目录
一、实验拓扑
1.1通用配置
1.1.1地址配置
1.1.2静态缺省指向R5,实现公网互通
1.1.3MGRE协议配置
1.1.4配置静态
二、Shortcut方式
三、Normal方式(非shortcut)
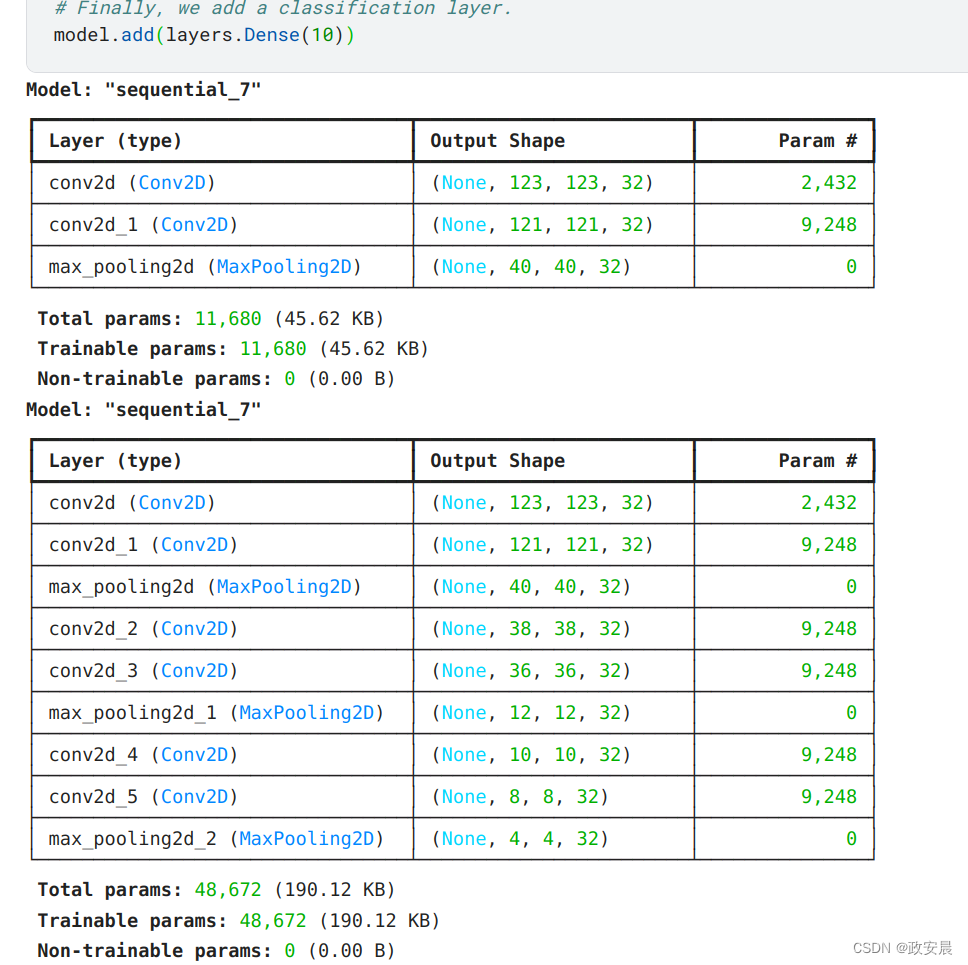
四、总结
一、实验拓扑
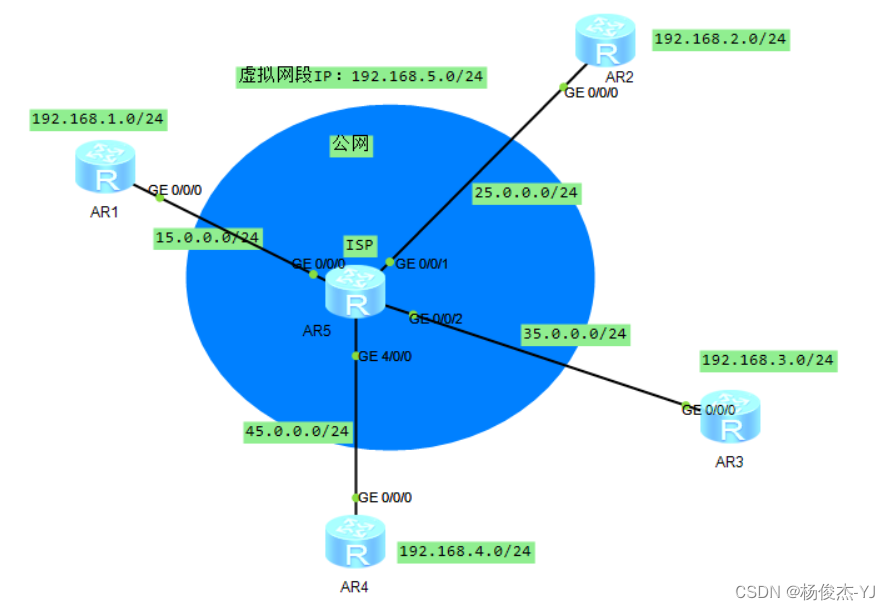
下面两种配置方法皆使用静态方式
1.1通用配置
1.1.1地址配置
[R1]int g0/0/0
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 15.0.0.1 24
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R1-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.1.1 24
[R2]int g0/0/0
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 25.0.0.1 24
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R2-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.2.1 24
[R3]int g0/0/0
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 35.0.0.1 24
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R3-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.3.1 24
[R4]int g0/0/0
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 45.0.0.1 24
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R4-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.4.1 24
[ISP]int g0/0/0
[ISP-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 15.0.0.2 24
[ISP-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[ISP-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 25.0.0.2 24
[ISP-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int g0/0/2
[ISP-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]ip add 5.0.0.2 243
[ISP-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]int g4/0/0
[ISP-GigabitEthernet4/0/0]ip add 45.0.0.2 24
[ISP-GigabitEthernet4/0/0]int l0
[ISP-LoopBack0]ip add 5.5.5.5 241.1.2静态缺省指向R5,实现公网互通
[R1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 15.0.0.2
[R2]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 25.0.0.2
[R3]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 35.0.0.2
[R4]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 45.0.0.2测试,实现公网的互通
1.1.3MGRE协议配置
[R1]int t0/0/0
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 192.168.5.1 24
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp 修改接口的封装协议为MGRE
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]source 15.0.0.1
[R2]int t0/0/0
[R2-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 192.168.5.2 24
[R2-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R2-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 192.168.5.1 15.0.0.1 register
第一个IP为隧道地址,第二个为物理地址
1、告知本端,hub节点的隧道IP与物理IP的对应关系;
2、向hub节点注册本地的隧道IP与物理IP的对应关系;
[R2-Tunnel0/0/0]source g0/0/0 规定封装源为GE0/0/0接口的IP地址
[R3]int t0/0/0
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]ip ad 192.168.5.3 24
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 192.168.5.1 15.0.0.1 register
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]source g0/0/0
[R4]int t0/0/0
[R4-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 192.168.5.4 24
[R4-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R4-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 192.168.5.1 15.0.0.1 register
[R4-Tunnel0/0/0]source g0/0/01.1.4配置静态
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.2
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.3
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.4二、Shortcut方式
[R2]undo ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.4
[R2]undo ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.3
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R3]undo ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.4
[R3]undo ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.2
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R4]undo ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.3
[R4]undo ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.2
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.1在R1上开启重定向
[R1]int t0/0/0
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp redirect
[R2]int t0/0/0
[R2-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp shortcut
在spoke节点配置,使能shortcut功能,未开启该功能,则代表分支站点无法响应重定向报文。
[R4]int t0/0/0
[R4-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp shortcut 三、Normal方式(非shortcut)
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.4
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.3
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.4.0 24 192.168.5.4
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.2
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 192.168.5.1
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.3.0 24 192.168.5.3
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 192.168.5.2
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 192.168.5.1四、总结
- shortcut方式:分支路由汇聚到总部,每一个分支编写的路由信息的下一跳均为hub节点
- 非shortcut方式:非便捷方式,分支之间相互学习路由。下一跳分别是分支的隧道IP地址。而非hub节点
1、配置上:
- shortcut方式,针对静态路由,走向的下一跳都是去Hub站点。且为了使得选路优化,需要在Hub上进行重定向操作,在spoke节点上开启快捷方式
- 非shortcut方式,针对静态路由,走向的 下一跳是去对应网段的隧道地址的下一跳,Hub和Spoke无需过多操作
2、原理上:shortcut方式比非shortcut方式多了一个重定向。
![[C++]内联函数(内联函数的概念,内联函数的特性,内联函数与宏的区别)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/66e1ed2b15e640a49efd8a8f5028c826.png)