kitti数据集简介
kitti数据集是比较早出来的3D检测方面的数据集,相对来说数据结构简单,适合做单目检测的工作,目前也是业界和学术界常用的公开数据集。
自己最近也在做单目3D检测的工作,所以也分享一些理解,希望能给到一些人启发和帮助。
kitti数据的目录结构如下:
只需要下载下图所示的四个zip包解压就行,做单目3D检测已经足够。
解压后以training为例,其中calib里面是传感器的标定参数,有一堆txt文件,内容格式如下:
P0: 7.215377000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 6.095593000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 7.215377000000e+02 1.728540000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 1.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00
P1: 7.215377000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 6.095593000000e+02 -3.875744000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 7.215377000000e+02 1.728540000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 1.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00
P2: 7.215377000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 6.095593000000e+02 4.485728000000e+01 0.000000000000e+00 7.215377000000e+02 1.728540000000e+02 2.163791000000e-01 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 1.000000000000e+00 2.745884000000e-03
P3: 7.215377000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 6.095593000000e+02 -3.395242000000e+02 0.000000000000e+00 7.215377000000e+02 1.728540000000e+02 2.199936000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 0.000000000000e+00 1.000000000000e+00 2.729905000000e-03
R0_rect: 9.999239000000e-01 9.837760000000e-03 -7.445048000000e-03 -9.869795000000e-03 9.999421000000e-01 -4.278459000000e-03 7.402527000000e-03 4.351614000000e-03 9.999631000000e-01
Tr_velo_to_cam: 7.533745000000e-03 -9.999714000000e-01 -6.166020000000e-04 -4.069766000000e-03 1.480249000000e-02 7.280733000000e-04 -9.998902000000e-01 -7.631618000000e-02 9.998621000000e-01 7.523790000000e-03 1.480755000000e-02 -2.717806000000e-01
Tr_imu_to_velo: 9.999976000000e-01 7.553071000000e-04 -2.035826000000e-03 -8.086759000000e-01 -7.854027000000e-04 9.998898000000e-01 -1.482298000000e-02 3.195559000000e-01 2.024406000000e-03 1.482454000000e-02 9.998881000000e-01 -7.997231000000e-01
p0到p4对应的是rect相机坐标系到像素坐标系的变换矩阵,一般论文中叫内参,实际上是相机内参和相机外参以及畸变矫正融合的矩阵。
这里提几点:
kitti有四个相机,两个彩色的,两个灰度的,左侧彩色(对应序号2)的是有对应的标注信息的,所以如果做单目的话,用p2。
rect相机坐标系是对参考坐标系进行旋转矫正,使得4个相机的光心共面,这样做有一定好处,具体好处是什么可以不用在意。
Tr_velo_to_cam是雷达坐标系到参考相机坐标系。
Tr_imu_to_velo是imu到雷达坐标系。
image_2里面就是图片了。
label_2里面就是对应的标注信息了,3D标注是在rect相机坐标系中的。
Pedestrian 0.00 0 -0.20 712.40 143.00 810.73 307.92 1.89 0.48 1.20 1.84 1.47 8.41 0.01
第一列是类别,第二列是截断程度(0~1),第三列是遮挡程度(0,1,2,3),第四列是观察者角度alpha(没啥用),接下来五列到八列是2d框的信息,xmin ymin xmax ymax四个坐标,九列到十一列是3D框的高宽长,十二到十四列是3D框下底面中心点,最后一列是绕y轴的旋转角。
velodyne里面是雷达。另外一个velodyne_reduced是mmdetection3d转数据格式时生成的,可以不在意。
可视化
main.py文件:
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import mayavi.mlab as mlab
from utils import draw_lidar, draw_2dbox, gen_3dbox, project_box3d, draw_project, draw_box3d_lidar
class Kitti:
def __init__(self, root_path="./kitti", ind=0) -> None:
self.root_path = root_path
train_file = os.path.join(root_path, "ImageSets/train.txt")
with open(train_file, 'r') as f:
names = f.readlines()
self.names = [name.rstrip() for name in names]
self.name = self.names[ind]
def get_image(self, show=False):
img_path = os.path.join(self.root_path, "training/image_2", self.name+".png")
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
if show and os.path.exists(img_path):
cv2.imshow("origin image", img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) == ord("q"):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return img
def get_lidar(self, show=False):
lidar_path = os.path.join(self.root_path, "training/velodyne", self.name+".bin")
lidar = np.fromfile(lidar_path, dtype=np.float32)
lidar = lidar.reshape((-1, 4))
if show:
fig = mlab.figure(figure=None, bgcolor=(0, 0, 0), engine=None,
size=(1000, 500))
draw_lidar(lidar, fig=fig)
mlab.show()
return lidar
def get_calib(self):
calib = {}
calib_path = os.path.join(self.root_path, "training/calib", self.name+".txt")
with open(calib_path, 'r') as cf:
infos = cf.readlines()
infos = [x.rstrip() for x in infos]
for info in infos:
if len(info) == 0:
continue
key, value = info.split(":", 1)
calib[key] = np.array([float(x) for x in value.split()])
calib_format = self.format_calib(calib)
return calib_format
def format_calib(self, calib):
calib_format = {}
# projection matrix from rect coord to image coord.
rect2image = calib["P2"]
rect2image = rect2image.reshape([3, 4])
calib_format["rect2image"] = rect2image
# projection matrix from lidar coord to reference cam coord.
lidar2cam = calib["Tr_velo_to_cam"]
lidar2cam = lidar2cam.reshape([3, 4])
calib_format["lidar2cam"] = lidar2cam
# projection matrix from rect cam coord to reference cam coord.
rect2ref = calib["R0_rect"]
rect2ref = rect2ref.reshape([3, 3])
calib_format["rect2ref"] = rect2ref
return calib_format
def get_anns(self):
anns = []
label_path = os.path.join(self.root_path, "training/label_2", self.name+".txt")
with open(label_path, 'r') as lf:
labels = lf.readlines()
labels = [label.rstrip() for label in labels]
for label in labels:
ann_format = {}
ann = label.split(" ")
class_name = ann[0]
ann_format["class_name"]=class_name
ann_ = [float(x) for x in ann[1:]]
truncation = ann_[0] # truncated pixel ratio [0..1]
ann_format["truncation"]=truncation
occlusion = ann_[1] # 0=visible, 1=partly occluded, 2=fully occluded, 3=unknown
ann_format["occlusion"]=occlusion
alpha = ann_[2]
ann_format["alpha"]=alpha # object observation angle [-pi..pi]
#2D box
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = ann_[3], ann_[4], ann_[5], ann_[6]
box2d = np.array([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
ann_format["box2d"]=box2d
#3D box
box3d = {}
h, w, l = ann_[7], ann_[8], ann_[9]
cx, cy, cz = ann_[10], ann_[11], ann_[12]
box3d["dim"] = np.array([l, w, h])
box3d["center"] = np.array([cx, cy, cz])
yaw = ann_[13]
box3d["rotation"] = yaw# yaw angle [-pi..pi]
ann_format["box3d"]=box3d
anns.append(ann_format)
return anns
class VisKitti:
def __init__(self, root_path="./kitti", ind=0) -> None:
self.kitti = Kitti(root_path=root_path, ind=ind)
self.calib = self.kitti.get_calib()
self.anns = self.kitti.get_anns()
def show_origin_image(self):
self.kitti.get_image(show=True)
def show_origin_lidar(self):
self.kitti.get_lidar(show=True)
def show_image_with_2dbox(self, save=False):
img = self.kitti.get_image()
bbox = []
names = []
for ann in self.anns:
bbox.append(ann["box2d"])
names.append(ann["class_name"])
draw_2dbox(img, bbox, names, save=save)
def show_image_with_project_3dbox(self, show=True):
img = self.kitti.get_image()
bbox = []
for ann in self.anns:
bbox.append(ann["box3d"])
bbox3d = gen_3dbox(bbox3d=bbox)
project_xy,_ = project_box3d(bbox3d, self.calib)
draw_project(img, project_xy, save=False)
def show_lidar_with_3dbox(self, img_fov=False):
img = self.kitti.get_image()
bbox = []
for ann in self.anns:
bbox.append(ann["box3d"])
bbox3d = gen_3dbox(bbox3d=bbox)
fig = mlab.figure(figure=None, bgcolor=(0, 0, 0), engine=None,
size=(1000, 500))
lidar = self.kitti.get_lidar()
fig = draw_lidar(lidar, fig=fig)
fig = draw_box3d_lidar(bbox3d, self.calib, fig)
mlab.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
vis = VisKitti()
print("1: show_origin_image")
print("2: show_origin_lidar")
print("3: show_image_with_2dbox")
print("4: show_image_with_project_3dbox")
print("5: show_lidar_with_3dbox")
choice = input("please choice number:")
if choice=="1":
vis.show_origin_image()
elif choice=="2":
vis.show_origin_lidar()
elif choice=="3":
vis.show_image_with_2dbox()
elif choice=="4":
vis.show_image_with_project_3dbox()
elif choice=="5":
vis.show_lidar_with_3dbox()
utils.py 文件
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import mayavi.mlab as mlab
def draw_lidar(pc,
color=None,
fig=None,
bgcolor=(0, 0, 0),
pts_scale=0.3,
pts_mode="point",
pts_color=None,
color_by_intensity=False,
):
if fig == None:
fig = mlab.figure(figure=None, bgcolor=bgcolor, engine=None,
size=(1600, 1000))
if color == None:
color = pc[:, 2]
s = pc[:, 3] if color_by_intensity else pc[:, 2]
mlab.points3d(pc[:, 0],
pc[:, 1],
pc[:, 2],
s,
color=pts_color,
mode=pts_mode,
colormap="gnuplot",
scale_factor=pts_scale,
figure=fig)
# draw origin point
mlab.points3d(0, 0, 0, color=(1, 1, 1), mode="sphere", scale_factor=0.2, figure=fig)
# draw axis
axis_xyz = np.array([[2, 0, 0],[0, 2, 0],[0, 0, 2]], dtype=np.float64)
# x axis
mlab.plot3d([0, axis_xyz[0, 0]],
[0, axis_xyz[0, 1]],
[0, axis_xyz[0, 2]],
color=(1, 0, 0),
tube_radius=None,
figure=fig)
# y axis
mlab.plot3d([0, axis_xyz[1, 0]],
[0, axis_xyz[1, 1]],
[0, axis_xyz[1, 2]],
color=(0, 1, 0),
tube_radius=None,
figure=fig)
# z axis
mlab.plot3d([0, axis_xyz[2, 0]],
[0, axis_xyz[2, 1]],
[0, axis_xyz[2, 2]],
color=(0, 0, 1),
tube_radius=None,
figure=fig)
mlab.view(
azimuth=180,
elevation=70,
focalpoint=[12.0909996, -1.04700089, -2.03249991],
distance=62.0,
figure=fig,
)
return fig
def draw_2dbox(img, bbox, names=None, save=False):
assert len(bbox)==len(names), "names not match bbox"
color_map = {"Car":(0, 255, 0), "Pedestrian":(255, 0, 0), "Cyclist":(0, 0, 255)}
for i, box in enumerate(bbox):
name = names[i]
if name not in color_map.keys():
continue
color = color_map[name]
cv2.rectangle(
img,
(int(box[0]), int(box[1])),
(int(box[2]), int(box[3])),
color,
2,
)
name_coord = (int(box[0]), int(max(box[1]-5, 0)))
cv2.putText(img, name, name_coord,
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, color, 1)
cv2.imshow("image_with_2dbox", img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) == ord("q"):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if save:
cv2.imwrite("image_with_2dbox.jpg", img)
def rotx(t):
""" 3D Rotation about the x-axis. """
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[1, 0, 0], [0, c, -s], [0, s, c]])
def roty(t):
""" Rotation about the y-axis. """
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[c, 0, s], [0, 1, 0], [-s, 0, c]])
def rotz(t):
""" Rotation about the z-axis. """
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[c, -s, 0], [s, c, 0], [0, 0, 1]])
def expand_matrix(matrix):
new_matrix = np.eye(4, 4)
new_matrix[:3, :] = matrix
return new_matrix
def gen_3dbox(bbox3d):
corners_3d_all = []
for box in bbox3d:
center = box["center"]
l, w, h = box["dim"]
angle = box["rotation"]
R = roty(angle)
# 3d bounding box corners
x_corners = [l / 2, l / 2, -l / 2, -l / 2, l / 2, l / 2, -l / 2, -l / 2]
y_corners = [0, 0, 0, 0, -h, -h, -h, -h]
z_corners = [w / 2, -w / 2, -w / 2, w / 2, w / 2, -w / 2, -w / 2, w / 2]
corners = np.vstack([x_corners, y_corners, z_corners])
corners_3d = np.dot(R, corners)
corners_3d[0, :] += center[0]
corners_3d[1, :] += center[1]
corners_3d[2, :] += center[2]
corners_3d_all.append(corners_3d)
return corners_3d_all
def project_box3d(bbox3d, calib):
P = calib["rect2image"]
P = expand_matrix(P)
project_xy = []
project_z = []
for box3d in bbox3d:
if np.any(box3d[:, 2] < 0.1):
continue
box3d = np.concatenate([box3d, np.zeros((1, 8))], axis=0)
project_3dbox = np.dot(P, box3d)[:3, :]
pz = project_3dbox[2, :]
px = project_3dbox[0, :]/pz
py = project_3dbox[1, :]/pz
xy = np.stack([px, py], axis=1)
project_xy.append(xy)
project_z.append(pz)
return project_xy, project_z
def draw_project(img, project_xy, save=False):
color_map = {"Car":(0, 255, 0), "Pedestrian":(255, 0, 0), "Cyclist":(0, 0, 255)}
for i, qs in enumerate(project_xy):
color = (0, 255, 0)
qs = qs.astype(np.int32)
for k in range(0, 4):
i, j = k, (k + 1) % 4
# use LINE_AA for opencv3
cv2.line(img, (qs[i, 0], qs[i, 1]), (qs[j, 0], qs[j, 1]), color, 1)
i, j = k + 4, (k + 1) % 4 + 4
cv2.line(img, (qs[i, 0], qs[i, 1]), (qs[j, 0], qs[j, 1]), color, 1)
i, j = k, k + 4
cv2.line(img, (qs[i, 0], qs[i, 1]), (qs[j, 0], qs[j, 1]), color, 1)
cv2.imshow("image_with_projectbox", img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) == ord("q"):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if save:
cv2.imwrite("image_with_projectbox.jpg", img)
def draw_gt_boxes3d(
gt_boxes3d,
fig,
color=(1, 1, 1),
line_width=1,
):
""" Draw 3D bounding boxes
Args:
gt_boxes3d: numpy array (n,8,3) for XYZs of the box corners
fig: mayavi figure handler
color: RGB value tuple in range (0,1), box line color
line_width: box line width
draw_text: boolean, if true, write box indices beside boxes
text_scale: three number tuple
color_list: a list of RGB tuple, if not None, overwrite color.
Returns:
fig: updated fig
"""
num = len(gt_boxes3d)
for n in range(num):
b = gt_boxes3d[n]
for k in range(0, 4):
i, j = k, (k + 1) % 4
mlab.plot3d(
[b[i, 0], b[j, 0]],
[b[i, 1], b[j, 1]],
[b[i, 2], b[j, 2]],
color=color,
tube_radius=None,
line_width=line_width,
figure=fig,
)
i, j = k + 4, (k + 1) % 4 + 4
mlab.plot3d(
[b[i, 0], b[j, 0]],
[b[i, 1], b[j, 1]],
[b[i, 2], b[j, 2]],
color=color,
tube_radius=None,
line_width=line_width,
figure=fig,
)
i, j = k, k + 4
mlab.plot3d(
[b[i, 0], b[j, 0]],
[b[i, 1], b[j, 1]],
[b[i, 2], b[j, 2]],
color=color,
tube_radius=None,
line_width=line_width,
figure=fig,
)
return fig
def inverse_rigid_trans(Tr):
""" Inverse a rigid body transform matrix (3x4 as [R|t])
[R'|-R't; 0|1]
"""
inv_Tr = np.zeros_like(Tr) # 3x4
inv_Tr[0:3, 0:3] = np.transpose(Tr[0:3, 0:3])
inv_Tr[0:3, 3] = np.dot(-np.transpose(Tr[0:3, 0:3]), Tr[0:3, 3])
return inv_Tr
def draw_box3d_lidar(bbox3d, calib, fig):
# method 1
# lidar2cam = calib["lidar2cam"]
# lidar2cam = expand_matrix(lidar2cam)
# cam2rect_ = calib["rect2ref"]
# cam2rect = np.eye(4, 4)
# cam2rect[:3, :3] = cam2rect_
# lidar2rec = np.dot(lidar2cam, cam2rect)
# rec2lidar = np.linalg.inv(lidar2rec) #(AB)-1 = B-1@A-1
# method 2
lidar2cam_ = calib["lidar2cam"]
cam2rect_ = calib["rect2ref"]
cam2rect = np.eye(4, 4)
cam2rect[:3, :3] = cam2rect_
# lidar2cam = np.eye(4, 4)
# lidar2cam[:3, :] = lidar2cam_
# cam2lidar = np.linalg.inv(lidar2cam)
cam2lidar_ = inverse_rigid_trans(lidar2cam_)
cam2lidar = np.eye(4, 4)
cam2lidar[:3, :] = cam2lidar_
all_lidar_box3d = []
for box3d in bbox3d:
if np.any(box3d[:, 2] < 0.1):
continue
box3d = np.concatenate([box3d, np.ones((1, 8))], axis=0)
box3d_in_refcam = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(cam2rect), box3d)
lidar_box3d = np.dot(cam2lidar, box3d_in_refcam)[:3, :]
lidar_box3d = np.transpose(lidar_box3d)
all_lidar_box3d.append(lidar_box3d)
print(all_lidar_box3d)
fig = draw_gt_boxes3d(all_lidar_box3d, fig)
return fig
可视化结果:

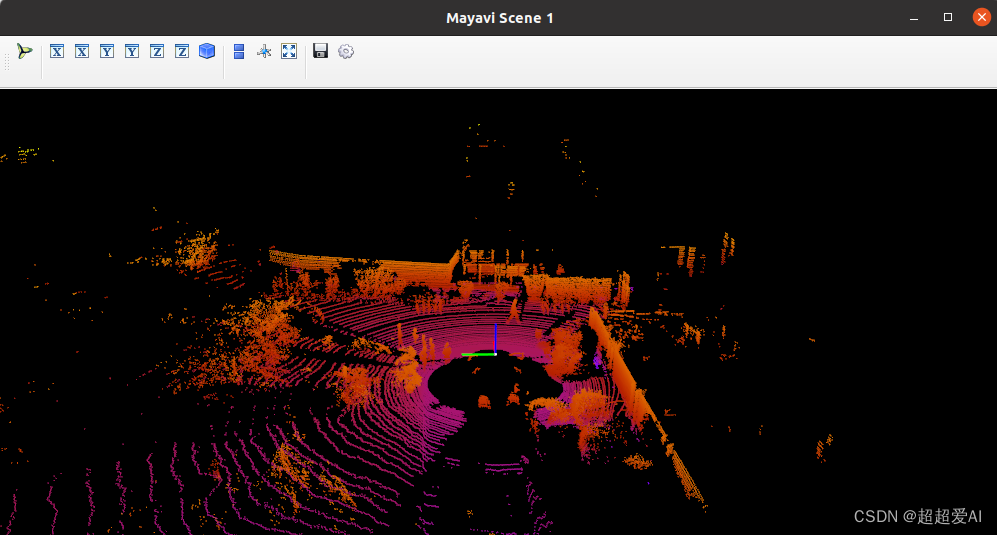
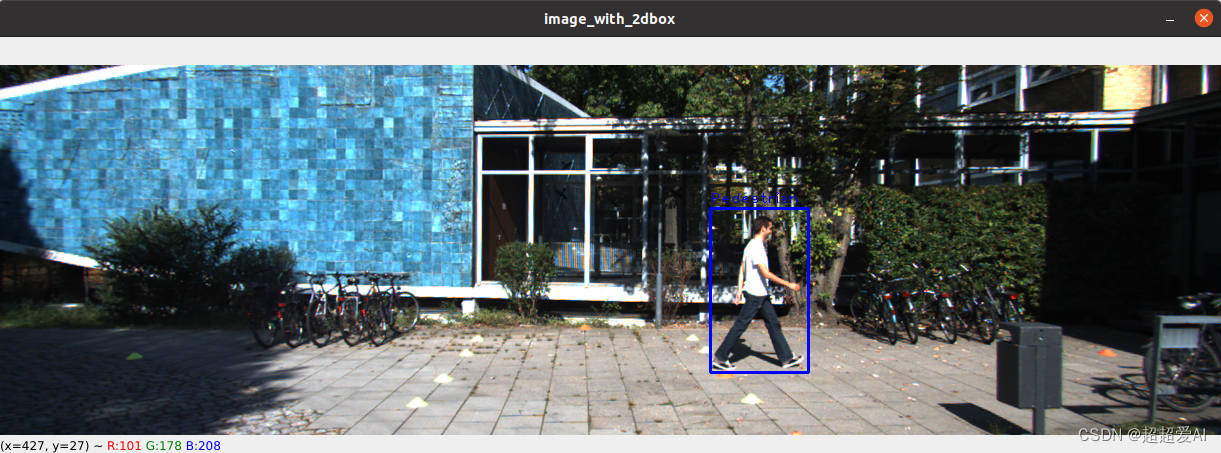

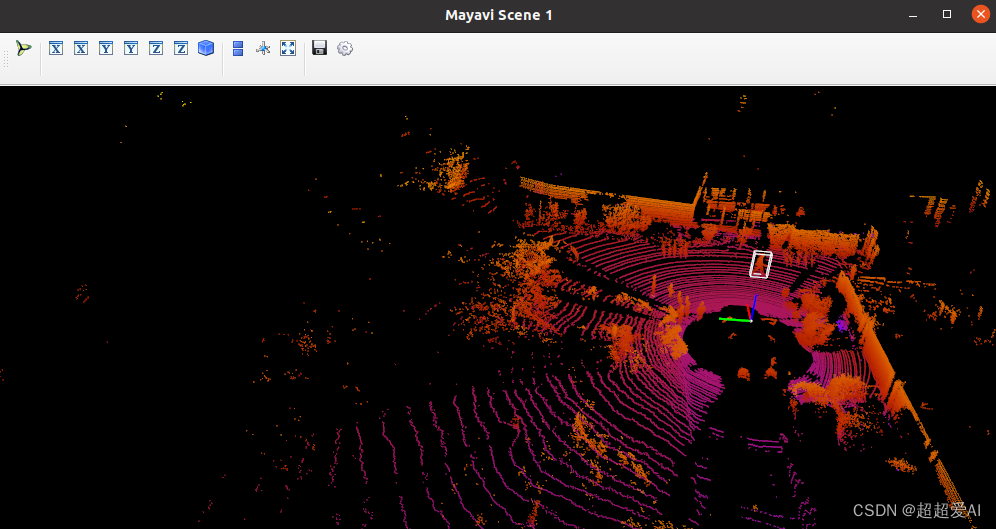
总结
本来是想一行行解释代码的,但是太累,所以就不解释了,自己代码是简化过的,应该很容易看懂。主要参考的kitti_object_vis。