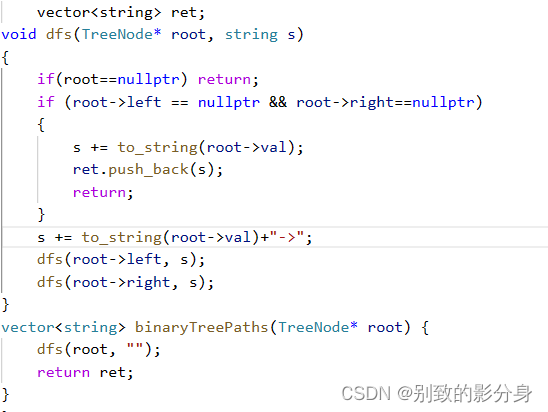
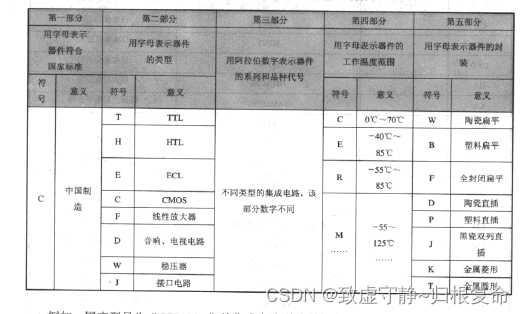
matplotlib 画图有个默认配色方案,在画不同图时会保持一致。如:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 图 1 数据
x = np.arange(12).astype(np.float32) + 1
y1 = np.log(x)
y2 = 1 / x
y3 = np.sin(x)
# 图 2 数据
a = np.random.randn(200)
b = np.random.randn(200)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
# 图 1
ax[0].plot(x, y1, label='y1')
ax[0].plot(x, y2, label='y2')
ax[0].plot(x, y3, label='y3')
# 图 2
ax[1].hist([a, b], label=['a', 'b'])
for _ax in ax:
_ax.legend(fancybox=True, framealpha=0)
plt.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("test.png", bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close(fig)
效果:

可见两幅图中头两种颜色(蓝、橙)是一样的。参考 [1],这种默认配色叫 default line color cycle。调用简例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cycle = plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'].by_key()['color']
print(len(cycle), cycle)
fig = plt.figure()
for i, c in enumerate(cycle):
plt.plot([0, 2], [i, i], c=c)
plt.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("test2.png", bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close(fig)
输出:
10 ['#1f77b4', '#ff7f0e', '#2ca02c', '#d62728', '#9467bd', '#8c564b', '#e377c2', '#7f7f7f', '#bcbd22', '#17becf']
只有 10 种颜色。效果:

References
- Get default line color cycle