常用类
Math类
基本介绍
Math类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数
方法一览(均为静态方法)
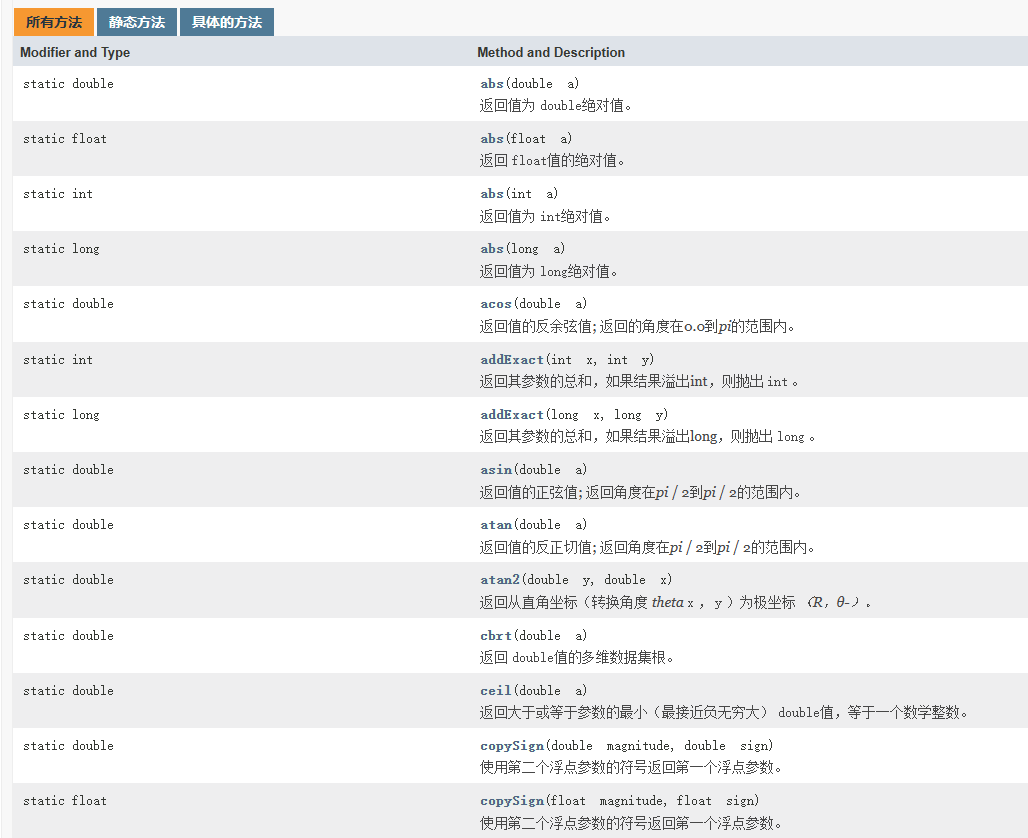
Math常见方法应用案例
1、 abs绝对值
2、pow求幂
3、ceil向上取整
4、floor 向下取整
5、round 四舍五入
6、sqrt 求开方
7、random求随机数//思考:请写出获取 a-b之间的一个随机整数,a,b均为整数? 2-7
8、max求两个数的最大值
9、min求两个数的最小值
练习题:获取一个a-b之间的一个随机整数
package com13.math_;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title MathMethod
* @package com13.math_
* @time 2023/1/11 21:04
*/
public class MathMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Math常用的方法(静态方法)
//1.abs绝对值
int abs = Math.abs(-9);
System.out.println(abs);//9
//2.pow求幂
double pow = Math.pow(2, 4);//2的4次方
System.out.println(pow);//16.0
//3.ceil向上取整,返回>=该参数的最小整数
double ceil = Math.ceil(-3.00001);
System.out.println(ceil);//-3.0
//4.floor向下取整,返回<=该参数的最大整数
double floor = Math.floor(-4.99999);
System.out.println(floor);//-5.0
//5.round四舍五入 Math.floor(该参数+0.5)
long round = Math.round(-5.001);
System.out.println(round);//-5
//6.sqrt求平方
double sqrt = Math.sqrt(9.0);
System.out.println(sqrt);//3.0
//7.random求随机数
//random返回的是 0 <= x < 1 之间的一个随机小数
//思考:请写出获取 a-b之间的一个随机整数,a,b均为整数? 2-7
//公式 (int) (a + Math.random() * (b - a + 1))
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println((int) (2 + Math.random() * (7 - 2 + 1)));
}
//max,min返回最大值和最小值
int min = Math.min(1, 9);
int max = Math.max(45, 1000);
System.out.println("min=" + min);
System.out.println("max=" + max);
}
}
Arrays类
Arrays类常见方法应用案例
Arrays里面包含了一系列静态方法,用于管理或操作数组(比如排序和搜索)
1、toString返回数组的字符串形式
Arrays.toString(arr)
2、sort 排序(自然排序和定制排序)
Integer arr[] = {1, -1, 7, 0, 89];
3、binarySearch通过二分搜索法进行查找,要求必须排好序
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 3);
4、copyOf 数组元素的复制
Integer[] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length);
5、fill 数组元素的填充
Integer[] num = new Integer[]{9.3.2];
Arrays.fill(num, 99);
6、equals 比较两个数组元素内容是否完全一致
boolean equals = Arrays.equals(arr, arr2);
7、asList 将一组值,转换成list
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1);
System.out.println("asList=" +asList);
package com13.arrays_;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title ArraysMethod01
* @package com13.arrays_
* @time 2023/1/11 22:00
*/
public class ArraysMethod01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] integers = {1, 20, 90};
//遍历数组
// for (int i = 0; i < integers.length; i++) {
// System.out.println(integers[i]);
// }
//直接使用Arrays.toString方法显示数组
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(integers));
//演示sort方法的使用
Integer arr[] = {1, -1, 7, 100, 96, 996};
//进行排序
//解读
//1. 可以使用冒泡排序,也可以使用Arrays提供的sort方法排序
//2. 因为数组是引用类型,所以通过sort排序后,会直接影响到 实参arr
//3. sort重载的,也可以通过传入一个接口Comparator实现定制排序
//4. 调用 定制排序 时 传入两个参数 (1)排序数组arr
//(2)实现了Comparator接口的匿名内部类,要求实现compare方法
//
// Arrays.sort(arr);//默认方法排序
//定制排序
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Integer i1 = (Integer) o1;
Integer i2 = (Integer) o2;
return i2 - i1;
}
});
System.out.println("==========排序后==========");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
package com13.arrays_;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title ArraysMethod02
* @package com13.arrays_
* @time 2023/1/11 22:32
*/
public class ArraysMethod02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr = {1, 2, 90, 123, 666};
// binarySearch 通过二分搜索法进行查找,要求必须排好
// 解读
//1.使用binarySearch二叉查找
//2.要求该数组是有序的。如果该数组是无序的,不能使用binarySearch
//3.如果数组中不存在该元素,就返回-1
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 123);
System.out.println("index=" + index);
//copyOf数组元素的复制
//解读
//1.从arr数组中,拷贝arr.length个元素到newArr数组中
//2.如果拷贝的长度>arr.length就在新数组的后面增加null
//3.如果拷贝长度<0就异常NegativeArraySizeException
Integer[] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length + 1);
System.out.println("=====拷贝执行完后=====");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArr));
//ill数组元素的填充
Integer[] num = new Integer[]{9, 3, 2};
//解读
//1.使用99去填充num数组,可以理解为是替换原来的元素
Arrays.fill(num, 99);
System.out.println("=======num数组填充后======");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
//equals 比较两个数组元素内容是否完全一致
Integer[] arr2 = {1, 2, 90, 123, 567};
//解读
//1.如果 arr 与 arr2 数组元素一样,则方法true
//2.如果不是完全一样,就返回false
boolean equals = Arrays.equals(arr, arr2);
System.out.println("equals=" + equals);
//asList 将一组值,转换成list
//解读
//1.asList方法,会将(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1)数据转成一个List集合
//2.返回的asList编译类型List(接口)
//3.asList运行类型 java.util.Arrays#ArrayList
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1);
System.out.println("asList=" + asList);
System.out.println("asList的运行类型" + asList.getClass());
}
}
Arrays类练习题
案例:自定义Book类,里面包含name和price,按price排序(从大到小)。
要求使用两种方式排序,对对象的某个属性排序,有一个 Book[] books= 5本书对象
使用前面学习过的传递实现Comparator接口匿名内部类,也称为定制排序。
package com13.arrays_;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title ArrayExercise
* @package com13.arrays_
* @time 2023/1/11 23:32
*/
public class ArrayExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
案例:自定义Book类,里面包含name和price,按price排序(从大到小)。
要求使用两种方式排序 , 有一个 Book[] books = 4本书对象.
使用前面学习过的传递 实现Comparator接口匿名内部类,也称为定制排序。
可以按照 price (1)从大到小 (2)从小到大 (3) 按照书名长度从大到小
*/
Book[] books = new Book[4];
books[0] = new Book("红楼梦", 100);
books[1] = new Book("金瓶梅新", 90);
books[2] = new Book("青年文摘20年", 5);
books[3] = new Book("java从入门到放弃~", 300);
//(1)price从大到小
// Arrays.sort(books, new Comparator() {
// //这里是对Book数组排序,因此 o1 和 o2 就是Book对象
// @Override
// public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// Book book1 = (Book) o1;
// Book book2 = (Book) o2;
// double priceVal = book2.getPrice() - book1.getPrice();
// //这里进行了一个转换
// //如果发现返回结果和我们输出的不一致,就修改一下返回的 1 和 -1
// if(priceVal > 0) {
// return 1;
// } else if(priceVal < 0) {
// return -1;
// } else {
// return 0;
// }
// }
// });
//(2)price从小到大
// Arrays.sort(books, new Comparator() {
// //这里是对Book数组排序,因此 o1 和 o2 就是Book对象
// @Override
// public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// Book book1 = (Book) o1;
// Book book2 = (Book) o2;
// double priceVal = book2.getPrice() - book1.getPrice();
// //这里进行了一个转换
// //如果发现返回结果和我们输出的不一致,就修改一下返回的 1 和 -1
// if(priceVal > 0) {
// return -1;
// } else if(priceVal < 0) {
// return 1;
// } else {
// return 0;
// }
// }
// });
//(3)按照书名长度从大到小
Arrays.sort(books, new Comparator() {
//这里是对Book数组排序,因此 o1 和 o2 就是Book对象
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Book book1 = (Book) o1;
Book book2 = (Book) o2;
//要求按照书名的长度来进行排序
return book2.getName().length() - book1.getName().length();
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(books));
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private double price;
public Book(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
System类
System类常见方法和案例
1、exit 退出当前程序
2、arraycopy:复制数组元素,比较适合底层调用,一般使用Arrays.copyOf完成复制数组
int[] src={1,2,3};
int[] dest = new int[3];
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, 3);
3、currentTimeMillens:返回当前时间距离1970-1-1的毫秒数
4、 gc:运行垃圾回收机制System.gc();
package com13.system_;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title System_
* @package com13.system_
* @time 2023/1/12 16:09
*/
public class System_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//exit 退出当前程序
System.out.println("ok1");
//解读
//1. exit(0)表示程序退出
//2. 0表示一个状态,正常状态
// System.exit(0);
// System.out.println("ok1");
//arraycopy:复制数组元素,比较适合底层调用
//一般使用Arrays.copyOf完成复制数组
int[] src = {1, 2, 3};
int[] dest = new int[3];//dest当前是{0, 0, 0}
//解读
//1.主要是搞清楚这五个参数的含义
// 源数组
// * @param src the source array.
// srcPos:从源数组的那个索引位置开始拷贝
// * @param srcPos starting position in the source array.
// dest:目标数组,即把源数组的数据拷贝到哪个数组
// * @param dest the destination array.
// destPos:把源数组的数据拷贝到目标数组的那个索引
// * @param destPos starting position in the destination data.
// length:从源数组拷贝多少个数据到目标数组
// * @param length the number of array elements to be copied.
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, src.length);
System.out.println("dest=" + Arrays.toString(dest));
//currentTimeMillens:返回当前时间距离1970-1-1的毫秒数
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
BigInteger和BigDecimal类
BigInteger和BigDecimal介绍
应用场景:
1、BigInteger适合保存比较大的整型
2、BigDecimal适合保存精度更高的浮点型(小数)
package com13.bignum;
import java.math.BigInteger;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title BigInteger_
* @package com13.bignum
* @time 2023/1/12 16:40
*/
public class BigInteger_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//编程时需要处理很大的整数,long不够用
//可以使用BigInteger的类来搞定
// long l = 2341654654564696999999999L;
// System.out.println("l=" + l);
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("2341654654564696999999999");
BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger("999999999");
System.out.println(bigInteger);
//解读
//1.在对BigInteger进行加减乘除的时候,需要用对应的方法,不能直接进行 + - * /
BigInteger add = bigInteger.add(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(add);//+
BigInteger subtract = bigInteger.subtract(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(subtract);//-
BigInteger multiply = bigInteger.multiply(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(multiply);//*
BigInteger divide = bigInteger.divide(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(divide);//除
}
}
package com13.bignum;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title BigDecimal_
* @package com13.bignum
* @time 2023/1/12 16:51
*/
public class BigDecimal_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需要保存一个精度很高的数时,double不够用
//可以使用BigDecimal
// double d = 1999.111121111111989891111111131111d;
// System.out.println(d);
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("1999.111121111111989891111111131111");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("9.265");
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
//解读
//1.如果对 BigDecimal进行运算,比如+ - * / ,需要调用对应的方法
//2.创建一个需要操作BigDecimal然后调用相应的方法即可
System.out.println(bigDecimal.add(bigDecimal2));//+
System.out.println(bigDecimal.subtract(bigDecimal2));//-
System.out.println(bigDecimal.multiply(bigDecimal2));//*
// System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal2));//除,可能抛出异常ArithmeticException
//在调用divide方法时,指定精度即可BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING
//如果有无线循环小数,就会保留分子的精度
System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal2, BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING));//除,可能抛出异常ArithmeticException
}
}
日期类
第一代日期类
1、Date:精确到毫秒,代表特定的瞬间
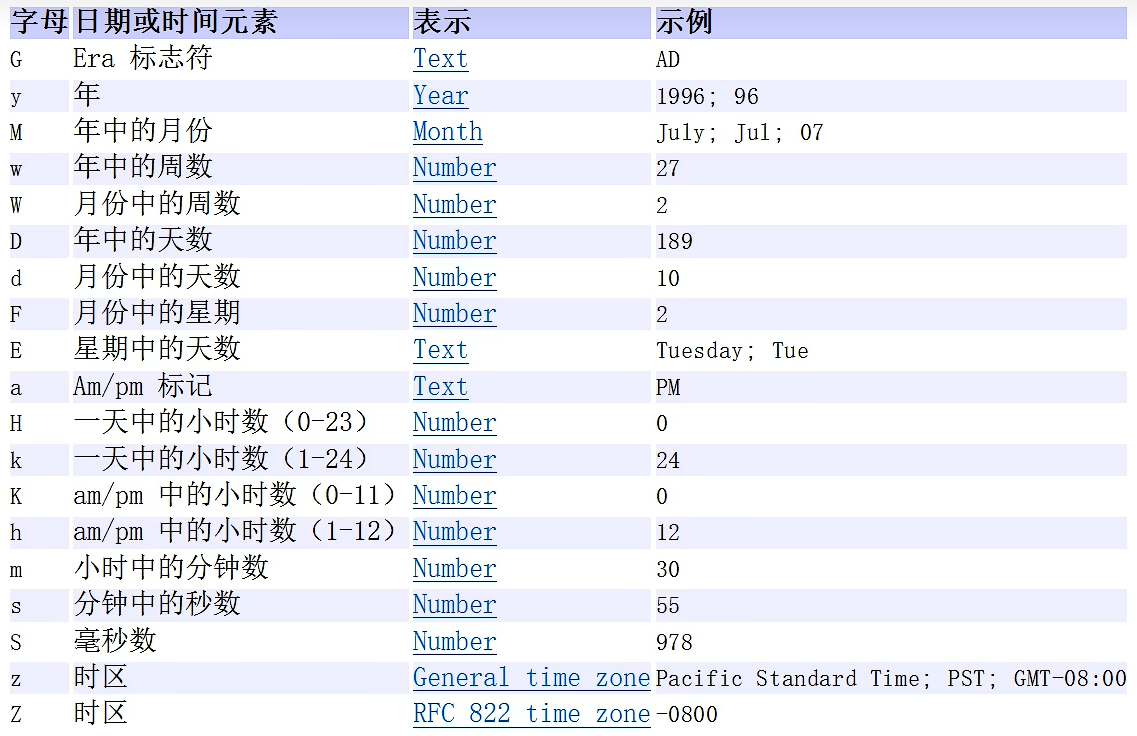
2、SimpleDateFormat:格式和解析日期的类SimpleDateFormat 格式化和解析日期的具体类。它允许进行格式化(日期->文本)、解析(文本->日期)和规范化
3、应用实例
package com13.date_;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title Date01
* @package com13.date_
* @time 2023/1/12 17:12
*/
public class Date01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//解读
//1.获取当前系统时间
//2.这里的Date类是在java.util包
//3.默认输出的日期格式是国外的方式,因此通常需要对格式进行转换
Date date = new Date();//获取当前系统时间
System.out.println("当前日期=" + date);
Date date1 = new Date(9234567);//通过指定毫秒数得到时间
System.out.println("date1=" + date1);//获取某个时间对应的毫秒数
//解读
//1.创建SimpleDateFormat对象,可以指定相应的格式
//2.这里的格式使用的字母是规定好的,不能乱写
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss E");
String format = sdf.format(date);//format 将日期转换成指定格式的字符串
System.out.println("当前日期=" + format);
//解读
//1.可以把一个格式化的String转成对应的Date
//2.得到Date仍然在输出时,还是按照国外的形式,如果希望指定格式输出,需要转换
//3.在把String -> Date 使用sdf格式需要和你给的String的格式一样,否则会抛出转换异常
String s = "1996年01月02日 10:30:45 星期二";
Date parse = sdf.parse(s);
System.out.println("parse=" + sdf.format(parse));
}
}
第二代日期类
1、第二代日期类,主要就是Calendar类(日历)。
public abstract class Calendar extends Object implements Serializable, Cloneable, Comparable<Calendar>
2、Calendar类是一个抽象类,它为特定瞬间与一组诸如YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR等日历室段之间的转换提供了一些方法,并为操作日历字段(例如获得下星期的日期)提供了一些方法。
3、应用实例
package com13.date_;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title Calendar_
* @package com13.date_
* @time 2023/1/12 17:40
*/
public class Calendar_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//解读
//1.Calendar是一个抽象类,并且构造器是private
//2.可以通过getInstance()来获取实例
//3.提供大量的方法和字段提供给程序员
//4.Calendar没有提供对应的格式化的类,因此需要程序员自己组合来输出(灵活)
//5.如果我们需要按照24小时进制来获取时间, Calendar .HOUR =改成=> Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();//创建日历类对象比较简单,自由
// System.out.println("c=" + c);
//2.获取日历对象的某个日历字段
System.out.println("年:" + c.get(Calendar.YEAR));
//这里为什么要 +1,因为Calendar返回月时候,是按照0开始编号
System.out.println("月:" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1));
System.out.println("日:" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("小时:" + c.get(Calendar.HOUR));
System.out.println("分钟:" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println("秒:" + c.get(Calendar.SECOND));
//Calender没有专门的格式化方法,所以需要程序员自己来组合显示
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "年" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "月" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) + "日");
}
}
第三代日期类
前面两代日期类的不足分析
JDK 1.0中包含了一个java.util.Date类,但是它的大多数方法已经在JDK 1.1引入Calendar类之后被弃用了。而Calendar也存在问题是:
1)可变性:像日期和时间这样的类应该是不可变的。
2)偏移性:Date中的年份是从1900开始的,而月份都从0开始。
3)格式化:格式化只对Date有用,Calendar则不行。
4)此外,它们也不是线程安全的;不能处理闰秒等(每隔2天,多出1s)
第三代日期类常见方法
1) LocalDate(日期/年月日)、LocalTime(时间/时分秒)、LocaIDateTime(日期时间/年月日时分秒)JDK8加入
LocalDate只包含日期,可以获取日期字段LocalTime只包含时间,可以获取时间字段
LocalDateTime包含日期+时间,可以获取日期和时间字段
案例演示
package com13.date_;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title LocalDate_
* @package com13.date_
* @time 2023/1/12 18:00
*/
public class LocalDate_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第三代日期
//解读
//1.使用now()返回当前日期时间的对象
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now(); //LocalDate.noW();//LocalTime.now
System.out.println(ldt);
System.out.println("年=" + ldt.getYear());
System.out.println("月=" + ldt.getMonth());
System.out.println("月=" + ldt.getMonthValue());
System.out.println("日=" + ldt.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println("时=" + ldt.getHour());
System.out.println("分=" + ldt.getMinute());
System.out.println("秒=" + ldt.getSecond());
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();//可以获取年月日
LocalTime now1 = LocalTime.now();//可以获取时分秒
System.out.println(now.getYear());
// System.out.println(now.getHour());
System.out.println(now1.getHour());
// ldt.getYear();
// ldt.getMonthValue();
// ldt.getMonth();
// ldt.getDayOfMonth();
// ldt.getHour();
// ldt.getMinute();
// ldt.getSecond();
}
}
2)DateTimeFormatter格式日期类
类似于SimpleDateFormat
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(格式);
String str = dtf.format(日期对象);
案例演示
package com13.date_;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title LocalDate_
* @package com13.date_
* @time 2023/1/12 18:00
*/
public class LocalDate_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第三代日期
//解读
//1.使用now()返回当前日期时间的对象
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now(); //LocalDate.noW();//LocalTime.now
System.out.println(ldt);
//2.使用DateTimeFormatter对象进行格式化
//创建DateTimeFormatter对象
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String str = dtf.format(ldt);
System.out.println("格式化日期=" + str);
}
}
3)Instant时间戳类似于Date
提供了一系列和Date类转换的方式
Instant->Date:
Date date = Date.from(instant);
Date->Instant:
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
案例演示
package com13.date_;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 甲柒
* @version 1.0
* @title Instant_
* @package com13.date_
* @time 2023/1/12 18:20
*/
public class Instant_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.通过静态方法 now()获取表示当前时间戳的对象
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now);
//2.通过 from可以把Instant转成 Date
Date date = Date.from(now);
//3.通过 date的toInstant()可以把 date转成Instant对象
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
}
}
4)第三代日期类更多方法LocalDateTime类
MonthDay类:检查重复事件是否是闰年
增加日期的某个部分
使用plus方法测试增加时间的某个部分
使用minus方法测试查看一年前和一年后的日期