一、CIFAR-10二进制数据集介绍
1、CIFAR-10数据集
CIFAR-10数据集由10个类别的60000个32x32彩色图像组成,每个类别有6000个图像。有50000个训练图像和10000个测试图像
2、数据集分为五个训练批次和一个测试批次,每个批次有10000个图像
3、data_batch_1.bin 到 data_batch_5.bin 训练集
4、test_batch.bin 测试集
5、这些类别完全相互互斥,汽车和卡车之间没有重叠。汽车包括轿车、SUV,卡车只包括大卡车
6、二进制数据文件内容格式
二进制数据文件包含data_batch_1.bin 到 data_batch_5.bin、test_batch.bin
这些文件中每一个格式如下,数据中每个样本包含了特征值和目标值:
<1x标签> <3072x像素>
...
<1x标签> <3072x像素>
每3073个字节是一个样本:
1个目标值+3072个像素
7、格式说明
第一个字节,是第一个图像的标签(目标值:飞机是0,汽车是2,鸟是3。。。),它是一个0-9范围内的数字。接下来的3072个字节是图像像素的值。前1024个字节是红色通道值,下1024个是绿色通道值,最后1024个是蓝色通道值
值以行优先顺序存储,因此前32个字节是图像第一行的红色通道值
每个文件都包含10000个这样的3073字节的“行”图像,但没有任何分隔行的限制。因此每个文件应该完全是30730000字节长
二、CIFAR-10二进制数据读取
1、分析
(1)构造文件名列表
(2)读取二进制数据并进行解码
(3)将数据的标签和图片进行分割
对tensor对象进行切片
label
一个样本image(3072字节 = 1024r + 1024g + 1024b)
[[1024r],
[1024g],
[1024b]]
shape = (3, 32, 32) = (channels, height, width)
因为tensorflow的图像表示习惯是(height, width, channel)
所以需要转换
(4)处理图片数据形状以及数据类型
(5)运行
2、代码day02_binary_read.py
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
import tensorflow as tf
class Cifar(object):
def __init__(self):
# 初始化操作
self.height = 32
self.width = 32
self.channels = 3
# 字节数
self.image_bytes = self.height * self.width * self.channels
self.label_bytes = 1
self.all_bytes = self.label_bytes + self.image_bytes
def read_and_decode(self):
decoded_data = []
# 1、构造文件名列表
filenames = tf.data.Dataset.list_files("./cifar-10-batches-bin/data_batch_*.bin")
for filename in filenames:
print(filename)
# 2、读取与解码
for filename in filenames:
raw = tf.io.read_file(filename)
# 解码为一维的uint8数组
data = tf.io.decode_raw(raw, out_type=tf.uint8)
print(data)
decoded_data.append(data)
# 3、运行
# 将文件按照样本切片切开
for data in decoded_data:
for i in range(10000):
cut_data = tf.slice(data, [i*self.all_bytes], [self.all_bytes])
#print(cut_data)
label = tf.slice(cut_data, [0], [self.label_bytes])
image = tf.slice(cut_data, [self.label_bytes], [self.image_bytes])
#print("label: ", label)
#print("image: ", image)
# 调整图片形状
image_reshaped = tf.reshape(image, shape=[self.channels, self.height, self.width])
#print("image_reshaped: ", image_reshaped)
# 转置,将图片顺序转为height, width, channels
image_transposed = tf.transpose(image_reshaped, [1, 2, 0])
#print("image_transposed: ", image_transposed)
# 调整图像类型
image_cast = tf.cast(image_transposed, tf.float32)
print("image_cast: ", image_cast)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 实例化Cifar
cifar = Cifar()
cifar.read_and_decode()filename打印例子:
tf.Tensor(b'./cifar-10-batches-bin/data_batch_4.bin', shape=(), dtype=string)
tf.Tensor(b'./cifar-10-batches-bin/data_batch_3.bin', shape=(), dtype=string)
tf.Tensor(b'./cifar-10-batches-bin/data_batch_1.bin', shape=(), dtype=string)
tf.Tensor(b'./cifar-10-batches-bin/data_batch_2.bin', shape=(), dtype=string)
tf.Tensor(b'./cifar-10-batches-bin/data_batch_5.bin', shape=(), dtype=string)
解码后打印例子:
tf.Tensor([ 8 26 17 ... 127 124 116], shape=(30730000,), dtype=uint8)
tf.Tensor([ 6 59 43 ... 130 130 131], shape=(30730000,), dtype=uint8)
tf.Tensor([ 0 178 178 ... 182 175 174], shape=(30730000,), dtype=uint8)
tf.Tensor([ 1 35 27 ... 119 127 136], shape=(30730000,), dtype=uint8)
tf.Tensor([ 1 255 252 ... 173 162 161], shape=(30730000,), dtype=uint8)
切片后打印例子:
label: tf.Tensor([6], shape=(1,), dtype=uint8)
image: tf.Tensor([255 254 255 ... 79 81 76], shape=(3072,), dtype=uint8)
调整图片形状后打印例子:
image_reshaped: tf.Tensor(
[[[229 236 234 ... 217 221 222]
[222 239 233 ... 223 227 210]
[213 234 231 ... 220 220 202]
...
[150 140 132 ... 224 230 241]
[137 130 125 ... 181 202 212]
[122 118 120 ... 179 164 163]]
[[229 237 236 ... 219 223 223]
[221 239 234 ... 223 228 211]
[206 232 233 ... 220 219 203]
...
[143 135 127 ... 222 228 241]
[132 127 121 ... 180 201 211]
[119 116 116 ... 177 164 163]]
[[239 247 247 ... 233 234 233]
[229 249 246 ... 236 238 220]
[211 239 244 ... 232 232 215]
...
[135 127 120 ... 218 225 238]
[126 120 115 ... 178 198 207]
[114 110 111 ... 173 162 161]]], shape=(3, 32, 32), dtype=uint8)
转置后打印例子:
image_transposed: tf.Tensor(
[[[235 252 252]
[239 251 251]
[239 251 251]
...
[225 251 252]
[228 251 252]
[228 252 252]]
[[249 255 255]
[251 253 255]
[252 254 255]
...
[229 255 255]
[231 255 255]
[232 255 255]]
[[241 250 254]
[243 248 252]
[245 248 252]
...
[231 253 251]
[232 253 252]
[233 253 252]]
...
[[ 81 118 176]
[ 85 123 178]
[ 83 123 175]
...
[167 167 168]
[168 168 170]
[165 166 169]]
[[ 79 119 176]
[ 69 108 163]
[ 67 105 158]
...
[170 172 174]
[163 164 167]
[161 164 169]]
[[ 46 87 142]
[ 45 83 137]
[ 52 88 141]
...
[175 179 182]
[168 172 175]
[163 169 174]]], shape=(32, 32, 3), dtype=uint8)调整图像类型后打印例子:
image_cast: tf.Tensor(
[[[229. 229. 239.]
[236. 237. 247.]
[234. 236. 247.]
...
[217. 219. 233.]
[221. 223. 234.]
[222. 223. 233.]]
[[222. 221. 229.]
[239. 239. 249.]
[233. 234. 246.]
...
[223. 223. 236.]
[227. 228. 238.]
[210. 211. 220.]]
[[213. 206. 211.]
[234. 232. 239.]
[231. 233. 244.]
...
[220. 220. 232.]
[220. 219. 232.]
[202. 203. 215.]]
...
[[150. 143. 135.]
[140. 135. 127.]
[132. 127. 120.]
...
[224. 222. 218.]
[230. 228. 225.]
[241. 241. 238.]]
[[137. 132. 126.]
[130. 127. 120.]
[125. 121. 115.]
...
[181. 180. 178.]
[202. 201. 198.]
[212. 211. 207.]]
[[122. 119. 114.]
[118. 116. 110.]
[120. 116. 111.]
...
[179. 177. 173.]
[164. 164. 162.]
[163. 163. 161.]]], shape=(32, 32, 3), dtype=float32)3、切片函数
tf.slice(inputs, begin, size, name=None)
说明:
inputs:输入的数组
begin:表示从inputs的哪几个维度上的哪个元素开始抽取,元素的索引
size:表示在inputs的各个维度上抽取的元素个数,要切多长
In [1]: import tensorflow as tf
In [2]: a = tf.constant([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
In [3]: a
Out[3]: <tf.Tensor: shape=(10,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], dtype=int32)>
In [4]: tf.slice(a, [4], [3])
Out[4]: <tf.Tensor: shape=(3,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([4, 5, 6], dtype=int32)>
In [5]: b = tf.constant([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
In [6]: b
Out[6]:
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=int32)>
In [7]: tf.slice(b, [0,1], [2,1])
Out[7]:
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 1), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[2],
[5]], dtype=int32)>
第一个例子,[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]从第4个索引位置,截取3个长度,所以是[4,5,6]
第二个例子,[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]是从0行1列开始,就是[1,2,3]的2,对x的第一个维度(行)抽取2个元素,在对x的第二个维度(列)抽取1个元素,所以是[2,5]
4、NHWC和NCHW
这里的图片形状设置从1维的排列到3维数据的时候,涉及到NHWC与NCHW的概念
在读取设置图片形状的时候有两种格式:
设置为“NHWC”时,排列顺序为 [batch, height, width, channels]
设置为“NCHW”时,排列顺序为 [batch, channels, height, width]
其中N表示这批图像有几张,H表示图像在竖直方向有多少像素,W表示水平方向像素,C表示通道数
tensorflow默认的是[height, width, channels]
假设RGB三通道两种格式的区别如下图所示:
理解
假设1,2,3,4-红色,5,6,7,8-绿色,9,10,11,12-蓝色
(1)如果通道在最低维度0[channel, height, width],RGB三颜色分成三组,在第一维度上找到三个RGB颜色(NCHW)
(2)如果通道在最高维度2[height, width, channel],在第三维度上找到RGB三个颜色(NHWC)
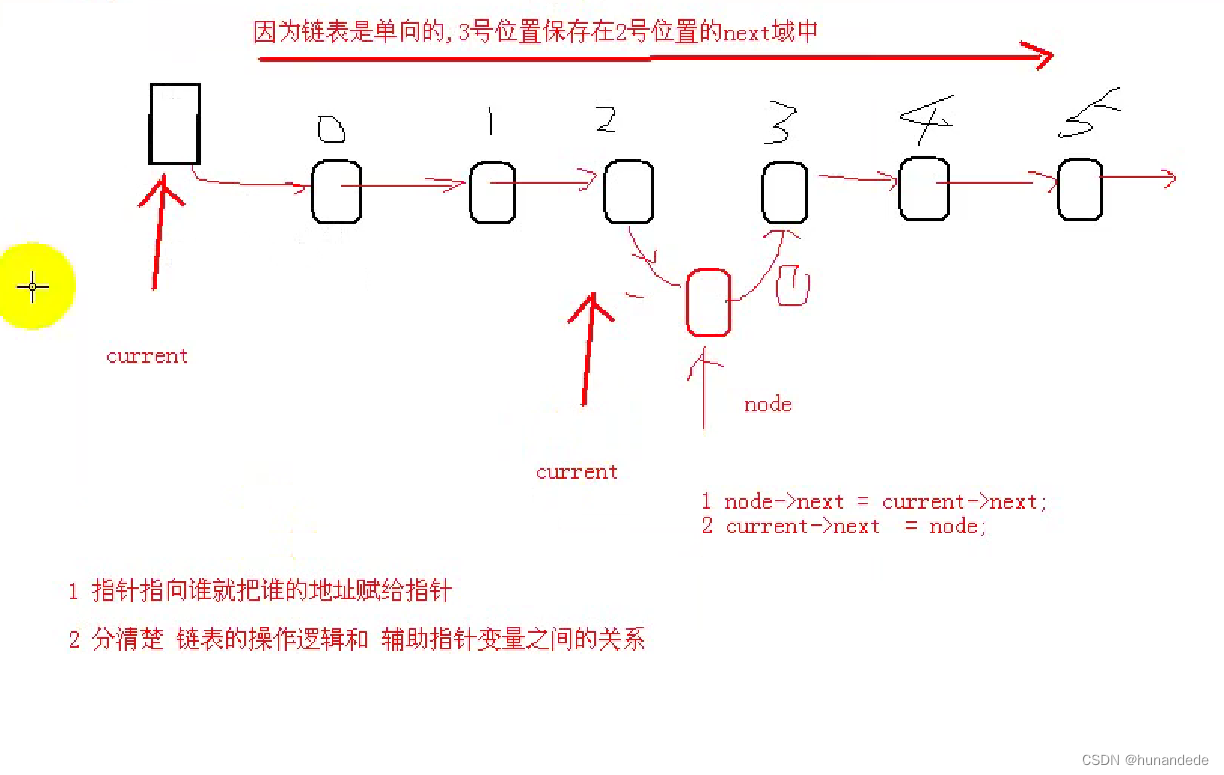
5、tf.transpose(image_reshaped, [1, 2, 0])
[1, 2, 0]表示,原来在1号位置的现在在0号位置,原来在2号位置的在1号位置,原来在0号位置的在1号位置
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/Aidam_Bo/article/details/91908637
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41845265/article/details/107067012