1.随机数生成
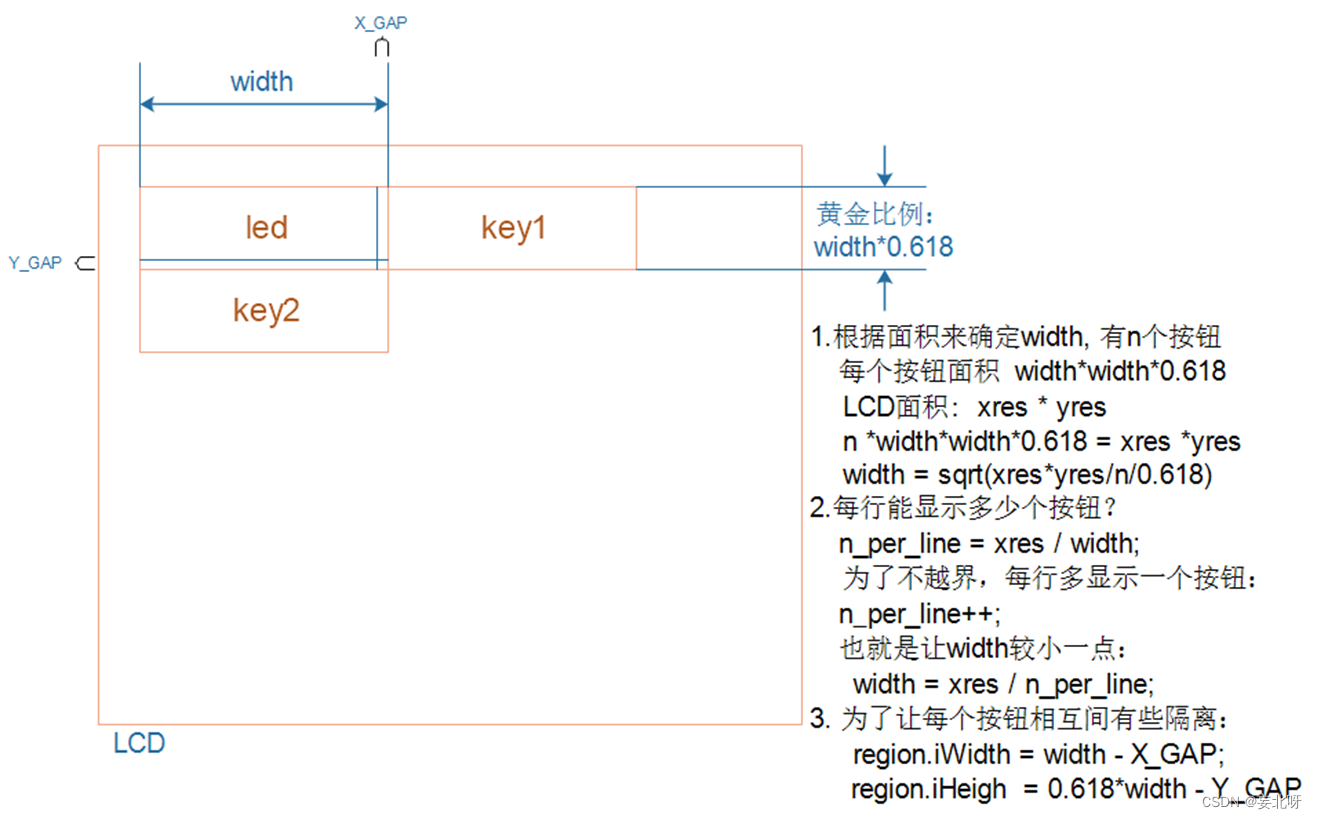
要想实现猜数字小游戏,依赖于随机数的生成
1.1 rand()函数
这个函数是用来生成随机数的,返回值是正整数,他的值的范围是0到rand_max之间的,rand_max的值在大多数编译器上面是32767,rand()函数的使用必须包含头文件#include<stdlib.h>,下面是对rand()函数的使用
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", rand());
printf("%d\n", rand());
printf("%d\n", rand());
printf("%d\n", rand());
return 0;
}程序的运行结果
第一次

第二次

我们发现,无论是运行多少次,生成的随机数都是一样的,其实rand函数⽣成的随机数是伪随机的,伪随机数不是真正 的随机数,是通过某种算法⽣成的随机数。真正的随机数的是⽆法预测下⼀个值是多少的。⽽rand函 数是对⼀个叫“种⼦”的基准值进⾏运算⽣成的随机数。 之所以前⾯每次运⾏程序产⽣的随机数序列是⼀样的,那是因为rand函数⽣成随机数的默认种⼦是1。 如果要⽣成不同的随机数,就要让种⼦是变化的。
1.2 srand()函数
这个函数是用来生成种子的,想要产生不同的的随机数,就要生成不同的种子
void srand (unsigned int seed);
1.3 time
在程序中我们⼀般是使⽤程序运⾏的时间作为种⼦的,因为时间时刻在发⽣变化的。 在C语⾔中有⼀个函数叫time,就可以获得这个时间,time函数原型如下:(使用时候包含头文件time.h)
time_t time (time_t* timer);
time 函数会返回当前的⽇历时间,其实返回的是1970年1⽉1⽇0时0分0秒到现在程序运⾏时间之间的 差值,单位是秒。返回的类型是time_t类型的,time_t类型本质上其实就是32位或者64位的整型类 型
time函数的参数timer如果是⾮NULL的指针的话,函数也会将这个返回的差值放在timer指向的内存 中带回去。 如果timer是NULL,就只返回这个时间的差值。time函数返回的这个时间差也被叫做:时间戳。
如果只是让time函数返回时间戳,我们就可以这样写:
time(NULL);
下面是这个函数的使用
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
printf("%d\n", rand());
printf("%d\n", rand());
printf("%d\n", rand());
printf("%d\n", rand());
return 0;
}运行程序


可以发现,前面两次的的随机数产生的不一样了
1.4 产生1到100的随机数
int r=rand()%100+1;
在里可能会有一个误区,觉得ranf_max是32767,那么上面的就应该是1到68之间,这样的理解是错误的,正确的理解是:先产生一个数,这个数是0到32767中的任何一个,比如32699,这个数先取余100,再加1,得到100
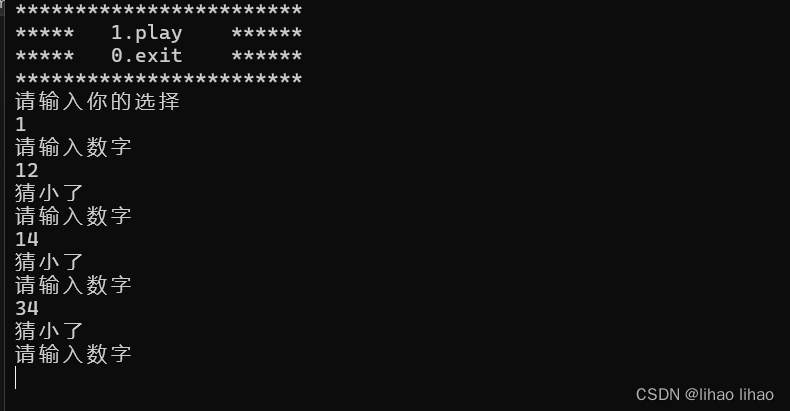
2.猜数字游戏的实现
光是猜数字游戏可能有点枯燥,在程序里面可以使用关机语句,如果几次都没有猜中就让电脑关机,下面提供两个语句(需要包含头文件#include<stdlib.h>)
system("shutdown -s -t 60 ");//60秒后关机
system("shutdown -a");//取消关机
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
void menu()
{
printf("************************\n");
printf("***** 1.play ******\n");
printf("***** 0.exit ******\n");
printf("************************\n");
}
void game()
{
int count = 0;
srand(time(NULL));
int number = rand()%100+1;
int guess = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("请输入数字\n");
scanf("%d", &guess);
if (guess < number)
{
printf("猜小了\n");
}
else if (guess > number)
{
printf("猜大了\n");
}
else
{
printf("猜对了\n");
break;
}
count++;
if (count == 5)//5次都未猜中,关机
{
system("shutdown -s -t 0");
}
}
}
int main()
{
int option = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请输入你的选择\n");
scanf("%d", &option);
switch (option)
{
case 1:
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出成功\n");
break;
default:
printf("无效输入\n");
break;
}
} while (option);
return 0;
}程序的运行