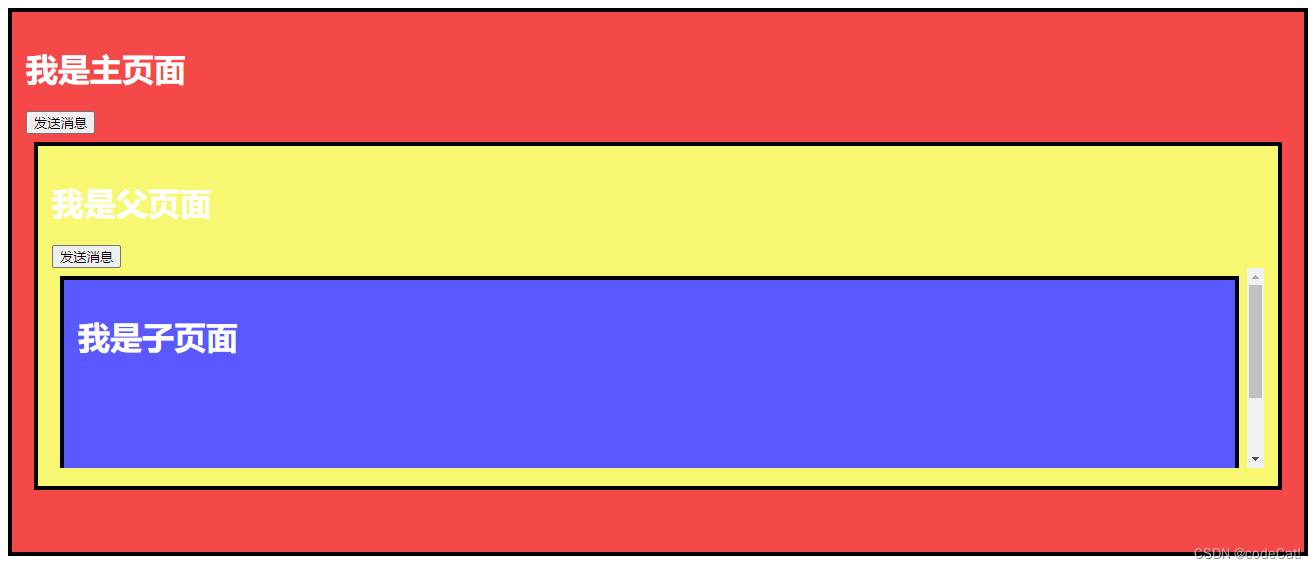
在上一集的坐牢文章中,我们介绍了非官方的很多中方案,其中不乏一些江湖秘术。今天的这个,绝对的正统,纯正的官方打造。我们赶紧来看看。
1.什么是CORS?
CORS 是一个 W3C 标准,全称是“跨域资源共享”(Cross-origin resource sharing)。它允许浏览器向跨域的服务器,发出XMLHttpRequest请求,从而克服了 AJAX 只能同源使用的限制。
CORS 需要浏览器和服务器同时支持。目前,所有浏览器都支持该功能。
整个 CORS 通信过程,都是浏览器自动完成,不需要用户参与。对于开发者来说,CORS 通信与普通的 AJAX 通信没有差别,代码完全一样。浏览器一旦发现 AJAX 请求跨域,就会自动添加一些附加的头信息,有时还会多出一次附加的请求,但用户不会有感知。因此,实现 CORS 通信的关键是服务器。只要服务器实现了 CORS 接口,就可以跨域通信。
到底是官方,就这么简单。
2.CORS的两种请求
CORS 请求分成两类:简单请求(simple request)和非简单请求(not-so-simple request)。
只要同时满足以下两大条件,就属于简单请求。
1.请求方法是
HEAD、GET、POST之一
2.HTTP 的头信息不超出以下几种字段。
- Accept
- Accept-Language
- Content-Language
- Last-Event-ID
- Content-Type:只限于三个值
application/x-www-form-urlencoded、multipart/form-data、text/plain
凡是不同时满足上面两个条件,就属于非简单请求。一句话,简单请求就是简单的 HTTP 方法与简单的 HTTP 头信息的结合。
这样划分的原因是,表单在历史上一直可以跨域发出请求。简单请求就是表单请求,浏览器沿袭了传统的处理方式,不把行为复杂化,否则开发者可能转而使用表单,规避 CORS 的限制。对于非简单请求,浏览器会采用新的处理方式。
2.1 简单请求
2.1.1 基本流程
对于简单请求,浏览器直接发出 CORS 请求。具体来说,就是在头信息之中,增加一个Origin字段。
下面是一个例子,浏览器发现这次跨域 AJAX 请求是简单请求,就自动在头信息之中,添加一个Origin字段。
GET /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Host: api.alice.com
Accept-Language: en-US
Connection: keep-alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
上面的头信息中,Origin字段用来说明,本次请求来自哪个域(协议 + 域名 + 端口)。服务器根据这个值,决定是否同意这次请求。
如果Origin指定的源,不在许可范围内,服务器会返回一个正常的 HTTP 回应。浏览器发现,这个回应的头信息没有包含Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段(详见下文),就知道出错了,从而抛出一个错误,被XMLHttpRequest的onerror回调函数捕获。注意,这种错误无法通过状态码识别,因为 HTTP 回应的状态码有可能是200。
如果Origin指定的域名在许可范围内,服务器返回的响应,会多出几个头信息字段。
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://api.bob.com
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: FooBar
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
上面的头信息之中,有三个与 CORS 请求相关的字段,都以Access-Control-开头。
(1)Access-Control-Allow-Origin
该字段是必须的。它的值要么是请求时Origin字段的值,可以是一个*,表示接受任意域名的请求。
(2)Access-Control-Allow-Credentials
该字段可选。它的值是一个布尔值,表示是否允许发送 Cookie。默认情况下,Cookie 不包括在 CORS 请求之中。设为true,即表示服务器明确许可,浏览器可以把 Cookie 包含在请求中,一起发给服务器。这个值也只能设为true,如果服务器不要浏览器发送 Cookie,不发送该字段即可。
(3)Access-Control-Expose-Headers
该字段可选。CORS 请求时,XMLHttpRequest对象的getResponseHeader()方法只能拿到6个服务器返回的基本字段:Cache-Control、Content-Language、Content-Type、Expires、Last-Modified、Pragma。如果想拿到其他字段,就必须在Access-Control-Expose-Headers里面指定。上面的例子指定,getResponseHeader('FooBar')可以返回FooBar字段的值。
2.1.2 withCredentials 属性
上面说到,CORS 请求默认不包含 Cookie 信息(以及 HTTP 认证信息等),这是为了降低 CSRF 攻击的风险。但是某些场合,服务器可能需要拿到 Cookie,这时需要服务器显式指定Access-Control-Allow-Credentials字段,告诉浏览器可以发送 Cookie。
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
同时,开发者必须在 AJAX 请求中打开withCredentials属性。
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.withCredentials = true;
否则,即使服务器要求发送 Cookie,浏览器也不会发送。或者,服务器要求设置 Cookie,浏览器也不会处理。
但是,有的浏览器默认将withCredentials属性设为true。这导致如果省略withCredentials设置,这些浏览器可能还是会一起发送 Cookie。这时,可以显式关闭withCredentials。
建议设置,使用AJAX是显示关闭withCredentials需要使用的时候在进行开启。
xhr.withCredentials = false;
需要注意的是,如果服务器要求浏览器发送 Cookie,Access-Control-Allow-Origin就不能设为星号,必须指定明确的、与请求网页一致的域名。同时,Cookie 依然遵循同源政策,只有用服务器域名设置的 Cookie 才会上传,其他域名的 Cookie 并不会上传,且(跨域)原网页代码中的document.cookie也无法读取服务器域名下的 Cookie。
2.2 非简单请求
2.2.1 预检请求
非简单请求是那种对服务器提出特殊要求的请求,比如请求方法是PUT或DELETE,或者Content-Type字段的类型是application/json。
非简单请求的 CORS 请求,会在正式通信之前,增加一次 HTTP 查询请求,称为“预检”请求(preflight)。浏览器先询问服务器,当前网页所在的域名是否在服务器的许可名单之中,以及可以使用哪些 HTTP 方法和头信息字段。只有得到肯定答复,浏览器才会发出正式的XMLHttpRequest请求,否则就报错。这是为了防止这些新增的请求,对传统的没有 CORS 支持的服务器形成压力,给服务器一个提前拒绝的机会,这样可以防止服务器收到大量DELETE和PUT请求,这些传统的表单不可能跨域发出的请求。
下面是一段浏览器的 JavaScript 脚本。
var url = 'http://api.alice.com/cors';
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('PUT', url, true);
xhr.setRequestHeader('X-Custom-Header', 'value');
xhr.send();
上面代码中,HTTP 请求的方法是PUT,并且发送一个自定义头信息X-Custom-Header。
浏览器发现,这是一个非简单请求,就自动发出一个“预检”请求,要求服务器确认可以这样请求。下面是这个“预检”请求的 HTTP 头信息。
OPTIONS /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Access-Control-Request-Method: PUT
Access-Control-Request-Headers: X-Custom-Header
Host: api.alice.com
Accept-Language: en-US
Connection: keep-alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
“预检”请求用的请求方法是OPTIONS,表示这个请求是用来询问的。头信息里面,关键字段是Origin,表示请求来自哪个源。
除了Origin字段,“预检”请求的头信息包括两个特殊字段。
(1)Access-Control-Request-Method
该字段是必须的,用来列出浏览器的 CORS 请求会用到哪些 HTTP 方法,上例是PUT。
(2)Access-Control-Request-Headers
该字段是一个逗号分隔的字符串,指定浏览器 CORS 请求会额外发送的头信息字段,上例是X-Custom-Header。
2.2.2 预检请求的回应
服务器收到“预检”请求以后,检查了Origin、Access-Control-Request-Method和Access-Control-Request-Headers字段以后,确认允许跨源请求,就可以做出回应。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Mon, 01 Dec 2008 01:15:39 GMT
Server: Apache/2.0.61 (Unix)
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://api.bob.com
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, PUT
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-Custom-Header
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Length: 0
Keep-Alive: timeout=2, max=100
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Type: text/plain
上面的 HTTP 回应中,关键的是Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段,表示http://api.bob.com可以请求数据。该字段也可以设为星号,表示同意任意跨源请求。
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
如果服务器否定了“预检”请求,会返回一个正常的 HTTP 回应,但是没有任何 CORS 相关的头信息字段,或者明确表示请求不符合条件。
OPTIONS http://api.bob.com HTTP/1.1
Status: 200
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://notyourdomain.com
Access-Control-Allow-Method: POST
上面的服务器回应,Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段明确不包括发出请求的http://api.bob.com。
这时,浏览器就会认定,服务器不同意预检请求,因此触发一个错误,被XMLHttpRequest对象的onerror回调函数捕获。控制台会打印出如下的报错信息。
XMLHttpRequest cannot load http://api.alice.com.
Origin http://api.bob.com is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Origin.
服务器回应的其他 CORS 相关字段如下。
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, PUT
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-Custom-Header
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Max-Age: 1728000
(1)Access-Control-Allow-Methods
该字段必需,它的值是逗号分隔的一个字符串,表明服务器支持的所有跨域请求的方法。注意,返回的是所有支持的方法,而不单是浏览器请求的那个方法。这是为了避免多次“预检”请求。
(2)Access-Control-Allow-Headers
如果浏览器请求包括Access-Control-Request-Headers字段,则Access-Control-Allow-Headers字段是必需的。它也是一个逗号分隔的字符串,表明服务器支持的所有头信息字段,不限于浏览器在“预检”中请求的字段。
(3)Access-Control-Allow-Credentials
该字段与简单请求时的含义相同。
(4)Access-Control-Max-Age
该字段可选,用来指定本次预检请求的有效期,单位为秒。上面结果中,有效期是20天(1728000秒),即允许缓存该条回应1728000秒(即20天),在此期间,不用发出另一条预检请求。
2.2.3 浏览器的正常请求和回应
一旦服务器通过了“预检”请求,以后每次浏览器正常的 CORS 请求,就都跟简单请求一样,会有一个Origin头信息字段。服务器的回应,也都会有一个Access-Control-Allow-Origin头信息字段。
下面是“预检”请求之后,浏览器的正常 CORS 请求。
PUT /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Host: api.alice.com
X-Custom-Header: value
Accept-Language: en-US
Connection: keep-alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
上面头信息的Origin字段是浏览器自动添加的。
下面是服务器正常的回应。
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://api.bob.com
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
上面头信息中,Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段是每次回应都必定包含的。
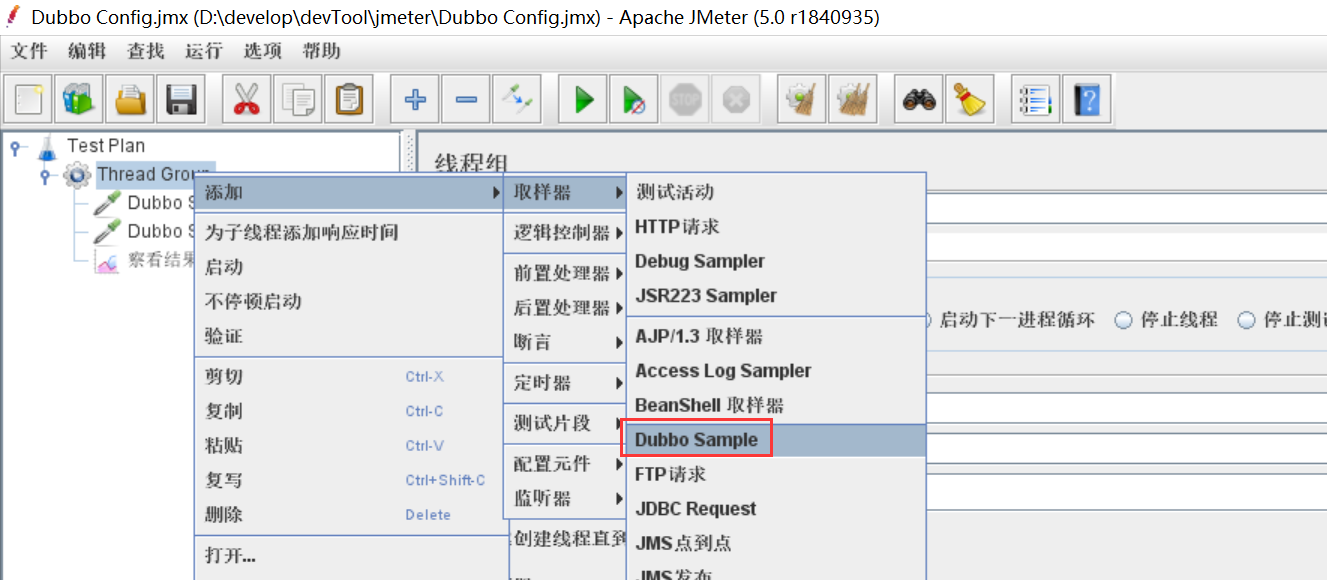
3.CORS的实现
3.1 PHP实现CORS
示例1:基础跨域 - GTE方法
aaa域页面JS:
<script>
//AXJX构建跨域请求
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('get','http://www.bbb.com/cors.php',true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4) {
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
}
xhr.send(null);
</script>
bbb域的php文件:
<?php
//设置CORS允许头字段
header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.aaa.com');
echo "cors sucessfully !!!";
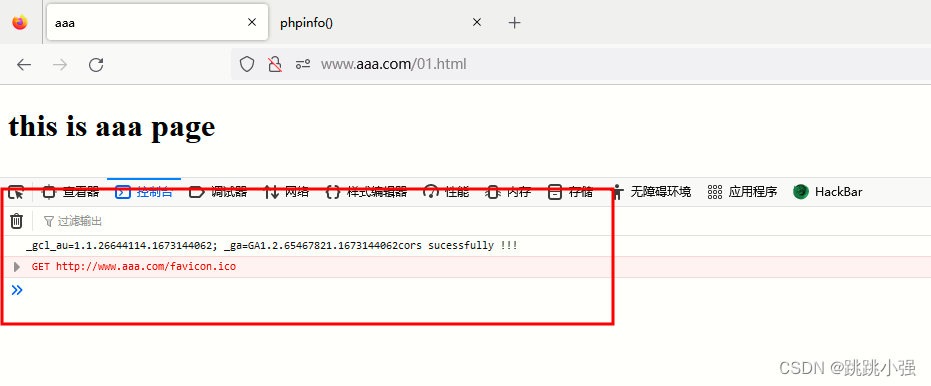
测试:
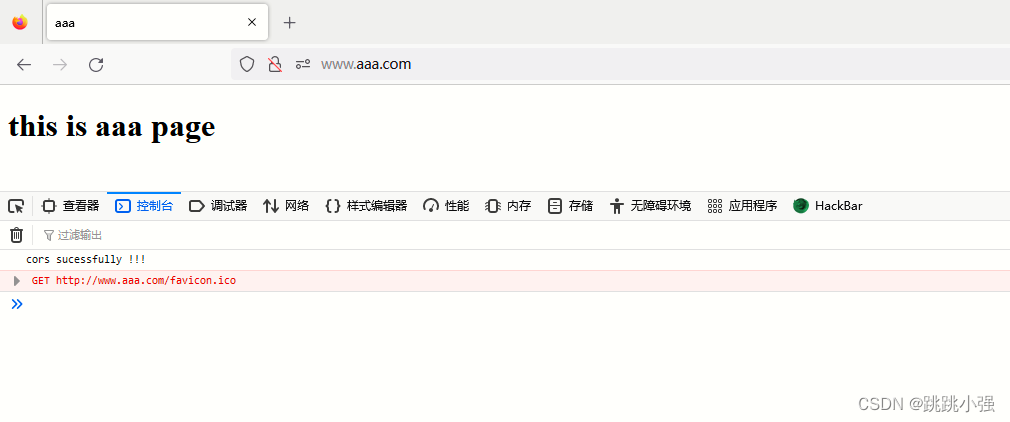
示例2:传递cookie - POST方法
aaa域页面JS:
<script>
//AXJX构建跨域请求
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
var data = 'cookie=' + encodeURIComponent(document.cookie);
xhr.open('post','http://www.bbb.com/cors.php',true);
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
//设置允许cookie的传递
xhr.withCredentials = true;
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4) {
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.response);
}
}
}
xhr.send(data);
</script>
bbb域的php文件:
<?php
//设置CORS允许头字段
header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.aaa.com');
//允许共享客户端cookie
header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true');
echo $_POST['cookie'];
echo "cors sucessfully !!!";
测试:
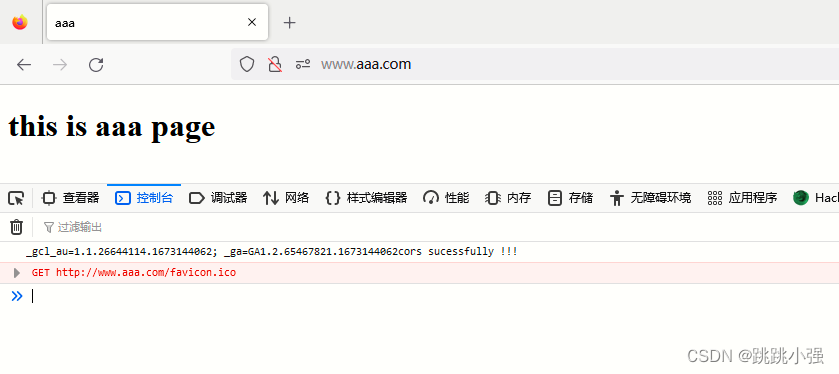
可以看到,传递cookie成功。
3.2 nodejs实现CORS
示例1:基础跨域 - GTE方法
aaa域JS:
<script>
//AXJX构建跨域请求
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('get','http://127.0.0.1:9999/cors',true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4) {
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
}
xhr.send(null);
</script>
本地NODEJS服务器:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.disable('etag');
//设置监听端口为9999
const port = 9999;
app.all("*",function(req,res,next){
//设置允许跨域的域名,*代表允许任意域名跨域
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin","http://www.aaa.com");
//设置允许方法
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods","GET, POST, PUT");
next();
})
app.get('/cors',(req,res) => {
res.send('cors is sucefully!!!');
});
app.listen(port,() => {
console.log('listening on ${port}...');
})
测试:
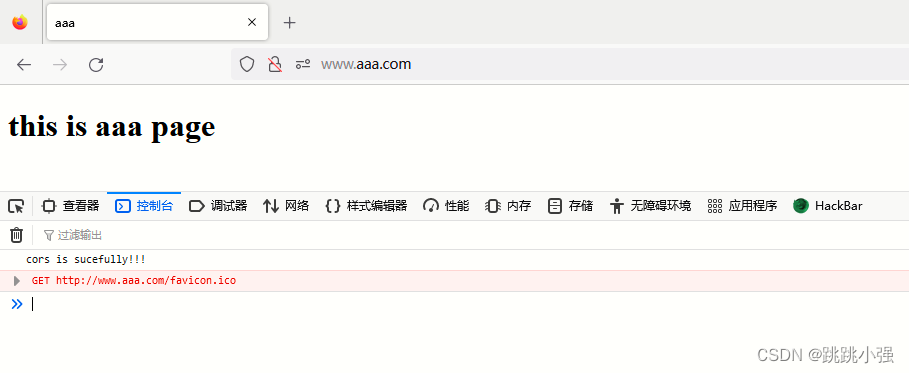
示例2:传递cookie - POST方法
客户端页面JS:
<script>
//AXJX构建跨域请求
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
var data = 'cookie=' + encodeURIComponent(document.cookie);
xhr.open('post','http://127.0.0.1:9999/cors',true);
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
//设置允许cookie的传递
xhr.withCredentials = true;
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4) {
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.response);
}
}
}
xhr.send(data);
</script>
服务端nodejs:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const querystring = require('querystring');
app.disable('etag');
const port = 9999;
app.all("*",function(req,res,next){
//设置允许跨域的域名,*代表允许任意域名跨域
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin","http://www.aaa.com");
//设置允许方法
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods","GET, POST, PUT");
//设置cookie允许传递
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials",true);
next();
})
//接受post传参
app.post("/cors",(req,res) => {
req.on("data",myData => {
console.log(querystring.parse(myData.toString()));
})
})
app.listen(port,() => {
console.log('listening on ${port}...');
})
测试结果:
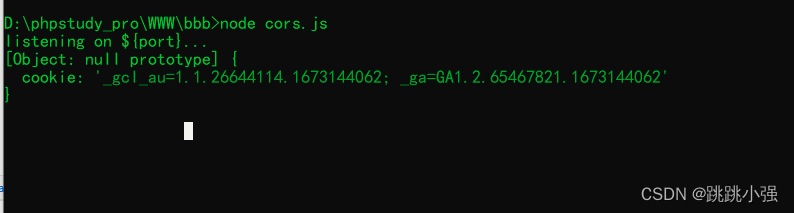
3.3 nginx中间件实现CORS
环境配置
环境配置:直接编辑配置文件即可,其中aaa域和bbb域作为测试对象
测试环境:centos7
[root@blackstone ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
[root@blackstone ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@blackstone ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
配置文件:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location ~ \.php(.*)$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
#*星号代表任意跨源请求都支持
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin '*';
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials "true";
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
#v-domain
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.aaa.com;
location / {
root /var/www/aaa;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.bbb.com;
location / {
root /var/www/bbb;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
}
location ~ \.php(.*)$ {
root /var/www/bbb;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /var/www/bbb$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
#*星号代表任意跨源请求都支持
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin 'http://www.aaa.com';
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials "true";
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
}
#v-ip
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.2.100;
location / {
root /var/www/ip1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.2.200;
location / {
root /var/www/ip2;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
#v-port
server {
listen 81;
server_name 192.168.2.169;
location / {
root /var/www/port81;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 82;
server_name 192.168.2.169;
location / {
root /var/www/port82;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
示例:POST方法跨域
aaa目录下的页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>aaa</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>this is aaa page</h1>
</body>
<script>
//AXJX构建跨域请求
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
var data = 'cookie=' + encodeURIComponent(document.cookie);
xhr.open('post','http://www.bbb.com/cors.php',true);
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
//设置允许cookie的传递
xhr.withCredentials = true;
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4) {
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.response);
}
}
}
xhr.send(data);
</script>
</html>
bbb目录下的页面:
<?php
echo $_POST['cookie'];
echo "cors sucessfully !!!";
测试:
修改本地的host文件指向centos7的地址
192.168.2.169 www.bbb.com
192.168.2.169 www.aaa.com
浏览器测试: