论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.10133.pdf
代码链接:GitHub - DanJun6737/TransFace: Code of TransFace
背景
尽管ViTs在多种视觉任务中展示了强大的表示能力,但作者发现,当应用于具有极大数据集的人脸识别场景时,ViTs的性能却较差。通过深入研究,作者发现现有的数据增强方法和难例挖掘策略与基于ViT的FR模型不兼容,原因在于缺乏对面部结构信息的保留和利用每个局部token信息的专门考虑。
创新点
1、由于ViT模型缺乏像卷积那样的归纳偏置,使得ViT模型难以训练并容易过拟合。为了缓解ViTs的过拟合现象,现有工作尝试了几种数据增强策略,如Random Erasing、Mixup、CutMix、RandAugment及其变种,以构建多样化的训练样本。然而,这些实例级数据增强策略并不适用于人脸识别任务,因为它们不可避免地会破坏面部身份的关键结构信息,这可能导致ViTs朝错误的方向优化。此外,最近的研究发现ViTs在训练过程中容易对某些局部区域过拟合,导致模型的泛化性能变差。例如,在人脸识别任务中,ViT的预测可能由少数面部区域(如眼睛和前额)主导。因此,一旦这些关键区域被遮挡(例如,戴墨镜或帽子),模型就倾向于做出错误的决策。这些问题严重影响了基于ViT的人脸识别模型在真实场景中的应用。为了解决上述问题,作者提出Dominant Patch Amplitude Perturbation(DPAP)的Patch级数据增强策略。DPAP不破坏面部的保真度和结构信息,可以有效地扩展样本多样性。具体来说,DPAP使用Squeeze-and-Excitation(SE)模块筛选出K个patches(主导patches),然后随机混合它们的幅度信息,并与原始相位信息结合,生成多样化的样本。与以往的数据增强策略不同,所提出的DPAP巧妙地利用了模型提供的先验知识(即主导patches的位置)来增强数据,这可以更精确地缓解ViTs中的过拟合问题。此外,随着多样化patches的不断生成,DPAP也间接鼓励ViTs利用其他面部区域,特别是深层网络容易忽略的一些区域(如耳朵、嘴巴和鼻子),以做出更优的决策。
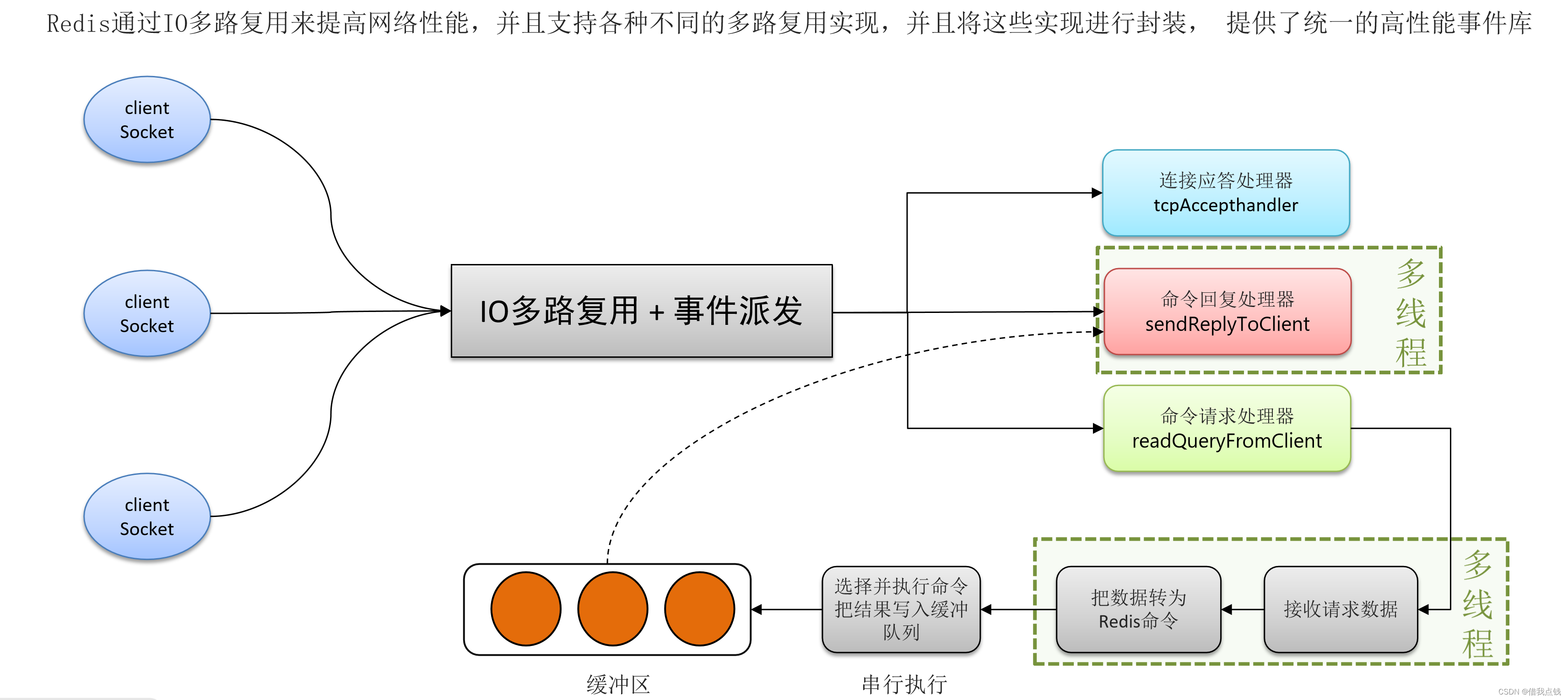
2、以前的难例挖掘策略大都是为CNN设计的,它们通常采用样本的实例级指标(如预测概率、预测损失、潜在特征)来挖掘难例。然而,ViT的预测主要由几个patch tokens决定,ViT的全局token可能被几个局部token主导。因此,直接使用这样有偏见的指标来挖掘难例对于ViTs来说是次优的(特别是当一些主导的局部token被忽略时)。为了更好地挖掘难例,作者提出Entropy-guided Hard Sample Mining(EHSM)的新难例挖掘策略。EHSM将ViT视为一个信息处理系统,它根据局部token中包含的总信息量动态调整简单样本和困难样本的重要性权重。EHSM鼓励ViT充分利用每个面部patches中包含的细粒度信息,特别是一些较少关注的面部线索(如嘴唇和下巴),这极大地增强了每个局部token的特征表示能力。这样,即使一些重要的patches被破坏,模型也可以充分利用剩余的面部线索来泛化全局token,从而做出更稳定的预测。

方法论
模型的整体框架图如下,

DPAP
为了解决ViT模型在人脸识别任务中的过拟合问题,论文提出Dominant Patch Amplitude Perturbation(DPAP)的新型patch级数据增强策略。该策略的主要步骤如下:
1、在transformer编码器的输出端插入一个SE模块,并使用SE模块生成的权重(权重反映了局部tokens在预测中的重要性)找出原始图像的K个patches(即K个主导patches),这些patches对最终预测贡献最大
将图片输入到模型中,以得到权重weight(注意,此次前向传播不会产生梯度,该步骤的目的是利用模型生成先验知识)
with torch.no_grad():
local_embeddings, weight, local_patch_entropy = backbone(img) ## [n, 512], [n, 144], [n, 144]
loss: torch.Tensor = module_partial_fc(local_embeddings, local_labels, opt, local_patch_entropy) 模型网络结构的代码如下,
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
"""
Vision Transformer with support for patch or hybrid CNN input stage
"""
def __init__(self,
img_size: int = 112,
patch_size: int = 16,
in_channels: int = 3,
num_classes: int = 1000,
embed_dim: int = 768,
depth: int = 12,
num_heads: int = 12,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = False,
qk_scale: Optional[None] = None,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.,
hybrid_backbone: Optional[None] = None,
norm_layer: str = "ln",
mask_ratio = 0.1,
using_checkpoint = False,
):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes ## 512
self.num_features = self.embed_dim = embed_dim ## 512
if hybrid_backbone is not None:
raise ValueError
else:
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_channels=in_channels, embed_dim=embed_dim)
self.mask_ratio = mask_ratio
self.using_checkpoint = using_checkpoint
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches ## 144
self.num_patches = num_patches ## 144
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim)) ## [1, 144, 512]
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# stochastic depth decay rule
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, depth)] ## drop_path_rate = 0.05, depth = 12
patch_n = (img_size//patch_size)**2 ## 144
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList(
[
Block(dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate, drop_path=dpr[i], norm_layer=norm_layer,
num_patches=num_patches, patch_n=patch_n)
for i in range(depth)]
)
self.extra_gflops = 0.0
for _block in self.blocks:
self.extra_gflops += _block.extra_gflops
if norm_layer == "ln":
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim)
elif norm_layer == "bn":
self.norm = VITBatchNorm(self.num_patches)
# features head
self.feature = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=embed_dim * num_patches, out_features=embed_dim, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=embed_dim, eps=2e-5),
nn.Linear(in_features=embed_dim, out_features=num_classes, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=num_classes, eps=2e-5)
)
self.mask_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
torch.nn.init.normal_(self.mask_token, std=.02)
trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=.02)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
## SEModule FC
self.senet = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=embed_dim * num_patches, out_features=num_patches, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=num_patches, out_features=num_patches, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
@torch.jit.ignore
def no_weight_decay(self):
return {'pos_embed', 'cls_token'}
def get_classifier(self):
return self.head
def random_masking(self, x, mask_ratio=0.1):
"""
Perform per-sample random masking by per-sample shuffling.
Per-sample shuffling is done by argsort random noise.
x: [N, L, D], sequence
"""
N, L, D = x.size() # n, 144, 512
len_keep = int(L * (1 - mask_ratio))
noise = torch.rand(N, L, device=x.device) ## [n, 144], noise in [0, 1]
# sort noise for each sample
# ascend: small is keep, large is remove
ids_shuffle = torch.argsort(noise, dim=1)
ids_restore = torch.argsort(ids_shuffle, dim=1)
# keep the first subset
ids_keep = ids_shuffle[:, :len_keep] ## [n, 129]
x_masked = torch.gather(
x, dim=1, index=ids_keep.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, 1, D)) ## [n, 129, 512]
# generate the binary mask: 0 is keep, 1 is remove
mask = torch.ones([N, L], device=x.device) ## [n, 144]
mask[:, :len_keep] = 0 ## [n, 144]
# unshuffle to get the binary mask
mask = torch.gather(mask, dim=1, index=ids_restore)
return x_masked, mask, ids_restore ## [n, 129, 512], [n, 144], [n, 144]
def forward_features(self, x):
B = x.shape[0]
x = self.patch_embed(x) ## [n, 144, 512]
x = x + self.pos_embed ## [n, 144, 512]
x = self.pos_drop(x) ## [n, 144, 512]
if self.training and self.mask_ratio > 0:
x, _, ids_restore = self.random_masking(x) ## [n, 129, 512], [n, 144], [n, 144]
for func in self.blocks:
if self.using_checkpoint and self.training:
from torch.utils.checkpoint import checkpoint
x = checkpoint(func, x)
else:
x = func(x)
x = self.norm(x.float()) ## [n, 129, 512]
if self.training and self.mask_ratio > 0:
mask_tokens = self.mask_token.repeat(x.shape[0], ids_restore.shape[1] - x.shape[1], 1) ## [n, 15, 512]
x_ = torch.cat([x[:, :, :], mask_tokens], dim=1) ## [n, 144, 512]
x_ = torch.gather(x_, dim=1, index=ids_restore.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, 1, x.shape[2])) ## [n, 144, 512]
x = x_ ## [n, 144, 512]
orginal = x ## [n, 144, 512]
out = torch.reshape(x, (B, self.num_patches * self.embed_dim)) ## [n, 144*512]
out = self.senet(out) ## [n, 144]
out_softmax = out.softmax(dim=1) ## [n, 144]
out = torch.reshape(out, (B, self.num_patches, 1)) ## [n, 144, 1]
out = out * orginal ## [n, 144, 512]
return torch.reshape(out, (B, self.num_patches * self.embed_dim)), out_softmax ## [n, 144*512], [n, 144]
def forward(self, x):
x, weight = self.forward_features(x) ## [n, 144*512], [n, 144]
out_x = torch.reshape(x, (x.shape[0], self.num_patches, self.embed_dim)) ## [n, 144, 512]
patch_std = torch.std(out_x, dim=2) ## [n, 144]
patch_entropy = torch.log(patch_std) + 0.5 + 0.5*torch.log( torch.tensor(2*math.pi) ) ## Entropy
# patch_entropy = patch_std ## [n, 144]
x = self.feature(x) ## [n, 512]
return x, weight, patch_entropy ## [n, 512], [n, 144], [n, 144]其中,输出weight就是由上面所述的SE模块生成的权重。
随后,找出原始图像的K个patches(即K个主导patches),
## TopK
K = 7
TopK_ALL = torch.argsort(weight, dim=1, descending=True)
TopK_ALL = TopK_ALL.cpu().numpy()
TopK = TopK_ALL[:, :K] ## [n, 7]2、使用线性混合机制随机扰动这些主导patches的幅度信息
probability = 0.2
batch_index = 0
for index in TopK:
if random.random() <= probability:
for j in range(TopK.shape[1]):
patch_index_h = int(np.floor(index[j] / 12)) ## 0 < patch_index_h < 12
patch_index_w = int((index[j] - patch_index_h * 12))
img_src = img_original[batch_index, 9*patch_index_h:9*(1+patch_index_h), 9*patch_index_w:9*(1+patch_index_w), :] ## [9, 9, 3]
random_index = int(np.random.randint(0, img.size()[0], 1)) ## 0 < random_index < n
random_h = int(np.random.randint(0, 12, 1)) ## 0 < random_h < 12
random_w = int(np.random.randint(0, 12, 1)) ## 0 < random_w < 12
img_random = img_original[random_index, 9*random_h:9*(1+random_h), 9*random_w:9*(1+random_w), :] ## [9, 9, 3]
img_src_random = amplitude_spectrum_mix(img_src, img_random, alpha=1)
img_original[batch_index, 9*patch_index_h:9*(1+patch_index_h), 9*patch_index_w:9*(1+patch_index_w), :] = img_src_random
batch_index = batch_index + 1def amplitude_spectrum_mix(img1, img2, alpha, ratio=1.0): ## img_src, img_random, alpha=1, ratio=1.0
"""Input image size: ndarray of [H, W, C], ps: [9, 9, 3]"""
lam = np.random.uniform(0, alpha) ## 0 < lam < 1
assert img1.shape == img2.shape
h, w, c = img1.shape ## 9, 9, 3
h_crop = int(h * sqrt(ratio)) ## 1
w_crop = int(w * sqrt(ratio)) ## 1
h_start = h // 2 - h_crop // 2 ## 4
w_start = w // 2 - w_crop // 2 ## 4
img1_fft = np.fft.fft2(img1, axes=(0, 1)) ## 计算二维的傅里叶变换
img2_fft = np.fft.fft2(img2, axes=(0, 1))
img1_abs, img1_pha = np.abs(img1_fft), np.angle(img1_fft)
img2_abs, img2_pha = np.abs(img2_fft), np.angle(img2_fft)
img1_abs = np.fft.fftshift(img1_abs, axes=(0, 1)) ## 将FFT输出中的直流分量移动到频谱中央
img2_abs = np.fft.fftshift(img2_abs, axes=(0, 1))
img1_abs_ = np.copy(img1_abs)
img2_abs_ = np.copy(img2_abs)
img1_abs[h_start:h_start + h_crop, w_start:w_start + w_crop] = \
lam * img2_abs_[h_start:h_start + h_crop, w_start:w_start + w_crop] + (1 - lam) * img1_abs_[h_start:h_start + h_crop, w_start:w_start + w_crop]
img1_abs = np.fft.ifftshift(img1_abs, axes=(0, 1))
img2_abs = np.fft.ifftshift(img2_abs, axes=(0, 1))
img_src_random = img1_abs * (np.e ** (1j * img1_pha))
img_src_random = np.real(np.fft.ifft2(img_src_random, axes=(0, 1)))
img_src_random = np.uint8(np.clip(img_src_random, 0, 255))
return img_src_random3、将重建的图像输入TransFace模型进行监督训练(该步骤会正常产生梯度,优化参数)
img_fft = torch.tensor(img_original).cuda()
img_fft = img_fft.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) ## [n, 3, 112, 112]
img_fft = ((img_fft / 255) - 0.5) / (0.5)
local_embeddings, weight, local_patch_entropy = backbone(img_fft) ## [n, 512], [n, 144], [n, 144]
loss: torch.Tensor = module_partial_fc(local_embeddings, local_labels, opt, local_patch_entropy)EHSM
为了更精确地挖掘难例,论文提出新的难例挖掘策略Entropy-guided Hard Sample Mining (EHSM)。EHSM通过信息论的启发,将ViT视为一个信息处理系统,根据局部tokens中包含的总信息量动态调整简单样本和困难样本的重要性权重。
具体来说,
1、EHSM首先估计每个局部token的局部信息熵(即下面代码中的patch_entropy)
x, weight = self.forward_features(x) ## [n, 144*512], [n, 144]
out_x = torch.reshape(x, (x.shape[0], self.num_patches, self.embed_dim)) ## [n, 144, 512]
patch_std = torch.std(out_x, dim=2) ## [n, 144]
patch_entropy = torch.log(patch_std) + 0.5 + 0.5*torch.log( torch.tensor(2*math.pi) ) ## Entropy
# patch_entropy = patch_std ## [n, 144]
x = self.feature(x) ## [n, 512]
return x, weight, patch_entropy ## [n, 512], [n, 144], [n, 144]信息熵的计算公式如下,

2、然后,将所有局部信息熵聚合为样本的全局信息熵
gamma = 1.0
K_ = 144
entropy_topK, _ = torch.topk(patch_entropy_, k = K_, dim=1)
entropy = gamma * torch.mean(entropy_topK, dim=1)3、最后,EHSM使用熵感知权重机制来适应性地为每个样本分配重要性权重
sample_weight = 1 + torch.exp(-entropy)
G_weight = sample_weight通过这种方式,EHSM明确鼓励模型关注信息量较少的难样本。
为了最小化目标Loss,模型在训练过程中必须同时优化权重和基本分类损失,这将带来两个好处:(1) 最小化基本分类损失可以鼓励模型从多样化的训练样本中学习更好的面部特征;(2) 最小化权重(即最大化总信息)将促进模型充分挖掘每个面部patches中包含的特征信息,特别是一些较少关注的面部线索(如鼻子、嘴唇和下巴),这显著增强了每个局部token的特征表示能力。
![]()

实验
数据集
使用MS1MV2和Glint360K数据集训练模型。使用LFW、AgeDB-30、CFP-FP和IJB-C评估模型。
训练设置
使用Pytorch在8个NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPU上训练。采用ArcFace作为基本分类损失,并将所有输入图像裁剪到112×112大小。使用AdamW优化器进行优化。对于MS1MV2,基础学习率设置为1e-3;对于Glint360K,学习率设置为1e-4。
与SOTA方法的结果对比
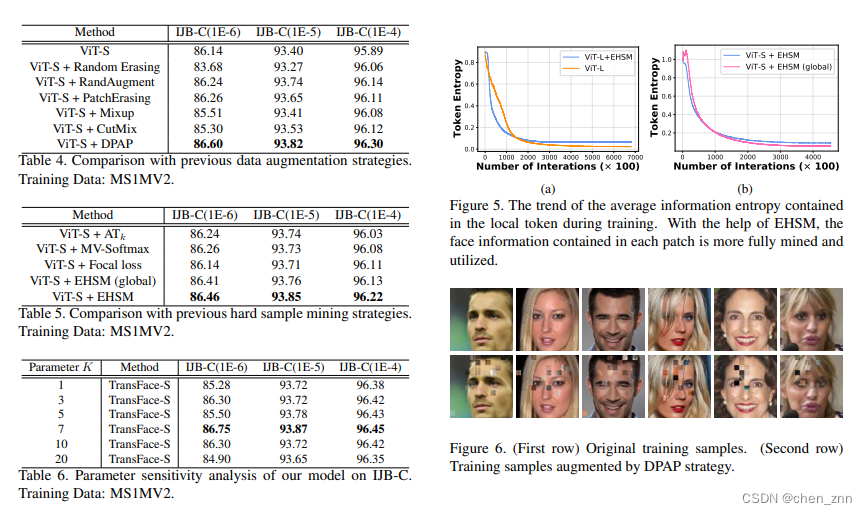
在LFW、CFP-FP和AgeDB-30上评估TransFace并与其它方法比较,发现TransFace的性能已经接近饱和状态。TransFace-L在三个数据集上的性能分别比ViT-L高出0.03%、0.22%和0.15%

在MS1MV2和Glint360K上训练TransFace,并与IJB-C基准上的SOTA比较。TransFace在MS1MV2数据集上训练的模型在“TAR@FAR=1E-4”上大幅超越其他基于ResNet的模型。例如,与CurricularFace相比,TransFace-B在“TAR@FAR=1E-4”上提高了0.45%。此外,TransFace-S在“TAR@FAR=1E-4”上比ViT-S高出0.56%。在Glint360K上训练的模型,TransFace显著优于其他竞争对手。特别是,TransFace-L在“TAR@FAR=1E-4”和“TAR@FAR=1E-5”上分别比ViT-L高出0.48%和0.51%

消融实验

结论
作者提出TransFace,引入DPAP的patch级数据增强策略和EHSM的难例挖掘策略。其中,DPAP采用线性混合机制来扰动主导patches的幅度信息,以缓解ViTs中的过拟合问题。EHSM充分利用多个局部tokens中的信息熵来衡量样本难度,极大地增强了局部tokens的特征表示能力。TransFace除了添加SE模块外,没有引入任何重大的架构变化。