目录
从C到C++
嵌入式领域常用的GUI
语法的升级
引用
默认参数
函数重载
堆内存
概念和思维的升级
类和对象
类的申明
类的成员函数
常成员、常对象(C++推荐const而不用#define, mutable )
静态成员(属于类不属于对象)
友元(破坏封装)
由于电脑没有有线网口和网卡,所以最近一周改为学习C++。而C++的学习只是为了后面做QT开发,人工智能领域多用python和C++做算法,后面我很想往这个方向发展,所以大概会学习这个方向的内容,现在就先学习简单的C++和QT吧,等我的拓展坞到了开始继续学习系统移植和驱动开发。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
从C到C++
嵌入式领域常用的GUI
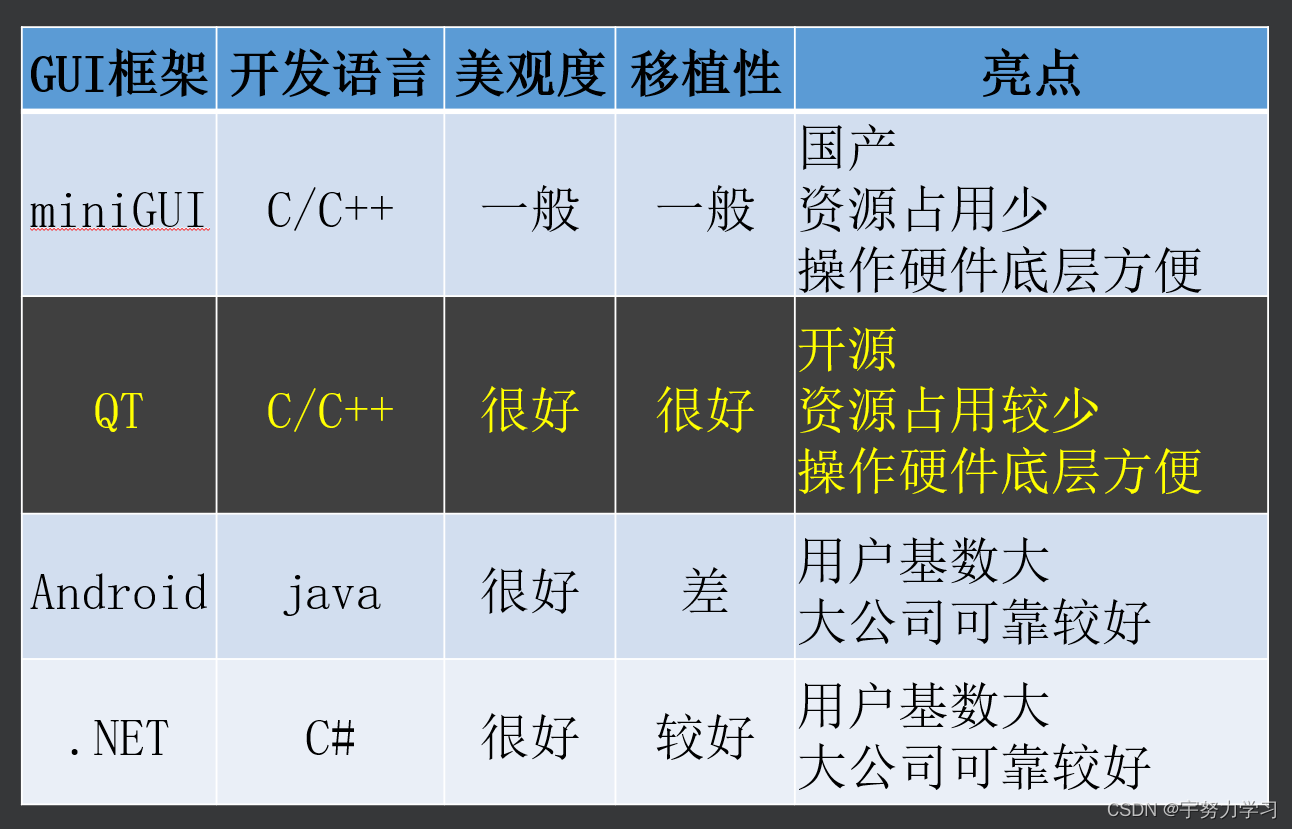
mini一般会用在军工领域,因为是国产的嘛,不容易被入侵
.NET Windows上用的多我们天天见,微软主推的。
https://baike.baidu.com/item/.NET/156737?fr=aladdin

汽车仪表盘,医院的监护仪,智能家居的显示,还可以开发PC上的软件
语法的升级

引用
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int &b = a;
printf("a = %d\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
printf("addr: a = %p\n", &a);
printf("addr: b = %p\n", &b);
return 0;
} 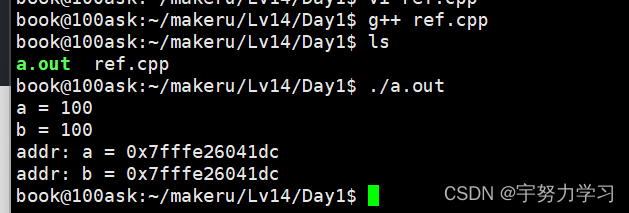
我们发现这两个变量的地址和值是相等的,C++支持为变量取别名
这样做有什么好处吗?
交换两个变量的值:
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int a, int b)
{
a ^= b;
b ^= a;
a ^= b;
}
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int b = 10;
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
swap(a, b);
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
}
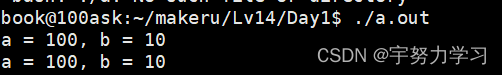
我们发现不行,那么我们正常应该是这样做的:
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
*p ^= *q;
*q ^= *p;
*p ^= *q;
}
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int b = 10;
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
swap(&a, &b);
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
} 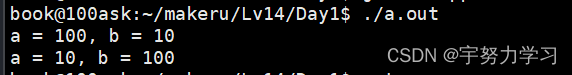
没有问题。但是这*来*去的很难让人理解。那么用C++的这个特性就会很好解决这个问题:
#include <stdio.h>
/*
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
*p ^= *q;
*q ^= *p;
*p ^= *q;
}
*/
void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
a ^= b;
b ^= a;
a ^= b;
}
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int b = 10;
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
//swap(&a, &b);
swap(a, b);
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
}
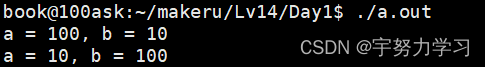
我们通过取别名的方式解决这个问题就看起来不是那么难懂了。
大家可能好奇这个swap怎么实现的看这个:
a1=a^b
b=b^a1=b^a^b=a
//此时a1=a^b b=a
a=a1^a=a^b^a=b默认参数
#include <stdio.h>
void debug(const char *ptr = "----------" )
{
printf("%s\n", ptr);
}
int main()
{
debug();
debug();
debug();
debug();
debug("hello");
debug("world");
}
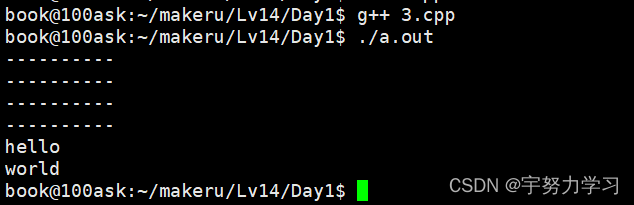
不传参数时使用默认值
这样如果参数很多的时候用户有时可以不用传参直接使用默认值,如果有三个参数但是只传入了两个,它是默认从右到左赋值的。
函数重载
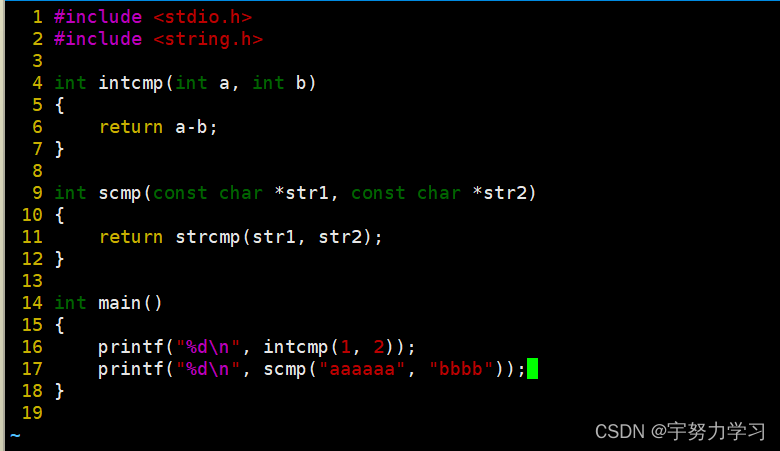
C语言分别比较整型和字符串,两个函数要不同名接下来我们看看C++
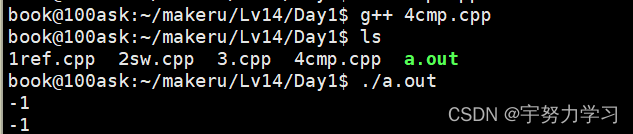
这就是函数重载,两个有相同功能的函数处理不同的数据类型可以名字一样,系统会根据你传入的参数自动匹配函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
int intcmp(int a, int b)
{
return a-b;
}
int scmp(const char *str1, const char *str2)
{
return strcmp(str1, str2);
}
*/
int cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a-b;
}
int cmp(const char *str1, const char *str2)
{
return strcmp(str1, str2);
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", cmp(1, 2));
printf("%d\n", cmp("aaaaaa", "bbbb"));
}
堆内存
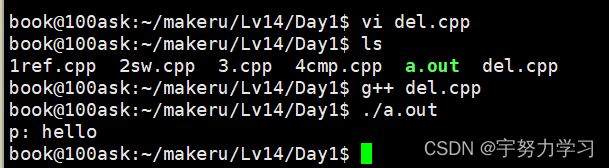
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char *p = (char*)malloc(10);
strcpy(p, "hello");
printf("p: %s\n", p);
free(p);
}
上面是C的处理方式,下面我们来看看C++的方式
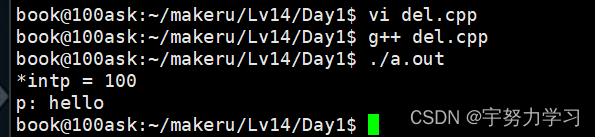
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
/*
char *p = (char*)malloc(10);
strcpy(p, "hello");
printf("p: %s\n", p);
free(p);
*/
int *intp = new int;
*intp = 100;
printf("*intp = %d\n", *intp);
delete intp;
char *p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, "hello");
printf("p: %s\n", p);
delete [] p;
}
当我们申请一个的时候就释放一个就行,当我们申请的是一堆也就是数组这种的时候,释放也要释放一堆,再前面加个【】。
概念和思维的升级
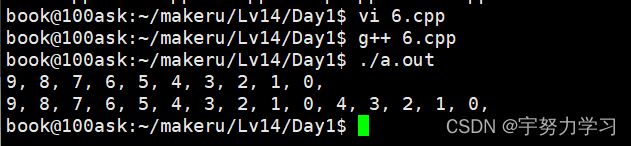
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[100] = {0};
//sizeof ??? strlen ???
int tail = 0;
int n = 10;
while(n--)
arr[tail++] = n;
int i = 0;
for(;i<tail; i++)
printf("%d, ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
n = 5;
while(n--)
arr[tail++] = n;
for(i=0; i<tail; i++)
printf("%d, ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
这样的程序看着很乱,虽然正确执行了,但是相同作用的程序我们可以拿出来写成一个函数,而相关联的变量也可以写进一个集合,封装起来,一般就是结构体

.h文件
#ifndef _ARR_
#define _ARR_
typedef struct arr{
int data[100];
int tail;
}ARR;
void init(ARR *arr);
void addtail(ARR *arr, int data);
void show(ARR *arr);
#endif.c文件
#include "arr.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void init(ARR *arr)
{
arr->tail = 0;
}
void addtail(ARR *arr, int data)
{
arr->data[arr->tail++] = data;
}
void show(ARR *arr)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<arr->tail; i++)
printf("%d, ", arr->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
主函数文件
#include "arr.h"
int main()
{
ARR arr;
init(&arr);
int n = 10;
while(n--)
addtail(&arr, n);
show(&arr);
ARR arr1;
init(&arr1);
int i = 0;
for(;i<10; i++)
addtail(&arr1, i);
show(&arr1);
}但是这样写再C高级工程师眼中还是不行,我们把他升升级
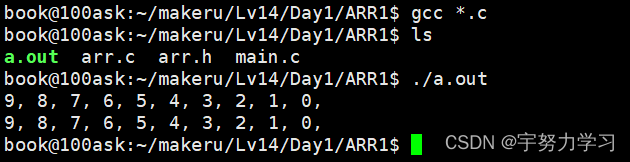
.h
#ifndef _ARR_
#define _ARR_
typedef struct arr{
int data[100];
int tail;
void (*addtail)(struct arr *arr, int data);
void (*show)(struct arr *arr);
}ARR;
void init(struct arr *arr);
#endif
.c
#include "arr.h"
#include <stdio.h>
static void addtail(ARR *arr, int data)
{
arr->data[arr->tail++] = data;
}
static void show(ARR *arr)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<arr->tail; i++)
printf("%d, ", arr->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void init(ARR *arr)
{
arr->tail = 0;
arr->addtail = addtail;
arr->show = show;
}
主函数
#include "arr.h"
int main()
{
ARR arr;
init(&arr);
int n = 10;
while(n--)
arr.addtail(&arr, n);
arr.show(&arr);
// arr.tail = 0;
arr.show(&arr);
}
这样就有面向对象的意思了。
但是避免不了,C语言一个语句就能操纵成员值的特性。一个不留神就会导致项目的崩溃。
还有已经找到arr了为什么还要再传一次,直接再内部处理不行吗?
而且你都已经定义了对象还要再初始化,能不能再定义对象的时候就初始化呢。
类和对象

类的申明

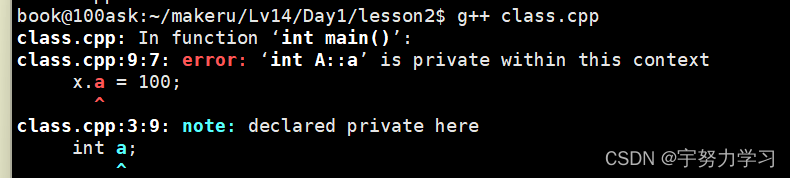
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
int a;
};
int main()
{
A x;
x.a = 100;
}
他说这个成员是私有的,如果这是一个结构体肯定没问题,这就是C++升级的地方
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
int a;
};
int main()
{
A x;
x.a = 100;
}
C++还可以在这里面写函数。
但是一编译同样他也是私有的。
然后我们修饰一下:
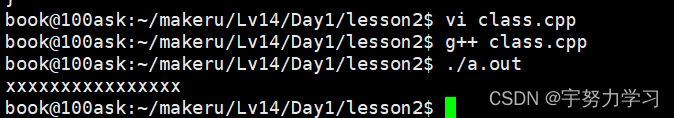
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
private:
int a;
};
int main()
{
A x;
x.show();
// x.a = 100;
}没有问题了。 这就是公有型和私有型。当你想让别人直接用的时候就让他是公有的,不想让别人直接用就让他是私有的。
那么我想用这个私有的怎么办呢

#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
void setdata(int data)
{
a = data;
}
int getdata(void);
private:
int a;
};
int A::getdata(void)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
A x;
x.show();
x.setdata(100);
printf("%d\n", x.getdata() );
// x.a = 100;
}
我们设置这个私有的成员可以直接再这个公有成员里写个函数,而调用它可以再里面也可以再外面,因为C++规定只要是类的成员就可以使用它的私有变量。
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("construct !!!!!!!!!!!\n");
}
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
void setdata(int data)
{
a = data;
}
int getdata(void);
private:
int a;
};
int A::getdata(void)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
A x;
x.show();
x.setdata(100);
printf("%d\n", x.getdata() );
// x.a = 100;
}
我们发现这里多了一个和类同名的函数,这就是类的构造函数,再对象生成的时候一定会先调用这个函数,我们开始的程序虽然没有写,但是他会默认的生成一个无参构造函数。
构造函数一般用来初始化
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("construct !!!!!!!!!!!\n");
a = 100;
}
A(int data)
{
a = data;
}
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
void setdata(int data)
{
a = data;
}
int getdata(void);
private:
int a;
};
int A::getdata(void)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
A x(100);
x.show();
// x.setdata(100);
printf("%d\n", x.getdata() );
// x.a = 100;
}
C++支持函数重载所以我们写一个同名的有参构造函数,再生成对象的时候传进去一个100,他会将这个100传给a。
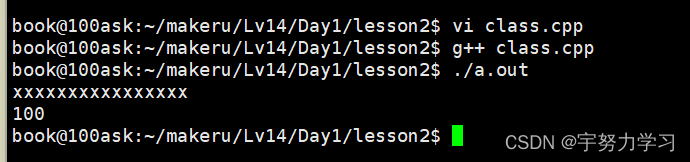 既然有构造就一定有销毁,他的名字叫析构函数,和类同名,但是前面要加个取反(~)
既然有构造就一定有销毁,他的名字叫析构函数,和类同名,但是前面要加个取反(~)
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("construct !!!!!!!!!!!\n");
a = 100;
}
A(int data)
{
a = data;
}
~A()
{
printf("ddddddddddddddddddddddddd\n");
}
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
void setdata(int data)
{
a = data;
}
int getdata(void);
private:
int a;
};
int A::getdata(void)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
A x(100);
x.show();
// x.setdata(100);
printf("%d\n", x.getdata() );
// x.a = 100;
}
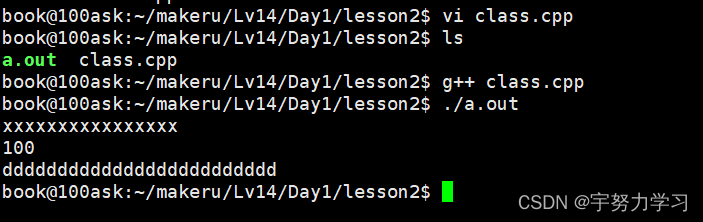
我们发现我们没调用他但是再最后他自动执行了。对象再栈区创建,再他的生存域结束后会调用这个函数。学了这么多我们用C++来回头完成那个实现一个数组再尾部加
arr.h
#ifndef _ARR_
#define _ARR_
#if 0
typedef struct arr{
int data[100];
int tail;
void (*addtail)(struct arr *arr, int data);
void (*show)(struct arr *arr);
}ARR;
void init(struct arr *arr);
#endif
class ARR{
public:
ARR():tail(0){
// tail = 0;
}
void addtail(int data);
void show(void);
friend void rev(ARR &arr);
private:
int data[100];
int tail;
};
#endif
arr.c
#include "arr.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void ARR::addtail(int data)
{
this->data[tail++] = data;
}
void ARR::show(void)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<tail; i++)
printf("%d, ", data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/*
void init(ARR *arr)
{
arr->tail = 0;
arr->addtail = addtail;
arr->show = show;
}
*/
main.c
#include "arr.h"
void rev(ARR &arr)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<arr.tail/2; i++)
{
int tem = arr.data[i];
arr.data[i] = arr.data[arr.tail-i-1];
arr.data[arr.tail-i-1] = tem;
}
}
int main()
{
#if 0
ARR arr;
init(&arr);
int n = 10;
while(n--)
arr.addtail(&arr, n);
arr.show(&arr);
// arr.tail = 0;
arr.show(&arr);
#endif
ARR arr;
arr.addtail(1);
arr.addtail(2);
arr.addtail(3);
arr.addtail(4);
arr.show();
//reverse
rev(arr);
arr.show();
}
用什么语言都可以实现面向对象,只不过用面向对象的语言更加适合。写的程序不是那么赘余。C语言的高手一样可以用C写出面向对象的感觉就像前面写的那样,用函数指针,回调机制什么的,比如写Linux内核的那些大佬。为了给我们提供接口,同时防止我们破坏,他们就是用面向对象的思维写的内核。但是内核大部分都是C实现的,只有少量的汇编。
类的成员函数

我们详细的来学习一下,避免以后开发时出现错误
#include <stdio.h>
calss A{
public:
~A(){
printf("A~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
};
int main()
{
A x;
A m(100);
A y = 10;
A z = y;
}
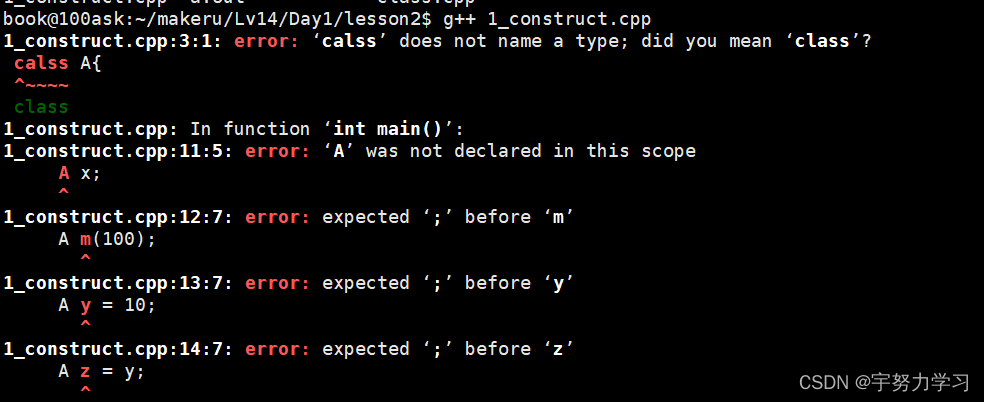
class拼错了哈哈
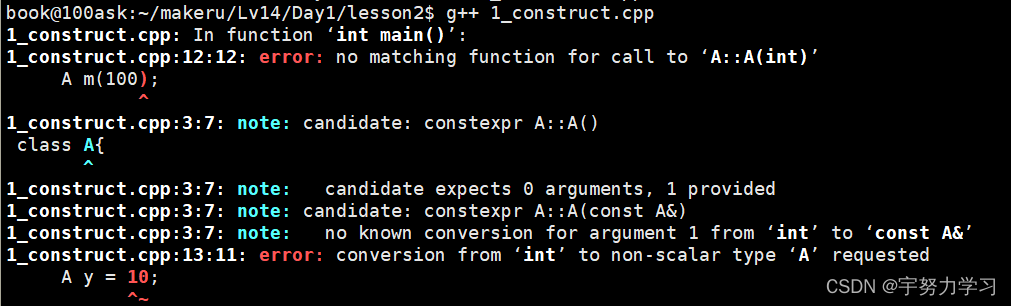
他想要一个整型我们就加个整型
加了还是不行,因为构造函数如果有有参的了就不会自动生成无参的了
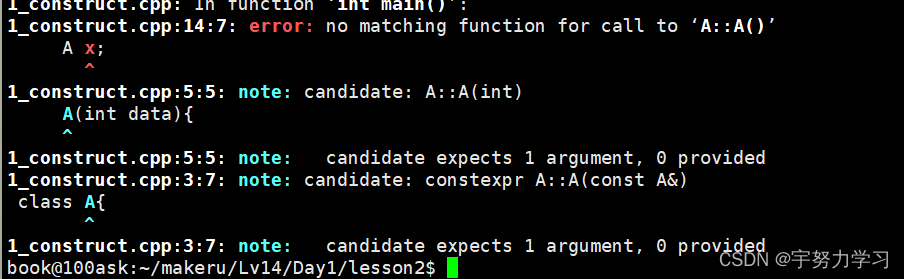 补上这个无参构造函数
补上这个无参构造函数
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A(int data){
printf("A(int)\n");
}
A(){
printf("A()\n");
}
~A(){
printf("A~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
};
int main()
{
A x;
A m(100);
A y = 10;
A z = y;
}
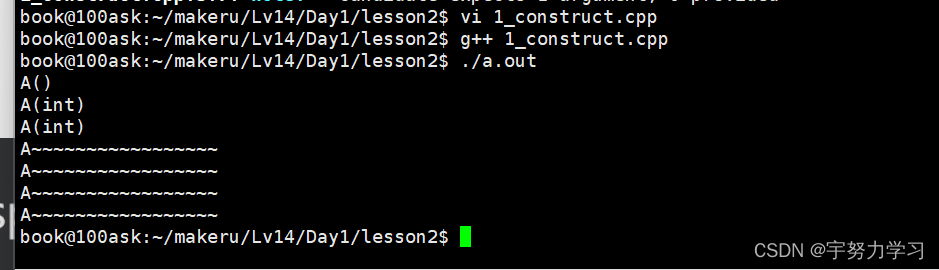
有参构造调用两次,无参构造调用一次。析构调用四次
原因呢就是第二个是显式调用,第三个是隐式调用,第四个也是隐式调用,但是在他调用的是拷贝函数。还有下面再堆中申请的也会隐式调用
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A(int data){
printf("A(int)\n");
}
A(){
printf("A()\n");
}
~A(){
printf("A~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
};
int main()
{
A *p = new A(1000);
A x;
A m(100);
A y = 10;
A z = y;
delete(p);
}

但是这种拷贝有时是好事又是又是一种坏事:
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("A()\n");
p = new char[10];
}
~A()
{
printf("~A()\n");
delete [] p;
}
private:
char *p;
};
int main()
{
A x;
}
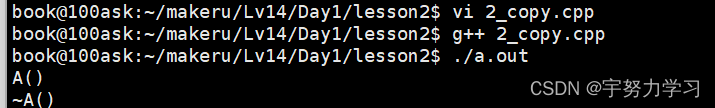
现在没有问题正常运行,然后我们稍微修改一下
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("A()\n");
p = new char[10];
}
~A()
{
printf("~A()\n");
delete [] p;
}
private:
char *p;
};
int main()
{
A x;
A y = x;
}
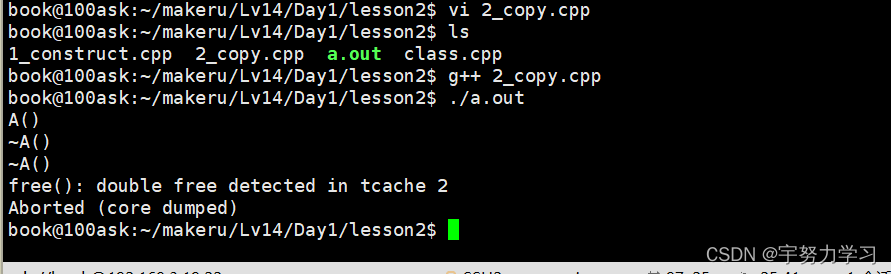
问题来了段错误:
由于y的值是x所以他没有调用构造函数调用的是拷贝函数,但是这个构造函数涉及到了指针,所以我们需要完善一下这个拷贝函数,我们刚刚的拷贝是浅拷贝相当于只是拷贝过来了一个快捷方式,而没有将内容拷贝过来。把内容也拷贝过来的叫深拷贝,这就需要一个新的概念叫拷贝构造函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("A()\n");
p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, "hello");
}
A(const A &x)
{
printf("A(const A &x)\n");
p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, x.p);
}
~A()
{
printf("~A()\n");
delete [] p;
}
private:
char *p;
};
int main()
{
A x;
A y = x;
}
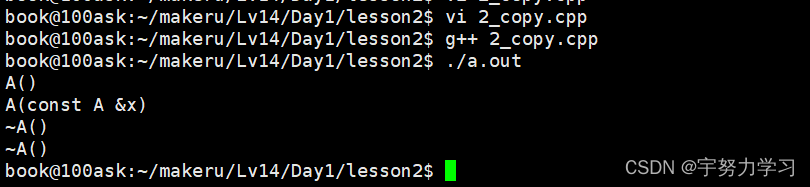
这次没有段错误了,并且第二个构造函数是拷贝构造函数的内容。
浅拷贝使用的是同一个资源两个人都释放这一个资源导致段错误。
那么当再主函数中直接 x = y 时我们怎么解决呢后面再说。
说一下this关键字
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("A()\n");
p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, "hello");
printf("p: %s\n", p);
printf("p: %s\n", this->p);
}
A(const A &x)
{
printf("A(const A &x)\n");
p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, x.p);
}
~A()
{
printf("~A()\n");
delete [] p;
}
private:
char *p;
};
int main()
{
A x;
A y = x;
}
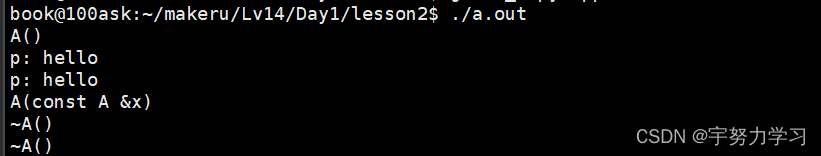
当局部变量和成员变量重名时,使用this可以区分局部变量和成员变量,this.变量名可以访问成员变量 。这个实例不好区分。但是大概就是干这个用的,还有别的作用可以自己查查比较多。
常成员、常对象(C++推荐const而不用#define, mutable )
!!! const 数据成员只在某个对象生存期内是常量,而对于整个类而言却是可变的(static 例外)。

#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A(int a = 50, int data = 1000):b(data){//b = data
this->a = a;
printf("AAAAAAAAAAAAAAA\n");
}
~A(){
printf("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
void show(void)const
{
printf("b = %d\n", b);
printf("a = %d\n", a);
}
private:
int a;
const int b;
};
int main()
{
A x(10);
x.show();
A y(100);
y.show();
A z;
z.show();
}
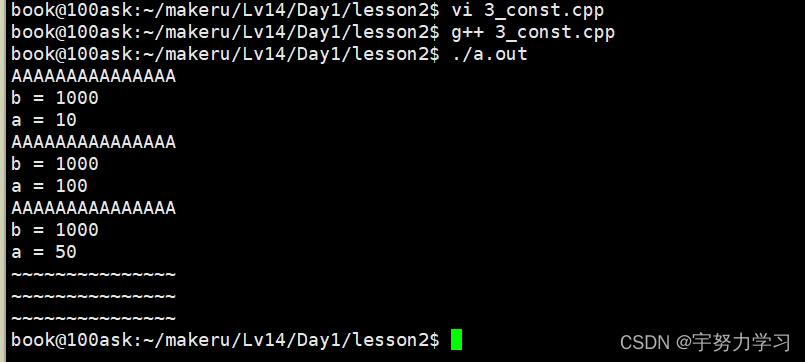
这样有没有参数都能调用构造函数,这里析构函数中b的写法就是说明他是一个常量。

#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A(int a = 50, int data = 1000):b(data){//b = data
this->a = a;
printf("AAAAAAAAAAAAAAA\n");
}
~A(){
printf("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
void show(void)const
{
printf("b = %d\n", b);
printf("a = %d\n", a);
a++;
}
private:
int a;
const int b;
};
int main()
{
A x(10);
x.show();
A y(100);
y.show();
A z;
z.show();
}
我们加了个a++报错了,他说const类型的我们不能修改。 他是只读的。
静态成员(属于类不属于对象)

#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
void func(void)
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
};
int main()
{
A a;
a.func();
}
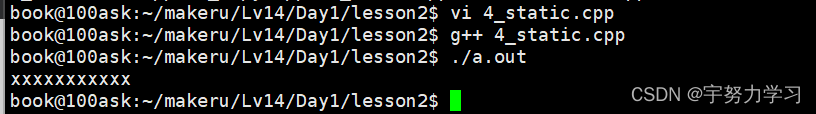
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
static void func(void)
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
};
int main()
{
A a;
a.func();
A::func();
}
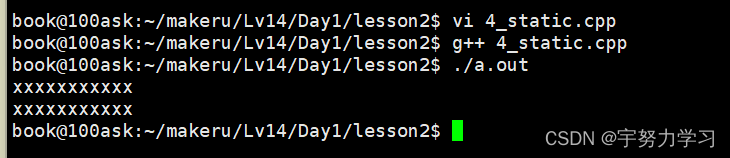
当我们去掉static时
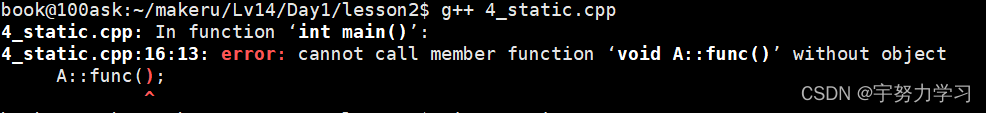
所以我们想没有对象直接调用类的成员函数,就需要用static修饰一下
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
static void func(void)
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
static int data;
};
int A::data = 10;
int main()
{
A a;
a.func();
A::func();
A x;
x.data = 100;
printf("x.data = %d\n", x.data);
A::data = 1000;
printf("x.data = %d\n", x.data);
}
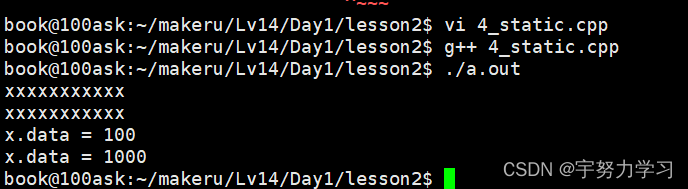
所以说static是基于类的不是基于对象的。
友元(破坏封装)

希望别人可以随便用自己,破坏面向对象,那么这样有什么好处呢?
比如我需要给数组排序:
//arr.c
#include "arr.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void ARR::addtail(int data)
{
this->data[tail++] = data;
}
void ARR::show(void)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<tail; i++)
printf("%d, ", data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/*
void init(ARR *arr)
{
arr->tail = 0;
arr->addtail = addtail;
arr->show = show;
}
*/
//arr.h
#ifndef _ARR_
#define _ARR_
#if 0
typedef struct arr{
int data[100];
int tail;
void (*addtail)(struct arr *arr, int data);
void (*show)(struct arr *arr);
}ARR;
void init(struct arr *arr);
#endif
class ARR{
public:
ARR():tail(0){
// tail = 0;
}
void addtail(int data);
void show(void);
friend void rev(ARR &arr);
private:
int data[100];
int tail;
};
#endif
//main.c
#include "arr.h"
void rev(ARR &arr)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<arr.tail/2; i++)
{
int tem = arr.data[i];
arr.data[i] = arr.data[arr.tail-i-1];
arr.data[arr.tail-i-1] = tem;
}
}
int main()
{
#if 0
ARR arr;
init(&arr);
int n = 10;
while(n--)
arr.addtail(&arr, n);
arr.show(&arr);
// arr.tail = 0;
arr.show(&arr);
#endif
ARR arr;
arr.addtail(1);
arr.addtail(2);
arr.addtail(3);
arr.addtail(4);
arr.show();
//reverse
rev(arr);
arr.show();
}
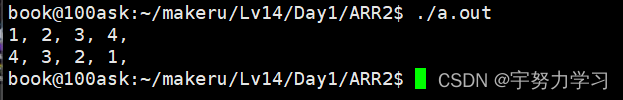
一堆程序可以用一个friend关键字解决
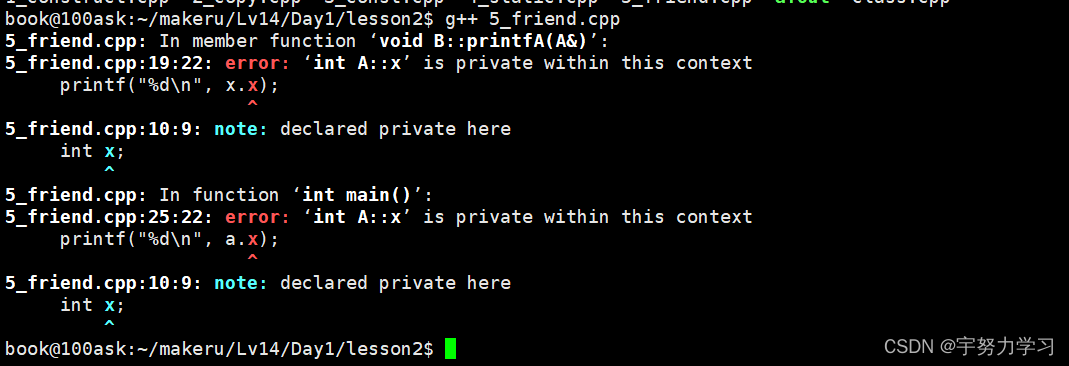
他是私有的我们不能用,接下来我们加上friend
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
x = 100;
}
friend class B;
private:
int x;
};
class B{
public:
void printfA(A &x);
};
void B::printfA(A &x)
{
printf("%d\n", x.x);
}
int main()
{
A a;
// printf("%d\n", a.x);
B b;
b.printfA(a);
}
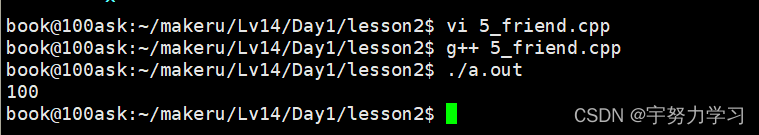 如果B中还有其它函数我们最好是只把需要的函数声明称朋友。
如果B中还有其它函数我们最好是只把需要的函数声明称朋友。
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
x = 100;
}
// friend class B;
friend void B::printfA(A &x);
private:
int x;
};
class B{
public:
void printfA(A &x);
void show(void)
{
}
};
void B::printfA(A &x)
{
printf("%d\n", x.x);
}
int main()
{
A a;
// printf("%d\n", a.x);
B b;
b.printfA(a);
}
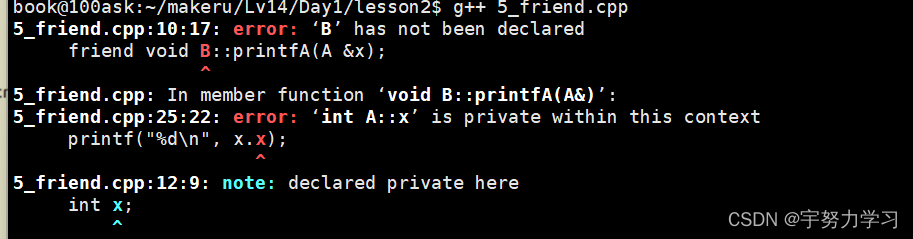
但是说不认识,我们没有定义,确实没有,我们在最前面class B声明一下
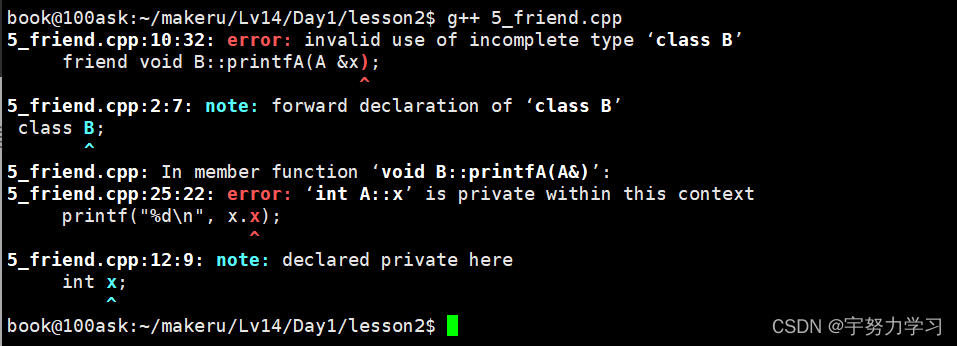
还是不行他说我们声明的不完整,主要是想表达它可以这样,这种破坏封装的行为C++不太允许。
我们调换一下顺序:
#include <stdio.h>
class A;
class B{
public:
void printfA(A &x);
};
class A{
public:
A()
{
x = 100;
}
// friend class B;
friend void B::printfA(A &x);
private:
int x;
};
void B::printfA(A &x)
{
printf("%d\n", x.x);
}
int main()
{
A a;
// printf("%d\n", a.x);
B b;
b.printfA(a);
}
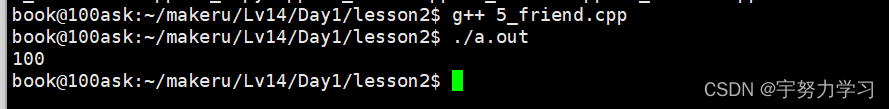 下面用C++来实现一个顺序表
下面用C++来实现一个顺序表
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 100;
using ElemType = int;//可以采用自定义类型,重载类的输入、输出、==、>等
class SqList
{
private:
ElemType* elem;
int length;
public:
//1.初始化
SqList()
{
elem = new ElemType[MAXSIZE];
if (!elem)
{
cout << "初始化错误!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
length = 0;
}
~SqList()
{
delete[]elem;
}
//2.取值(按照位置i)
bool GetElem(const int&i, ElemType& e)
{
if (i<1 || i>length)
{
cout << "位置错误!" << endl;
return false;
}
e = elem[i - 1];
return true;
}
//3.查找(按值查找)
int LocateElem(const ElemType &e)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i<=length-1;i++)
{
if (e == elem[i])
{
return i+1;//实际序号i+1
}
}
return false;//查找失败,返回false
}
//4.插入(按照位置i)
bool ListInsert(const int &i, const ElemType &e)
{
if (i<1 || i>length + 1)
{
cout << "位置错误!" << endl;
return false;
}
if (length == MAXSIZE)
{
cout << "当前存储空间已满!" << endl;//可以在大于等于的情况下再次进行动态分配
return false;
}
int j;
for (j = length - 1; j >= i - 1; j--)
{
elem[j+1] = elem[j];//强记忆点
}
elem[i - 1] = e;
++length;
return true;
}
//5.删除(按照位置i)
bool ListDelete(const int &i)
{
if (i<1 || i>length)
{
cout << "位置错误!" << endl;
return false;
}
int j;
for (j = i; j <= length - 1; j++)
{
elem[j-1] = elem[j];
}
--length;
return true;
}
//修改元素
bool AmendElem(const ElemType &oldelem,const ElemType &newelem)
{
int i = LocateElem(oldelem);
if (!i)
{
cout << "旧元素错误" << endl;
return false;
}
elem[i - 1] = newelem;
return true;
}
//展示顺序表
void Display()
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= length - 1; i++)
{
cout << elem[i] << '\t';
}
cout << endl;
}
//重载[]运算符
ElemType& operator[](const int &i)
{
if (i<0 || i>length - 1)
{
cout << "位置错误!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
return elem[i];
}
//顺序表长度
int GetLength()
{
return length;
}
};
int main()
{
SqList list;
int i,num;
ElemType e;
cout << "请输入数据个数:" << endl;
cin >> num;
for (i = 1; i <= num; i++)
{
cout << "input" << endl;
cin >> e;
list.ListInsert(i, e);
}
cout << "原顺序表:" << endl;
list.Display();
cout << "再次添加:" << endl;
cout << "请输入再次添加个数:" << endl;
cin >>num;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
cin >> e;
if (list.ListInsert(list.GetLength() + 1, e))
{
cout << "再次添加成功" << endl;
}
}
list.Display();
cout << "operator[]" << endl;
cout <<list[3] << endl;
cout << "删除元素" << endl;
cout << "input" << endl;
cin >> i;
if (list.ListDelete(i))
{
cout << "删除元素成功" << endl;
}
list.Display();
cout << "查找元素的位置:" << endl;
cout << "input" << endl;
cin >> e;
if (!list.LocateElem(e))
{
cout<< "查找失败!" <<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "元素位置为:" << list.LocateElem(e) << endl;
}
cout << "修改元素:" << endl;
ElemType olde, newe;
cout << "input old:" << endl;
cin >> olde;
cout << "input new:" << endl;
cin >> newe;
if (list.AmendElem(olde, newe) )
{
cout << "修改成功" << endl;
}
list.Display();
return 0;
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
最近事情有点多,花了近一周确认某人的态度,前几天影响较大耽误了学习。这几天又因为要过年了,被抓去当了壮丁。现在没什么事可以影响我了,接下来会抓紧学习。一篇文章写了四天,太不像话了。