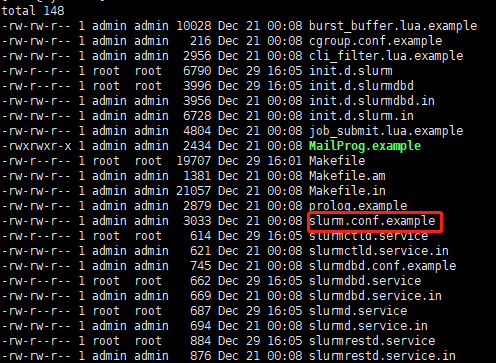
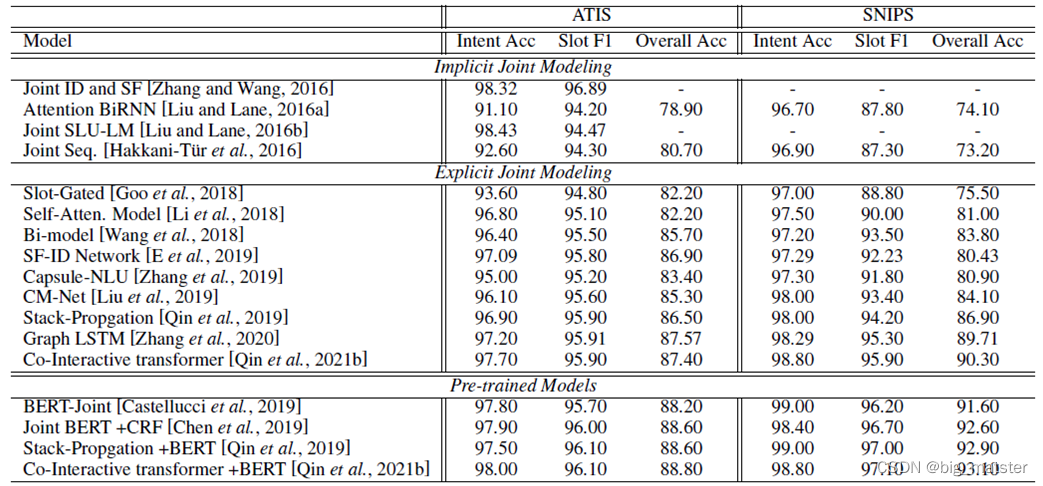
二叉树求从根到叶子结点的所有路径的方法整理
1. 利用递归和回溯方法求解
思路: 利用递归和回溯的方法求解
- 首先将当前结点加入到path中,然后判断是否为叶子结点,如果为叶子结点,则保存path路径
- 如果不是叶子结点,则继续递归访问左右子树,访问结束后需要进行回溯。
class solution {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList;
private LinkedList<Integer> path;
public void test(TreeNode root) {
pathList = new ArrayList<>();
path = new LinkedList<>();
recurision(root);
}
public void recurision(TreeNode node) {
// 将node加入到path中
path.add(node.val);
// 判断当前结点是否为叶子结点
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
// 为叶子结点,则将path中保存的路径,保存到pathList中
pathList.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 如果不是叶子结点,那么就继续访问左右子树
if (node.left != null) {
recurision(node.left);
path.removeLast(); // 回溯
}
if (node.right != null) {
recurision(node.right);
path.removeLast(); // 回溯
}
}
}
下面我画了一个图解,描述递归过程
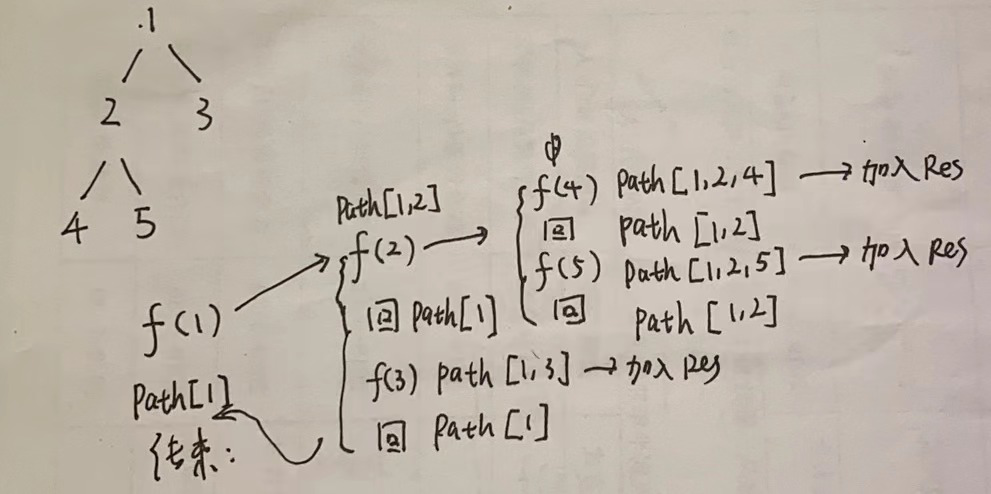
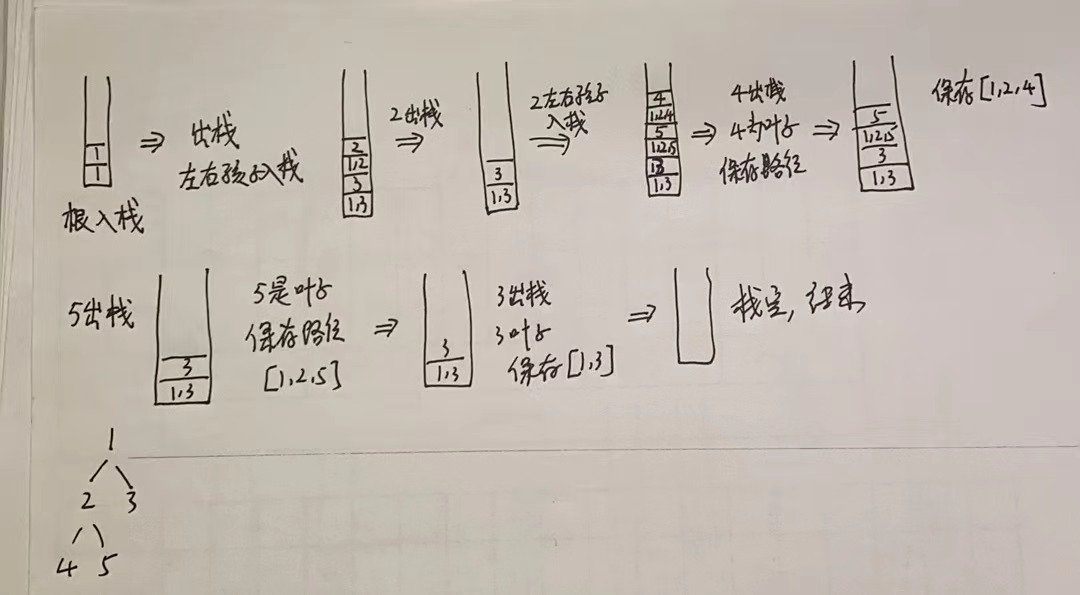
2. 利用栈
利用栈同时保存结点信息和路径信息。
- 首先根结点入栈
- 只要是栈不为空,就出栈。因此根结点首先出栈,根结点的左右孩子入栈。
- 然后一直进行循环,每次判断出栈元素是否为叶子,如果是叶子,则保存路径。
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return arrayList;
// 根结点入栈
Stack<Object> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new ArrayList<Integer>(root.val));
stack.push(root);
// 开始循环
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 取出结点
TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop();
ArrayList<Integer> path = (ArrayList<Integer>) stack.pop();
// 判断是不是叶子结点
if (node.left == null || node.right == null) {
// 如果是叶子结点
arrayList.add(path);
}
// 如果不是叶子结点
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(new ArrayList<>(path).add(node.right.val));
stack.push(node.right.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(new ArrayList<>(path).add(node.left.val));
stack.push(node.left.val);
}
}
return arrayList;
}
下面用一个图来掩饰一下:
3. 利用层序遍历记录路径
我们可以使用层序遍历。使用两个队列来记录,一个队列用来实现层序遍历,另一个队列用来记录经过的路径。当遍历到叶子结点的时候, 就把路径保存带pathList
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return pathList;
// 根结点入队
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQ = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<ArrayList<Integer>> pathQ = new LinkedList<>();
nodeQ.offer(root);
pathQ.offer(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(root.val)));
while (!nodeQ.isEmpty()) {
// 出队
TreeNode node = nodeQ.poll();
ArrayList<Integer> currentPath = pathQ.poll();
// 判断是否为叶子结点
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
pathList.add(currentPath);
}
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQ.offer(node.left);
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(currentPath);
temp.add(node.left.val);
pathQ.offer(temp);
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQ.offer(node.right);
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(currentPath);
temp.add(node.right.val);
pathQ.offer(temp);
}
}
return pathList;
}