目录
- 一、什么是网络编程
- 二、网络编程三要素
- 2.1 IP
- 2.2 InetAddress的使用
- 2.3 端口号
- 2.4 协议
- 三、UDP通信程序
- 3.1 发送数据
- 3.2 接收数据
- 3.3 练习
- 四、UDP的三种通信方式
- 五、TCP的通信程序
- 六、三次握手和四次挥手
- 七、练习
- 7.1 TCP通信练习1——多发多收
- 7.2 TCP通信练习2——接收和反馈
- 7.3 TCP通信练习3——上传文件
- 7.4 TCP通信练习4——上传文件(文件名重复问题)
- 7.5 TCP通信练习5——上传文件(多线程版)
- 7.6 TCP通信练习6——上传文件(线程池优化)
- 7.7 TCP通信练习7——BS(接收浏览器的消息并打印)
一、什么是网络编程


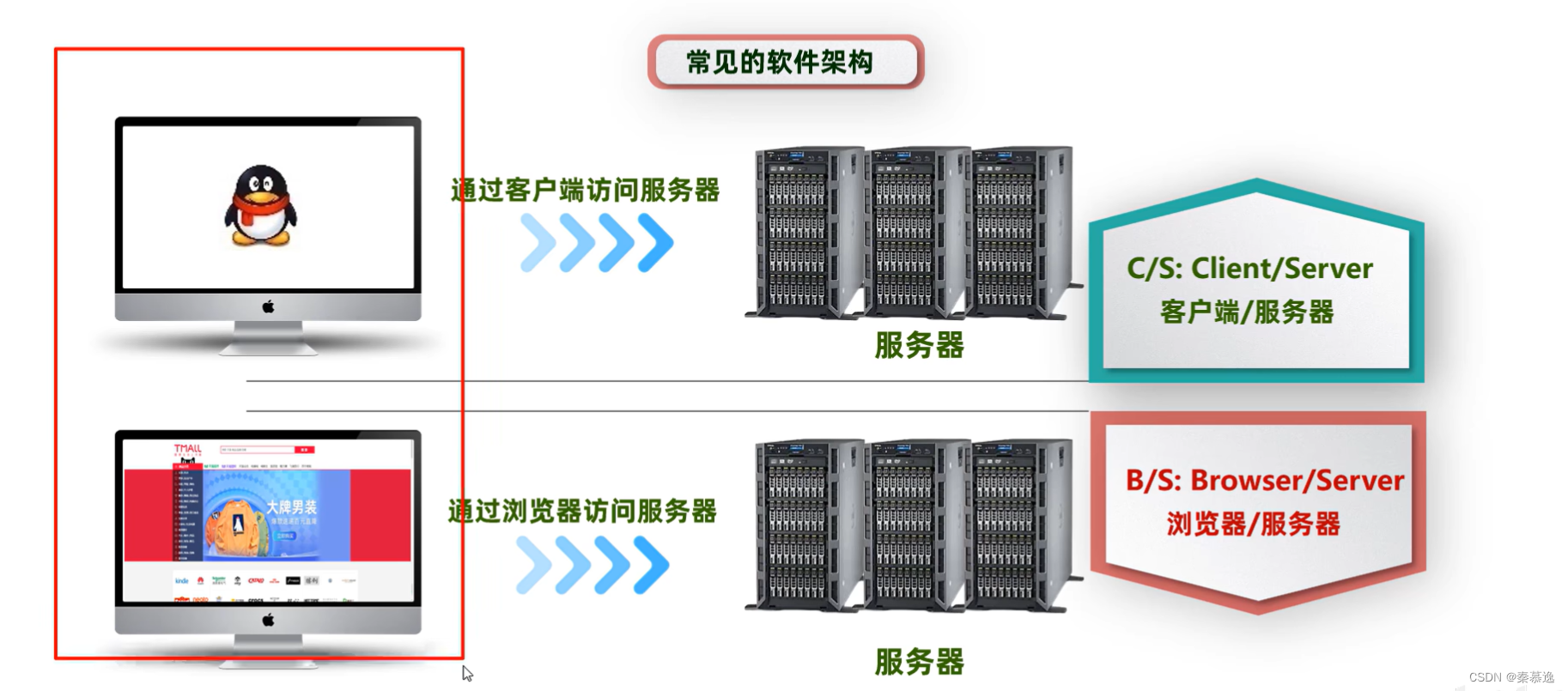




二、网络编程三要素


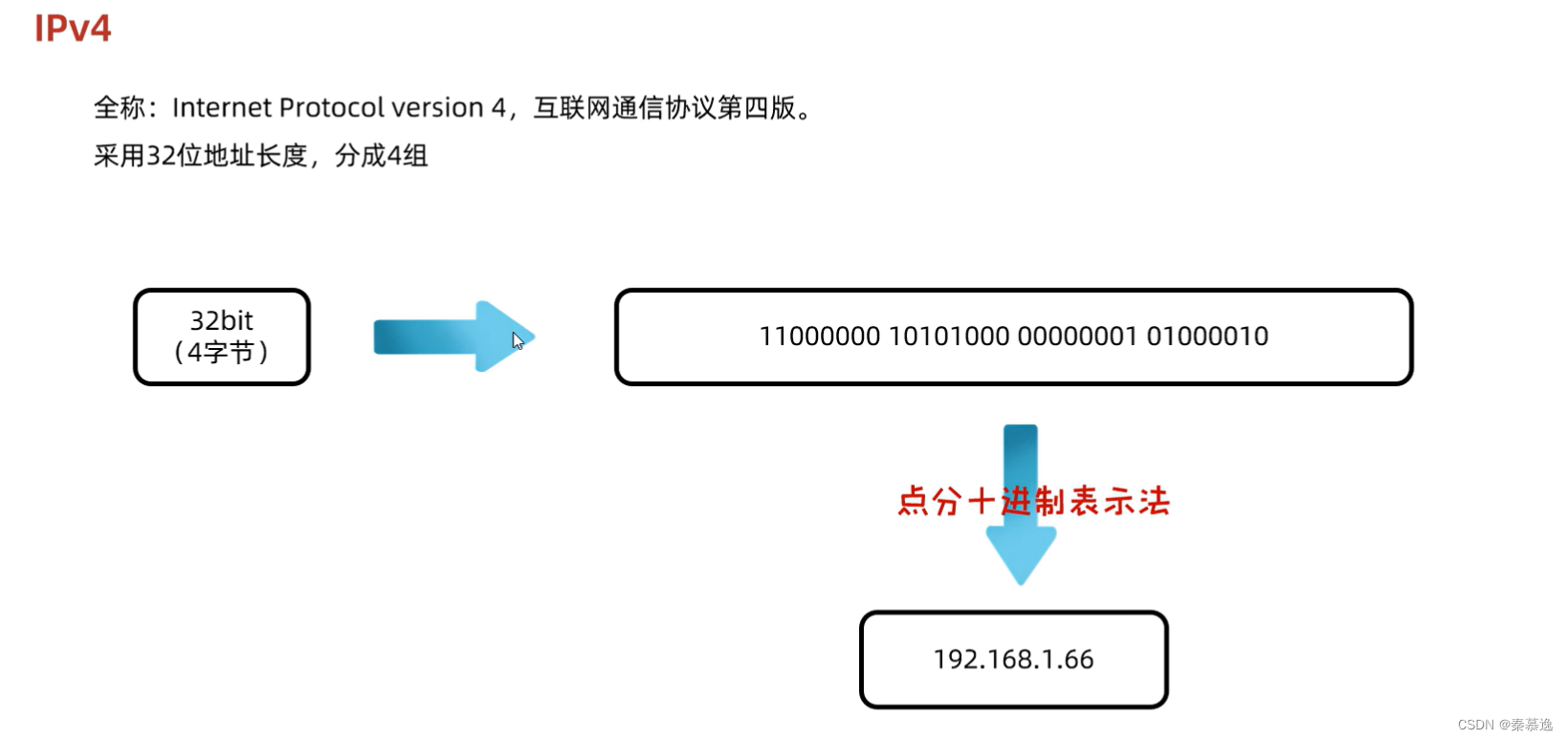
2.1 IP

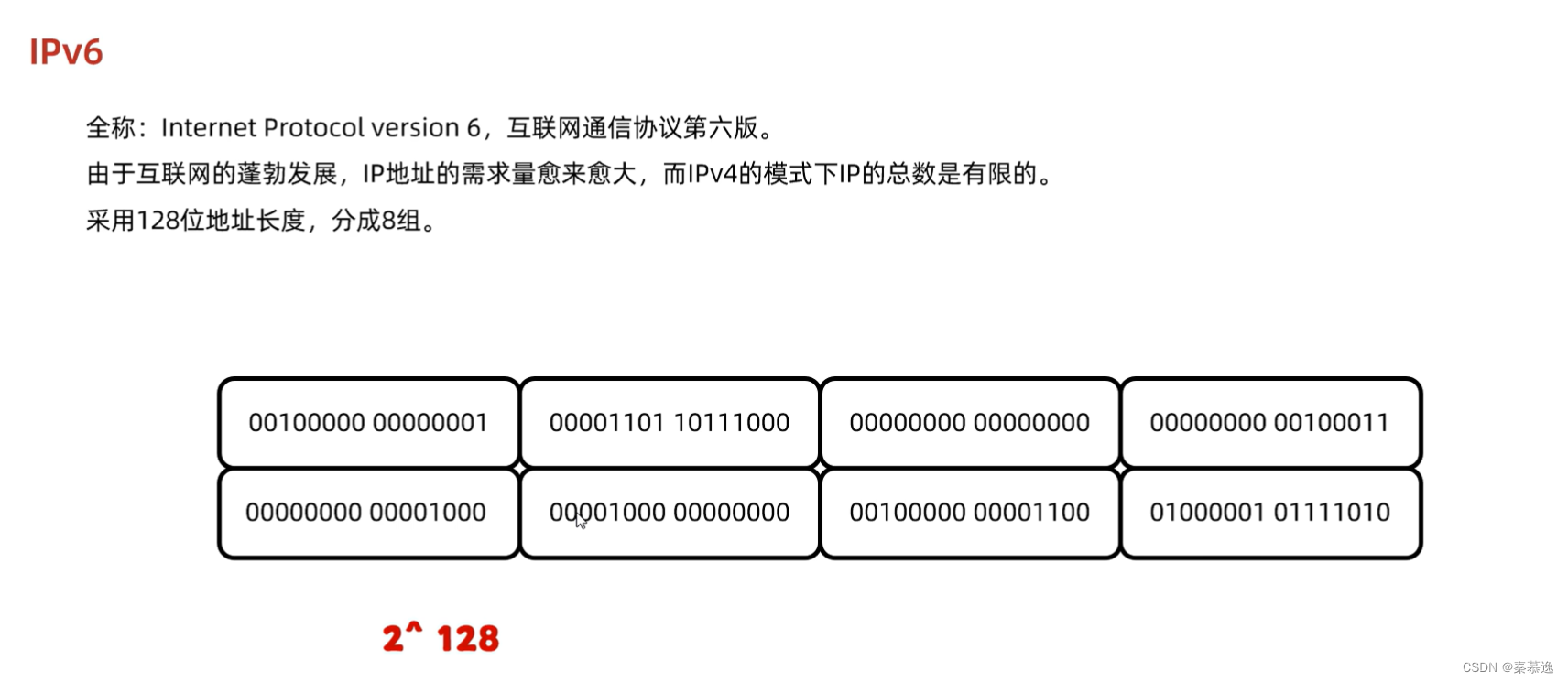
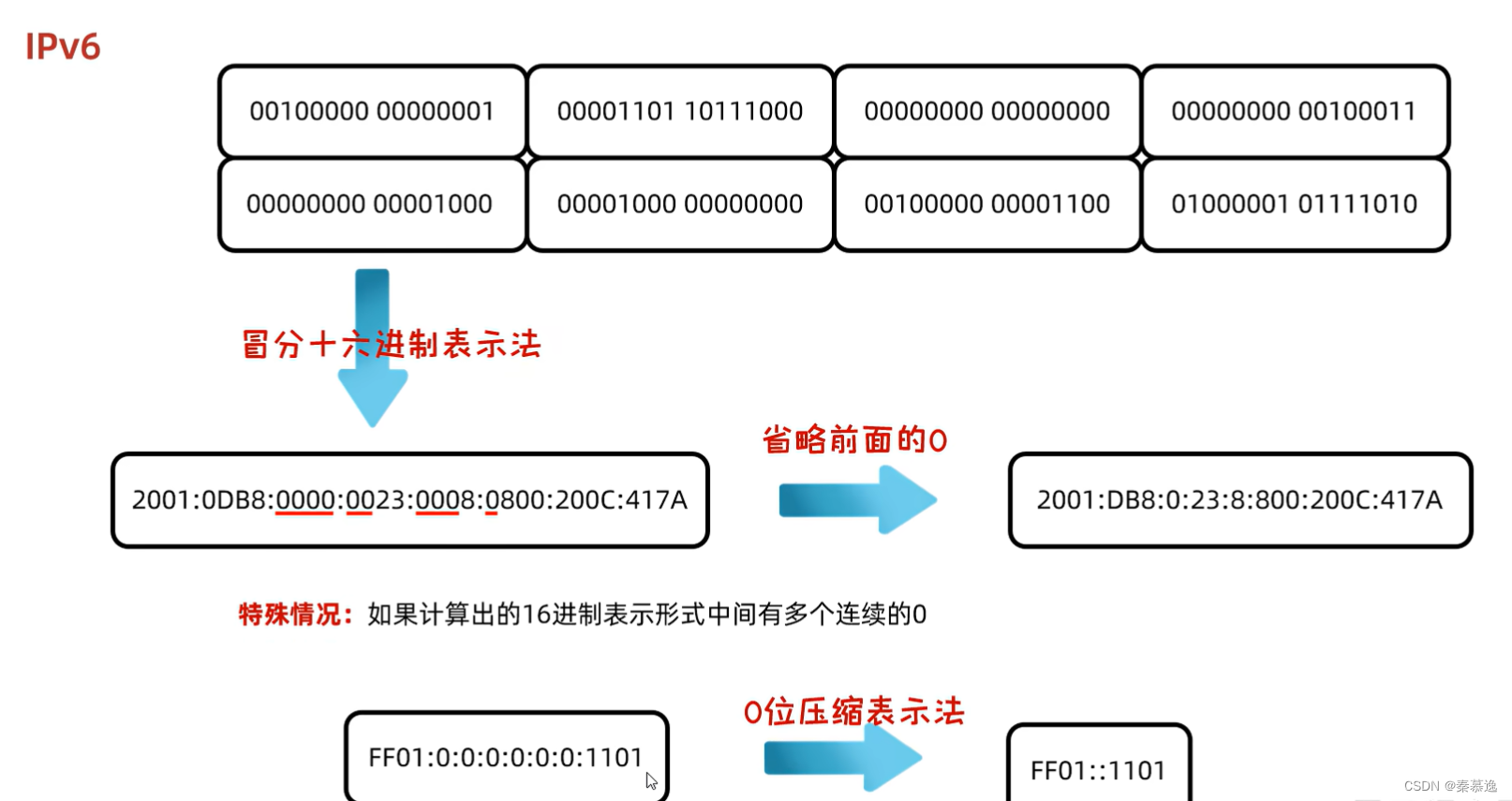




2.2 InetAddress的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
/*
static InetAddress getByName(String host) 确定主机名称的IP地址。主机名称可以是机器名称,也可以是IP地址
String getHostName() 获取此IP地址的主机名
String getHostAddress() 返回文本显示中的IP地址字符串
*/
//0.获取InetAddress对象
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("摆烂小T");
System.out.println(address);
String hostName = address.getHostName();
System.out.println(hostName);
String hostAddress = address.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(hostAddress);
}
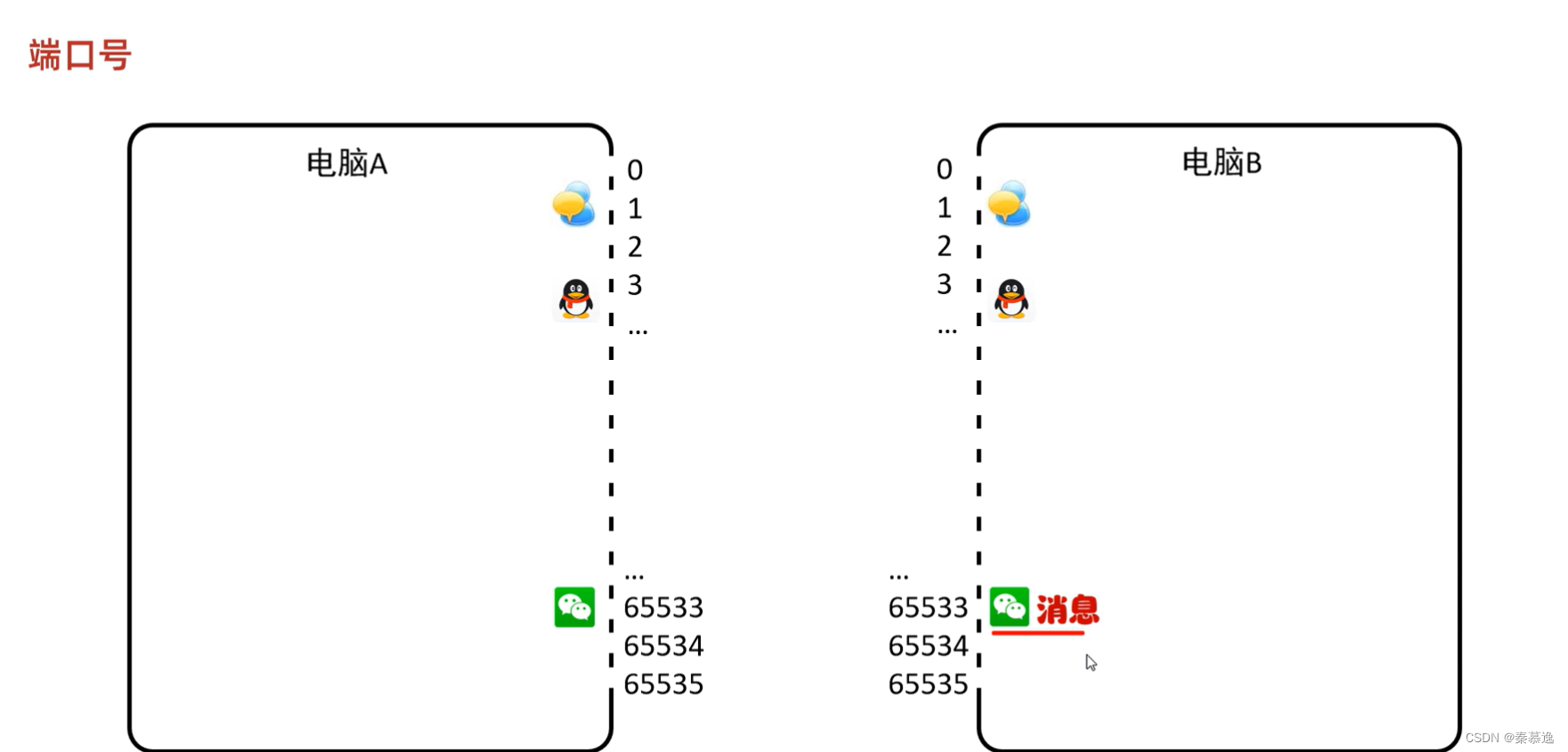
2.3 端口号

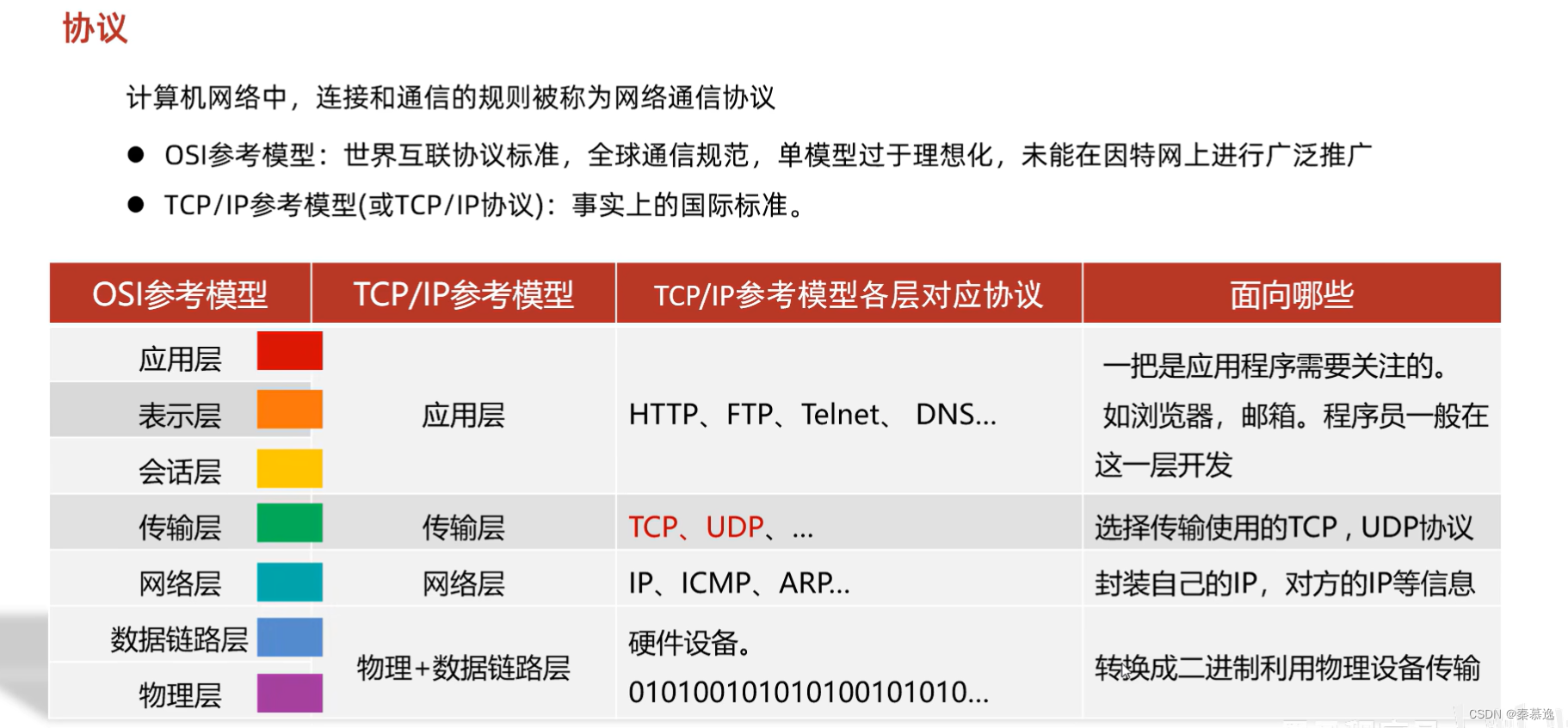
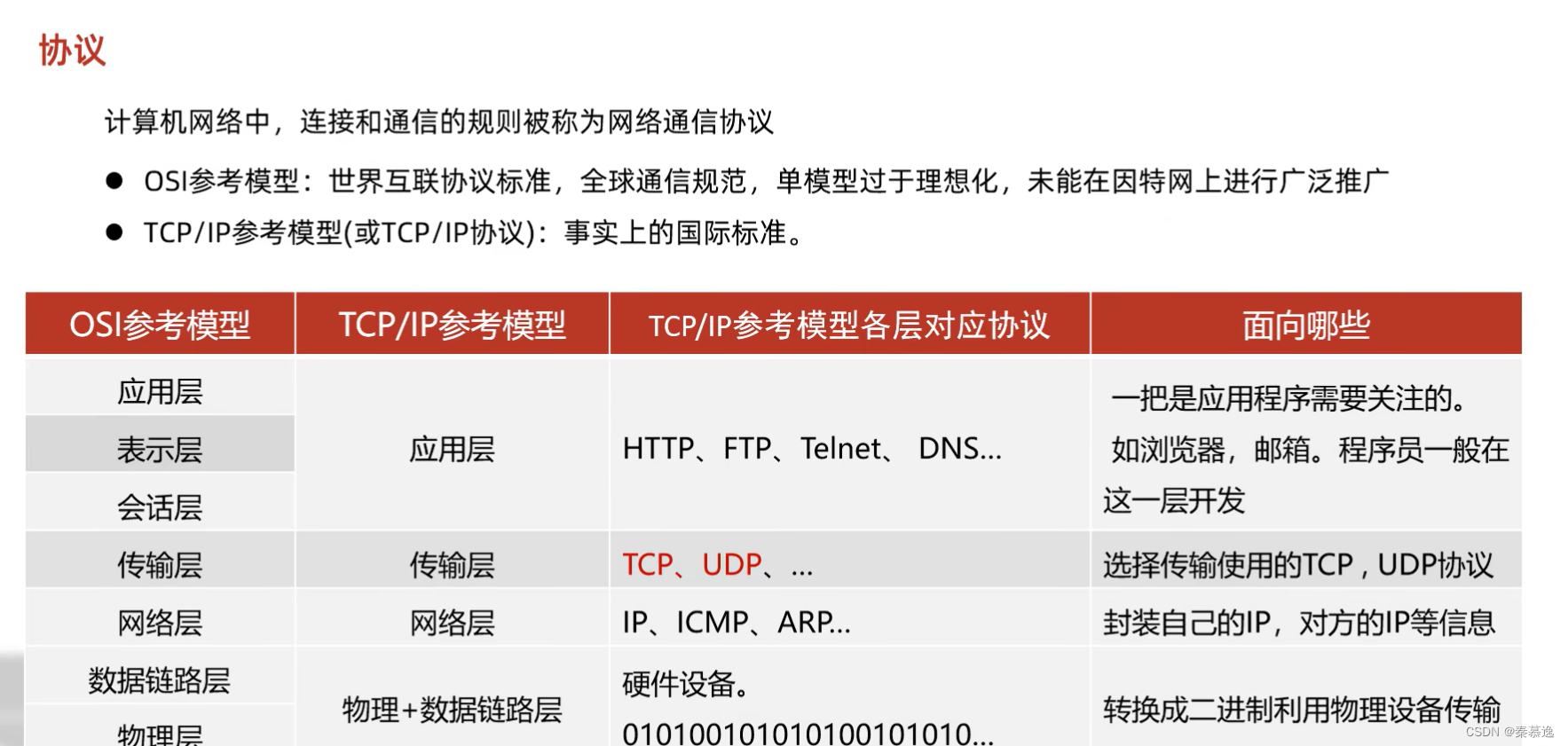
2.4 协议

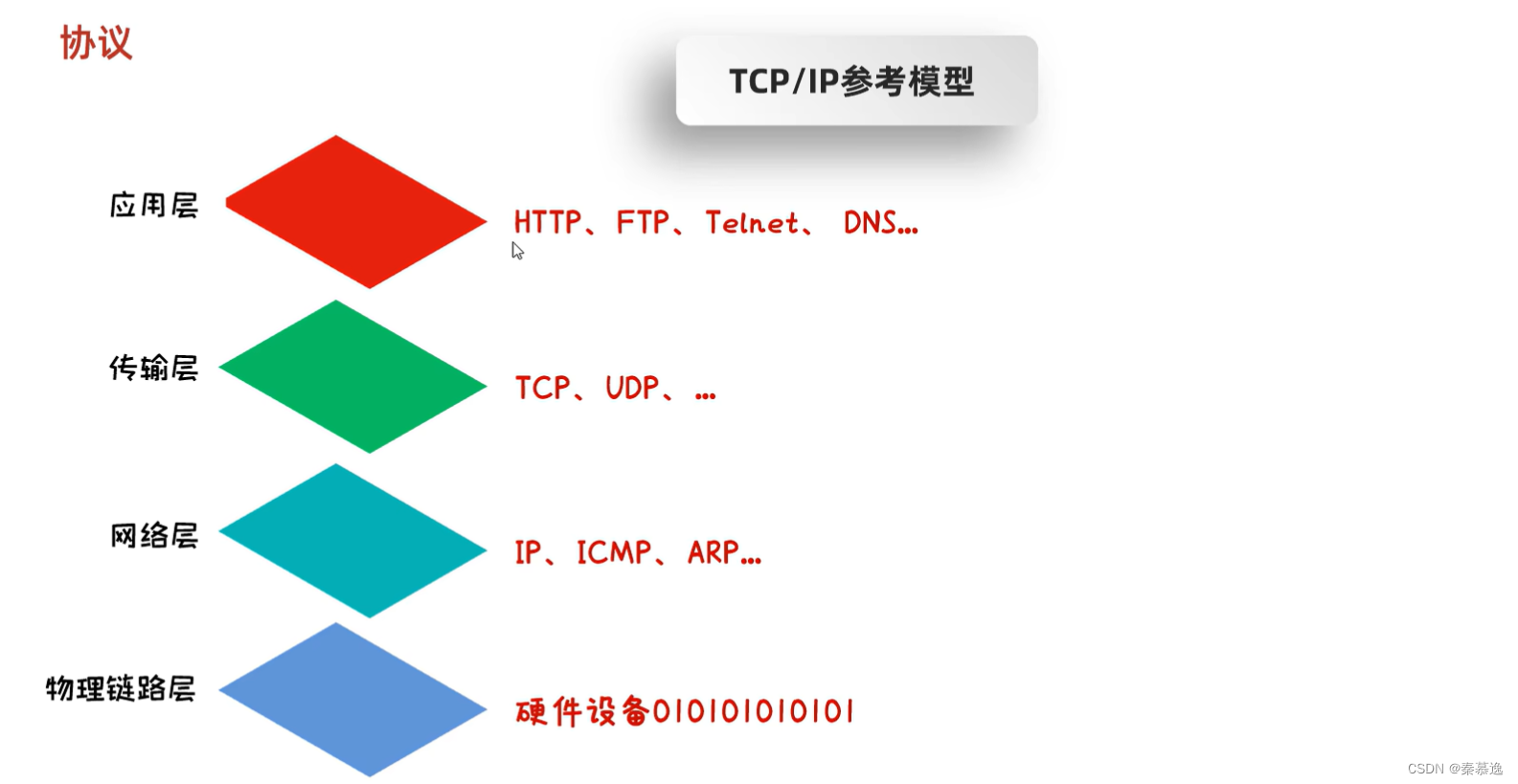
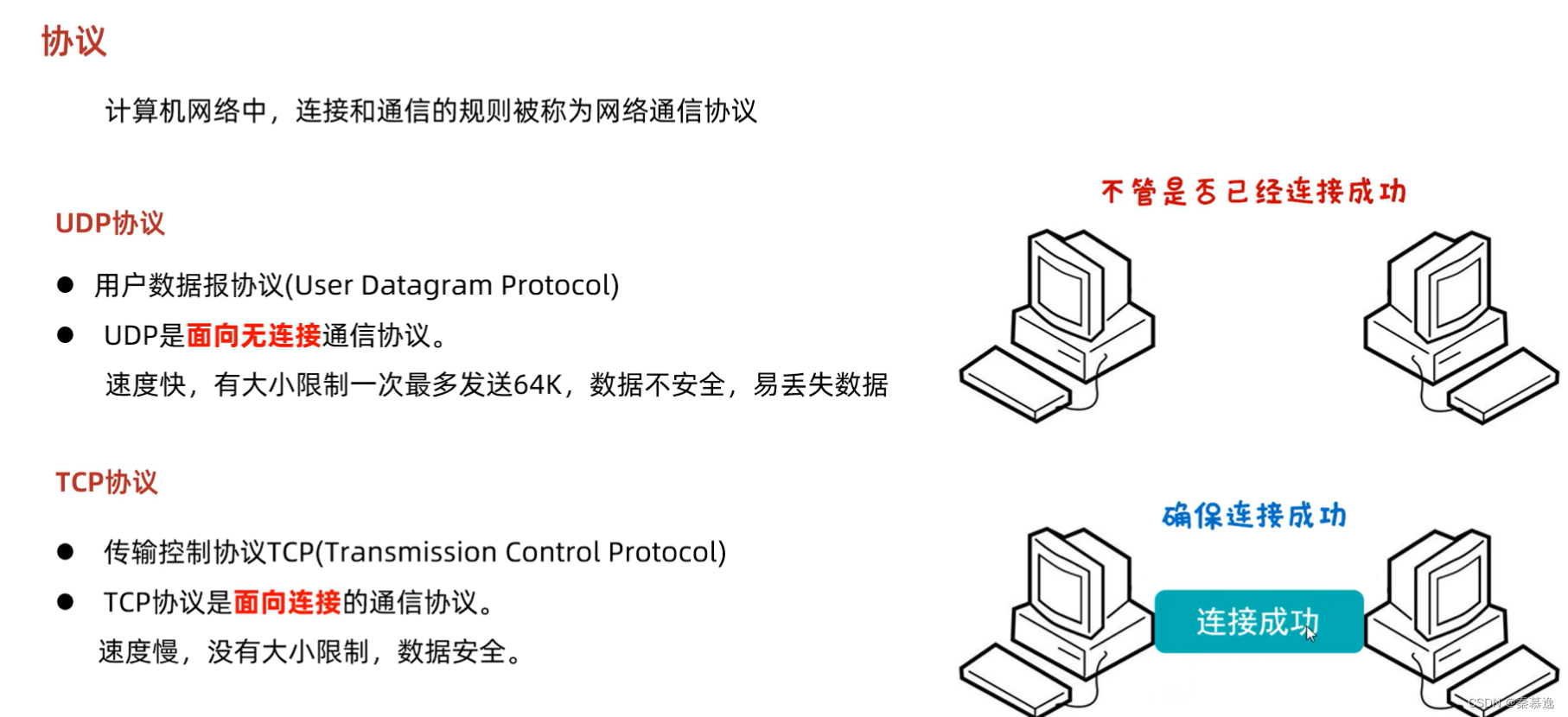
三、UDP通信程序
3.1 发送数据

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建DatagramSocket对象(快递公司)
//细节:
//绑定端口,以后我们就是通过这个端口往外发送
//空参:所有可用的端口中随机一个进行使用
//有参:指定端口号进行绑定
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
//1.打包数据
String str = "你好啊!";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, address, port);
//2.发送数据
ds.send(dp);
//3.释放资源
ds.close();
}
3.2 接收数据

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//0.创建对象
//细节:
//在接收的时候,一定要绑定端口
//而且绑定的端口一定要跟发送的端口保持一致
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);
//1.接收数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length);
//该方法是阻塞的
//程序执行到这一步的时候,会在这里死等
//等发送端发送消息
ds.receive(dp);
//2.解析数据
byte[] data = dp.getData();
InetAddress address = dp.getAddress();
int port = dp.getPort();
int length = dp.getLength();
System.out.println("发送的数据是:" + new String(data, 0, length));
System.out.println("这条数据是从" + address + "的" + port + "端口发送出来的");
//3.释放资源
ds.close();
}
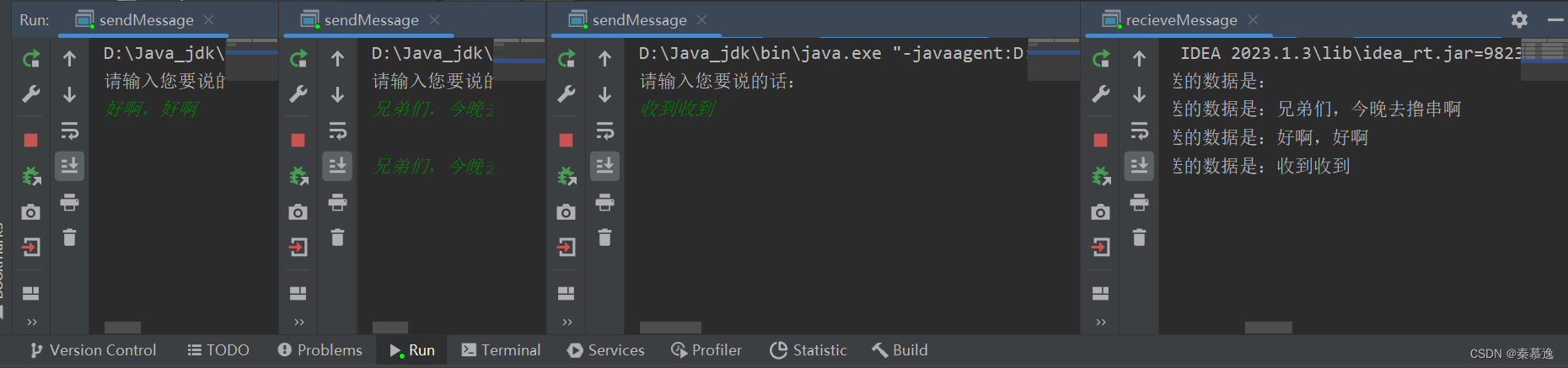
3.3 练习

接收端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length);
while (true) {
ds.receive(dp);
byte[] data = dp.getData();
String hostAddress = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String hostName = dp.getAddress().getHostName();
int length = dp.getLength();
System.out.println("ip为:" + hostAddress + ",主机名为:" + hostName + "发送的数据是:" + new String(data, 0, length));
}
}
发送端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您要说的话:");
while (true) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
if(str.equals("886")){
break;
}
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, address, port);
ds.send(dp);
}
ds.close();
}
四、UDP的三种通信方式
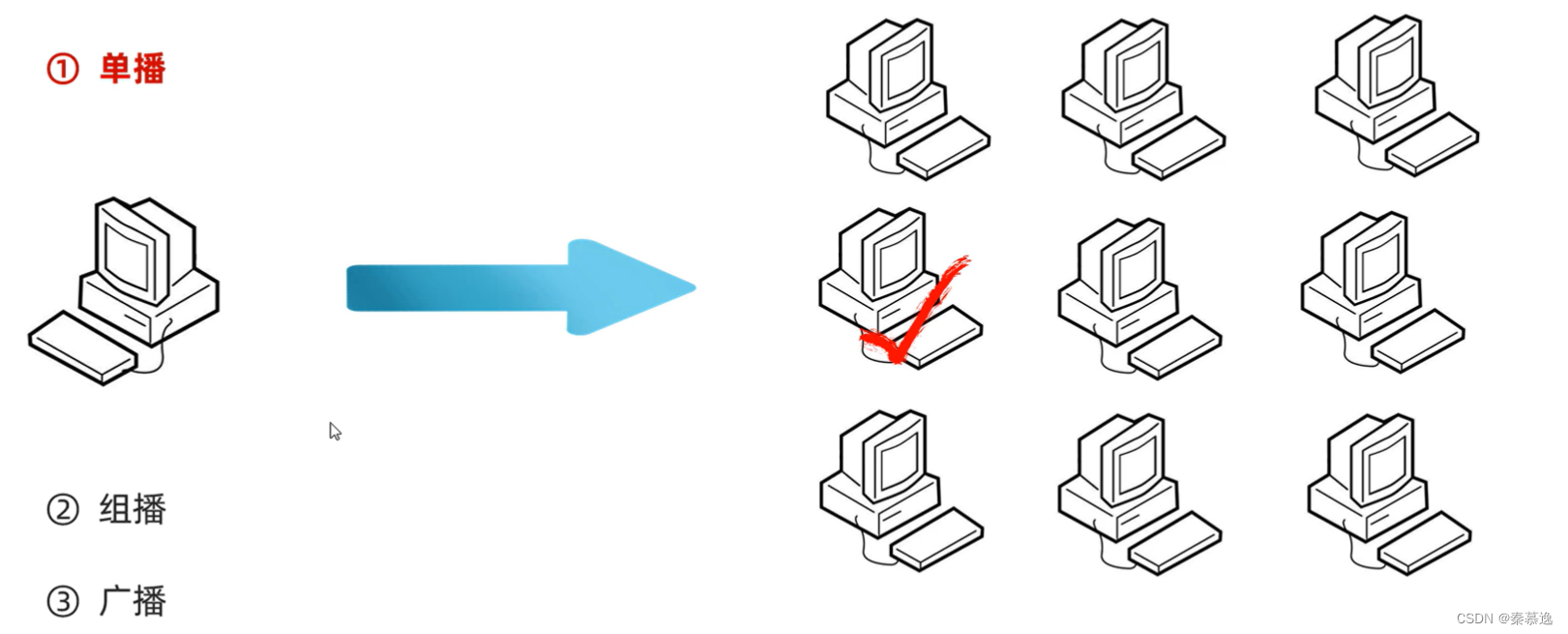
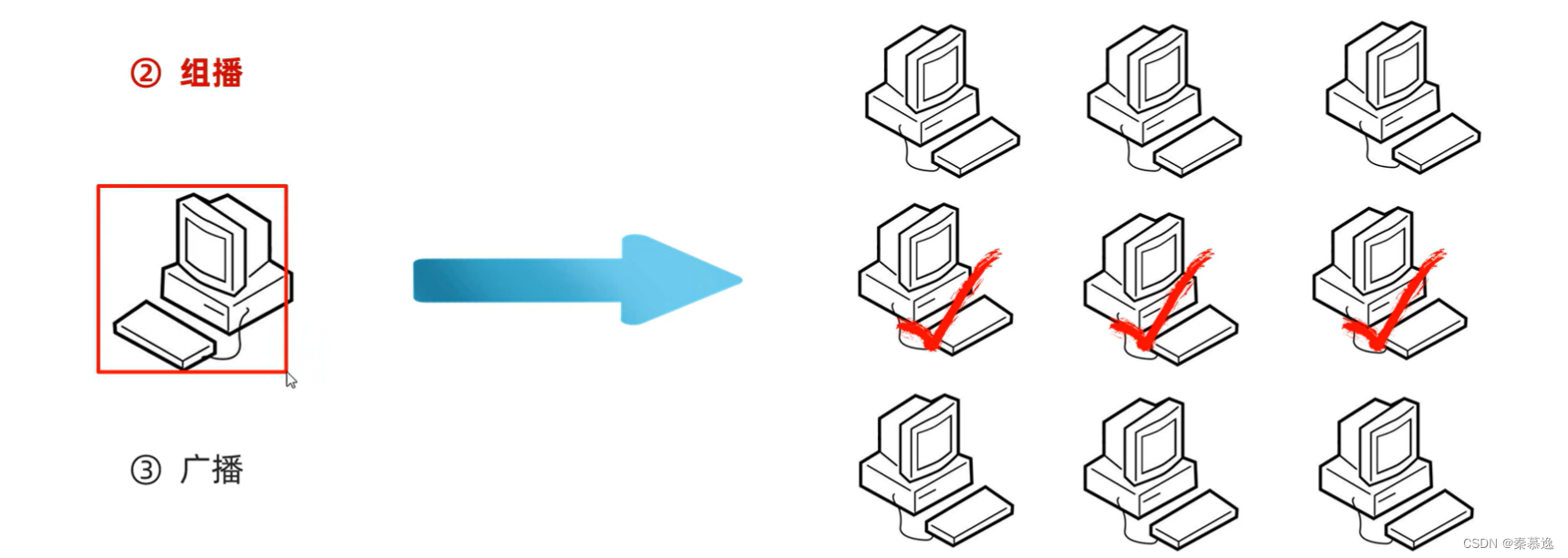
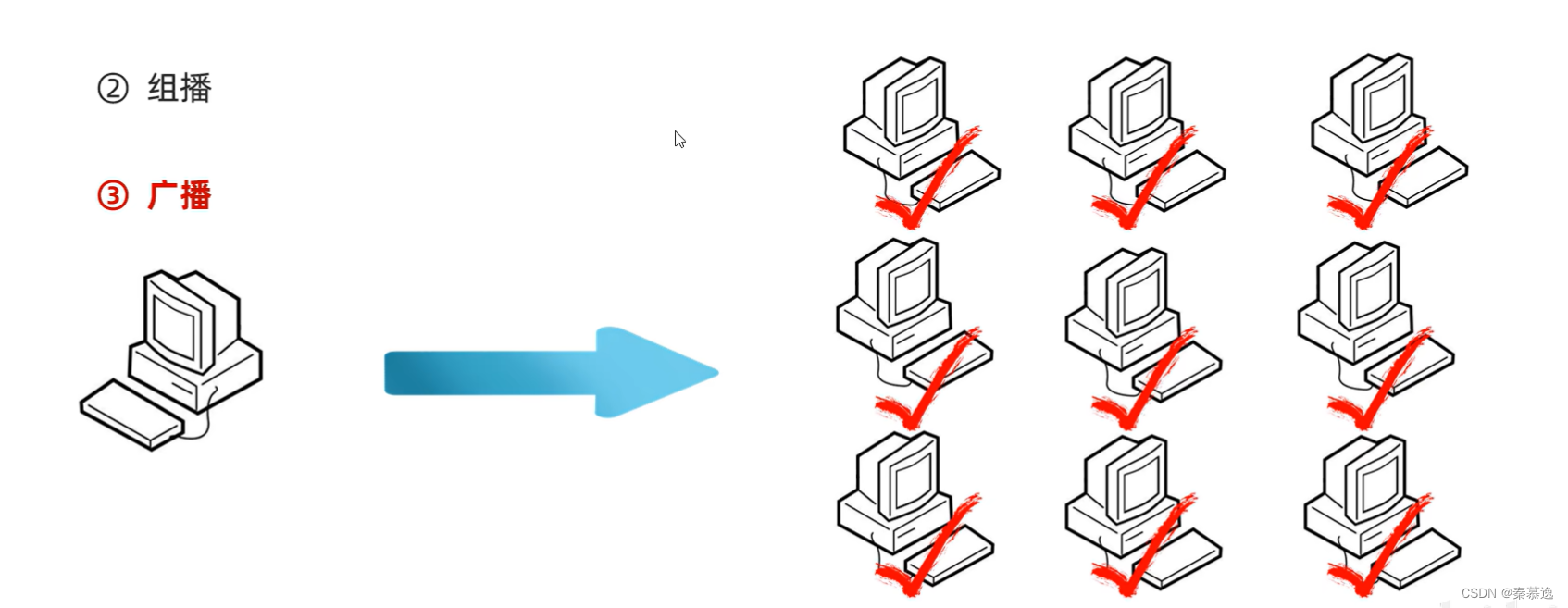

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//组播发送代码
MulticastSocket ms = new MulticastSocket();
String s = "你好你好";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("224.0.0.2");
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, address, port);
//发送数据
ms.send(dp);
//释放资源
ms.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
MulticastSocket ms = new MulticastSocket(10086);
//将当前本机,添加到224.0.0.2的这一组当中
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("224.0.0.2");
ms.joinGroup(address);
//创建数据包对象
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length);
//接收数据
ms.receive(dp);
//解析数据
String hostAddress = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String hostName = dp.getAddress().getHostName();
byte[] data = dp.getData();
int length = dp.getLength();
int port = dp.getPort();
System.out.println("ip为:" + hostAddress + ",主机名为:" + hostName + "的人,发送了数据:" + new String(data, 0, length));
ms.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//广播发送代码
MulticastSocket ms = new MulticastSocket();
String s = "你好你好";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("255.255.255.255");
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, address, port);
//发送数据
ms.send(dp);
//释放资源
ms.close();
}
五、TCP的通信程序


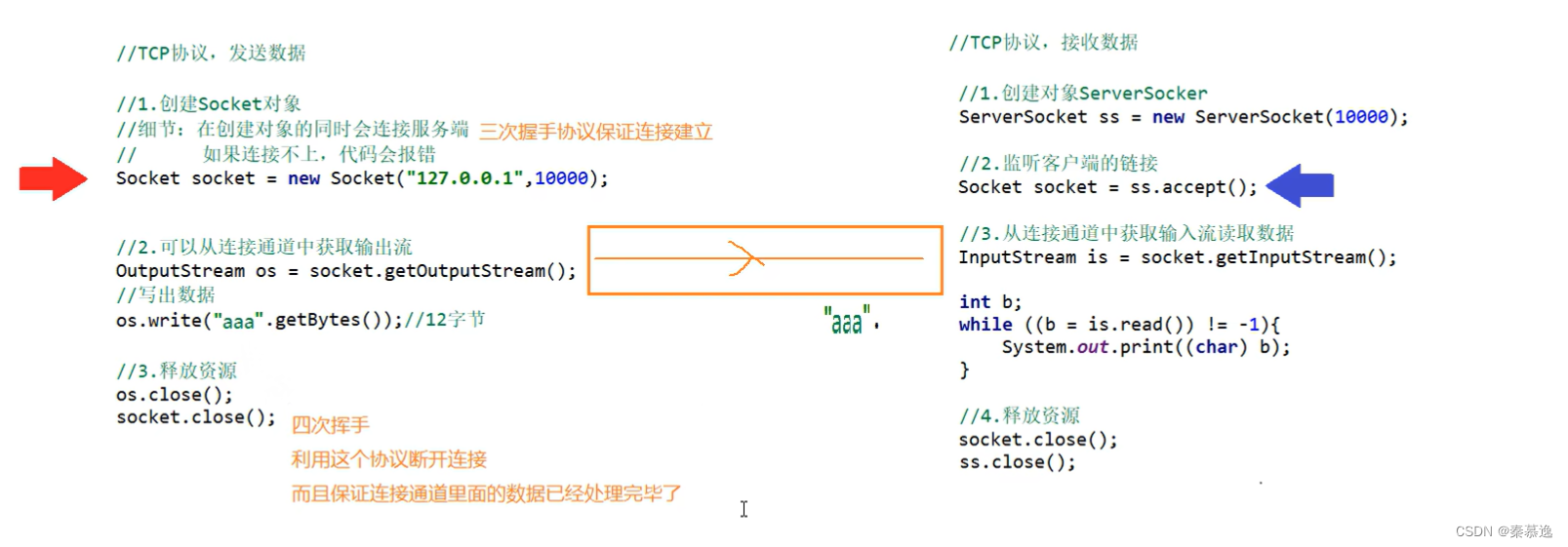
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//TCP协议 接收数据
//0.创建对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//1.监听客户端
Socket accept = ss.accept();
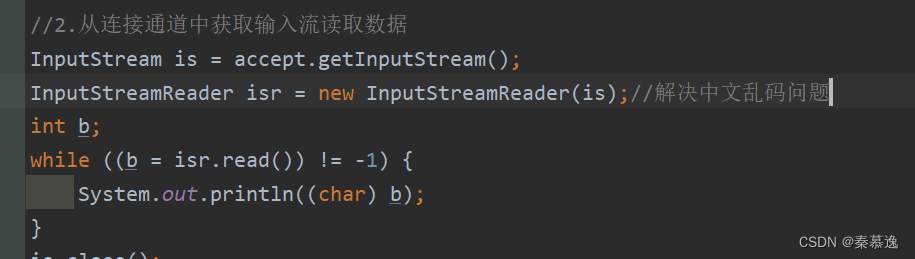
//2.从连接通道中获取输入流读取数据
InputStream is = accept.getInputStream();
int b;
while ((b = is.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) b);
}
is.close();
accept.close();
ss.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//TCP协议发送数据
//1.创建Socket对象
//细节:在创建对象时会连接服务端, 如果连接不上,代码会报错
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",10086);
//从连接通道中获取输出流
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("aaa".getBytes());
os.close();
socket.close();
}
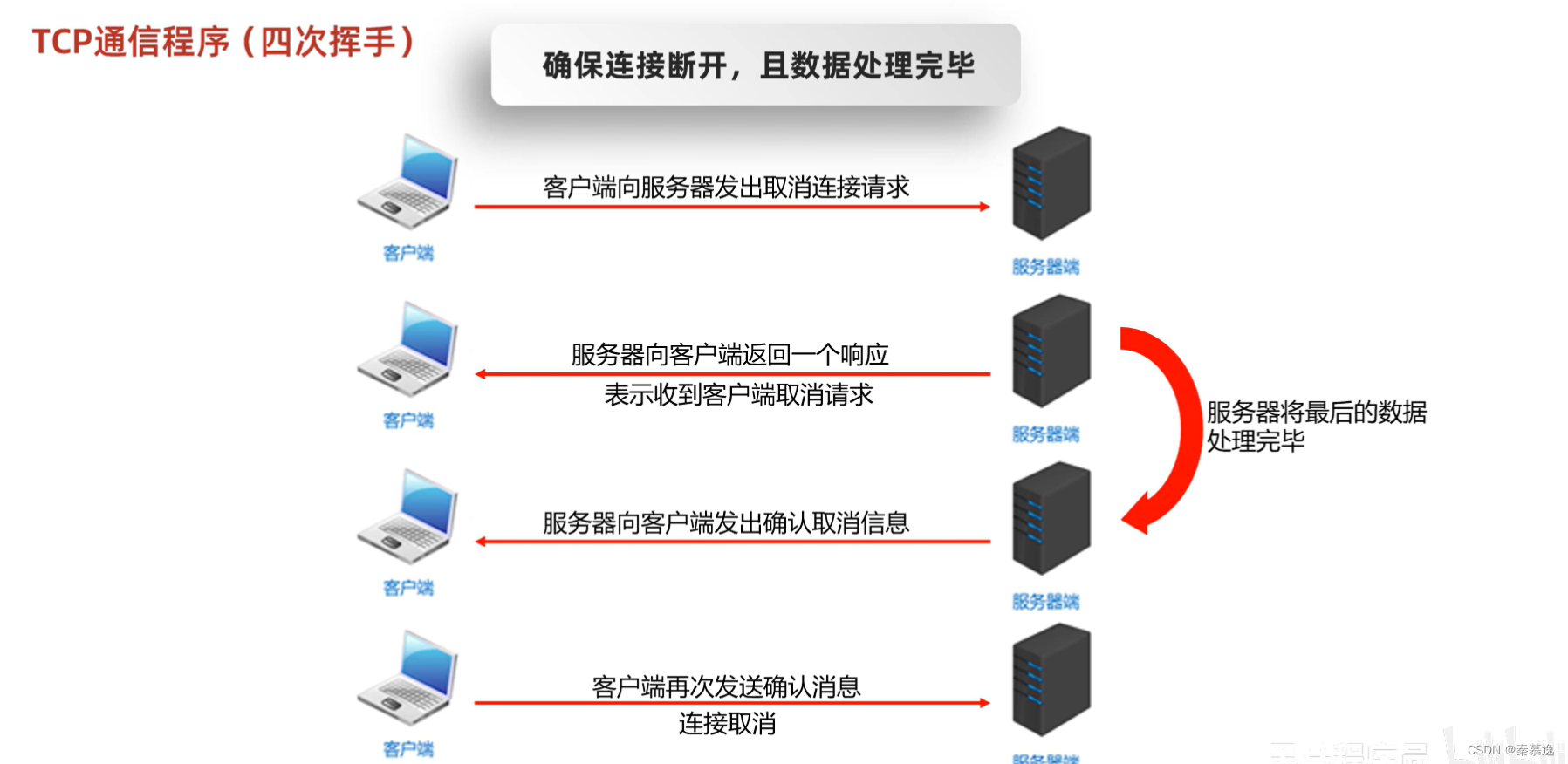
六、三次握手和四次挥手

七、练习
7.1 TCP通信练习1——多发多收
客户端:多次发送数据
服务器:接收多次数据,并打印
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*客户端:多次发送数据
服务器:接收多次数据,并打印*/
//0.创建Socket对象
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10086);
//写出数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入您要发送的消息:");
String str = sc.nextLine();
if (str.equals("886")){
break;
}
os.write(str.getBytes());
}
//释放资源
socket.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//等待客户端连接
Socket accept = ss.accept();
//读取数据
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(accept.getInputStream());
int b;
while ((b = isr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) b);
}
//释放资源
ss.close();
}
7.2 TCP通信练习2——接收和反馈
客户端:发送一条数据,接收服务端反馈的消息并打印
服务器:接收数据并打印,再给客户端反馈消息
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*客户端:发送一条数据,接收服务端反馈的消息并打印
服务器:接收数据并打印,再给客户端反馈消息*/
//0.创建一个Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10086);
//1.写出数据
String str = "见到你很高兴!";
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write(str.getBytes());
//结束标记
s.shutdownOutput();
//3.接收服务器回写的数据
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
int b;
while ((b = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) b);
}
//释放资源
s.close();
}
}
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//0.创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//1.等待客户端连接
Socket accept = ss.accept();
//2.获取数据
InputStream is = accept.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
int b;
while ((b = isr.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char) b);
}
//3.会写数据
String str = "到底有多开心呢?";
OutputStream os = accept.getOutputStream();
os.write(str.getBytes());
//释放资源
accept.close();
ss.close();
}
}
7.3 TCP通信练习3——上传文件
客户端:将本地文件上传到服务器。接收服务器的反馈。
服务器:接收客户端上传的文件,上传完毕之后给出反馈。

public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//等待客户端连接
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//读取数据并保存到本地文件中
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day32_code\\ServerDir\\a.jpg"));
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
bos.close();
//会写数据
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("上传成功");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//0.创建Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10086);
//1.创建BufferedWriter关联本地文件
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("day32_code\\ClientDir\\a.jpg"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
s.shutdownOutput();
//接收服务器的回写数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
//释放资源
s.close();
}
}
7.4 TCP通信练习4——上传文件(文件名重复问题)
解决上一题文件名重复问题

public class UUIDTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
String filename = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day32_code\\ServerDir\\" + filename + "+.jpg"));
7.5 TCP通信练习5——上传文件(多线程版)
想要服务器不停止,能接收很多用户上传的图片。
该怎么做呢?
提示:可以用循环或者多线程。
但是循环不合理,最优解发是用循环+多线程改写
public class MyRunable implements Runnable {
Socket socket;
public MyRunable(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
String filename = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day32_code\\ServerDir\\" + filename + "+.jpg"));
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
bos.close();
//会写数据
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("上传成功");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
while (true) {
//等待客户端连接
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//读取数据并保存到本地文件中
//开启一条线程
//一个用户对应服务端的一条线程
new Thread(new MyRunable(socket)).start();
}
}
}
7.6 TCP通信练习6——上传文件(线程池优化)
频繁创建线程并销毁非常浪费系统资源,所以需要用线程池优化
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//创建线程池对象
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3, // 核心线程数量
16, // 线程池总大小
60, // 空闲时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS, // 空闲时间(单位)
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2) , // 队列
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), // 线程工厂
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 阻塞队列
);
while (true) {
//等待客户端连接
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//读取数据并保存到本地文件中
//开启一条线程
//一个用户对应服务端的一条线程
new Thread(new MyRunable(socket)).start();
}
}
}
7.7 TCP通信练习7——BS(接收浏览器的消息并打印)
客户端:不需要写
服务器:接收数据并打印。
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//等待客户端连接
Socket accept = ss.accept();
//读取数据
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(accept.getInputStream());
int b;
while ((b = isr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) b);
}
//释放资源
ss.close();
}
}
运行以上代码,打开浏览器,输入回环地址127.0.0.1加端口号
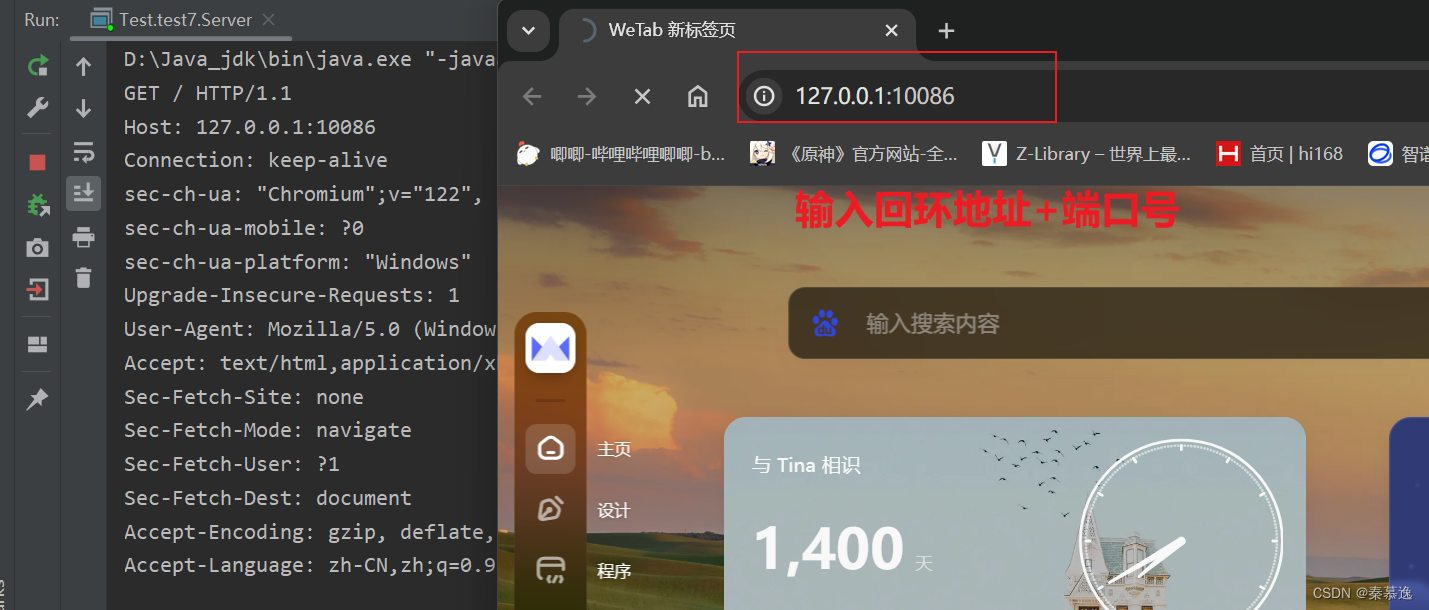
如图,idea控制台就会出现相应的信息。
![每日一题 --- 27. 移除元素 - 力扣 [Go]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/edb3655aca7349ed941562b162820103.png)