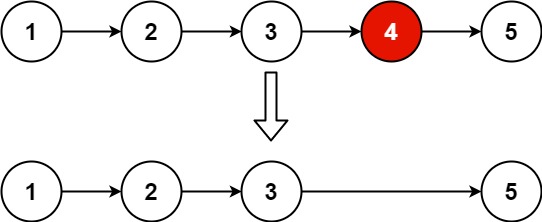
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
首先从头节点开始对链表进行一次遍历,得到链表的长度 L。随后我们再从头节点开始对链表进行一次遍历,当遍历到第 L−n+1个节点时,它就是我们需要删除的节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {
//设置一个虚拟头结点
struct ListNode* list=malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
list->val=0;
list->next=head;
struct ListNode* cur,*cur1;
cur=list;
cur1=list;
int count=0;
//记录一共有多少个结点
while(cur->next!=NULL)
{
count++;
cur=cur->next;
}
if(count==1)
return NULL;
for(int t=1;t<count-n+1;t++)
{
cur1=cur1->next;
}
cur1->next=cur1->next->next;
return list->next;
}给你单链表的头指针
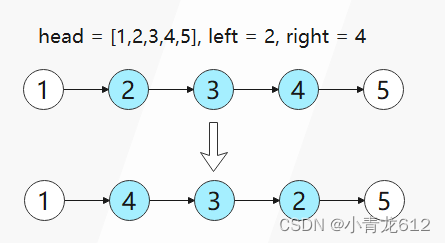
head和两个整数left和right,其中left <= right。请你反转从位置left到位置right的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 输出:[1,4,3,2,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 输出:[5]
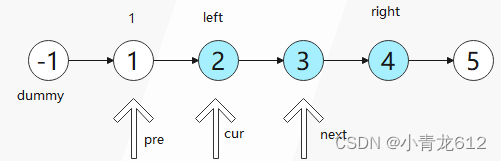
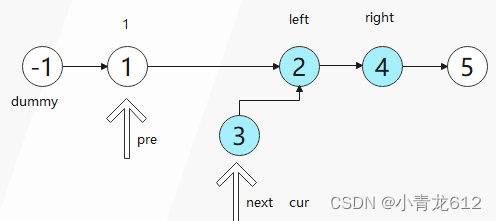
因为头节点有可能发生变化,使用虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论;
从 1 到 left , pre 节点往后移动;
pre和cur节点不变起初指针:
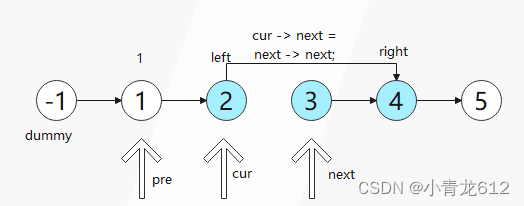
cur -> next = next -> next;
next -> next = pre -> next;
pre -> next = next;
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseBetween(struct ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
//设置虚拟结点
struct ListNode *dummy = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummy -> val = -1;
dummy -> next = head;
struct ListNode *pre = dummy;
for (int i = 1;i < left;i++)
pre = pre -> next;
struct ListNode *cur = pre->next;
struct ListNode *next;
for (int i = left;i < right;i++) {
next = cur -> next;
cur -> next = next -> next;
next -> next = pre -> next;
pre -> next = next;
}
return dummy -> next;
}




![[Halcon学习笔记]在Qt上实现Halcon窗口的字体设置颜色设置等功能](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/bc2637cb32ac52760605e4b939ab57ba.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)