1. 前言
Spring支持两种事务管理的方式:声明式事务和编程式事务。编程式事务的优点是可以在代码里控制事务的粒度,实现细粒度的事务控制,缺点是对业务代码存在侵入性,代码复杂度较高,一般很少使用。声明式事务的优点是使用简单无侵入性,仅需在方法上加一个@Transactional注解或者通过xml配置即可, 声明式事务通过AOP实现,所以事务的粒度只能是方法级别的。本文重点分析Spring声明式事务的实现原理!!!
开启Spring事务很简单,首先在启动类上添加@EnableTransactionManagement注解,再注入一个PlatformTransactionManager事务管理器即可。
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
}
这样就开启了Spring事务功能,接下来只需要在事务方法上加上@Transactional注解,该方法就会被Spring当作事务方法来处理,发生异常时自动回滚,无异常时自动提交事务。
为什么加一个@EnableTransactionManagement注解就可以开启事务功能呢???
2. @EnableTransactionManagement
首先从这个注解本身突破,看看它做了啥。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
/**
* 是否基于类代理,也就是通过CGLIB
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**
* 默认通过JDK动态代理来增强事务,可选ASPECTJ
*/
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
/**
* Advisor执行的顺序
*/
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@EnableTransactionManagement注解可以配置事务的增强是通过JDK动态代理实现,还是通过CGLIB代理实现,一般推荐使用JDK动态代理。该注解的核心在于它引入了TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类。

TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector是ImportSelector的子类,所以它必须重写ImportSelector#selectImports()方法,Spring会自动注册该方法返回的bean集合。
public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> {
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[]{
AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[]{determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}
private String determineTransactionAspectClass() {
return (ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", getClass().getClassLoader()) ?
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.JTA_TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME :
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
}
}
TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类的目的主要是向Spring容器注册了两个bean:
1、AutoProxyRegistrar
往容器内注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,基于Advisor创建bean代理对象,让bean拥有事务增强的能力。
2、ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
往容器内注册BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor以及依赖的bean,织入该Advisor的bean将拥有事务增强的能力。
由此可见,Spring事务是基于AOP实现的。AutoProxyRegistrar用来创建bean的代理对象,ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration用来注册事务增强器。
3. AutoProxyRegistrar
AutoProxyRegistrar主要用来注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类,它的作用是基于Advisor创建bean的代理对象,如此一来bean就被这些Advisor增强了。
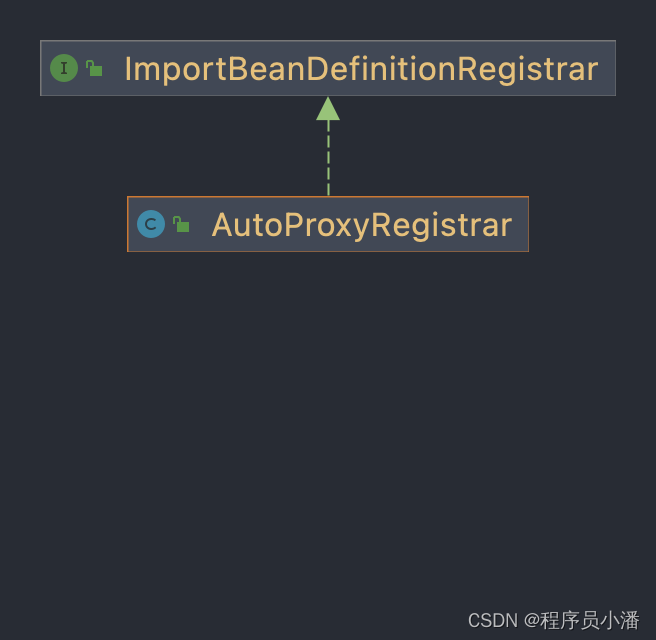
AutoProxyRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,所以要重写ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions()方法,主要是往容器内注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator。
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean candidateFound = false;
Set<String> annTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes();
for (String annType : annTypes) {
AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annType);
if (candidate == null) {
continue;
}
Object mode = candidate.get("mode");
Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass");
if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() &&
Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) {
candidateFound = true;
if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) {
// 注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
4. InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator

InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类就很复杂了,它的主要作用是基于容器内的Advisor给需要被增强的bean创建代理对象。
它通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口,重写postProcessAfterInitialization()方法来增强bean,这个逻辑和AOP是一样的。

关于AOP是如何通过创建代理对象来增强bean的,大家可以查看AOP的文章,这里不再赘述。
5. 哪些bean需要被增强?
这个问题本身其实有点问题,与其说哪些bean需要被增强,倒不如说哪些方法需要被增强?
因为增强(Advice)是应用在连接点(Joinpoint)上的,而Spring AOP仅支持方法级别的连接点,所以是方法需要被增强而不是bean。只不过方法隶属于bean,Spring AOP通过创建代理对象的方式来增强,所以只要bean中有任一方法需要被增强,bean就需要创建代理对象来增强。
连接点是否需要被增强,是通过切点(Pointcut)来判断的,所以PointcutAdvisor接口会关联一个Pointcut:
public interface PointcutAdvisor extends Advisor {
/**
* 获取切点,判断方法是否要增强
*/
Pointcut getPointcut();
}
Pointcut用来判断方法是否需要被增强,所以会关联一个类过滤器ClassFilter和方法匹配器MethodMatcher:
public interface Pointcut {
/**
* 先匹配类
*/
ClassFilter getClassFilter();
/**
* 再匹配方法
*/
MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();
Pointcut TRUE = TruePointcut.INSTANCE;
}
事务增强器是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类,它本身肯定是一个Advisor,所以也会关联一个Pointcut:
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
它关联的是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,默认所有Class都通过,只判断方法是否加了@Transaction注解。
/**
* 目标类的给定方法,是否可以应用事务增强器?
* 条件:方法事务属性不为空,方法事务属性就是通过解析@Transaction注解获取的
* @see AopUtils#canApply(org.springframework.aop.Pointcut, java.lang.Class, boolean)
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PlatformTransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
事务增强器的切点规则我们清楚了,就是判断方法是否具有事务属性TransactionAttribute,即是否加了@Transaction注解。
这个切点规则是在哪里触发的呢???
Spring AOP判断bean是否需要被增强,是通过AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors()查找bean是否有可用的Advisor来判断的。
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
/**
* 查找容器内所有的Advisor:@Aspect类里定义的各种增强方法
*/
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
/**
* 根据切点表达式,过滤出可以应用到beanClass的Advisor
*/
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
/**
* 将ExposeInvocationInterceptor拦截器插入到第一个
* @see ExposeInvocationInterceptor
*/
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
先获取容器内所有的Advisor,再遍历Advisor和bean是否匹配,这个匹配过程就是通过Advisor.Pointcut切点来判断的,方法是AopUtils#canApply(),代码不贴了。
6. ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类的主要作用是往容器内注册了三个与事务息息相关的bean。
@Configuration
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
/**
* 注入事务增强器Advisor
*/
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
/**
* 注入事务属性源
*/
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
/**
* 注入事务增强Advice
* 增强的核心逻辑
*/
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
1、BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
事务增强器,Spring AOP基于它给bean创建代理对象,让bean拥有事务增强的能力。本身不具备事务能力,依赖TransactionInterceptor。
2、TransactionAttributeSource
事务属性源的策略接口,目的是获取事务属性。默认通过SpringTransactionAnnotationParser解析事务方法属性,即解析方法上的@Transaction注解。
3、TransactionInterceptor
事务增强Advice,事务增强的核心逻辑,本质是一个方法拦截器。
7. TransactionInterceptor
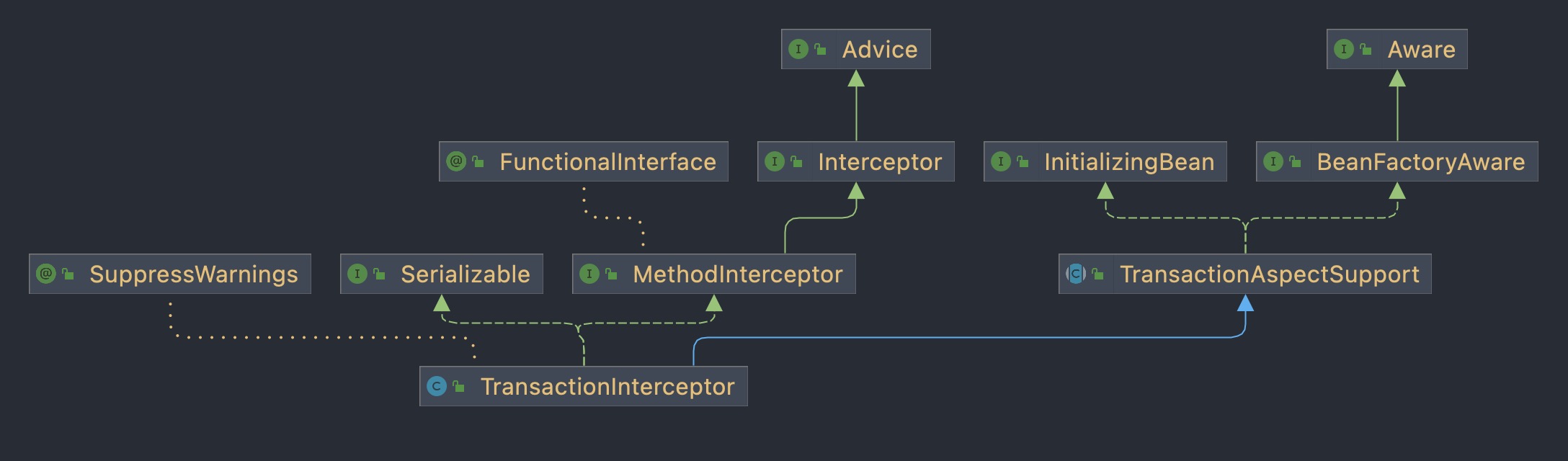
TransactionInterceptor是一个增强Advice,因为Spring AOP连接点只支持方法级别,所以Advice在Spring里面是通过方法拦截器来实现的,所以TransactionInterceptor实现了MethodInterceptor接口,核心在于它重写的invoke()方法。
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
方法以事务的方式去执行,是通过invokeWithinTransaction()实现的,在这个方法里,Spring同时处理了声明式事务和编程式事务两种管理方式,因为对于Spring来说,这两种方式并无太大差别。
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// 事务属性源,用来获取事务方法的事务属性
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 事务属性:隔离级别 传播行为 超时 是否只读等
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 事务管理器
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 事务增强的连接点唯一标识:类全限定名+方法名
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
/**
* 声明式事务和编程式事务,这里统一处理了,对于Spring来说,差别不大
* 编程式事务侵入性太大,重点看声明式事务
*/
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// 声明式事务
/**
* 必要时创建新事务
* 1.当前是否存在事务
* 2.事务传播行为
* 数据库连接已经建立
*/
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// 执行业务方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 异常判断是否回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
// 清理当前线程绑定的TransactionInfo
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 无异常,提交事务 最终:Connection.commit()
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
} else {
// 编程式事务
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
} else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
} else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
} finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
} catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
} catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
} catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
编程式事务用的少,主要看声明式事务的处理。Spring主要做了三件事:
- createTransactionIfNecessary():必要时创建事务。
- completeTransactionAfterThrowing():异常时回滚事务。
- commitTransactionAfterReturning():无异常时提交事务。
7.1 createTransactionIfNecessary()
Spring是否要创建新的事务,主要依据两点:
- 当前是否存在事务
- 目标方法的事务传播行为
当前没有事务,则开启新事务执行目标方法;当前存在事务,则直接执行目标方法。这一点很好理解,但是Spring事务并没有这么简单,即使存在事务也可能创建新事务,因为Spring支持7种事务传播行为。
| 传播行为 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED | 如果当前没有开启事务,就开启一个新事务,如果当前开启了事务,就加入该事务,默认行为。 |
| SUPPORTS | 如果当前开启了事务,就加入该事务,否则非事务执行。 |
| MANDATORY | 如果当前开启了事务,就加入该事务,否则抛出异常。说白了,强制事务,不允许非事务执行。 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 始终创建新事务,如果当前开启了事务,则将当前事务挂起。 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 强制以非事务执行,如果当前开启了事务就将当前事务挂起再执行。 |
| NEVER | 非事务执行,如果当前开启了事务则抛出异常。 |
| NESTED | 如果当前开启了事务,则在嵌套事务内执行,否则开启一个事务执行。 |
是复用事务还是创建新事务,核心在于获取到的事务状态对象TransactionStatus,方法是PlatformTransactionManager#getTransaction():
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
/**
* 获取DataSourceTransactionObject
* 里面有ConnectionHolder,如果当前线程已经持有连接,则复用同一个连接,这是保证事务的基础
*/
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
/**
* 是否已经存在事务,则根据传播行为进一步处理
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.ConnectionHolder#isTransactionActive()
*/
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
}
// 必须在事务中运行,如果当前不存在事务,则报错
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
} else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
// 当前没有事务,挂起null
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 新事务,获取连接,设置连接属性 autoCommit=false
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 设置TransactionSynchronizationManager
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
} else {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
该方法主要做了几件事:
- 获取事务对象DataSourceTransactionObject,里面有ConnectionHolder,通过ThreadLocal获取,如果当前线程已经持有连接,则复用同一个连接,这是保证事务的基础。
- 如果当前已经存在事务,则调用
handleExistingTransaction()根据事务传播行为进一步处理。 - 当前没有事务,则创建新事务,创建新的TransactionStatus对象。
doBegin()开启新事务,获取数据库连接,设置autoCommit=false,将Connection绑定到线程等。prepareSynchronization()设置TransactionSynchronizationManager,将事务信息写入当前线程。
如果当前没有事务,则在doBegin()方法中Spring会获取数据库连接,然后设置连接的属性,其中最重要的属性设置就是autoCommit=false,然后将连接通过ThreadLocal绑定到线程,后续再操作数据库就可以复用同一个Connection了,这是保证事务的基础。
createTransactionIfNecessary()方法执行完,不管是复用事务还是创建新事务,总之事务已经准备好了,Spring现在可以去执行目标方法了,也就是invocation.proceedWithInvocation()。
7.2 completeTransactionAfterThrowing()
目标方法放在try/catch语句里面,一旦目标方法执行异常,Spring就要判断是否需要回滚了。
为啥还要判断是否需要回滚呢?直接回滚不就好了嘛。Spring并不是所有异常都会回滚的,默认必须是RuntimeException才会回滚,否则会提交事务,这一点要注意!!!
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 回滚异常是否匹配,默认只匹配RuntimeException
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
// 异常匹配,事务回滚 最终:Connection.rollback()
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
} catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
} else {
// 异常不匹配,只能提交事务
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
} catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
判断异常是否符合回滚条件的方法是TransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(),默认只匹配RuntimeException或Error。
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}
事务的回滚操作由事务管理器负责,最终会调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#processRollback()来回滚事务,底层还是调用了Connection#rollback(),只不过在回滚事务前后会触发一些事件,以及清理线程事务信息等等。
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
try {
// 触发 beforeCompletion()
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
} else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
doRollback(status);
} else {
// Participating in larger transaction
if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
} else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
} else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
// Unexpected rollback only matters here if we're asked to fail early
if (!isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = false;
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw ex;
}
// 触发 afterCompletion()
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
// Raise UnexpectedRollbackException if we had a global rollback-only marker
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
} finally {
// 清理线程事务信息
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
7.3 commitTransactionAfterReturning()
如果目标方法运行一切正常,那么就会调用commitTransactionAfterReturning()方法来处理目标方法运行后的事务提交,但是不一定会提交事务。
目标方法执行完毕,不一定真的会提交事务,怎么理解???
因为目标方法可能是一个嵌入式事务,或者外层事务触发的一个子事务方法,内层事务是无权替外层事务提交的,这样逻辑就不对了,所以这也是Spring要处理的。
处理事务提交的方法是AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#processCommit():
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
prepareForCommit(status);
// 触发 beforeCommit()
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
// 触发 beforeCompletion()
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
/**
* NESTED传播行为 内嵌事务会开启保存点
* 存在保存点则仅仅是释放保存点,无权替外层事务提交
*/
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 释放保存点
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
} else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
/**
* 新事务/最外层事务 真正的commit操作
*/
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// Connection.commit()
doCommit(status);
} else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
} catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
} catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
} else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
triggerAfterCommit(status);
} finally {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
} finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
- 首先是触发一些事件回调。
- 如果有保存点,说明是
NESTED传播行为开启的内嵌式事务。这种情况下,应该是释放保存点,事务需要等待外层事务判断是否要提交。 status.isNewTransaction()为true代表是新开的事务或者最外层事务,此时需要做真正的事务提交。- 其它情况则不做处理,等待最外层事务提交。
doCommit()底层最终会调用Connection#commit()方法提交事务。
8. Connection复用
事务是基于连接的,要保证多次数据库操作在同一个事务内,首先得保证使用的是同一个连接,即同一个Connection对象。
Spring在开启一个新事务的时候,DataSourceTransactionManager#doBegin()会获取数据库连接Connection,然后将其包装成ConnectionHolder对象。那如何让下次数据库操作复用同一个连接呢?Spring的做法是将Connection写入ThreadLocal,方法是TransactionSynchronizationManager#bindResource():
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
// DataSource对象作为Key
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");
// ThreadLocal取出Map
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
// set ThreadLocal Map if none found
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap<>();
resources.set(map);
}
// 指定数据源对应的连接ConnectionHolder 写入ThreadLocal
Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
if (oldValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already value [" + oldValue + "] for key [" +
actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Bound value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
}
下次操作数据库时,优先通过TransactionSynchronizationManager#doGetResource()从ThreadLocal获取连接对象,如果已经有了连接则复用同一个连接。
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
// 从ThreadLocal取出Map
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
// 获取数据源对应的连接,如果已有连接,则复用
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
但是,还有一个问题需要解决。事务是上层功能,作为操作DB的底层类而言是不知道有没有开启事务的,也就是说,每次操作完数据库都会把Connection给释放掉,如果连接被关闭,事务就无从谈起了,Spring是怎么解决的呢???
以JdbcTemplate#execute()为例,JdbcTemplate执行完SQL语句后,会在finally释放掉Connection。
public <T> T execute(StatementCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
// 获取连接,如果ThreadLocal有,则复用连接
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 执行SQL
stmt = con.createStatement();
applyStatementSettings(stmt);
T result = action.doInStatement(stmt);
handleWarnings(stmt);
return result;
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock
// in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet.
String sql = getSql(action);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
stmt = null;
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
con = null;
throw translateException("StatementCallback", sql, ex);
} finally {
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
// 释放连接
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
}
}
核心就在DataSourceUtils#doReleaseConnection(),Spring并不会无脑关闭连接,而是判断要释放的连接和ThreadLocal里的事务连接是不是同一个,如果是的话就不能关闭连接了,仅仅是扣减一下Connection的引用次数。
public static void doReleaseConnection(@Nullable Connection con, @Nullable DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
if (con == null) {
return;
}
if (dataSource != null) {
// 如果要关闭的连接和ThreadLocal里的是同一个
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
if (conHolder != null && connectionEquals(conHolder, con)) {
// 事务连接,不能关闭,仅仅是扣减引用次数
conHolder.released();
return;
}
}
// 真正的关闭连接,当然,也可能是归还到连接池
doCloseConnection(con, dataSource);
}





![P4391 [BOI2009]Radio Transmission 无线传输](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e4680246c010499a9b8663b05072dd18.png)