目录
1.服务器端实现思路
2.服务器端代码
3.客户端代码
4.内核链表代码
5.运行格式
一、服务器端
二、客户端
6.效果
1.服务器端实现思路
-
Tcp广播服务初始化
-
等待客户端连接
-
广播发送
2.服务器端代码
#include "list.h"
#include <signal.h>
#define EXIT_MASK "exit"
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
volatile int is_down = 0;
void *Tcp_Pthreads_Broadcast(void *arg)
{
service_inf_poi sip = (service_inf_poi)arg;
// 设置线程分离
if (pthread_detach(pthread_self()) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_detach error");
close(sip->ser_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)(-1));
}
char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN] = "\0";
while (!is_down)
{
memset(msg, 0, sizeof(char) * MSG_MAX_LEN);
// 保存当前已经连接的客户端的IP地址和套接字
int cur_client_id = sip->cur_client_node->client_own_id;
char cur_client_ip_addr[IP_ADDR_LEN] = "\0";
strcpy(cur_client_ip_addr, sip->cur_client_node->client_ip_addr);
// 根据套接字读取数据
int read_ret = read(cur_client_id, msg, MSG_MAX_LEN);
if (read_ret == -1)
{
perror("read error...");
close(sip->ser_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)(-1));
}
else if (read_ret == 0 || strcmp(msg, EXIT_MASK) == 0)
{
printf("%s 断开连接\n", cur_client_ip_addr);
client_link pos = NULL;
// 删除该客户端节点,并结束该进程
list_for_each_entry(pos, &sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head, little_pointer_head)
{
if (pos->client_own_id == cur_client_id) // 根据套接字 号码来找
{
break;
}
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 上锁
list_del(&pos->little_pointer_head);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁
printf("删除节点成功\n\n");
// 判断当前是否有客户
if (list_empty(&sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head) == 1 || sip->client_list_head == NULL || &sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head == NULL)
{
printf("================当前无客户连接======================\n\n");
printf("服务器端即将断开!!!\n\n");
// 退出,并释放,结束服务器端
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 上锁
Tcp_Server_Broadcast_Free(sip);
is_down = 1;
close(sip->ser_fd);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁
if (kill(getpid(), SIGKILL) == -1)
{
perror("kill error...");
pthread_exit((void *)-1);
}
break;
}
else
{
pos = NULL;
printf("=============当前客户端列表==========================\n");
list_for_each_entry(pos, &sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head, little_pointer_head)
{
printf("%s\n", pos->client_ip_addr);
}
printf("===================================================\n\n");
}
break; // 结束当前线程
}
else
{
printf("%s : %s\n", cur_client_ip_addr, msg);
// 广播转发
client_link pos = NULL;
// 将前16个字节作为ip地址
char new_msg[MSG_MAX_LEN] = "\0";
sprintf(new_msg, "%s:【%s】", cur_client_ip_addr, msg);
printf("new_msg = %s\n", new_msg);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head, little_pointer_head)
{
if (strcmp(cur_client_ip_addr, pos->client_ip_addr) != 0) // 自己不转发给自己
{
if (write(pos->client_own_id, new_msg, strlen(new_msg)) == -1)
{
perror("write error...");
break;
}
printf("转发给:%s成功!\n", pos->client_ip_addr);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
pthread_exit((void *)0);
return NULL;
}
void Tcp_Server_Broadcast_Free(service_inf_poi sip)
{
free(sip);
return;
}
// 创建新节点
client_link Create_New_Client_Node()
{
client_link new_client_node = (client_link)malloc(sizeof(client_node));
if (new_client_node == (client_link)NULL)
{
perror("malloc new_big_node error");
return (client_link)-1;
}
memset(new_client_node, 0, sizeof(client_node));
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&new_client_node->little_pointer_head);
return new_client_node;
}
// Tcp广播服务初始化
service_inf_poi Tcp_Server_Broadcast_Init(int ser_port)
{
service_inf_poi sip = (service_inf_poi)malloc(sizeof(service_inf));
if (sip == (service_inf_poi)NULL)
{
perror("malloc error...");
return (service_inf_poi)-1;
}
memset(sip, 0, sizeof(service_inf));
if ((sip->ser_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1)
{
perror("socket error...");
return (service_inf_poi)-1;
}
// 创建客户端头结点
sip->client_list_head = Create_New_Client_Node();
if (sip->client_list_head == (client_link)-1)
{
return (service_inf_poi)-1;
}
// 设置基本信息
struct sockaddr_in ser_inf;
memset(&ser_inf, 0, sizeof(ser_inf));
ser_inf.sin_family = AF_INET;
ser_inf.sin_port = htons(ser_port); // 将小端变成大端
ser_inf.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// 绑定
if (bind(sip->ser_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&ser_inf, sizeof(ser_inf)) == -1)
{
perror("bind error...");
return (service_inf_poi)-1;
}
// 监听
if (listen(sip->ser_fd, CLIENT_MAX_CONNECT_NUM / 4) == -1) // 最大等待队列是CLIENT_MAX_CONNECT_NUM / 4个
{
perror("listen error...");
return (service_inf_poi)-1;
}
// 初始化互斥锁
if (pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL))
{
perror("pthread_mutex error...\n");
return (service_inf_poi)-1;
}
return sip;
}
// 等待客户端连接
int Waiting_For_Connnect(service_inf_poi sip)
{
struct sockaddr_in client_inf;
int len = sizeof(client_inf);
while (1)
{
memset(&client_inf, 0, len);
int new_client_fd = accept(sip->ser_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_inf, &len);
if (new_client_fd == -1)
{
perror("accept error...");
return -1;
}
printf("%s已经连接服务器\n", inet_ntoa(client_inf.sin_addr));
// 创建新节点
client_link new_client_node = Create_New_Client_Node();
if (new_client_node == (client_link)-1)
{
return -1;
}
// 将ip和新的套接字 赋值
new_client_node->client_own_id = new_client_fd;
strcpy(new_client_node->client_ip_addr, inet_ntoa(client_inf.sin_addr));
sip->cur_client_node = new_client_node; // 保存当前的结点
// 将新节点插入到客户端列表中
list_add_tail(&new_client_node->little_pointer_head, &sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head);
printf("添加头结点成功!\n\n");
printf("======================当前客户端列表=======================\n");
client_link pos;
list_for_each_entry(pos, &sip->client_list_head->little_pointer_head, little_pointer_head)
{
printf("%s\n", pos->client_ip_addr);
}
printf("==========================================================\n\n");
// 创建线程进行广播发送
pthread_t pid;
if (pthread_create(&pid, NULL, Tcp_Pthreads_Broadcast, sip) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create error...");
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
return -1;
service_inf_poi sip = Tcp_Server_Broadcast_Init(atoi(argv[1]));
if (sip == (service_inf_poi)-1)
{
printf("Tcp服务器初始化失败!\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("Tcp服务器初始化成功!正在等待接受数据.......\n");
}
Waiting_For_Connnect(sip);
return 0;
}3.客户端代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define IP_ADDR_LEN 16
#define MSG_MAX_LEN 256
#define CLIENT_MAX_CONNECT_NUM 100
#define EXIT_MASK "exit"
volatile int is_over = 0;
int Client_Init(char *server_ip_addr, int server_prot_num);
int Client_Running(int cli_fd);
void *Send_Msg(void *arg);
void *Rec_Msg(void *arg);
void *Send_Msg(void *arg)
{
int *client_fd = (int *)(arg);
int cli_fd = *(client_fd);
printf("Send_msg = %d\n", cli_fd);
if (pthread_detach(pthread_self()) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_detach error");
close(cli_fd);
free(client_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)(-1));
}
char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN] = "\0";
while (!is_over)
{
memset(msg, 0, MSG_MAX_LEN);
printf("请输入要发送的数据:");
scanf("%s", msg);
if (write(cli_fd, msg, strlen(msg)) == -1)
{
perror("Send_Msg:write error...");
close(cli_fd);
free(client_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)-1);
}
if (strcmp(EXIT_MASK, msg) == 0)
{
printf("我要断了\n");
is_over = 1;
if (kill(getpid(), SIGKILL) == -1)
{
perror("kill error...");
close(cli_fd);
free(client_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)-1);
}
break;
}
}
close(cli_fd);
free(client_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)0);
return NULL;
}
void *Rec_Msg(void *arg)
{
int cli_fd = *((int *)arg);
if (pthread_detach(pthread_self()) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_detach error");
close(cli_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)(-1));
}
char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN] = "\0";
while (!is_over)
{
memset(msg, 0, MSG_MAX_LEN);
int read_ret = read(cli_fd, msg, MSG_MAX_LEN);
if (read_ret == -1)
{
perror("write error...");
close(cli_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)-1);
}
else if (read_ret != 0)
{
printf("\n%s\n", msg);
}
}
close(cli_fd);
pthread_exit((void *)0);
return NULL;
}
int Client_Init(char *server_ip_addr, int server_prot_num)
{
// 创建套接字
int cli_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (cli_fd == -1)
{
perror("socket error...");
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("socket success %d\n", cli_fd);
}
struct sockaddr_in cli_inf;
memset(&cli_inf, 0, sizeof(cli_inf));
cli_inf.sin_family = AF_INET;
cli_inf.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(server_ip_addr);
cli_inf.sin_port = htons(server_prot_num);
// 连接
if (connect(cli_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&cli_inf, sizeof(cli_inf)) == -1)
{
perror("connect error...");
close(cli_fd);
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("连接成功!\n");
}
return cli_fd;
}
int Client_Running(int cli_fd)
{
int *client_fd = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*client_fd = cli_fd;
pthread_t pid_send, pid_rec;
if (pthread_create(&pid_send, NULL, Send_Msg, client_fd) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create error...");
return -1;
}
if (pthread_create(&pid_rec, NULL, Rec_Msg, client_fd) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create error...");
return -1;
}
pause();
return 0;
}
// a.out ip port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("输入的参数不对!\n");
return -1;
}
int cli_fd = Client_Init(argv[1], atoi(argv[2]));
printf("Client_Init success %d\n", cli_fd);
if (cli_fd == -1)
{
printf("Client Init error\n");
return -1;
}
if (Client_Running(cli_fd) == -1)
{
printf("Client_Running error\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}4.内核链表代码
#ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H
#define _LINUX_LIST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define IP_ADDR_LEN 16
#define MSG_MAX_LEN 256
#define CLIENT_MAX_CONNECT_NUM 100
/*
* Simple doubly linked list implementation.
*
* Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when
* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as
* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can
* generate better code by using them directly rather than
* using the generic single-entry routines.
*/
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) \
{ \
&(name), &(name) \
}
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
struct list_head
{
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
typedef struct big_list_node
{
int client_own_id; // 客户端的套接字
char client_ip_addr[IP_ADDR_LEN]; // 客户端的ip地址
struct list_head little_pointer_head;
} client_node, *client_link;
typedef struct tcp_service_inf
{
int ser_fd; // 服务端的套接字
client_link cur_client_node; // 存放当前客户端的结点
client_link client_list_head; // 存放客户端链表的头结点
} service_inf, *service_inf_poi;
client_link Create_New_Client_Node();
service_inf_poi Tcp_Server_Broadcast_Init(int ser_port);
client_link Create_Client_Node();
int Waiting_For_Connnect(service_inf_poi sip);
void Tcp_Server_Broadcast_Free(service_inf_poi sip);
void *Tcp_Pthreads_Broadcast(void *arg);
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list; // 游离节点指向小头
list->prev = list;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
extern bool __list_add_valid(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next);
extern bool __list_del_entry_valid(struct list_head *entry);
#else
static inline bool __list_add_valid(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
return true;
}
static inline bool __list_del_entry_valid(struct list_head *entry)
{
return true;
}
#endif
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
if (!__list_add_valid(new, prev, next))
return;
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
/**
* list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
{
if (!__list_del_entry_valid(entry))
return;
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
entry->next = NULL;
entry->prev = NULL;
}
/**
* list_replace - replace old entry by new one
* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
/**
* list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
*/
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
/**
* list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add(list, head);
}
/**
* list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
/**
* list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head
* @list: the entry to test
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
const struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}
/**
* list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/**
* list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified
* @head: the list to test
*
* Description:
* tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be
* in the process of modifying either member (next or prev)
*
* NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization
* can only be safe if the only activity that can happen
* to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used
* if another CPU could re-list_add() it.
*/
static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *next = head->next;
return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
}
/**
* list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first;
if (!list_empty(head))
{
first = head->next;
list_move_tail(first, head);
}
}
/**
* list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry.
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}
static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
struct list_head *new_first = entry->next;
list->next = head->next;
list->next->prev = list;
list->prev = entry;
entry->next = list;
head->next = new_first;
new_first->prev = head;
}
/**
* list_cut_position - cut a list into two
* @list: a new list to add all removed entries
* @head: a list with entries
* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself
* and if so we won't cut the list
*
* This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and
* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should
* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list
* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about
* losing its data.
*
*/
static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
if (list_empty(head))
return;
if (list_is_singular(head) &&
(head->next != entry && head != entry))
return;
if (entry == head)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
else
__list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
}
static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
}
/**
* list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
{
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
/**
* list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* Each of the lists is a queue.
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
{
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
// 在stddef.h中
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) & ((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
// 在kernel.h中
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) ); })
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
/**
* list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
/**
* list_last_entry - get the last element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_last_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->prev, type, member)
/**
* list_first_entry_or_null - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note that if the list is empty, it returns NULL.
*/
#define list_first_entry_or_null(ptr, type, member) ({ \
struct list_head *head__ = (ptr); \
struct list_head *pos__ = head__->next; \
pos__ != head__ ? list_entry(pos__, type, member) : NULL; \
})
/**
* list_next_entry - get the next element in list
* @pos: the type * to cursor
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_next_entry(pos, member) \
list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member)
/**
* list_prev_entry - get the prev element in list
* @pos: the type * to cursor
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_prev_entry(pos, member) \
list_entry((pos)->member.prev, typeof(*(pos)), member)
/**
* list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); pos = pos->prev)
/**
* list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; \
pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->prev)
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_last_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_prev_entry(pos, member))
/**
* list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue()
* @pos: the type * to use as a start point
* @head: the head of the list
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue().
*/
#define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \
((pos) ?: list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_next_entry(pos, member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_prev_entry(pos, member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_prev_entry(pos, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \
for (; &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_next_entry(pos, member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_next_entry(n, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_continue - continue list iteration safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point,
* safe against removal of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_next_entry(pos, member), \
n = list_next_entry(pos, member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_next_entry(n, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_from - iterate over list from current point safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against
* removal of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \
for (n = list_next_entry(pos, member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_next_entry(n, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse - iterate backwards over list safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal
* of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_last_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_prev_entry(pos, member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_prev_entry(n, member))
/**
* list_safe_reset_next - reset a stale list_for_each_entry_safe loop
* @pos: the loop cursor used in the list_for_each_entry_safe loop
* @n: temporary storage used in list_for_each_entry_safe
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* list_safe_reset_next is not safe to use in general if the list may be
* modified concurrently (eg. the lock is dropped in the loop body). An
* exception to this is if the cursor element (pos) is pinned in the list,
* and list_safe_reset_next is called after re-taking the lock and before
* completing the current iteration of the loop body.
*/
#define list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member) \
n = list_next_entry(pos, member)
/*
* Double linked lists with a single pointer list head.
* Mostly useful for hash tables where the two pointer list head is
* too wasteful.
* You lose the ability to access the tail in O(1).
*/
#endif
5.运行格式
一、服务器端
gcc xx.c -pthrad -o s
./s 8888
其中8888是端口号
二、客户端
gcc xxx.c -pthrad -o c
./s 192.xxx.xxx.xxx 8888
第二个参数是:服务器端的ip地址
第三个参数是:端口号
(注意:如果是同一台主机,则端口号不能相同)
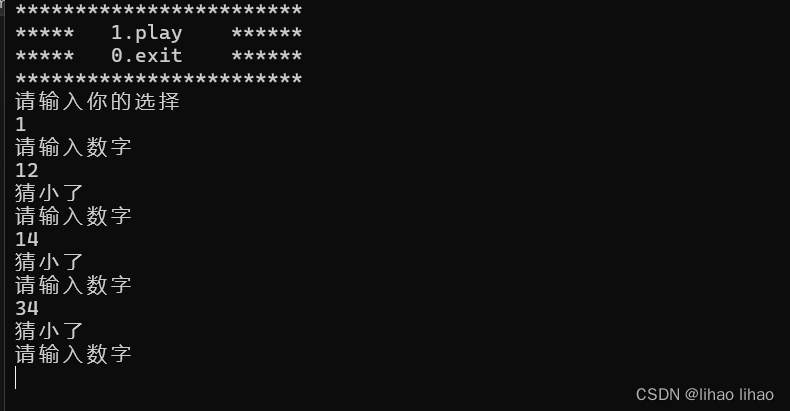
6.效果
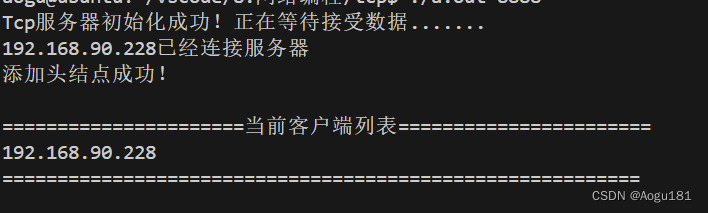
连接效果
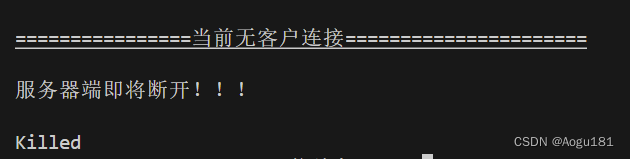
断开效果


![[嵌入式系统-75]:RT-Thread-快速上手:正点原子探索者 STM32F407示例](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/26603420183b22ef3cc660398726387e.gif)