1. 概念图
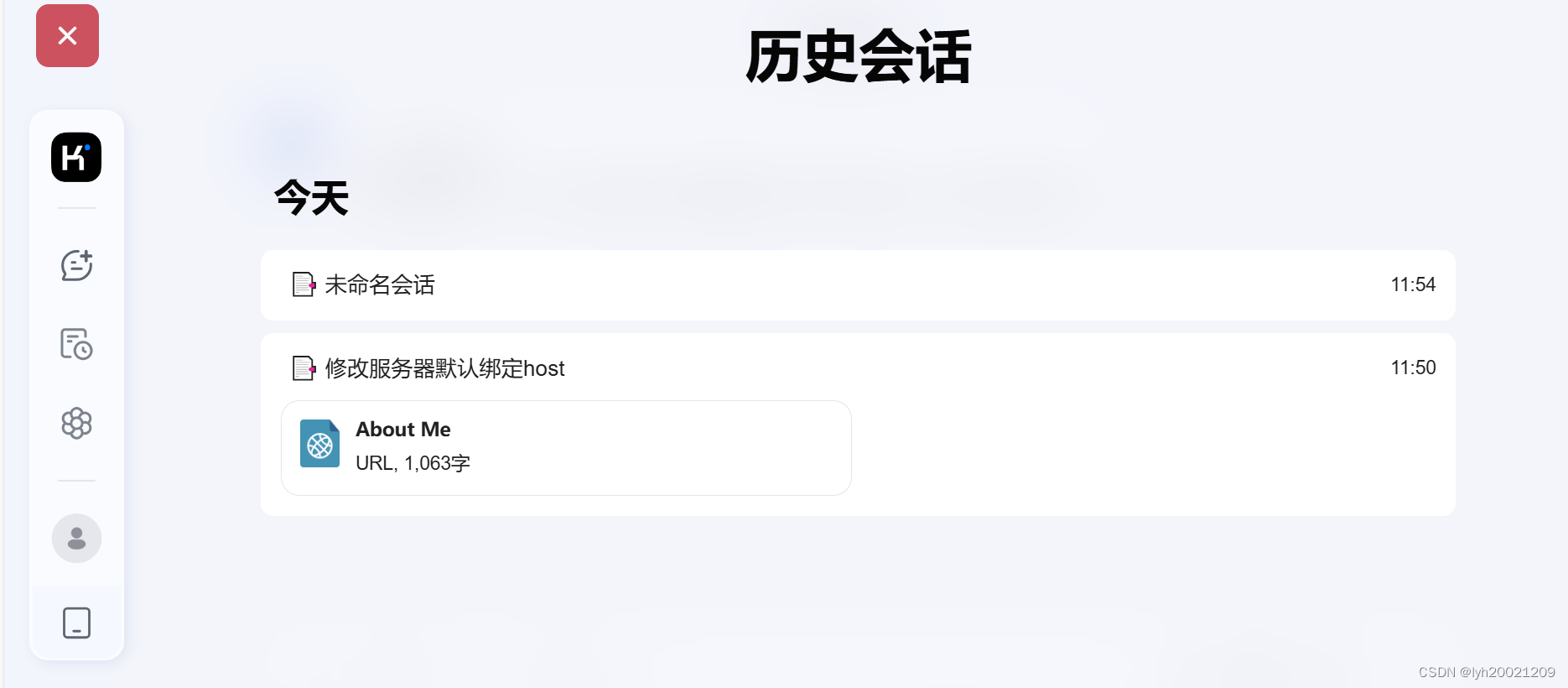
类似于Kimi,文心一言,chatGPT等市面上主流的大模型,我们的大模型也支持同一个用户的多个会话,并且提供支持联系上下文给出解答的能力。
2. 基于会话的对话
在langchain chatchat这个对langchain框架进行二次封装的第三方框架中,提供了一个chat函数接口:
async def chat(query: str = Body(..., description="用户输入", examples=["恼羞成怒"]),
conversation_id: str = Body("", description="对话框ID"),
history_len: int = Body(-1, description="从数据库中取历史消息的数量"),
history: Union[int, List[History]] = Body([],
description="历史对话,设为一个整数可以从数据库中读取历史消息",
examples=[[
{"role": "user",
"content": "我们来玩成语接龙,我先来,生龙活虎"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "虎头虎脑"}]]
),
stream: bool = Body(False, description="流式输出"),
model_name: str = Body(LLM_MODELS[0], description="LLM 模型名称。"),
temperature: float = Body(TEMPERATURE, description="LLM 采样温度", ge=0.0, le=2.0),
max_tokens: Optional[int] = Body(None, description="限制LLM生成Token数量,默认None代表模型最大值"),
# top_p: float = Body(TOP_P, description="LLM 核采样。勿与temperature同时设置", gt=0.0, lt=1.0),
prompt_name: str = Body("default", description="使用的prompt模板名称(在configs/prompt_config.py中配置)"),
):
2.1. 提取上下文
这里使用conversation_id对每次会话进行标记,并且在当前对话中,查询数据库中对应会话id的消息记录,使得能够进行联系上下文的对话。
memory = ConversationBufferDBMemory(conversation_id=conversation_id,
llm=model,
message_limit=history_len)
这个ConversationBufferDBMemory的功能是管理和维护与特定对话ID相关的消息缓存,以支持基于历史对话的智能助手响应生成。他继承自Langchain提供的一个基类:BaseChatMemory
class BaseChatMemory(BaseMemory, ABC):
"""Abstract base class for chat memory."""
chat_memory: BaseChatMessageHistory = Field(default_factory=ChatMessageHistory)
output_key: Optional[str] = None
input_key: Optional[str] = None
return_messages: bool = False
def _get_input_output(
self, inputs: Dict[str, Any], outputs: Dict[str, str]
) -> Tuple[str, str]:
if self.input_key is None:
prompt_input_key = get_prompt_input_key(inputs, self.memory_variables)
else:
prompt_input_key = self.input_key
if self.output_key is None:
if len(outputs) != 1:
raise ValueError(f"One output key expected, got {outputs.keys()}")
output_key = list(outputs.keys())[0]
else:
output_key = self.output_key
return inputs[prompt_input_key], outputs[output_key]
def save_context(self, inputs: Dict[str, Any], outputs: Dict[str, str]) -> None:
"""Save context from this conversation to buffer."""
input_str, output_str = self._get_input_output(inputs, outputs)
self.chat_memory.add_user_message(input_str)
self.chat_memory.add_ai_message(output_str)
def clear(self) -> None:
"""Clear memory contents."""
self.chat_memory.clear()
_get_input_output: 一个私有方法,用于获取输入和输出的键。如果没有设置input_key或output_key,则使用get_prompt_input_key函数或默认输出键。save_context: 一个公共方法,用于保存对话上下文到缓冲区。它从inputs和outputs字典中提取输入和输出字符串,并调用chat_memory的方法来添加用户消息和AI消息。clear: 一个公共方法,用于清除记忆内容,通过调用chat_memory的clear方法实现。
我们要做的就是覆写这个基类,由于我们是基于conversation_id(也即会话id)进行上下文关联记录的,因此这个覆写的子类中,最重要的就是这个会话id属性。此外,提取历史记录时,需要区分ai与人类的角色,因此还需要消息前缀,来区分是ai回复的,还是用户提问的:
conversation_id: str
human_prefix: str = "Human"
ai_prefix: str = "Assistant"
llm: BaseLanguageModel
memory_key: str = "history"
max_token_limit: int = 2000
message_limit: int = 10
提取上下文完毕后,将生成类似于:
[
HumanMessage(content="你好,助手。"),
AIMessage(content="你好!有什么可以帮助你的吗?"),
HumanMessage(content="我想了解天气预报。"),
AIMessage(content="请告诉我你的城市。"),
...
]
的缓冲区历史记录
2.2. 生成prompt模板
我们想方设法的还原上下文,是为了让ai知道之前和他的对话中都发生过什么。从而基于这个语境回答用户之后的问题。因此从ConversationBuffer中拿到之前的会话信息后,我们就需要生成prompt模板,使得模型能够基于上下文环境回答问题。
这个过程是开发者根据具体需求手动去写prompt进行,随后调用langchain中已经封装好的prompt template库进行优化的。
# 使用memory 时必须 prompt 必须含有memory.memory_key 对应的变量
prompt = get_prompt_template("llm_chat", "with_history")
chat_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(prompt)
# 根据conversation_id 获取message 列表进而拼凑 memory
memory = ConversationBufferDBMemory(conversation_id=conversation_id,
llm=model,
message_limit=history_len)
chain = LLMChain(prompt=chat_prompt, llm=model, memory=memory)
其中from_template与LLMChain都是langchain封装好的,前者是用来优化开发者的prompt模板的,后者是使用优化的prompt模板与历史会话信息(也即memory)进行大模型对话。
而开发者编写的模板,其实就和平时我们与大模型进行对话差不多:
"with_history":
'The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. '
'The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. '
'If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.\\n\\n'
'Current conversation:\\n'
'{history}\\n'
'Human: {input}\\n'
'AI:',
例如,我们可以在基于上下文会话信息的对话中,告诉他,接下来我们给他的对话是一个人类和一个AI之间的对话,如果AI不知道人类的问题的答案,他就诚实的说不知道。并且告诉他这个对话的格式是先Human,再AI的,对应了我们上面的human/ai_prefix。
2.3. 与大模型对话
随后的部分,交给大模型与RAG技术,利用预训练与微调后的大模型自身的能力,通过RAG技术与向量知识库建立连接,检索相关知识,给出回答。
3. 接口实现
首先这个新建会话的功能肯定是异步的,因为一个用户新建一个会话和另一个用户新建会话是没有任何依赖关系的。
在为每个会话生成唯一标识时,我采用了python的uuid。随后向Conversation表中添加这个新的会话的记录。
注意这里防止用户伪造请求,我们要捕获user_id不存在引发的外键约束的异常。
async def new_conversation(nc: NewConv) -> BaseResponse:
"""
用户建立新的对话:
1. 为新的对话生成一个全局唯一的uuid
2. 将这个conversation_id插入到数据库中 同时确保外键约束
"""
conv_id = uuid.uuid4().hex
try:
with Session(engine) as session:
session.add(Conversation(id=conv_id, conv_name=nc.conv_name, create_time=datetime.datetime.utcnow(),
user_id=nc.user_id))
session.commit()
logging.info(f"{nc.user_id} 创建了会话 {conv_id} 会话名{nc.conv_name}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"{nc.user_id} 创建会话失败 {e}")
return BaseResponse(code=200, message="会话创建失败", data={"error": f'{e}'})
return BaseResponse(code=200, message="会话创建成功", data={"conv_id": conv_id})
随后将这个函数作为post接口调用的回调函数即可。
app.post(self.generate_route_path(["new-conversation"]), tags=self.tag, response_model=BaseResponse,
summary="用户创建新会话")(new_conversation)
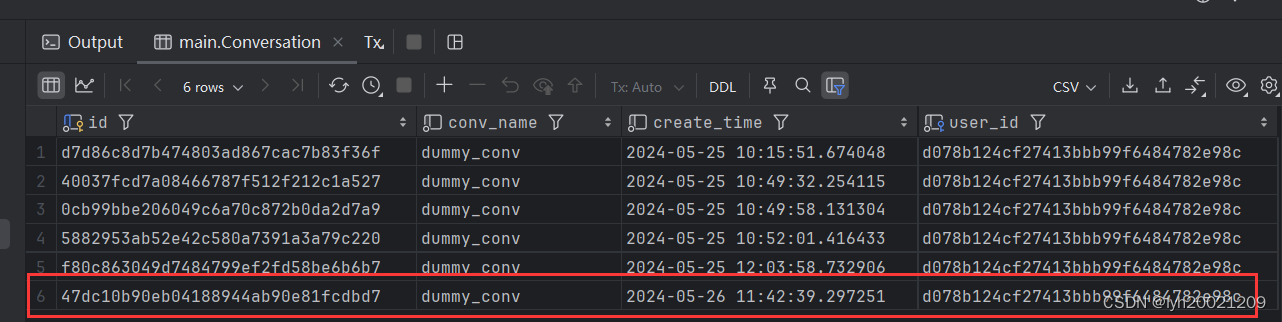
4. 接口测试
我们可以利用.http文件编写接口测试
假设数据库中现在有一个名叫lyh的用户,他的id是:d078b124cf27413bbb99f6484782e98c
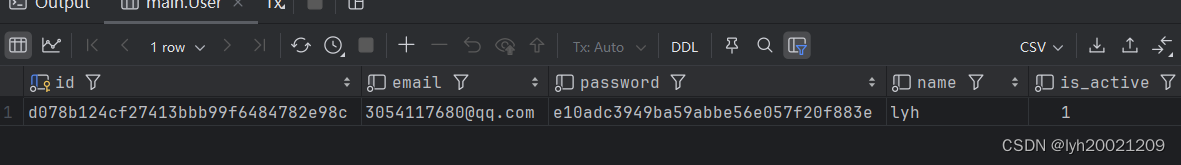
基于这个id,我们进行新会话的创建:
POST <http://127.0.0.1:9090/conversation/new-conversation>
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: application/json
{
"user_id": "d078b124cf27413bbb99f6484782e98c",
"conv_name": "dummy_conv"
}
回环地址是因为目前测试环境和开发环境是一个,都是在本机。
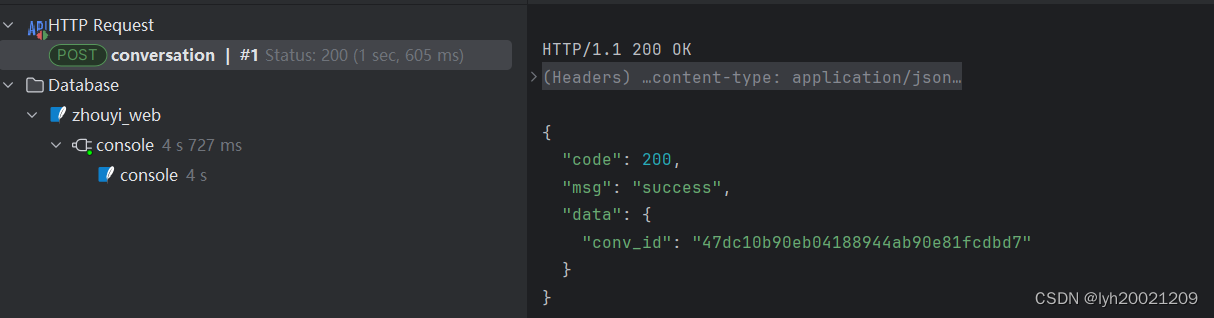
成功,返回了会话id。
可以看到数据库中新插入了一条会话记录。