作者:Rachit Belwariar
编译:东岸因为@一点人工一点智能
路径规划算法 | A* 搜索算法![]() https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lTVkknLWZ4ERYnv8m0JCGQ
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lTVkknLWZ4ERYnv8m0JCGQ
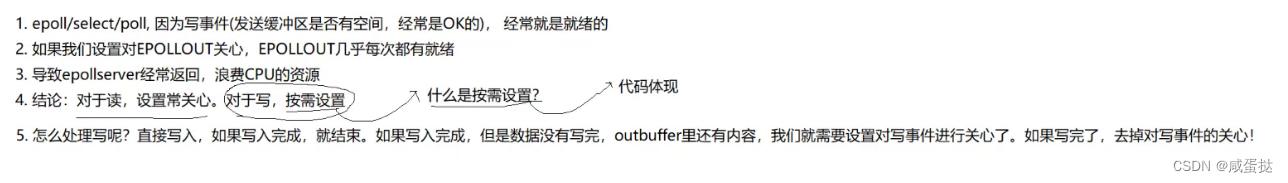
动机:为了在现实生活中近似求解最短路径,例如地图、游戏等存在许多障碍物的情况。我们可以考虑一个含有多个障碍物的二维网格图,我们从起始单元格(下方红色标记)开始,朝着目标单元格(下方绿色标记)前进。
01 什么是A*搜索算法
A*搜索算法是一种用于路径搜索和图遍历的效果很好、主流的技术之一。
1.1 为什么选择A*搜索算法?
简单地说,A*搜索算法与其他遍历技术不同,它具有“智能”。这意味着它是一种非常智能的算法,与其他传统算法有所区别。下面的部分将详细解释这一点。
值得一提的是,许多游戏和基于Web的地图使用这个算法来高效地找到最短路径(近似)。
1.2 解释
考虑一个有许多障碍物的正方形网格,给定一个起始单元格和一个目标单元格。我们希望尽快从起始单元格到达目标单元格(如果可能)。这时A*搜索算法就派上用场了。
A*搜索算法在每一步中选择一个节点,根据一个值f来确定,该值是两个其他参数g和h的函数。在每一步中,它选择具有最低f值的节点/单元格,并处理该节点/单元格。
我们将g和h定义如下:
g:从起点到网格上的某个给定方格的移动成本,沿着生成的路径进行移动。
h:从给定方格到最终目的地的估计移动成本。这通常被称为启发式,它只是一种聪明的猜测。在找到路径之前,我们真的不知道实际距离,因为各种东西可能阻会妨碍规划的路径(墙壁、水等)。有许多计算这个h值的方法,这些方法在后面的部分中进行了讨论。
02 算法
我们创建两个列表 - 开放列表(Open list)和封闭列表(Closed list)(就像Dijkstra算法一样)。
// A* Search Algorithm
1. Initialize the open list
2. Initialize the closed list
put the starting node on the open
list (you can leave its f at zero)
3. while the open list is not empty
a) find the node with the least f on
the open list, call it "q"
b) pop q off the open list
c) generate q's 8 successors and set their
parents to q
d) for each successor
i) if successor is the goal, stop search
ii) else, compute both g and h for successor
successor.g = q.g + distance between
successor and q
successor.h = distance from goal to
successor (This can be done using many
ways, we will discuss three heuristics-
Manhattan, Diagonal and Euclidean
Heuristics)
successor.f = successor.g + successor.h
iii) if a node with the same position as
successor is in the OPEN list which has a
lower f than successor, skip this successor
iV) if a node with the same position as
successor is in the CLOSED list which has
a lower f than successor, skip this successor
otherwise, add the node to the open list
end (for loop)
e) push q on the closed list
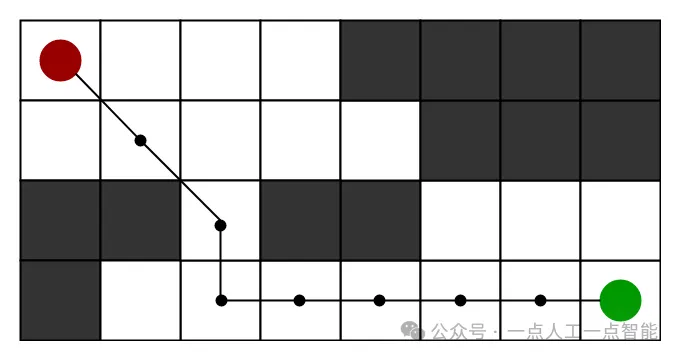
end (while loop)所以假设如下图所示,如果我们想要从起始单元格到达目标单元格,A*搜索算法将按照下图所示的路径进行搜索。请注意,下图是根据欧几里德距离作为启发式算法生成的。

03 启发式算法
我们可以计算g,但如何计算h呢?
我们可以采取以下方法:A) 要么计算h的精确值(这肯定是耗时的),或者 B) 使用某些启发式方法来近似计算h(时间消耗较少)。
我们将讨论这两种方法。
3.1 精确启发式
我们可以找到h的精确值,但通常这需要很长时间。
以下是一些计算h精确值的方法。
1) 在运行A*搜索算法之前,预先计算每对单元格之间的距离。
2) 如果没有阻塞单元格(障碍物),我们可以使用距离公式/欧几里德距离,在不进行任何预先计算的情况下找到h的精确值。
3.2 近似启发式
通常有三种近似启发式方法来计算h:
1) 曼哈顿距离:
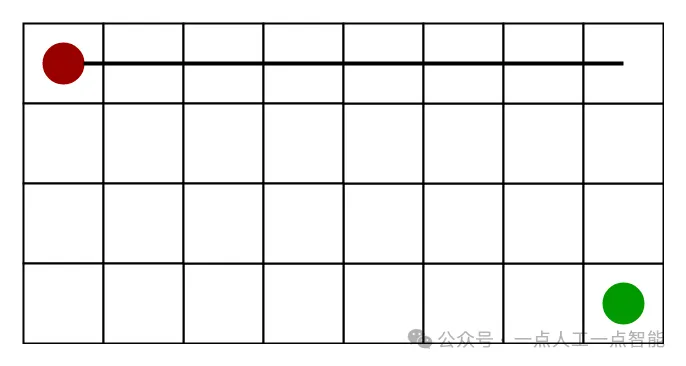
· 它是目标点的x坐标和y坐标与当前单元格的x坐标和y坐标之间差值的绝对值之和,即:
h = abs (current_cell.x – goal.x) + abs (current_cell.y – goal.y)· 当只允许在四个方向上移动(右、左、上、下)时,我们可以使用这个启发式算法。曼哈顿距离启发式算法可以通过下图表示(假设红点为起始单元格,绿点为目标单元格)。
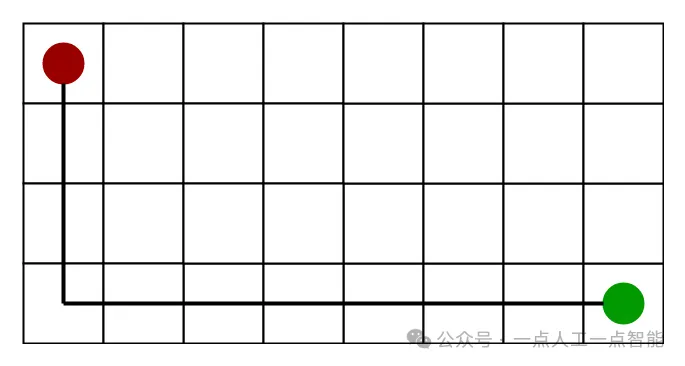
2) 对角线距离:
· 它是目标点的x坐标和y坐标与当前单元格的x坐标和y坐标之间差值的绝对值的最大值,即:
dx = abs(current_cell.x – goal.x)
dy = abs(current_cell.y – goal.y)
h = D * (dx + dy) + (D2 - 2 * D) * min(dx, dy)
where D is length of each node(usually = 1) and D2 is diagonal distance between each node (usually = sqrt(2) ).· 当只允许在八个方向上移动时(类似于国际象棋中的国王移动),我们可以使用这个启发式算法。
对角线距离启发式算法可以通过下图表示(假设红点为起始单元格,绿点为目标单元格)。
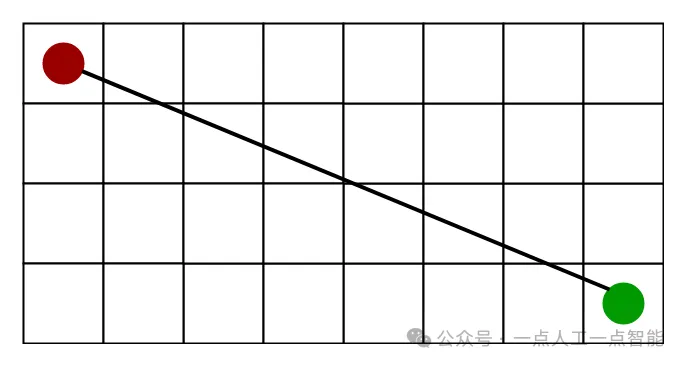
3) 欧几里德距离:
· 顾名思义,它就是使用距离公式计算当前单元格与目标单元格之间的距离。
h = sqrt ( (current_cell.x – goal.x)2 + (current_cell.y – goal.y)2 )· 这个启发式算法什么时候使用呢?- 当我们被允许在任意方向上移动时。
欧几里德距离启发式算法可以通过下图表示(假设红点为起始单元格,绿点为目标单元格)。
与其他算法的关系(相似性和差异):Dijkstra算法是A*搜索算法的特例,其中所有节点的h值都为0。
04 实现
我们可以使用任何数据结构来实现开放列表和封闭列表,但为了获得最佳性能,我们使用C++ STL中的集合数据结构(实现为红黑树)和一个布尔哈希表用于封闭列表。
实现与Dijkstra算法类似。如果我们使用斐波那契堆来实现开放列表,而不是使用二叉堆/自平衡树,那么性能将会更好(因为斐波那契堆在平均情况下需要O(1)的时间来插入到开放列表并减小键值)。
此外,为了减少计算g所需的时间,我们将使用动态规划。
// A C++ Program to implement A* Search Algorithm
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ROW 9
#define COL 10
// Creating a shortcut for int, int pair type
typedef pair<int, int> Pair;
// Creating a shortcut for pair<int, pair<int, int>> type
typedef pair<double, pair<int, int> > pPair;
// A structure to hold the necessary parameters
struct cell {
// Row and Column index of its parent
// Note that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1
int parent_i, parent_j;
// f = g + h
double f, g, h;
};
// A Utility Function to check whether given cell (row, col)
// is a valid cell or not.
bool isValid(int row, int col)
{
// Returns true if row number and column number
// is in range
return (row >= 0) && (row < ROW) && (col >= 0)
&& (col < COL);
}
// A Utility Function to check whether the given cell is
// blocked or not
bool isUnBlocked(int grid[][COL], int row, int col)
{
// Returns true if the cell is not blocked else false
if (grid[row][col] == 1)
return (true);
else
return (false);
}
// A Utility Function to check whether destination cell has
// been reached or not
bool isDestination(int row, int col, Pair dest)
{
if (row == dest.first && col == dest.second)
return (true);
else
return (false);
}
// A Utility Function to calculate the 'h' heuristics.
double calculateHValue(int row, int col, Pair dest)
{
// Return using the distance formula
return ((double)sqrt(
(row - dest.first) * (row - dest.first)
+ (col - dest.second) * (col - dest.second)));
}
// A Utility Function to trace the path from the source
// to destination
void tracePath(cell cellDetails[][COL], Pair dest)
{
printf("\nThe Path is ");
int row = dest.first;
int col = dest.second;
stack<Pair> Path;
while (!(cellDetails[row][col].parent_i == row
&& cellDetails[row][col].parent_j == col)) {
Path.push(make_pair(row, col));
int temp_row = cellDetails[row][col].parent_i;
int temp_col = cellDetails[row][col].parent_j;
row = temp_row;
col = temp_col;
}
Path.push(make_pair(row, col));
while (!Path.empty()) {
pair<int, int> p = Path.top();
Path.pop();
printf("-> (%d,%d) ", p.first, p.second);
}
return;
}
// A Function to find the shortest path between
// a given source cell to a destination cell according
// to A* Search Algorithm
void aStarSearch(int grid[][COL], Pair src, Pair dest)
{
// If the source is out of range
if (isValid(src.first, src.second) == false) {
printf("Source is invalid\n");
return;
}
// If the destination is out of range
if (isValid(dest.first, dest.second) == false) {
printf("Destination is invalid\n");
return;
}
// Either the source or the destination is blocked
if (isUnBlocked(grid, src.first, src.second) == false
|| isUnBlocked(grid, dest.first, dest.second)
== false) {
printf("Source or the destination is blocked\n");
return;
}
// If the destination cell is the same as source cell
if (isDestination(src.first, src.second, dest)
== true) {
printf("We are already at the destination\n");
return;
}
// Create a closed list and initialise it to false which
// means that no cell has been included yet This closed
// list is implemented as a boolean 2D array
bool closedList[ROW][COL];
memset(closedList, false, sizeof(closedList));
// Declare a 2D array of structure to hold the details
// of that cell
cell cellDetails[ROW][COL];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < COL; j++) {
cellDetails[i][j].f = FLT_MAX;
cellDetails[i][j].g = FLT_MAX;
cellDetails[i][j].h = FLT_MAX;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_i = -1;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_j = -1;
}
}
// Initialising the parameters of the starting node
i = src.first, j = src.second;
cellDetails[i][j].f = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].g = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].h = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_j = j;
/*
Create an open list having information as-
<f, <i, j>>
where f = g + h,
and i, j are the row and column index of that cell
Note that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1
This open list is implemented as a set of pair of
pair.*/
set<pPair> openList;
// Put the starting cell on the open list and set its
// 'f' as 0
openList.insert(make_pair(0.0, make_pair(i, j)));
// We set this boolean value as false as initially
// the destination is not reached.
bool foundDest = false;
while (!openList.empty()) {
pPair p = *openList.begin();
// Remove this vertex from the open list
openList.erase(openList.begin());
// Add this vertex to the closed list
i = p.second.first;
j = p.second.second;
closedList[i][j] = true;
/*
Generating all the 8 successor of this cell
N.W N N.E
\ | /
\ | /
W----Cell----E
/ | \
/ | \
S.W S S.E
Cell-->Popped Cell (i, j)
N --> North (i-1, j)
S --> South (i+1, j)
E --> East (i, j+1)
W --> West (i, j-1)
N.E--> North-East (i-1, j+1)
N.W--> North-West (i-1, j-1)
S.E--> South-East (i+1, j+1)
S.W--> South-West (i+1, j-1)*/
// To store the 'g', 'h' and 'f' of the 8 successors
double gNew, hNew, fNew;
//----------- 1st Successor (North) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i - 1, j) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i - 1, j, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i - 1][j] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i - 1, j)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i - 1, j, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i - 1][j].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i - 1][j].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i - 1, j)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 2nd Successor (South) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i + 1, j) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i + 1, j, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i + 1][j] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i + 1, j)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i + 1, j, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i + 1][j].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i + 1][j].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i + 1, j)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 3rd Successor (East) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i, j + 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i, j + 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i][j + 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i, j + 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i, j + 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i][j + 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i][j + 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i, j + 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i][j + 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 4th Successor (West) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i, j - 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i, j - 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i][j - 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i, j - 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i, j - 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i][j - 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i][j - 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i, j - 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i][j - 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 5th Successor (North-East)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i - 1, j + 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i - 1, j + 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i - 1][j + 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i - 1, j + 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i - 1, j + 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i - 1, j + 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 6th Successor (North-West)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i - 1, j - 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i - 1, j - 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i - 1][j - 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i - 1, j - 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i - 1, j - 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i - 1, j - 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 7th Successor (South-East)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i + 1, j + 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i + 1, j + 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i + 1][j + 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i + 1, j + 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i + 1, j + 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i + 1, j + 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 8th Successor (South-West)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i + 1, j - 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i + 1, j - 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i + 1][j - 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i + 1, j - 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i + 1, j - 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i + 1, j - 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
}
// When the destination cell is not found and the open
// list is empty, then we conclude that we failed to
// reach the destination cell. This may happen when the
// there is no way to destination cell (due to
// blockages)
if (foundDest == false)
printf("Failed to find the Destination Cell\n");
return;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Description of the Grid-
1--> The cell is not blocked
0--> The cell is blocked */
int grid[ROW][COL]
= { { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 } };
// Source is the left-most bottom-most corner
Pair src = make_pair(8, 0);
// Destination is the left-most top-most corner
Pair dest = make_pair(0, 0);
aStarSearch(grid, src, dest);
return (0);
}限制:尽管A*搜索算法是目前最好的路径搜索算法,但它并不总是能够产生最短路径,因为它在计算h值时严重依赖启发式/近似方法。
05 应用
这是A*搜索算法最有趣的部分。它们被用在游戏中!但是如何使用呢?
你玩过塔防游戏吗?
塔防是一种策略类视频游戏,目标是通过阻挡敌人的攻击来保卫玩家的领土或财产,通常是通过在敌人的攻击路径上或沿着其攻击路径上放置防御结构来实现的。
A*搜索算法经常用于找到从一个点到另一个点的最短路径。你可以为每个敌人使用它来找到通向目标的路径。
其中一个例子是非常流行的游戏《魔兽争霸III》。
5.1 如果搜索空间不是一个网格而是一个图,该怎么办?
相同的规则也适用于图。选择网格作为例子是为了简单理解。因此,我们可以使用A*搜索算法在图中找到源节点和目标节点之间的最短路径,就像我们在二维网格中做的那样。
5.2 时间复杂度
考虑到图,我们可能需要遍历所有的边才能从源节点到达目标节点(例如,考虑一个图,源节点和目标节点之间通过一系列边连接,如0(源)->1->2->3(目标))。
因此,最坏情况下的时间复杂度是O(E),其中E是图中的边数。
辅助空间 在最坏的情况下,我们可能需要将所有的边存储在开放列表中,因此最坏情况下所需的辅助空间是O(V),其中V是顶点的总数。
06 总结
那么何时使用广度优先搜索(BFS)而不是A*算法,何时使用Dijkstra算法而不是A*算法来寻找最短路径呢?
我们可以总结如下:
1)一个起点和一个目的地:
· 使用A*搜索算法(适用于无权图和加权图)。
2)一个起点,多个目的地:
· 对于无权图:使用广度优先搜索(BFS)。
· 对于非负权值的加权图:使用Dijkstra算法。
· 对于带有负权值的加权图:使用Bellman Ford算法。
3)任意两个节点之间的最短路径:
· 使用Floyd-Warshall算法。
· 使用Johnson算法。