准备工作
服务器:Ubuntu 18
sudo apt install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf(arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc (v7.4, 安装方法: sudo apt install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf))
sudo apt install flex
sudo apt install bison
sudo apt install u-boot-tools
目标开发板
CPU (Exynos4412,四核Cortex-A9,主频为1.4GHz-1.6GHz)
RAM (1GB 双通道 DDR3)
ROM (8GB EMMC)
内核代码下载
git clone https://github.com/jason416/linux.git
Note:移植好的源码见github仓库的iTop4412分支。
文章目录
- 准备工作
- 1 基础知识
- 源码目录
- 设备树
- 2 配置内核
- 2.1 修改存储介质编号
- 2.2 编译内核
- 3 匹配开发板设备树
- 参考
1 基础知识
linux 系统由 User Space 和 Kernel Space 两部分组成,今天是编译Kernel 部分。现代CPU 通常实现不同的工作模式。
以ARM 为例,ARM 实现了7 种工作模式,不同模式下 CPU 可以执行的指令和访问的寄存器是不同的。
- 用户模式 usr
- 系统模式 sys
- 管理模式 svc
- 快速终端 fiq
- 外部中断 irq
- 数据访问终止 abt
- 未定义指令异常
x86 是定义了 4种不同级别的权限,
- Ring0 特权指令,可以访问 IO 设备
- Ring3 很多限制
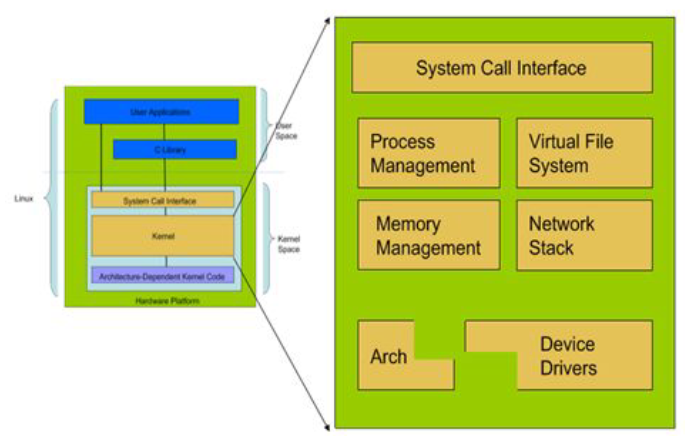
用户空间和内核空间是程序执行的两种不同状态,我们可以通过”系统调用“和”硬件中断“来完成用户空间到内核空间的转移。
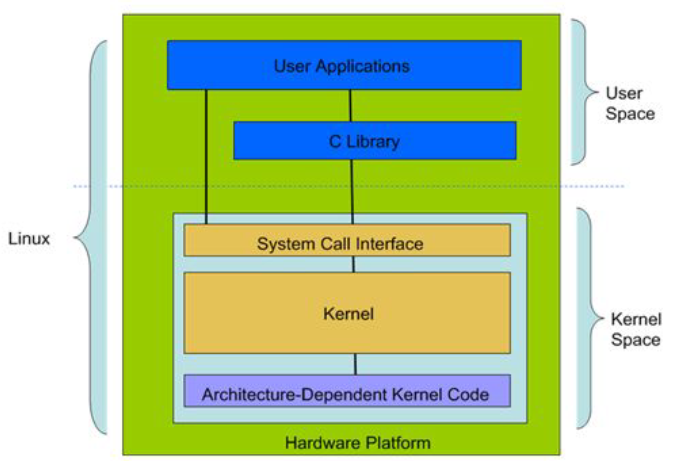
Kernel 里面
• System Call Interface (SCI层)
– 为用户空间提供了一套标准的系统调用函数来访问Linux内核。
• Procees Management(PM)
– 进程管理是创建进程(fork、exec),停止进程(kill、exit),并控制他们之
间的通信(signal等)。还包括进程调度,控制活动进程如何共享CPU
• Memory Management(MM)
– 内存管理的主要作用是控制多个进程安全的共享内存区域
• Device Drivers设备驱动
– Linux内核中有大量的代码在设备驱动程序部分,用于控制特定的硬件设
备。
– Linux驱动一般分为网络设备、块设备、字符设备、杂项设备
• 网络协议栈
– 内核网络协议栈为Linux提供了丰富的网络协议实现。
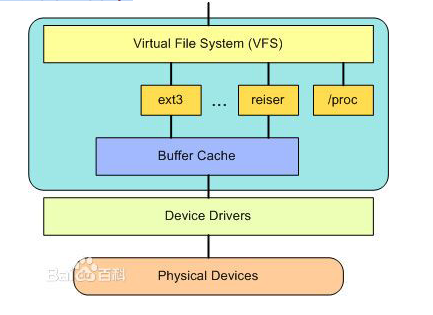
• Virtual File Systems(VFS)
– 虚拟文件系统,隐藏各种文件系统的具体细节,为文件操作提供统一的
接口
– Linux提供了一个大的通用模型,使这个模型包含了所有文件系统功能的
集合(一切皆文件)
源码目录
Linux内核源码采用树形结构。功能相关的文件放到不同的子目录下面,使程序更具有可读行。
arch目录是平台目录。内核支持的所有CPU架构,在该目录下都有对应的子目录。每个CPU的子目录,又进一步分解为boot,mm,kernel等子目录,分别控制系统引导,内存管理,系统调用。还有动态调频,主频率设置部分等
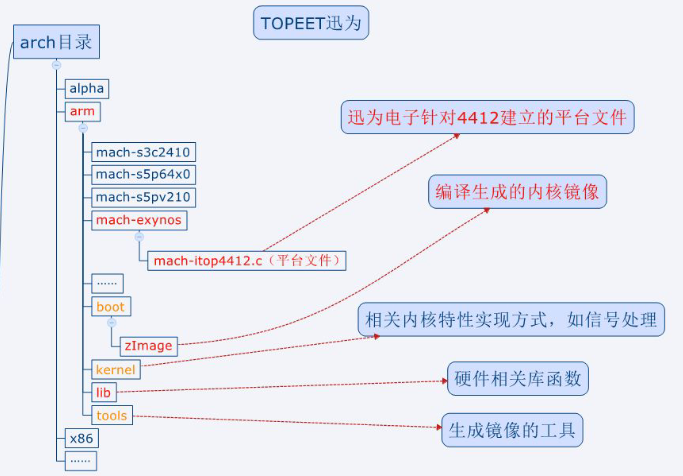
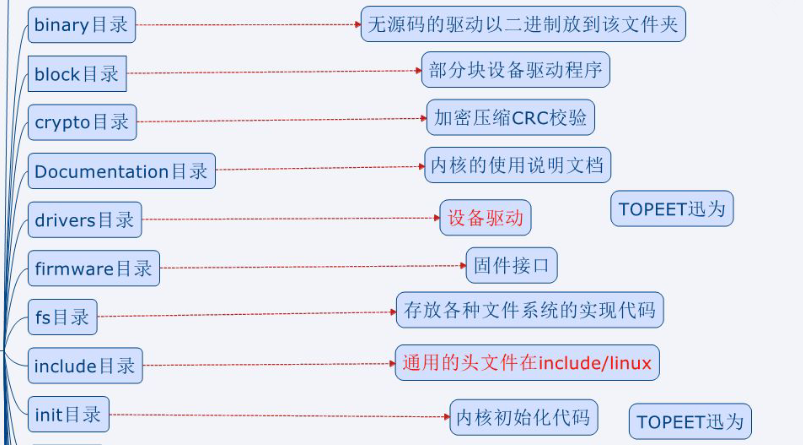
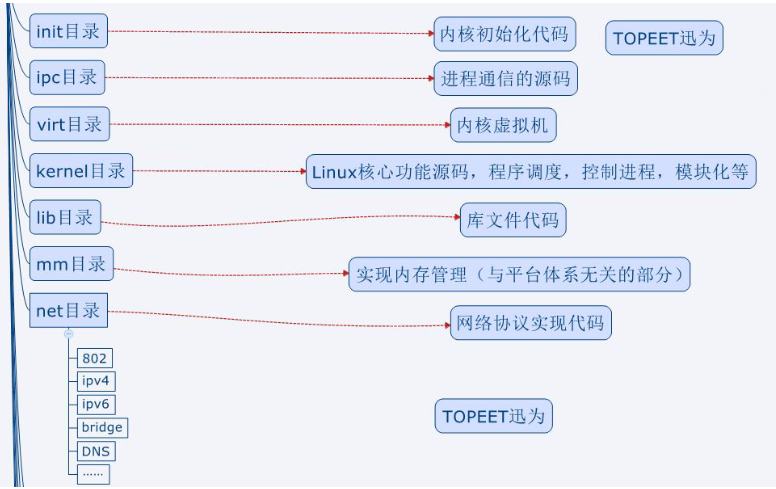
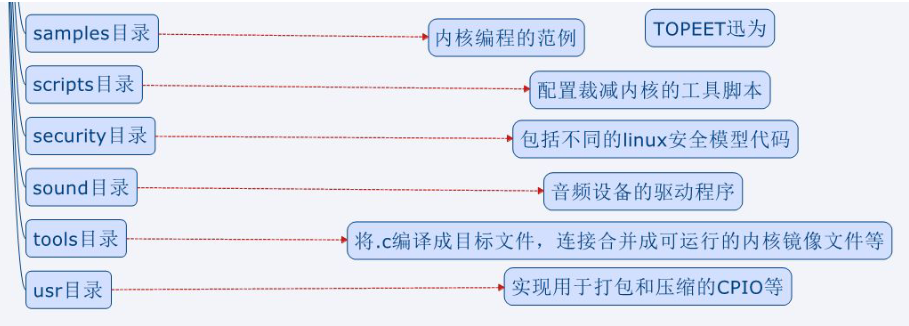
个人觉得,对于红色标记的一部分是需要重点看的,因为作为开发者需要学会使用它,我们要重点学习只是其中很小的一部
分。对架构有一定的了解,学习的重点是驱动开发相关的知识、函数的调用、驱动的协议、硬件知识。
设备树
什么是设备树
设备树device tree,简称dt在linux中用来做参数的表示和传递。在早期的linux版本其实也有参数的表示和传递的行为,例如uboot给kernel通过bootages传参,只不过那种做法并不太好,而设备树则更巧妙的解决了这种问题。
设备树是一个合集,主要包含了dts(device tree source)设备树源文件、dtc(device tree compiler)设备树编译/反编译/调试工具、dtb(device tree blob)二进制设备树镜像文件,dtb其实就是利用dtc将dts编译后的可执行的二进制文件。即.dtb 文件相当于 bin文件 或者 可执行文件,可由 dtc工具将 .dts 编译成 .dtb 文件。
为什么需要设备树
设备树的典型需求就是驱动,我们知道,在内核驱动中通常分为函数(操作方法)和数据,.c用来写函数,.h用来描述寄存器地址或者要写入寄存器的数据。随着芯片越来越多,如果我们把可能用到的各种芯片都写一个.c和.h,那么我们的内核就会有大量的这种芯片驱动的文件,把内核变成一个大胖子,且根本不可能囊括所有芯片。显然这套方法已经无法满足需求,所以就发明了设备树,来解决这个问题。
设备树基本工作原理
基于芯片日益增长的问题,所以内核开发者们引入了新的方法,就是在内核中只保留函数,而数据则不包含,由用户(应用程序员)自己把数据按照规定的格式编写,并放在约定的地方,为了不占用过多的内存,还要求数据以根精简的方式编写。在内核内部专门集成了设备树编译器生成代码,内核编译时先编译内核中用来编译设备树的编译器源码,生成一个设备树专用编译器,新编译器将驱动的数据编译成二进制文件dtb,在移植系统时则需要给设备树一个独立地址段。
boot启动时,传参给内核,告诉内核设备树文件和kernel的位置,内核启动时根据地址去找到设备树文件,再利用专用的编译器去反编译dtb文件,将dtb还原成数据结构,以供驱动的函数去调用。
2 配置内核
进入内核源码目录
~/linux-5.4$ ls
arch COPYING Documentation include Kbuild lib Makefile README security usr
block CREDITS drivers init Kconfig LICENSES mm samples sound virt
certs crypto fs ipc kernel MAINTAINERS net scripts tools
生成默认配置
~/linuux-5.4$ make exynos_defconfig
官方提供了所有三星系列的默认配置,需要先生成一个exynos的配置为基础,再上面再修改成跟板子一致的配置选项即可。
为了避免每次都需要指定ARCH和CROSS_COMPILE变量,可以直接在顶层Makefile直接指定好,如下所示:
选择系统类型
System Type --->
[*] Samsung EXYNOS --->
--- Samsung EXYNOS
[ ] SAMSUNG EXYNOS3
[*] SAMSUNG EXYNOS4
[ ] SAMSUNG EXYNOS5
*** EXYNOS SoCs ***
-*- SAMSUNG EXYNOS4210
[*] SAMSUNG EXYNOS4412
配置调试串口 - 设置为UART2
Kernel hacking --->
[*] Kernel low-level debugging functions (read help!)
Kernel low-level debugging port (Use Samsung S3C UART 2 for low-level debug) --->
开启串口调试驱动
Device Drivers --->
Character devices --->
Serial drivers --->
<*> Samsung SoC serial support
[*] Samsung SoC serial debug
[*] Support for console on Samsung SoC serial port
开启DM96XX网卡驱动
Device Drivers --->
[*] Network device support --->
<*> USB Network Adapters --->
<*> Davicom DM96xx based USB 10/100 ethernet devices
设置内核压缩模式为LZMA(非必须,可减小文件大小)
General setup --->
() Build ID Salt
Kernel compression mode (LZMA) --->
2.1 修改存储介质编号
我们刷写uboot 后,需要查看存储介质的编号。
修改
arch/arm/configs/iTop-4412_scp_defconfig
vim打开,查找
/mmcblk
修改mmcblk0p2

修改后

文件系统为只读
修改 arch/arm/configs/iTop-4412_scp_defconfig,
文件中搜索root .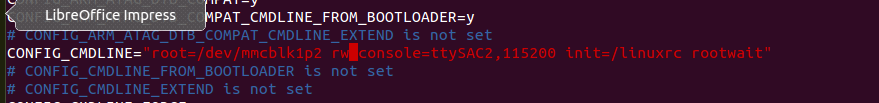 在root=/dev/mmcblk1p2 后面添加 rw,表示文件系统可读可写,否则只能读,就不能新建文件夹和文件.
在root=/dev/mmcblk1p2 后面添加 rw,表示文件系统可读可写,否则只能读,就不能新建文件夹和文件.
2.2 编译内核
~/linux-5.4$ make uImage LOADADDR=0x40008000 -j$(nproc)
...
OBJCOPY arch/arm/boot/zImage
Kernel: arch/arm/boot/zImage is ready
UIMAGE arch/arm/boot/uImage
Image Name: Linux-5.4.47
Created: Sun Jun 21 22:41:40 2020
Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (uncompressed)
Data Size: 5337464 Bytes = 5212.37 KiB = 5.09 MiB
Load Address: 40008000
Entry Point: 40008000
Kernel: arch/arm/boot/uImage is ready
为什么内核启动地址是0x40008000?
在内核目录 /Document/arm/Booting文档中有说明如下:
5. Calling the kernel image
Existing boot loaders: MANDATORY
New boot loaders: MANDATORY
There are two options for calling the kernel zImage. If the zImage
is stored in flash, and is linked correctly to be run from flash,
then it is legal for the boot loader to call the zImage in flash
directly.
The zImage may also be placed in system RAM (at any location) and
called there. Note that the kernel uses 16K of RAM below the image
to store page tables. The recommended placement is 32KiB into RAM.
The recommended placement is 32KiB into RAM
建议将内核放到RAM的32KB处,也就是偏移地址为0x8000处。
三星Exynos4412 内存起始地址为0x40000000,即内核地址为0x40008000

这里需要指定LOADADDR变量,才能生成正确的uImage文件。因为在uboot启动内核时,会先解析uImage中的前64B头信息,定义如下:
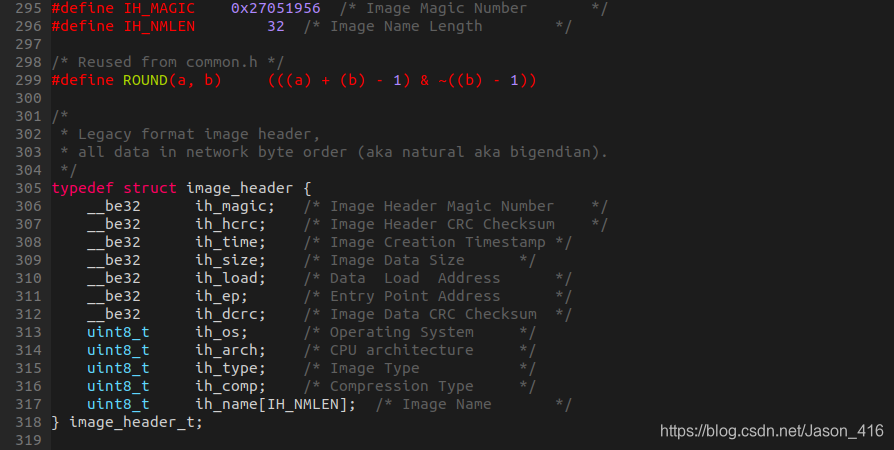
已经能够编译出可以运行的内核
3 匹配开发板设备树
修改
- 屏蔽掉firmware节点(安全相关,firmware是三星的一个固件的设备信息,因为找不到固件,所以内核启动不成功。注释掉29到32行的代码)
- 修改bus_dmc 节点devfreq-events为devfreq-event(因为没有events这个属性,所以我们要把72行的events修改成event)
- 修改regulators 节点参数(参考原理图中的参数,Exynos4412 芯片的POP和SCP两种封装形式,芯片的电源管理都是低功耗动态三星 S5M8767 电源管理架构。)
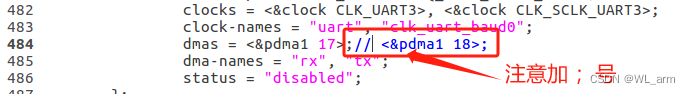
- 解决字符串溢出问题(打开编辑修改exynos4.dtsi文件,注释掉文件中的串口2节点serial_2中的dmas属性)
--- a/arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-itop-scp-core.dtsi
+++ b/arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-itop-scp-core.dtsi
@@ -23,10 +23,12 @@
reg = <0x40000000 0x40000000>;
};
+#if 0
firmware@203f000 {
compatible = "samsung,secure-firmware";
reg = <0x0203F000 0x1000>;
};
+#endif
fixed-rate-clocks {
xxti {
@@ -70,7 +72,7 @@
};
&bus_dmc {
- devfreq-events = <&ppmu_dmc0_3>, <&ppmu_dmc1_3>;
+ devfreq-event = <&ppmu_dmc0_3>, <&ppmu_dmc1_3>;
vdd-supply = <&buck1_reg>;
status = "okay";
};
@@ -167,8 +169,8 @@
regulators {
ldo1_reg: LDO1 {
regulator-name = "VDD_ALIVE";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1100000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <1100000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <1000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <1000000>;
regulator-always-on;
regulator-boot-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
@@ -230,8 +232,8 @@
ldo9_reg: LDO9 {
regulator-name = "VDD33_LCD";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -252,8 +254,8 @@
ldo12_reg: LDO12 {
regulator-name = "VDD33_UOTG";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
regulator-always-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -300,8 +302,8 @@
/* Used by HSIC */
ldo18_reg: LDO18 {
regulator-name = "VDDIOPERI_28";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <2800000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <2800000>;
regulator-always-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -313,15 +315,15 @@
ldo20_reg: LDO20 {
regulator-name = "VDD28_CAM";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1800000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <2800000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
ldo21_reg: LDO21 {
regulator-name = "VDD28_AF";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1800000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <2800000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -341,8 +343,8 @@
ldo24_reg: LDO24 {
regulator-name = "VDD33_A31";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -430,8 +432,8 @@
buck7_reg: BUCK7 {
regulator-name = "pvdd_buck7";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <750000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <2000000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <2050000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <2050000>;
regulator-boot-on;
regulator-always-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
注释掉文件中的串口2节点serial_2中的dmas属性
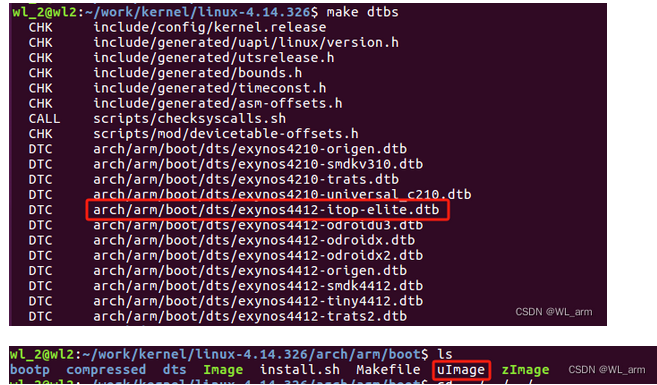
编译dts
~/linux-5.4$ make dtbs
# make dtbs ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-
等待编译结果如下图所示:
即为编译生成的设备树 dtb 文件“exynos4412-itop-elite.dtb” 和内核镜像uImage 。
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/Jason_416/article/details/106772698
https://blog.csdn.net/Eva20192020/article/details/133752417?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502