1的残差向量赋值,前三行是位移部分的差值,后三行是旋转部分的差值,vec是取四元数的虚部,这里不知道为什么乘了2。
// Scale the residuals by the measurement uncertainty.
residuals.applyOnTheLeft(sqrt_information_.template cast<T>());这里是加上了信息矩阵。
static ceres::CostFunction* Create(
const Pose3d& t_ab_measured,
const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>& sqrt_information) {
return new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<PoseGraph3dErrorTerm, 6, 3, 4, 3, 4>(
new PoseGraph3dErrorTerm(t_ab_measured, sqrt_information));
}这里是创建自动求导的代价函数,是因为四元数不能使用常规方法来求导,就使用了这个。其中
new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<PoseGraph3dErrorTerm, 6, 3, 4, 3, 4>第一个6表示residuals是6维的;
第二个3表示operator()函数哪里的p_a_ptr是3维的,后面的类似。
二、common/read_g2o.h部分
这是一个处理g2o文件的头文件,下面来简单解析一下。
结合一下g20文件的内容来看:
// Reads a single pose from the input and inserts it into the map. Returns false
// if there is a duplicate entry.
template <typename Pose, typename Allocator>
bool ReadVertex(std::ifstream* infile,
std::map<int, Pose, std::less<int>, Allocator>* poses) {
int id;
Pose pose;
*infile >> id >> pose;
// Ensure we don't have duplicate poses.
if (poses->find(id) != poses->end()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Duplicate vertex with ID: " << id;
return false;
}
(*poses)[id] = pose;
return true;
}阅读顶点部分,通过传入的文件,将分别传入id和pose数据结构里面。这里有一个if判断,判断的内容是查看poses是否有id,这里的处理很巧妙,它希望的是判断是否有重复的位姿,这里的poses应该还没有存入id和pose,存入操作在下面,find()stl函数所以如果发现有相同的就返回iterator值,没有就会返回end()后面的iterator值,所以判断是否等于,如果不等于说明poses里面已经有key为id的数据,说明重复输入了。然后有一个map数据格式的变量poses,将id和pose赋予它。
// Reads the contraints between two vertices in the pose graph
template <typename Constraint, typename Allocator>
void ReadConstraint(std::ifstream* infile,
std::vector<Constraint, Allocator>* constraints) {
Constraint constraint;
*infile >> constraint;
constraints->push_back(constraint);
}阅读两点之间限制的边部分,这里是将g2o中的两点之间限制的边部分传入,具体得看main里面怎么写。
// In 3D, a vertex is defined as follows:
//
// VERTEX_SE3:QUAT ID x y z q_x q_y q_z q_w
//
// where the quaternion is in Hamilton form.
// A constraint is defined as follows:
//
// EDGE_SE3:QUAT ID_a ID_b x_ab y_ab z_ab q_x_ab q_y_ab q_z_ab q_w_ab I_11 I_12 I_13 ... I_16 I_22 I_23 ... I_26 ... I_66 // NOLINT
//
// where I_ij is the (i, j)-th entry of the information matrix for the
// measurement. Only the upper-triangular part is stored. The measurement order
// is the delta position followed by the delta orientation.这部分注释主要的意思是说明g2o不同行的格式。

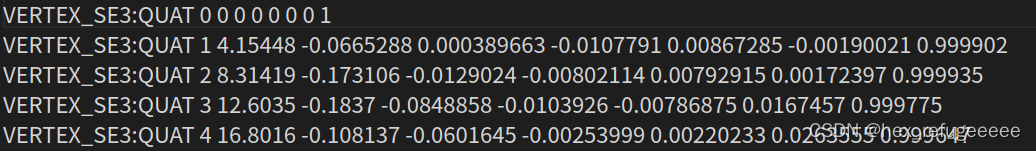
开头为VERTEX_SE3:QUAT的表示第一个参数是序号,后面3个是在世界坐标系下的位移值,最后四个是四元数。
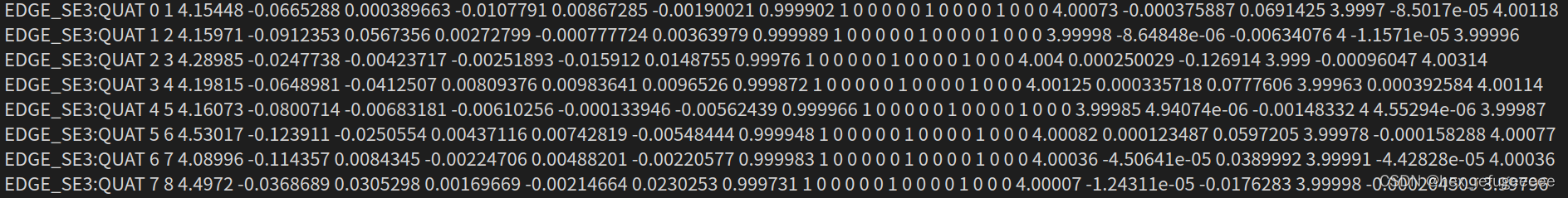 开头为EDGE_SE3:QUAT的表示由b到a坐标系下的相关值,
开头为EDGE_SE3:QUAT的表示由b到a坐标系下的相关值,
第一个值和第二个值表示从第二个到第一个的变换;
第三个值到第五个值表示从b到a坐标系下位移值的变换;
第六个值到第十个值表示从b到a坐标系下旋转的变换,以四元数表示;
后面的就是信息矩阵的上半部分,因为它是对称的所以存了一半。
template <typename Pose,
typename Constraint,
typename MapAllocator,
typename VectorAllocator>
bool ReadG2oFile(const std::string& filename,
std::map<int, Pose, std::less<int>, MapAllocator>* poses,
std::vector<Constraint, VectorAllocator>* constraints)
这是阅读g2o文件,
第一个参数是阅读的文件名;
第二个参数是关于顶点的poses;
第三个参数是关于两点之间的限制,边constraints。
poses->clear();
constraints->clear();
std::ifstream infile(filename.c_str());
if (!infile) {
return false;
}清空加判断是否有文件输入。
std::string data_type;
while (infile.good()) {
// Read whether the type is a node or a constraint.
infile >> data_type;
if (data_type == Pose::name()) {
if (!ReadVertex(&infile, poses)) {
return false;
}
} else if (data_type == Constraint::name()) {
ReadConstraint(&infile, constraints);
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unknown data type: " << data_type;
return false;
}
// Clear any trailing whitespace from the line.
infile >> std::ws;
}定义string类型data_type,它用来判断读入的是VERTEX_SE3:QUAT还是EDGE_SE3:QUAT来执行ReadVertex函数或者ReadConstraint函数。很妙的设计!
三、type.h部分
这部分主要是对于一些数据结构的定义优化和对于g2o文件读取的设置。
struct Pose3d {
Eigen::Vector3d p;
Eigen::Quaterniond q;
// The name of the data type in the g2o file format.
static std::string name() { return "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT"; }
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
};定义Pose3d的结构,包含一个vector3d的p和四元数q,并且name函数返回VERTEX_SE3:QUAT,正好是g2o文件中顶点开头的字符串。
inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& input, Pose3d& pose) {
input >> pose.p.x() >> pose.p.y() >> pose.p.z() >> pose.q.x() >> pose.q.y() >>
pose.q.z() >> pose.q.w();
// Normalize the quaternion to account for precision loss due to
// serialization.
pose.q.normalize();
return input;
}重写了>>运算符,将左侧数据写入pose里面,并将q正规化。
typedef std::map<int,
Pose3d,
std::less<int>,
Eigen::aligned_allocator<std::pair<const int, Pose3d>>>
MapOfPoses;定义了这么一个别名。
// The constraint between two vertices in the pose graph. The constraint is the
// transformation from vertex id_begin to vertex id_end.
struct Constraint3d {
int id_begin;
int id_end;
// The transformation that represents the pose of the end frame E w.r.t. the
// begin frame B. In other words, it transforms a vector in the E frame to
// the B frame.
Pose3d t_be;
// The inverse of the covariance matrix for the measurement. The order of the
// entries are x, y, z, delta orientation.
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> information;
// The name of the data type in the g2o file format.
static std::string name() { return "EDGE_SE3:QUAT"; }
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
};定义了Constraint3d的结构,有id_begin和id_end分别表示序号。
t_be表示由end到begin的变换旋转加平移;
information是6*6的信息矩阵;
name函数返回EDGE_SE3:QUAT字符串。
inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& input, Constraint3d& constraint) {
Pose3d& t_be = constraint.t_be;
input >> constraint.id_begin >> constraint.id_end >> t_be;
for (int i = 0; i < 6 && input.good(); ++i) {
for (int j = i; j < 6 && input.good(); ++j) {
input >> constraint.information(i, j);
if (i != j) {
constraint.information(j, i) = constraint.information(i, j);
}
}
}
return input;
}重写了>>运算符,并把相对应的量分别输入,注意对于信息矩阵的赋值,因为g2o文件的信息矩阵只存了上三角,所要要这样写。
typedef std::vector<Constraint3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Constraint3d>>
VectorOfConstraints;另一个别名。
四、pose_graph_3d.cc部分
从main开始看起:
ceres::examples::MapOfPoses poses;
ceres::examples::VectorOfConstraints constraints;前面部分都是一些读参,这两条是运用了上面type.h里面的两个别名。
poses是一个map,key为int类型,value是Pose3d类型的变量;
constraints是一个vector类型,存储为Constraint3d类型的变量。
CHECK(ceres::examples::ReadG2oFile(FLAGS_input, &poses, &constraints))
<< "Error reading the file: " << FLAGS_input;
std::cout << "Number of poses: " << poses.size() << '\n';
std::cout << "Number of constraints: " << constraints.size() << '\n';
CHECK(ceres::examples::OutputPoses("poses_original.txt", poses))
<< "Error outputting to poses_original.txt";进入ReadG2oFile函数读取g2o文件,并输出一些原始数据。
ceres::Problem problem;
ceres::examples::BuildOptimizationProblem(constraints, &poses, &problem);设置problem对象,并开始优化的相关操作。
具体看BuildOptimizationProblem函数。
// Constructs the nonlinear least squares optimization problem from the pose
// graph constraints.
void BuildOptimizationProblem(const VectorOfConstraints& constraints,
MapOfPoses* poses,
ceres::Problem* problem) 注释的意思是构造通过图限制来构造最小二乘的优化问题。BuildOptimizationProblem函数的第一个参数是constraints表示两点之间的约束的数据结构;
第二个是poses,代表顶点的数据;
第三个就是ceres的problem。
CHECK(poses != NULL);
CHECK(problem != NULL);
if (constraints.empty()) {
LOG(INFO) << "No constraints, no problem to optimize.";
return;
}判断参数是否为空。
ceres::LossFunction* loss_function = NULL;
ceres::LocalParameterization* quaternion_local_parameterization =
new EigenQuaternionParameterization;设置loss_function为空指针,说明没有设置核函数;
设置了ceres关于四元数相关计算变量。
for (VectorOfConstraints::const_iterator constraints_iter =
constraints.begin();
constraints_iter != constraints.end();
++constraints_iter) {
const Constraint3d& constraint = *constraints_iter;
MapOfPoses::iterator pose_begin_iter = poses->find(constraint.id_begin);
CHECK(pose_begin_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_begin << " not found.";
MapOfPoses::iterator pose_end_iter = poses->find(constraint.id_end);
CHECK(pose_end_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_end << " not found.";
const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> sqrt_information =
constraint.information.llt().matrixL();
// Ceres will take ownership of the pointer.
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function =
PoseGraph3dErrorTerm::Create(constraint.t_be, sqrt_information);
problem->AddResidualBlock(cost_function,
loss_function,
pose_begin_iter->second.p.data(),
pose_begin_iter->second.q.coeffs().data(),
pose_end_iter->second.p.data(),
pose_end_iter->second.q.coeffs().data());
problem->SetParameterization(pose_begin_iter->second.q.coeffs().data(),
quaternion_local_parameterization);
problem->SetParameterization(pose_end_iter->second.q.coeffs().data(),
quaternion_local_parameterization);
}在这个for循环中完成对于边限制数据的读取计算。下面进行详细的分析:
for (VectorOfConstraints::const_iterator constraints_iter =
constraints.begin();
constraints_iter != constraints.end();
++constraints_iter)因为是vector容器,所以可以使用迭代器。
const Constraint3d& constraint = *constraints_iter;
MapOfPoses::iterator pose_begin_iter = poses->find(constraint.id_begin);
CHECK(pose_begin_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_begin << " not found.";
MapOfPoses::iterator pose_end_iter = poses->find(constraint.id_end);
CHECK(pose_end_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_end << " not found.";取出begin_id和end_id,就是数据的前两个数值,分别赋值给pose_begin_iter和pose_end_iter。注意它是用find函数在poses里面取。
const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> sqrt_information =
constraint.information.llt().matrixL();将信息矩阵进行llt分解并赋值给sqrt_information矩阵,Eigen的LLT分解实现了Cholesky 分解。
Eigen的LLT分解_火星机器人life的博客-CSDN博客_eigen llt
// Ceres will take ownership of the pointer.
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function =
PoseGraph3dErrorTerm::Create(constraint.t_be, sqrt_information);通过Create构造函数生成cost_function。
problem->AddResidualBlock(cost_function,
loss_function,
pose_begin_iter->second.p.data(),
pose_begin_iter->second.q.coeffs().data(),
pose_end_iter->second.p.data(),
pose_end_iter->second.q.coeffs().data());这里是proble对象的AddResidualBlock模块,
第一个参数cost_function是设定的代价函数;
第二个参数loss_function是核函数,没有定义;
第三个参数pose_begin_iter->second.p.data()是第一个点的位置变量;
第四个参数pose_begin_iter->second.q.coeffs().data()是第一个点的旋转变量;coeffs()是xyzw的顺序;
后面两个参数类似。
problem->SetParameterization(pose_begin_iter->second.q.coeffs().data(),
quaternion_local_parameterization);
problem->SetParameterization(pose_end_iter->second.q.coeffs().data(),
quaternion_local_parameterization);这里的意思是说,四元数不符合常规运算的,eigen专门为它配置了运算,需要在problem配置时加入。
位姿图优化问题有六个未完全约束的自由度。 这通常称为规范自由度。
您可以对所有节点应用刚体变换,优化问题仍将具有完全相同的成本。
Levenberg-Marquardt 算法具有可缓解此问题的内部阻尼,但最好适当地约束规范自由度。
这可以通过将其中一个姿势设置为常量来实现,这样优化器就无法更改它。大概意思是第一个点固定?
MapOfPoses::iterator pose_start_iter = poses->begin();
CHECK(pose_start_iter != poses->end()) << "There are no poses.";
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(pose_start_iter->second.p.data());
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(pose_start_iter->second.q.coeffs().data());取出poses的第一个赋值给迭代器pose_start_iter,然后将它的p和q都在problem中设置成恒定值,就是上面那段翻译的意思。
再回到main里面来。
CHECK(ceres::examples::SolveOptimizationProblem(&problem))
<< "The solve was not successful, exiting.";开始优化,就是ceres求导的solve环节。
// Returns true if the solve was successful.
bool SolveOptimizationProblem(ceres::Problem* problem) {
CHECK(problem != NULL);
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.max_num_iterations = 200;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.FullReport() << '\n';
return summary.IsSolutionUsable();
}设置solver的options,最大迭代次数设置为200次;
采用ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY稀疏且可夫斯基模式求解?
然后开始solve,并输入summary的信息,最后返回是否成功标识。
CHECK(ceres::examples::OutputPoses("poses_optimized.txt", poses))
<< "Error outputting to poses_original.txt";最后将优化后的位姿输出到poses_optimized.txt文件中去。
结束,终于算是理解的比较透彻的了。
五、最终运行
在经过我一系列的修改后,终于成功的跑起来了。
以下是输出结果:
Number of poses: 1661
Number of constraints: 6275
Solver Summary (v 2.0.0-eigen-(3.4.0)-lapack-suitesparse-(5.1.2)-cxsparse-(3.1.9)-eigensparse-no_openmp)
Original Reduced
Parameter blocks 3322 3320
Parameters 11627 11620
Effective parameters 9966 9960
Residual blocks 6275 6275
Residuals 37650 37650
Minimizer TRUST_REGION
Sparse linear algebra library SUITE_SPARSE
Trust region strategy LEVENBERG_MARQUARDT
Given Used
Linear solver SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY
Threads 1 1
Linear solver ordering AUTOMATIC 3320
Cost:
Initial 8.362723e+03
Final 6.341883e-01
Change 8.362088e+03
Minimizer iterations 20
Successful steps 20
Unsuccessful steps 0
Time (in seconds):
Preprocessor 0.004724
Residual only evaluation 0.597028 (20)
Jacobian & residual evaluation 18.880399 (20)
Linear solver 0.425803 (20)
Minimizer 19.939410
Postprocessor 0.000370
Total 19.944509
Termination: CONVERGENCE (Function tolerance reached. |cost_change|/cost: 6.104042e-07 <= 1.000000e-06)

看一下生成的两个txt文件:

使用python可视化显示:
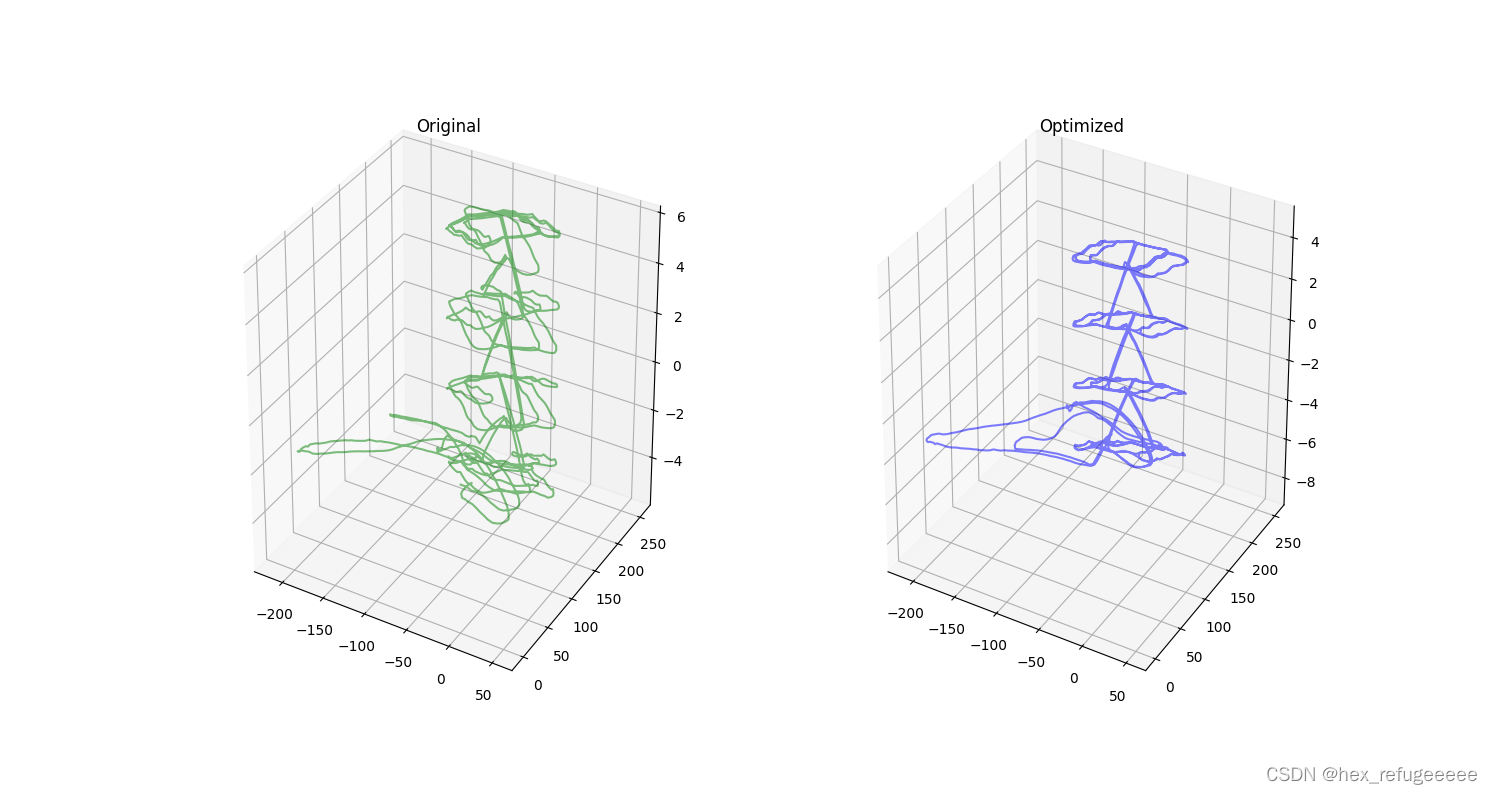
好像效果不明显,换个sphere看看。
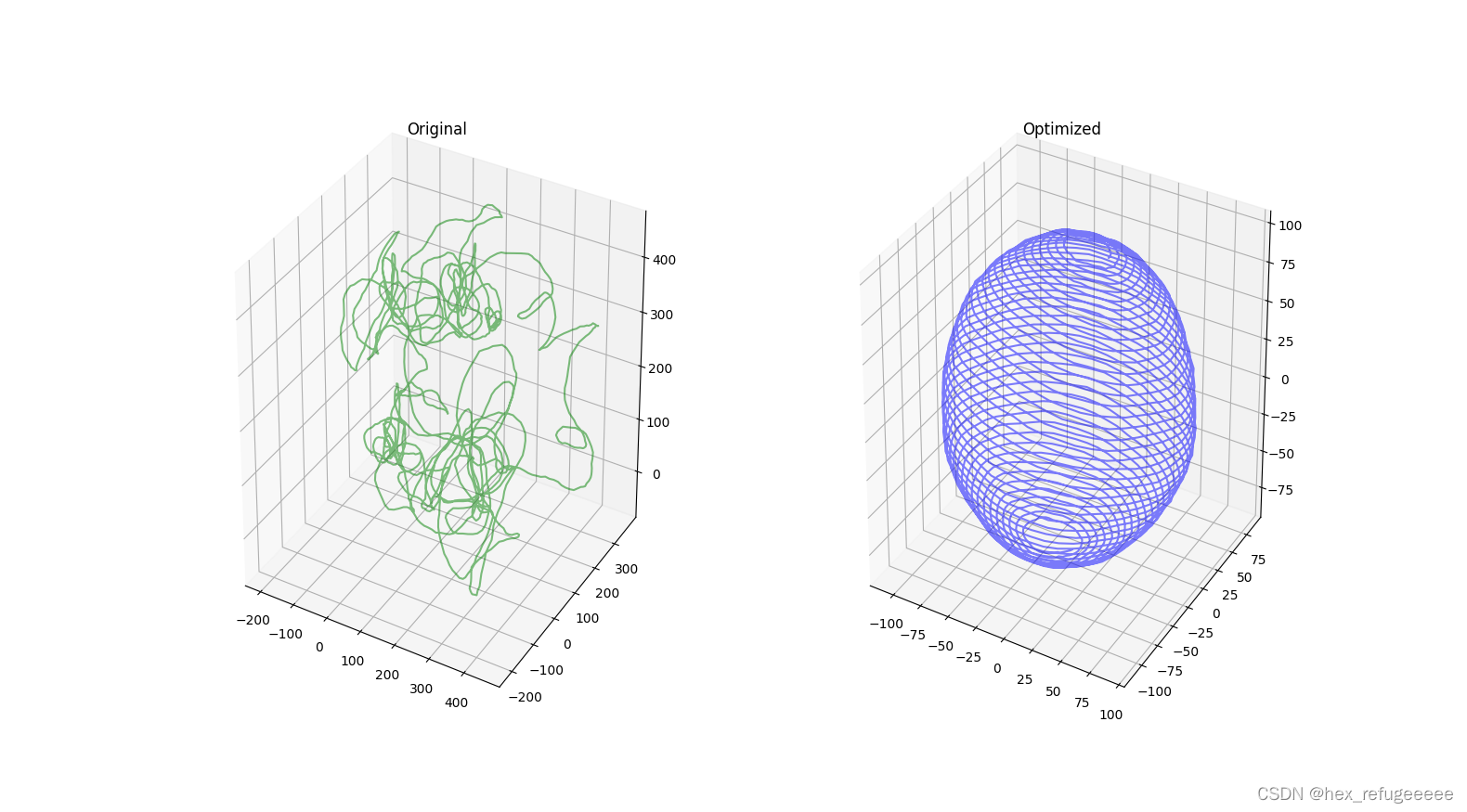
这就明显多了。CMakelists.txt内容比较简单,就不写了。
时间2023年1月17日23点06分,到这个时间为止,没有发现有比我对这个源码注释的最详细的。hhh,啦啦啦