学习视频:21-广度优先搜索练习_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Q:密码锁
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int s, e;
bool vis[10000];
struct node {
int state;
int step;
node(int s1, int s2) {
state = s1;
step = s2;
}
};
int bfs(int state, int step) {
node now = node(state, step);
queue<node> q;
q.push(now);
vis[now.state] = true;
if (now.state == e) {
return now.step;
}
//!!要标记状态后放进去
while (!q.empty()) {
now = q.front();
q.pop();
if (now.state == e) {
return now.step;
}
//+1、-1、交换
int a = now.state;
int tmp;
if (a % 10 == 9) {
tmp = a / 10 * 10 + 1;
if (!vis[tmp]) {
vis[tmp] = true;
q.push(node(tmp, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a + 1]) {
vis[a + 1] = true;
q.push(node(a + 1, now.step + 1));
}
}
if (a % 100 / 10 == 9) {
tmp = a / 100 * 100 + 10 + a % 10;
if (!vis[tmp]) {
q.push(node(tmp, now.step + 1));
vis[tmp] = true;
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a + 10]) {
vis[a + 10] = true;
q.push(node(a + 10, now.step + 1));
}
}
if (a % 1000 / 100 == 9) {
tmp = a / 1000 * 1000 + 100 + a % 100;
if (!vis[tmp]) {
vis[tmp] = true;
q.push(node(tmp, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a + 100]) {
vis[a + 100] = true;
q.push(node(a + 100, now.step + 1));
}
}
if (a / 1000 == 9) {
tmp = 1000 + a % 1000;
if (!vis[tmp]) {
vis[tmp] = true;
q.push(node(tmp, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a + 1000]) {
vis[1000 + a] = true;
q.push(node(a + 1000, now.step + 1));
}
}
//-
if (a % 10 == 1) {
if (!vis[a + 8]) {
vis[a + 8] = 1;
q.push(node(a + 8, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a - 1]) {
vis[a - 1] = 1;
q.push(node(a - 1, now.step + 1));
}
}
if (a % 100 / 10 == 1) {
if (!vis[a + 80]) {
vis[a + 80] = 1;
q.push(node(a + 80, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a - 10]) {
vis[a - 10] = 1;
q.push(node(a - 10, now.step + 1));
}
}
if (a % 1000 / 100 == 1) {
if (!vis[a + 800]) {
vis[a + 800] = 1;
q.push(node(a + 800, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a - 100]) {
vis[a - 100] = 1;
q.push(node(a - 100, now.step + 1));
}
}
if (a / 1000 == 1) {
if (!vis[a + 8000]) {
vis[a + 8000] = 1;
q.push(node(8000 + a, now.step + 1));
}
}
else {
if (!vis[a - 1000]) {
vis[a - 1000] = 1;
q.push(node(a - 1000, now.step + 1));
}
}
//
// 交换
int r1, r2, r3, r4;
r1 = a % 10;
r2 = a / 10 % 10;
r3 = a / 100 % 10;
r4 = a / 1000;
q.push(node(1000 * r4 + r3 * 100 + r1 * 10 + r2, now.step + 1));
q.push(node(1000 * r4 + r2 * 100 + r3 * 10 + r1, now.step + 1));
q.push(node(1000 * r3 + r4 * 100 + r2 * 10 + r1, now.step + 1));
}
}
int main() {
cin >> s >> e;
cout << bfs(s, 0);
return 0;
}
Q:乳草的侵占
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int X, Y, MX, MY;
char grace[105 ][105];
bool vis[105][105];
int dir[8][2] = { {0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0},{1,1},{-1,-1},{1,-1},{-1,1} };
bool in(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < Y && y >= 0 && y < X;
}
struct node {
int x;
int y;
int day;
node(int xx, int yy,int dd) {
x = xx;
y = yy;
day = dd;
}
};
int bfs(int x,int y) {
queue<node> q;
int ans = 0;
node now = node(x, y, 0);
q.push(now);
vis[x][y] = true;
while (!q.empty()){
node a = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int fx = a.x + dir[i][0];
int fy = a.y + dir[i][1];
if (!vis[fx][fy] && grace[fx][fy] != '*' && in(fx, fy)) {
vis[fx][fy] == true;
grace[fx][fy] = '*';
q.push(node(fx, fy, a.day + 1));
ans = a.day + 1;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
cin >> X >> Y >> MX >> MY;
MY = Y - MY;
MX = MX - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < Y; i++) {
cin >> grace[i];
}
cout << bfs(MY, MX);
return 0;
}
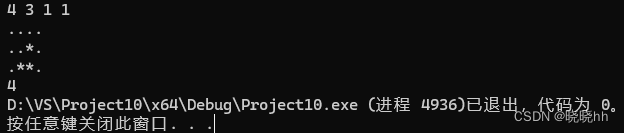
/*
4 3 1 1
....
..*.
.**.
*/
Q:一维跳棋
好难,不会
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = (1 << 20) * 21 + 5;
bool vis[1<<20][100];
struct node {
int s, x;
};
int p[N];
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<node> a;
queue<int> q;
int s1 = (1 << n) - 1; //999 B全在右边
int s2 = s1 << n; //999000 B全在左边(终止情况)
q.push(a.size()); //q放的是状态的下标,a记录的是实际的状态
vis[s1][n] = true; //初始空的位置在n的位置
a.push_back({ s1, n });
while (!q.empty()) {
int id = q.front();
q.pop();
int s = a[id].s, x = a[id].x;
if (s == s2 && x == n) { //成功了
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = id; i; i = p[i]) {
ans.push_back(2 * n - a[i].x + 1);
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
char ch = i % 5 == 4 ? 'n' : ' ';
cout << ans[i] << ch;
}
break;
}
//空格左边的棋子移到空格位置
if (x < 2 * n) {
int ts = s;
int tx = x + 1;
if (!vis[ts][tx]) {
q.push(a.size());
vis[ts][tx] = true;
p[a.size()] = id;
a.push_back({ ts,tx });
}
}
//空格右边的棋子移到空格位置
if (x > 0) {
int ts = s;
int tx = x - 1;
if (!vis[ts][tx]) {
q.push(a.size());
vis[ts][tx] = true;
p[a.size()] = id;
a.push_back({ ts,tx });
}
}
//空格左边棋子跳到空格
if (x <= 2 * n - 2 && ((s >> x + 1 & 1) ^ (s >> x & 1))) {
int ts = s ^ (3 << x);
int tx = x + 2;
if (!vis[ts][tx]) {
q.push(a.size());
vis[ts][tx] = true;
p[a.size()] = id;
a.push_back({ ts,tx });
}
}
//空格右边棋子跳到空格
if (x >= 2 && ((s >> x - 1 & 1) ^ (s >> x - 2 & 1))) {
int ts = s ^ (3 << x - 2);
int tx = x - 2;
if (!vis[ts][tx]) {
q.push(a.size());
vis[ts][tx] = true;
p[a.size()] = id;
a.push_back({ ts,tx });
}
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
4 3 1 1
....
..*.
.**.
*/放弃!!
Q:三阶平面魔方
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
bool vis[9876][54321] = {0};
int a[3];
struct node {
int id = 0;
int step = 0;
node(int idd, int st) {
id = idd;
step = st;
}
};
int num;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
num = a[i] + num * 1000;
}
queue<node> q;
node now = node(num, 0); //!!!怎么传参啊啊啊
int aa = now.id;
vis[aa / 100000][aa % 100000] = true;
q.push(now);
while (!q.empty()) {
now = q.front();
q.pop();
if (now.id == 123456789) {
cout<< now.step;
}
int hang1, hang2, hang3, hang, h;
hang1 = now.id / 1000000;
hang2 = now.id / 1000 % 1000;
hang3 = now.id % 1000;
//行变换右移
hang = hang1 % 10 * 100 + hang1 / 100 * 10 + hang1 % 10 % 10;
h = hang2 * 1000 + hang3 + 1000000 * hang;
if (!vis[h / 100000][h % 100000]) {
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = true;
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
}
hang = hang2 % 10 * 100 + hang2 / 100 * 10 + hang2 % 10 % 10;
h = hang * 1000 + hang3 + 1000000 * hang1;
if (!vis[h / 100000][h % 100000]) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
hang = hang3 % 10 * 100 + hang3 / 100 * 10 + hang3 % 10 % 10;
h = hang2 * 1000 + hang + 1000000 * hang1;
if (!vis[h / 100000][h % 100000]) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//行变换左移
hang = hang1 % 10 * 10 + hang1 / 100 + hang1 % 10 % 10 * 100;
h = hang2 * 1000 + hang3 + 1000000 * hang;
if (!vis[h/100000][h%100000]) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
hang = hang2 % 10 * 10 + hang2 / 100 + hang2 % 10 % 10 * 100;
h = hang * 1000 + hang3 + 1000000 * hang1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
hang = hang3 % 10 * 10 + hang3 / 100 + hang3 % 10 % 10 * 100;
h = hang2 * 1000 + hang + 1000000 * hang1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//列变换下移1
int h1, h2, h3;
h1 = hang1 - hang1 / 100 * 100 + hang3 / 100 * 100;
h2 = hang2 - hang2 / 100 * 100 + hang1 / 100 * 100;
h3 = hang3 - hang3 / 100 * 100 + hang2 / 100 * 100;
h = h2 * 1000 + h3 + 1000000 * h1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//列变换下移2
h1 = hang1 - hang1 / 10 % 10 * 10 + hang3 / 10 % 10 * 10;
h2 = hang2 - hang2 / 10 % 10 * 10 + hang1 / 10 % 10 * 10;
h3 = hang3 - hang3 / 10 % 10 * 10 + hang2 / 10 % 10 * 10;
h = h2 * 1000 + h3 + 1000000 * h1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//列变换下移3
h1 = hang1 - hang1 % 10 + hang3 % 10;
h2 = hang2 - hang2 % 10 + hang1 % 10;
h3 = hang3 - hang3 % 10 + hang2 % 10;
h = h2 * 1000 + h3 + 1000000 * h1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//列变换上移1
h1 = hang1 - hang1 / 100 * 100 + hang2 / 100 * 100;
h2 = hang2 - hang2 / 100 * 100 + hang3 / 100 * 100;
h3 = hang3 - hang3 / 100 * 100 + hang1 / 100 * 100;
h = h2 * 1000 + h3 + 1000000 * h1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//列变换上移2
h1 = hang1 - hang1 / 10 % 10 * 10 + hang2 / 10 % 10 * 10;
h2 = hang2 - hang2 / 10 % 10 * 10 + hang3 / 10 % 10 * 10;
h3 = hang3 - hang3 / 10 % 10 * 10 + hang1 / 10 % 10 * 10;
h = h2 * 1000 + h3 + 1000000 * h1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
//列变换上移3
h1 = hang1 - hang1 % 10 + hang2 % 10;
h2 = hang2 - hang2 % 10 + hang3 % 10;
h3 = hang3 - hang3 % 10 + hang1 % 10;
h = h2 * 1000 + h3 + 1000000 * h1;
if (vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] == 0) {
q.push(node(h, now.step + 1));
vis[h / 100000][h % 100000] = 1;
}
}
//cout << bfs();
return 0;
}
/*
412
756
389
*/我的狗屎代码已经废了,不知道错在了哪里,不管了,放弃!!!
Q:吃糖的时间

#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>using namespace std;
int n, p, c;
int m;
bool vis[10000];
int maxn;
struct child {
int v;
int step;
};
queue<child> q;vector<int> vec[100010];
void bfs() {
int i;
child p, t;
while (!q.empty()) {
p = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < vec[p.v].size(); i++) {
t.v = vec[p.v][i];
t.step = p.step + 1;
if (!vis[t.v]) {
q.push(t);
vis[t.v] = 1;
if (t.step > maxn) {
maxn = t.step;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> p >> c;
cin >> m;
int a, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= p; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
vec[a].push_back(b);
vec[b].push_back(a);
}
child ch;
ch.v = c;
ch.step = 1;
vis[ch.v] = 1;
q.push(ch);
bfs();
cout << maxn + m;
return 0;
}
/*
4 3 1
2
1 2
2 3
1 4
*/
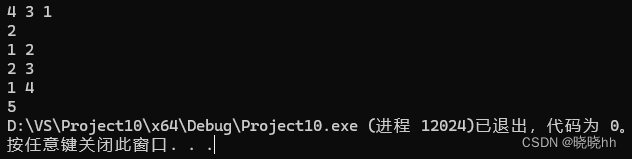
又写了一次:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n, r, c, m;
vector<int> vec[10001];
bool vis[10001];
struct node {
int id;
int time;
node(int c,int tt) {
time = tt;
id = c; //!!!写错了
}
};
int t = 0;
int num = 0;
int main() {
cin >> n >> r >> c >> m;
int a, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++) { //!!!写错了
cin >> a >> b;
vec[a].push_back(b);
vec[b].push_back(a);
}
queue<node> q;
node now(c, 1);
vis[c] = true; //!!忘写了
q.push(now);
while (!q.empty()) {
now = q.front();
num++;
q.pop();
if (num == n) {
cout << now.time + m;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vec[now.id].size(); i++) { //!!越界了
if (!vis[vec[now.id][i]]) {
vis[vec[now.id][i]] = true;
q.push(node(vec[now.id][i], now.time + 1));
}
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
4 3 1
2
1 2
2 3
1 4
*/
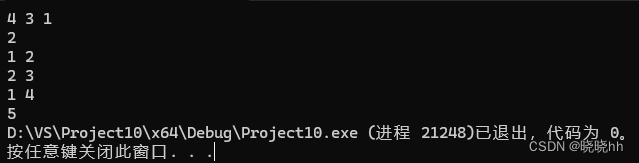
Q:蒜头军回家
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
char map[2000][2000];
bool vis[2000][2000][2]; //!!!取完钥匙剩下的路都可以走,要区分来时去时路
bool flag;
bool in(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m;
}
struct node {
int x, y;
int step;
char ch;
bool find = false;
node(int xx, int yy, int c, int s, bool f) {
x = xx;
y = yy;
step = s;
ch = c;
find = f;
}
node(int xx, int yy, int c, int s) {
x = xx;
y = yy;
step = s;
ch = c;
}
};
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
//先取了钥匙再回家
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> map[i];
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 'S') {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
queue<node> q;
node now = node(x, y, map[x][y], 0);
vis[x][y][0] = 1; //!!!别忘了
q.push(now);
while (!q.empty()) {
now = q.front();
q.pop();
if (now.find && now.ch == 'T') {
cout << now.step << endl;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int fx = now.x + dir[i][0];
int fy = now.y + dir[i][1];if (!vis[fx][fy][now.find] && map[fx][fy] != '#' && in(fx, fy)) {
if (map[fx][fy] == 'P') {
q.push(node(fx, fy, map[fx][fy], now.step + 1,true));
vis[fx][fy][now.find] = 1;
}
else {
vis[fx][fy][now.find] = 1;
q.push(node(fx, fy, map[fx][fy], now.step + 1, now.find));
}
}
}}
return 0;
}
/*
8 10
P.####.#P#
..#..#...#
..#T##.#.#
..........
..##.#####
..........
#####...##
###....S##
*/
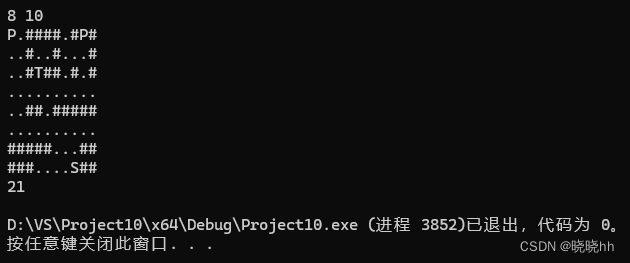
后面是选做,不做了,因为有点难

![[计算机效率] 时间记录工具:ManicTime](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1a14a747e6014a24a2e023fed6f39357.png)