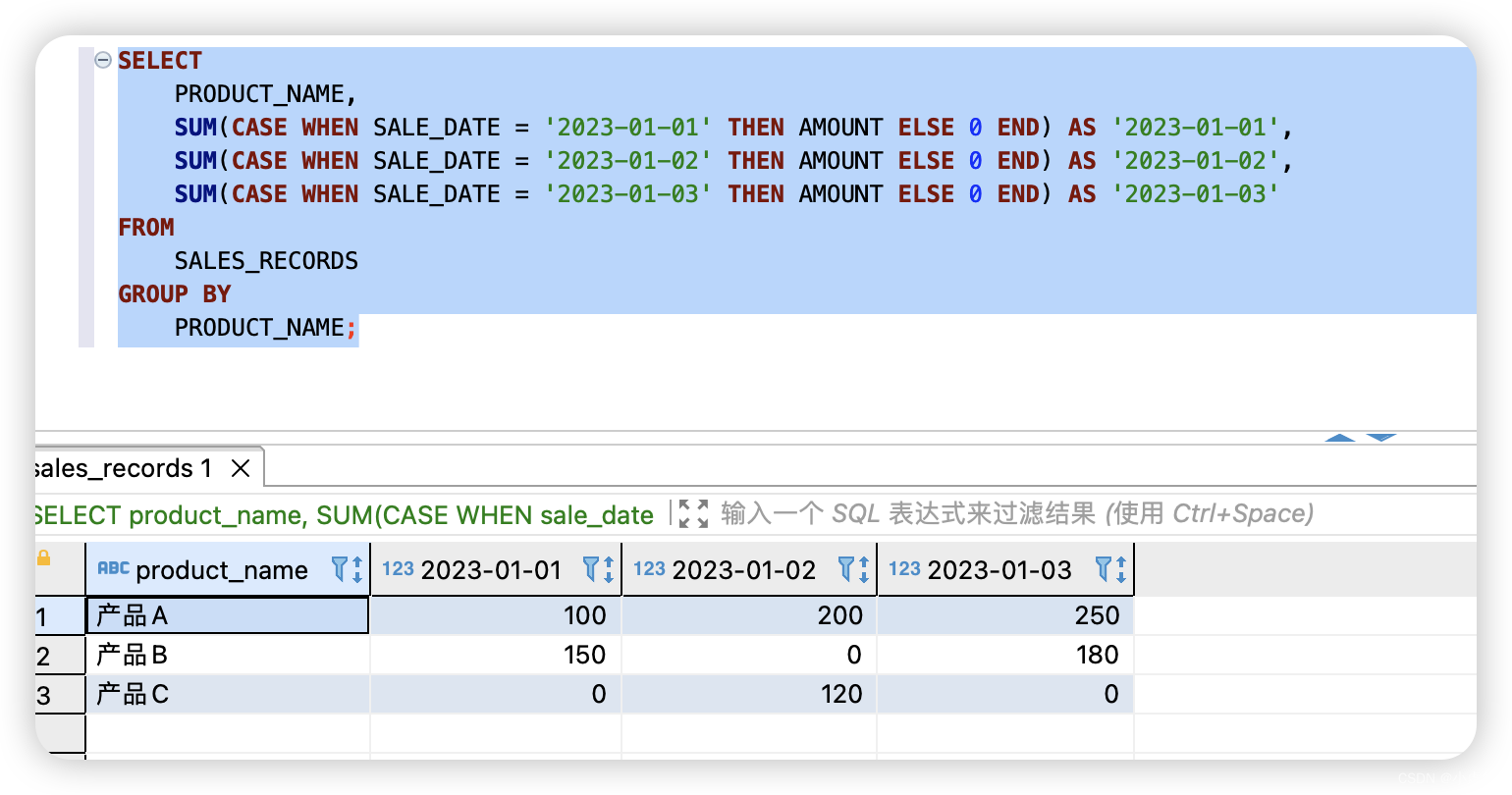
简述
处理全局异常的方法有IExceptionFilter(异常处理),使用中间件异常处理,使用框架自带异常中间件等。
考点
考察对异常处理方式的熟悉程度和广度,以及对中间件、过滤器熟练程度。
下面分别具体介绍三种处理异常的方法
1、异常处理 IExceptionFilter
开发过ASP.NET程序的人都知道:IExceptionFilter。这个过滤器同样在AspNetCore中也可以用来捕获异常。不过,对于使用IExceptionFilter,更建议使用它的异步版本:IAsyncExceptionFilter。那么该如何使用过滤器呢?下面以IAsyncExceptionFilter为例,对于同步版本其实也是一样的。
我们在项目中添加一个Model文件夹,存放返回结果实体类,这里定义一个泛型类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionDemo.Model
{
public class ResultModel<T>
{
/// <summary>
/// 返回结果编码 0:失败 1:成功
/// </summary>
public int ResultCode { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 返回结果内容 成功:Success 失败:异常内容
/// </summary>
public string ResultMsg { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 返回结果 成功:返回T类型数据 失败:默认null
/// </summary>
public T ResultData { get; set; }
}
}
我们在项目中添加一个Filter文件夹,所有的过滤器都放在该文件夹下面。然后添加一个类:CustomerExceptionFilter,并使该类继承自IAsyncExceptionFilter。代码如下:
using ExceptionDemo.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Filters;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionDemo.Filter
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义异常过滤器
/// </summary>
public class CustomerExceptionFilter : IAsyncExceptionFilter
{
/// <summary>
/// 重写OnExceptionAsync方法,定义自己的处理逻辑
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private readonly ILogger<CustomerExceptionFilter> _logger;
public CustomerExceptionFilter(ILogger<CustomerExceptionFilter> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public Task OnExceptionAsync(ExceptionContext context)
{
// 如果异常没有被处理则进行处理
if(context.ExceptionHandled==false)
{
// 定义返回类型
var result = new ResultModel<string>
{
ResultCode = 0,
ResultMsg = context.Exception.Message
};
_logger.LogInformation("502 Bad Gateway: ");
context.Result = new ContentResult
{
// 返回状态码设置为200,表示成功
StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status200OK,
// 设置返回格式
ContentType="application/json;charset=utf-8",
Content=JsonConvert.SerializeObject(result)
};
}
// 设置为true,表示异常已经被处理了
context.ExceptionHandled = true;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
}
上面的代码很简单,我们新建了一个自定义的异常过滤器,然后在OnExceptionAsync方法中定义自己的处理逻辑,报错之后依然让http返回状态码为200,并且将错误信息返回到客户端。
然后添加一个控制器,命名为ExceptionFilter,在控制器中模拟发生异常的情况:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using ExceptionDemo.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ExceptionDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ExceptionFilterController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public async Task<ResultModel<int>> Get()
{
int i = 0;
int k = 10;
// 这里会发生异常
int j = await Task.Run<int>(() =>
{
return k / i;
});
return new ResultModel<int>()
{
ResultCode=1,
ResultMsg="Success",
ResultData=j
};
}
}
}
最后我们需要把自定义的异常过滤器进行注入,这里选择使用全局注入的方式,在Startup类的ConfigureServices方法中进行注入:
builder.Services.AddLogging(logging =>
{
logging.AddConsole(); // 向控制台输出日志
// 你可以根据需要添加其他日志提供程序,比如文件日志、事件日志等
});
services.AddControllers(options =>
{
//因为CustomerExceptionFilter构造函数中使用了ILogger 所以必须现在前面注入AddLogging
options.Filters.Add<CustomerExceptionFilter>();
});
然后运行程序,查看结果:
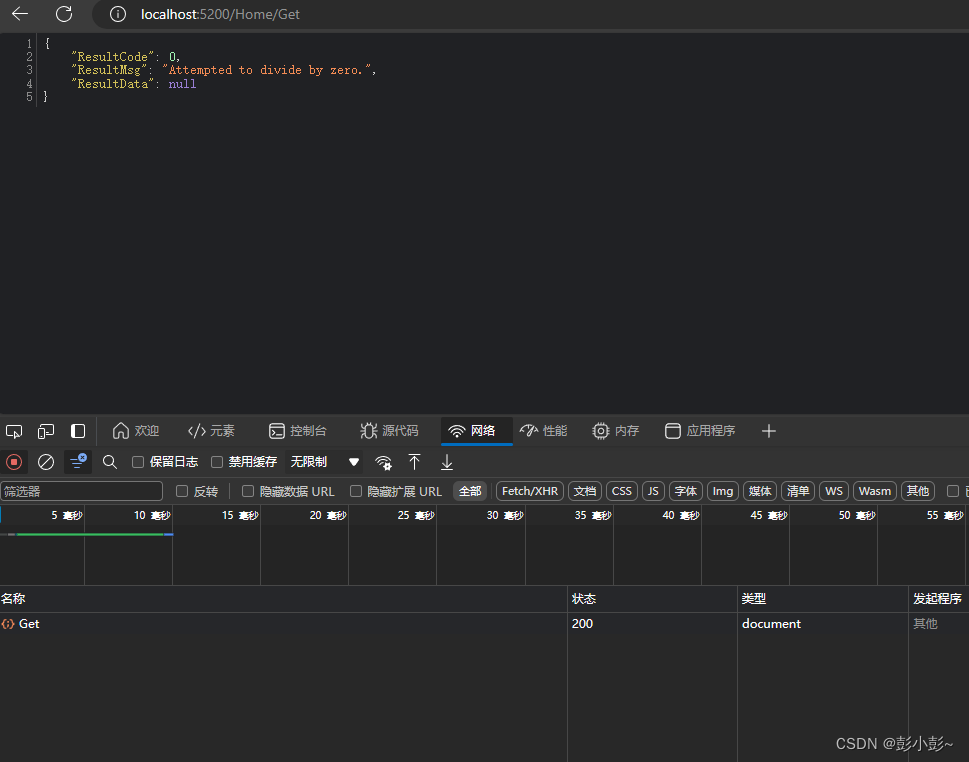
如何我们没有使用过滤器捕获和处理异常,我们将得到Http状态码为500的内部错误,这种错误不方便定位问题,而且给客户端返回的信息也不够友好。使用了过滤器处理异常,进行特殊处理之后就会显得很友好了。
在上面自定义过滤器的代码中,有下面的一行代码:
context.ExceptionHandled = true;
注意:这句代码很关键,当你处理完异常之后,一定要将此属性更改为true,表示异常已经处理过了,这样其他地方就不会在处理这个异常了。
2、使用中间件处理异常
我们知道,AspNetCore的管道模型具有层层传递的特点,那么我们就可以在管道中实现全局异常捕获。我们新创建一个自定义的异常中间件:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionDemo.Middleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义异常中间件
/// </summary>
public class CustomerExceptionMiddleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 委托
/// </summary>
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomerExceptionMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
try
{
await _next(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
context.Response.ContentType = "application/problem+json";
var title = "An error occured: " + ex.Message;
var details = ex.ToString();
var problem = new ProblemDetails
{
Status = 200,
Title = title,
Detail = details
};
var stream = context.Response.Body;
await JsonSerializer.SerializeAsync(stream, problem);
}
}
}
}
然后在新建一个扩展方法:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
namespace ExceptionDemo.Middleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 静态类
/// </summary>
public static class ExceptionMiddlewareExtension
{
/// <summary>
/// 静态方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="app">要进行扩展的类型</param>
public static void UseExceptionMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseMiddleware(typeof(CustomerExceptionMiddleware));
}
}
}
最后在Startup类的Configure方法中使用自定义的异常中间件:
app.UseExceptionMiddleware();
然后我们注释掉上面注册的异常过滤器,运行程序进行访问:
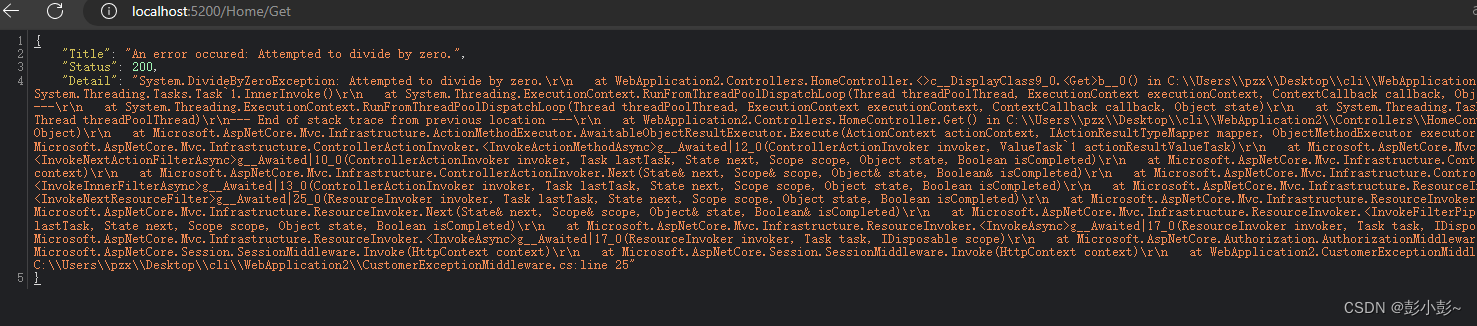
这样也可以捕获到异常。
3、使用框架自带异常中间件
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
这段代码在我们使用AspNetCore创建一个WebApi项目时就会看到,如果是创建的MVC项目,是下面一段代码:
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
}
这两段代码的作用就是捕获和处理异常,是第一个被添加到管道中的中间件。
UseDeveloperExceptionPage的意思很好理解:对于开发模式,一旦报错就跳转到错误堆栈页面。而第二个UseExceptionHandler也很有意思,从它的名字中我们大致可以猜出它肯定是个错误拦截程序。那么它和上面自定义的异常处理中间件有什么区别呢?
UseExceptionHandler其实就是默认的错误处理。它其实也是一个中间件,它的原名叫做ExceptionHandlerMiddleware。在使用UseExceptionHandler方法时,我们可以选填各种参数。比如上面的第二段代码,填入了“/Error”参数,表示当产生异常的时候,将定位到对应的路径,这里定位的页面就是“http://localhost:5001/Error”。这是MVC中自带的一个错误页面,当然,你也可以指定自己定义的一个页面。
UseExceptionHandler还有一个指定ExceptionHandlerOptions参数的扩展方法,该参数是ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中间件的重要参数:
参数名 说明
ExceptionHandlingPath 重定向的路径,比如刚才的 “”/Error"" 实际上就是指定的该参数
ExceptionHandler 错误拦截处理程序
ExceptionHandler允许我们在ExceptionHandlerMiddleware内部指定咱们自己的异常处理逻辑。而该参数的类型为RequestDelegate类型的委托。因此,UseExceptionHandler提供了一个简便的写法,可以让我们在ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中新建自定义的错误拦截管道来处理异常:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using ExceptionDemo.Filter;
using ExceptionDemo.Middleware;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace ExceptionDemo
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
#region 注册全局异常过滤器
//services.AddControllers(options =>
//{
// options.Filters.Add(new CustomerExceptionFilter());
//});
#endregion
services.AddControllers();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler(builder => builder.Use(ExceptionHandlerDemo));
}
app.UseExceptionMiddleware();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}
private async Task ExceptionHandlerDemo(HttpContext httpContext,Func<Task> next)
{
//该信息由ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中间件提供,里面包含了ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中间件捕获到的异常信息。
var exceptionDetails = httpContext.Features.Get<IExceptionHandlerFeature>();
var ex = exceptionDetails?.Error;
if (ex != null)
{
httpContext.Response.ContentType = "application/problem+json";
var title = "An error occured: " + ex.Message;
var details = ex.ToString();
var problem = new ProblemDetails
{
Status = 500,
Title = title,
Detail = details
};
var stream = httpContext.Response.Body;
await JsonSerializer.SerializeAsync(stream, problem);
}
}
}
}
中间件和过滤器的比较
在上面的例子中,我们分别使用了中间件和过滤器的方式来处理异常,那么中间件和过滤器有什么区别呢?两者的区别:拦截范围的不同。
IExceptionFilter作为一种过滤器,它需要在控制器发现错误之后将错误信息提交给它处理,因此它的异常处理范围是控制器内部。如果我们想捕获进入控制器之前的一些错误,IExceptionFilter是捕获不到的。而对于ExceptionHandlerMiddleware异常中间件来说就很容易了,它作为第一个中间件被添加到管道中,在它之后发生的任何异常都可以捕获的到。
那么为什么要有两种异常处理的方式呢?只使用ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中间件处理异常不可以吗?它可以捕获任何时候发生的异常,为什么还要有过滤器呢?如果你想在控制器发生异常时快速捕获和处理异常,那么使用过滤器处理异常是非常不错的选择。如果是控制器内部发生了异常,首先是由过滤器捕获到异常,最后才是中间件捕获到异常。
我们在自定义过滤器的时候有这样一段代码:context.ExceptionHandled = true;如果在自定义过滤器中将异常标记为已经处理之后,则第一个异常处理中间件就认为没有错误了,不会进入到处理逻辑中了。所以,如果不把 ExceptionHandled属性设置为true,可能出现异常处理结果被覆盖的情况。