1 背景
在之前的几篇文章中,不管是通过构建SL图《自动驾驶---Motion Planning之Path Boundary》,ST图《自动驾驶---Motion Planning之Speed Boundary》,又或者是构建SLT图《自动驾驶---Motion Planning之构建SLT Driving Corridor》,最终我们都是为了得到boundary的信息。
构造优化问题求解的前提:首先确定问题的代价函数,有初值,有边界(约束),接下来就可以进行求解了。 在之前的博客《自动驾驶---Motion Planning之轨迹Path优化》中讨论过横向的优化过程。本篇博客笔者继续阐述Apollo中纵向轨迹优化的问题。
2 轨迹纵向优化
前面也提到过,在Apollo中,横纵向的优化求解是解耦开的,因此在横纵向分别需要求解一次,最终得到得到横纵向的轨迹信息(s,s',s'',l,l',l'')------这里的 是
关于
的一阶导数,
是
关于
的一阶导数。
整体轨迹优化器的代码位于/apollo/modules/planning/tasks/optimizers。

2.1 构造优化问题
二次规划问题的形式:
其中是由二阶导构成的Hessian矩阵,
是由梯度构成的Jacobi矩阵;然后包括m个等式约束集合和n个不等约束集合。
Speed优化问题的自变量为:。
论文中主要考虑了纵向加速度、纵向Jerk、向心加速度、接近参考速度、终点的s,s'以及s''的限制,同样的在Apollo开源项目中增加了所有点的更接近参考线的惩罚函数。
论文中的代价函数如下所示:
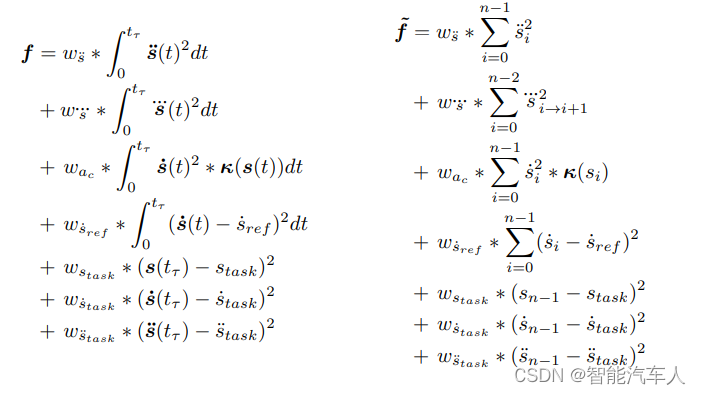
Apollo开源项目中的代价函数如下所示:
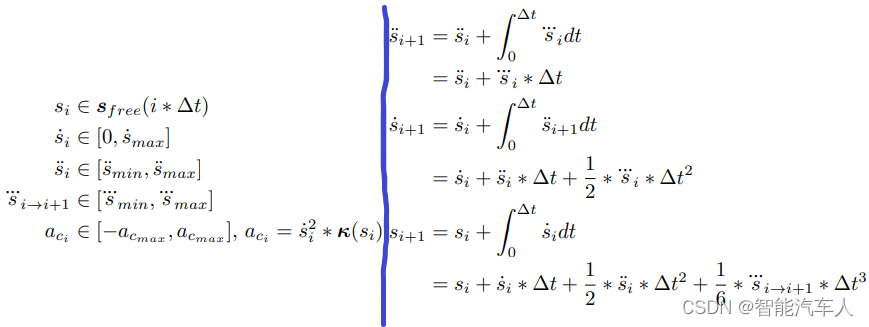
2.2 约束条件
接下来考虑的是约束条件(不等式约束+等式约束)。不等式约束主要考虑包括自车的速度,加速度,jerk以及向心加速度,等式约束主要考虑的是采样点之间s,s',s''的连续性。
2.3 求解二次规划问题
将2.1.2小节得到的代价函数依据阶次整理得到:
先看speed optimizer的Process()函数:
Status PiecewiseJerkSpeedOptimizer::Process(const PathData& path_data,
const TrajectoryPoint& init_point,
SpeedData* const speed_data) {
if (reference_line_info_->ReachedDestination()) {
return Status::OK();
}
ACHECK(speed_data != nullptr);
// 获取speed初值
SpeedData reference_speed_data = *speed_data;
if (path_data.discretized_path().empty()) {
std::string msg("Empty path data");
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// 得到speed decider等模块获取的st图
StGraphData& st_graph_data = *reference_line_info_->mutable_st_graph_data();
const auto& veh_param =
common::VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param();
std::array<double, 3> init_s = {0.0, st_graph_data.init_point().v(),
st_graph_data.init_point().a()};
double delta_t = 0.1;
double total_length = st_graph_data.path_length();
double total_time = st_graph_data.total_time_by_conf();
int num_of_knots = static_cast<int>(total_time / delta_t) + 1;
PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem piecewise_jerk_problem(num_of_knots, delta_t,
init_s);
// 设置权重系数和部分约束
const auto& config = config_.piecewise_jerk_speed_optimizer_config();
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_weight_ddx(config.acc_weight());
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_weight_dddx(config.jerk_weight());
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_x_bounds(0.0, total_length);
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dx_bounds(
0.0, std::fmax(FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit,
st_graph_data.init_point().v()));
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_ddx_bounds(veh_param.max_deceleration(),
veh_param.max_acceleration());
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dddx_bound(FLAGS_longitudinal_jerk_lower_bound,
FLAGS_longitudinal_jerk_upper_bound);
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dx_ref(config.ref_v_weight(),
reference_line_info_->GetCruiseSpeed());
// Update STBoundary
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> s_bounds;
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {
double curr_t = i * delta_t;
double s_lower_bound = 0.0;
double s_upper_bound = total_length;
for (const STBoundary* boundary : st_graph_data.st_boundaries()) {
double s_lower = 0.0;
double s_upper = 0.0;
if (!boundary->GetUnblockSRange(curr_t, &s_upper, &s_lower)) {
continue;
}
switch (boundary->boundary_type()) {
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::STOP:
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::YIELD:
s_upper_bound = std::fmin(s_upper_bound, s_upper);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::FOLLOW:
// TODO(Hongyi): unify follow buffer on decision side
s_upper_bound = std::fmin(s_upper_bound, s_upper - 8.0);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::OVERTAKE:
s_lower_bound = std::fmax(s_lower_bound, s_lower);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (s_lower_bound > s_upper_bound) {
std::string msg("s_lower_bound larger than s_upper_bound on STGraph!");
AERROR << msg;
speed_data->clear();
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
s_bounds.emplace_back(s_lower_bound, s_upper_bound);
}
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_x_bounds(std::move(s_bounds));
// Update SpeedBoundary and ref_s
std::vector<double> x_ref;
std::vector<double> penalty_dx;
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> s_dot_bounds;
const SpeedLimit& speed_limit = st_graph_data.speed_limit();
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {
double curr_t = i * delta_t;
// get path_s
SpeedPoint sp;
reference_speed_data.EvaluateByTime(curr_t, &sp);
const double path_s = sp.s();
x_ref.emplace_back(path_s);
// get curvature
PathPoint path_point = path_data.GetPathPointWithPathS(path_s);
penalty_dx.push_back(std::fabs(path_point.kappa()) *
config.kappa_penalty_weight());
// get v_upper_bound
const double v_lower_bound = 0.0;
double v_upper_bound = FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit;
v_upper_bound = speed_limit.GetSpeedLimitByS(path_s);
s_dot_bounds.emplace_back(v_lower_bound, std::fmax(v_upper_bound, 0.0));
}
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_x_ref(config.ref_s_weight(), std::move(x_ref));
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_penalty_dx(penalty_dx);
piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dx_bounds(std::move(s_dot_bounds));
// Solve the problem
if (!piecewise_jerk_problem.Optimize()) {
std::string msg("Piecewise jerk speed optimizer failed!");
AERROR << msg;
speed_data->clear();
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// Extract output
const std::vector<double>& s = piecewise_jerk_problem.opt_x();
const std::vector<double>& ds = piecewise_jerk_problem.opt_dx();
const std::vector<double>& dds = piecewise_jerk_problem.opt_ddx();
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {
ADEBUG << "For t[" << i * delta_t << "], s = " << s[i] << ", v = " << ds[i]
<< ", a = " << dds[i];
}
speed_data->clear();
speed_data->AppendSpeedPoint(s[0], 0.0, ds[0], dds[0], 0.0);
for (int i = 1; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {
// Avoid the very last points when already stopped
if (ds[i] <= 0.0) {
break;
}
speed_data->AppendSpeedPoint(s[i], delta_t * i, ds[i], dds[i],
(dds[i] - dds[i - 1]) / delta_t);
}
SpeedProfileGenerator::FillEnoughSpeedPoints(speed_data);
RecordDebugInfo(*speed_data, st_graph_data.mutable_st_graph_debug());
return Status::OK();
}
其中的二次项系数构建P矩阵的过程:
void PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem::CalculateKernel(std::vector<c_float>* P_data,
std::vector<c_int>* P_indices,
std::vector<c_int>* P_indptr) {
const int n = static_cast<int>(num_of_knots_);
const int kNumParam = 3 * n;
const int kNumValue = 4 * n - 1;
std::vector<std::vector<std::pair<c_int, c_float>>> columns;
columns.resize(kNumParam);
int value_index = 0;
// x(i)^2 * w_x_ref
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
columns[i].emplace_back(
i, weight_x_ref_ / (scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[0]));
++value_index;
}
// x(n-1)^2 * (w_x_ref + w_end_x)
columns[n - 1].emplace_back(n - 1, (weight_x_ref_ + weight_end_state_[0]) /
(scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[0]));
++value_index;
// x(i)'^2 * (w_dx_ref + penalty_dx)
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
columns[n + i].emplace_back(n + i,
(weight_dx_ref_ + penalty_dx_[i]) /
(scale_factor_[1] * scale_factor_[1]));
++value_index;
}
// x(n-1)'^2 * (w_dx_ref + penalty_dx + w_end_dx)
columns[2 * n - 1].emplace_back(
2 * n - 1, (weight_dx_ref_ + penalty_dx_[n - 1] + weight_end_state_[1]) /
(scale_factor_[1] * scale_factor_[1]));
++value_index;
auto delta_s_square = delta_s_ * delta_s_;
// x(i)''^2 * (w_ddx + 2 * w_dddx / delta_s^2)
columns[2 * n].emplace_back(2 * n,
(weight_ddx_ + weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square) /
(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));
++value_index;
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; ++i) {
columns[2 * n + i].emplace_back(
2 * n + i, (weight_ddx_ + 2.0 * weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square) /
(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));
++value_index;
}
columns[3 * n - 1].emplace_back(
3 * n - 1,
(weight_ddx_ + weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square + weight_end_state_[2]) /
(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));
++value_index;
// -2 * w_dddx / delta_s^2 * x(i)'' * x(i + 1)''
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
columns[2 * n + i].emplace_back(2 * n + i + 1,
-2.0 * weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square /
(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));
++value_index;
}
CHECK_EQ(value_index, kNumValue);
int ind_p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < kNumParam; ++i) {
P_indptr->push_back(ind_p);
for (const auto& row_data_pair : columns[i]) {
P_data->push_back(row_data_pair.second * 2.0);
P_indices->push_back(row_data_pair.first);
++ind_p;
}
}
P_indptr->push_back(ind_p);
}构建一次项矩阵的过程:
void PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem::CalculateOffset(std::vector<c_float>* q) {
CHECK_NOTNULL(q);
const int n = static_cast<int>(num_of_knots_);
const int kNumParam = 3 * n;
q->resize(kNumParam);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (has_x_ref_) {
q->at(i) += -2.0 * weight_x_ref_ * x_ref_[i] / scale_factor_[0];
}
if (has_dx_ref_) {
q->at(n + i) += -2.0 * weight_dx_ref_ * dx_ref_ / scale_factor_[1];
}
}
if (has_end_state_ref_) {
q->at(n - 1) +=
-2.0 * weight_end_state_[0] * end_state_ref_[0] / scale_factor_[0];
q->at(2 * n - 1) +=
-2.0 * weight_end_state_[1] * end_state_ref_[1] / scale_factor_[1];
q->at(3 * n - 1) +=
-2.0 * weight_end_state_[2] * end_state_ref_[2] / scale_factor_[2];
}
}
约束矩阵的构造同Path Optimizer:
void PiecewiseJerkProblem::CalculateAffineConstraint(
std::vector<c_float>* A_data, std::vector<c_int>* A_indices,
std::vector<c_int>* A_indptr, std::vector<c_float>* lower_bounds,
std::vector<c_float>* upper_bounds) {
// 3N params bounds on x, x', x''
// 3(N-1) constraints on x, x', x''
// 3 constraints on x_init_
const int n = static_cast<int>(num_of_knots_);
const int num_of_variables = 3 * n;
const int num_of_constraints = num_of_variables + 3 * (n - 1) + 3;
lower_bounds->resize(num_of_constraints);
upper_bounds->resize(num_of_constraints);
std::vector<std::vector<std::pair<c_int, c_float>>> variables(
num_of_variables);
int constraint_index = 0;
// set x, x', x'' bounds
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_variables; ++i) {
if (i < n) {
variables[i].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
x_bounds_[i].first * scale_factor_[0];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
x_bounds_[i].second * scale_factor_[0];
} else if (i < 2 * n) {
variables[i].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
dx_bounds_[i - n].first * scale_factor_[1];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
dx_bounds_[i - n].second * scale_factor_[1];
} else {
variables[i].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
ddx_bounds_[i - 2 * n].first * scale_factor_[2];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
ddx_bounds_[i - 2 * n].second * scale_factor_[2];
}
++constraint_index;
}
CHECK_EQ(constraint_index, num_of_variables);
// x(i->i+1)''' = (x(i+1)'' - x(i)'') / delta_s
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < n; ++i) {
variables[2 * n + i].emplace_back(constraint_index, -1.0);
variables[2 * n + i + 1].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
dddx_bound_.first * delta_s_ * scale_factor_[2];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) =
dddx_bound_.second * delta_s_ * scale_factor_[2];
++constraint_index;
}
// x(i+1)' - x(i)' - 0.5 * delta_s * x(i)'' - 0.5 * delta_s * x(i+1)'' = 0
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < n; ++i) {
variables[n + i].emplace_back(constraint_index, -1.0 * scale_factor_[2]);
variables[n + i + 1].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0 * scale_factor_[2]);
variables[2 * n + i].emplace_back(constraint_index,
-0.5 * delta_s_ * scale_factor_[1]);
variables[2 * n + i + 1].emplace_back(constraint_index,
-0.5 * delta_s_ * scale_factor_[1]);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) = 0.0;
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) = 0.0;
++constraint_index;
}
// x(i+1) - x(i) - delta_s * x(i)'
// - 1/3 * delta_s^2 * x(i)'' - 1/6 * delta_s^2 * x(i+1)''
auto delta_s_sq_ = delta_s_ * delta_s_;
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < n; ++i) {
variables[i].emplace_back(constraint_index,
-1.0 * scale_factor_[1] * scale_factor_[2]);
variables[i + 1].emplace_back(constraint_index,
1.0 * scale_factor_[1] * scale_factor_[2]);
variables[n + i].emplace_back(
constraint_index, -delta_s_ * scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[2]);
variables[2 * n + i].emplace_back(
constraint_index,
-delta_s_sq_ / 3.0 * scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[1]);
variables[2 * n + i + 1].emplace_back(
constraint_index,
-delta_s_sq_ / 6.0 * scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[1]);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) = 0.0;
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) = 0.0;
++constraint_index;
}
// constrain on x_init
variables[0].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) = x_init_[0] * scale_factor_[0];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) = x_init_[0] * scale_factor_[0];
++constraint_index;
variables[n].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) = x_init_[1] * scale_factor_[1];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) = x_init_[1] * scale_factor_[1];
++constraint_index;
variables[2 * n].emplace_back(constraint_index, 1.0);
lower_bounds->at(constraint_index) = x_init_[2] * scale_factor_[2];
upper_bounds->at(constraint_index) = x_init_[2] * scale_factor_[2];
++constraint_index;
CHECK_EQ(constraint_index, num_of_constraints);
int ind_p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_variables; ++i) {
A_indptr->push_back(ind_p);
for (const auto& variable_nz : variables[i]) {
// coefficient
A_data->push_back(variable_nz.second);
// constraint index
A_indices->push_back(variable_nz.first);
++ind_p;
}
}
// We indeed need this line because of
// https://github.com/oxfordcontrol/osqp/blob/master/src/cs.c#L255
A_indptr->push_back(ind_p);
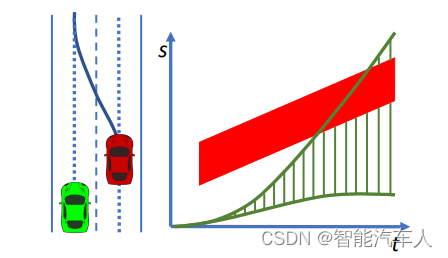
}最终根据不同地决策结果优化求解可得到下图中类似的曲线:
3 总结
总体看下来,如果对path optimizer比较熟悉的读者,对于speed optimizer应该可以很快的看懂整个过程,因为两者有着比较高的相似度。同时读者也会对二次规划问题有了更深的认识,二次规划问题的“三部曲”(1)构造代价函数(2)构造约束(3)QP求解。
自此,整个行车部分的planning模块讲解基本完结(还剩下STSC的轨迹优化问题),前面对Routing,Behavior Planning,Motion Planning等模块的内容都分别做了比较详细的阐述。后续会针对泊车部分、感知以及控制等其他模块开设博客,欢迎读者朋友们关注。