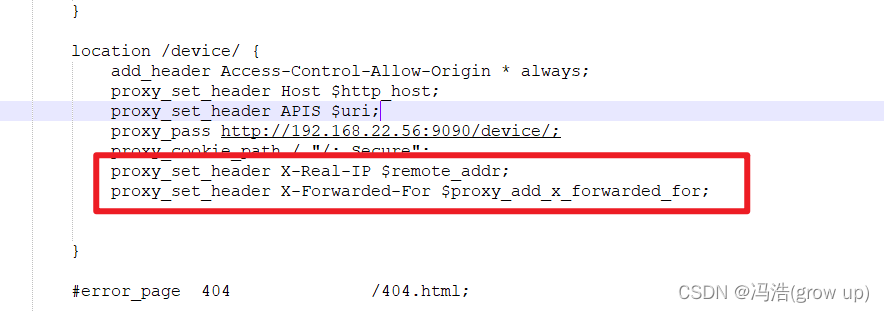
1.Pandas介绍
-
Pandas 是基于 NumPy 的一种工具,该工具是为解决数据分析任务而创建的,Pandas 提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的功能
-
Pandas 与出色的 Jupyter 工具包和其他库相结合,Python 中用于进行数据分析的环境在性能、生产率和协作能力方面都是卓越的
-
Pandas 的主要数据结构是 Series(一维数据)与 DataFrame(二维数据),这两种数据数据足以处理金融、统计、社会科学、工程等领域里的大多数案例
-
处理数据一般分为几个阶段:数据整理与清洗、数据分析与建模、数据可视化,Pandas 是处理数据的理想工具
2.Pandas安装
-
Anaconda 环境:无需安装
-
普通 Python 环境:pip install pandas -i Simple Index
3.导入 Pandas 模块
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
4.Series
-
Series 是一种类似于一维数组的对象,由下面两个部分组成
-
Values:一组数据(ndarray 类型)
-
index:相关的数据索引标签
-
5.Series 的创建
-
第一种方式:由列表或 NumPy 数组创建
-
默认索引为 0 到 N-1 的整数型索引
-
# 列表方式创建
list1 = [11,22,33,44]
s = pd.Series(list1)
s
# 执行结果
0 11
1 22
2 33
3 44
dtype: int32
# NumPy数组创建
n = np.array(list1)
s = pd.Series(n)
s
# 执行结果
0 11
1 22
2 33
3 44
dtype: int32
# 查看类型
type(s)
# 执行结果
pandas.core.series.Series-
-
index和values
-
# 值是ndarray的一维数组
s.values
# 执行结果
array([11, 22, 33, 44])
# 索引
s.index
# 转换成列表
#list(s.index)
# 执行结果
RangeIndex(start=0, stop=4, step=1)
# 修改索引index,确保与元素个数保持一致
s.index = ["A","B","C","D"]
# 或者
# s.index = list("BCDE")
s
# 执行结果
A 11
B 22
C 33
D 44
dtype: int32
# 通过索引获取值,数字索引只能使用中括号的方式
s.A,s.C,s["D"]
# 执行结果
(11, 33, 44)
# 通过索引修改值
s["D"] = 100
s
# 执行结果
A 11
B 22
C 33
D 100
dtype: int32-
由字典创建
d = {
"a":11,
"b":22,
"c":33,
"d":44
}
s = pd.Series(d)
s
# 执行结果
a 11
b 22
c 33
d 44
dtype: int64
# 修改索引
s.index = list("ABCD")
s
# 执行结果
A 11
B 22
C 33
D 44
dtype: int64
# 字典值为二维数组
d = {
"a":np.random.randint(0,10,size=(2,3)),
"b":np.random.randint(0,10,size=(2,3)),
"c":np.random.randint(0,10,size=(2,3)),
"d":np.random.randint(0,10,size=(2,3))
}
s = pd.Series(d)
s
# 执行结果
a [[6, 4, 7], [8, 8, 1]]
b [[3, 1, 8], [9, 1, 1]]
c [[9, 2, 3], [3, 7, 9]]
d [[6, 0, 8], [6, 7, 6]]
dtype: object
# 通过索引查看值
s["a"]
# 执行结果
array([[6, 4, 7],
[8, 8, 1]])
pd.Series([1,2,3],index=["鲁班","杜甫","李白"],name="历史人物")
# 执行结果
鲁班 1
杜甫 2
李白 3
Name: 历史人物, dtype: int64


![OpenHarmony其他工具类—libharu [GN编译]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/48b1e7eff01309fe163e3e6dcf6fba55.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)