文章目录
- 二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)
- 1、二叉搜索树概念
- 2、二叉搜索树的操作
- 2.1、二叉搜索树的查找
- 2.2、二叉搜索树的插入
- 2.2、二叉树的删除
- 3、二叉搜索树的实现(含递归版本)
- 4、二叉搜索树的应用
- 4.1、K模型
- 4.2、KV模型
- 5、二叉搜索树的性能分析
- 6、二叉树进阶面试题

二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)
1、二叉搜索树概念
**二叉搜索树又叫二叉排序树和二叉查找树。**二叉搜索树可以为空。若当前二叉搜索树不为空,它有以下性质:
若左子树不为空,则根结点的的值大于左子树中所有结点的值
若右子树不为空,则根结点的的值小于左子树中所有结点的值
左右子树也有以上性质
2、二叉搜索树的操作
插入序列:
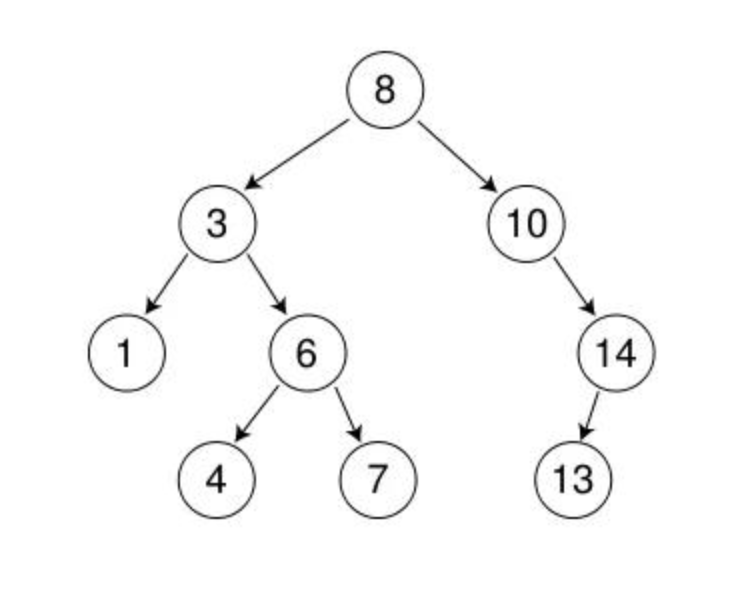
int arr[] = {8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13};
2.1、二叉搜索树的查找
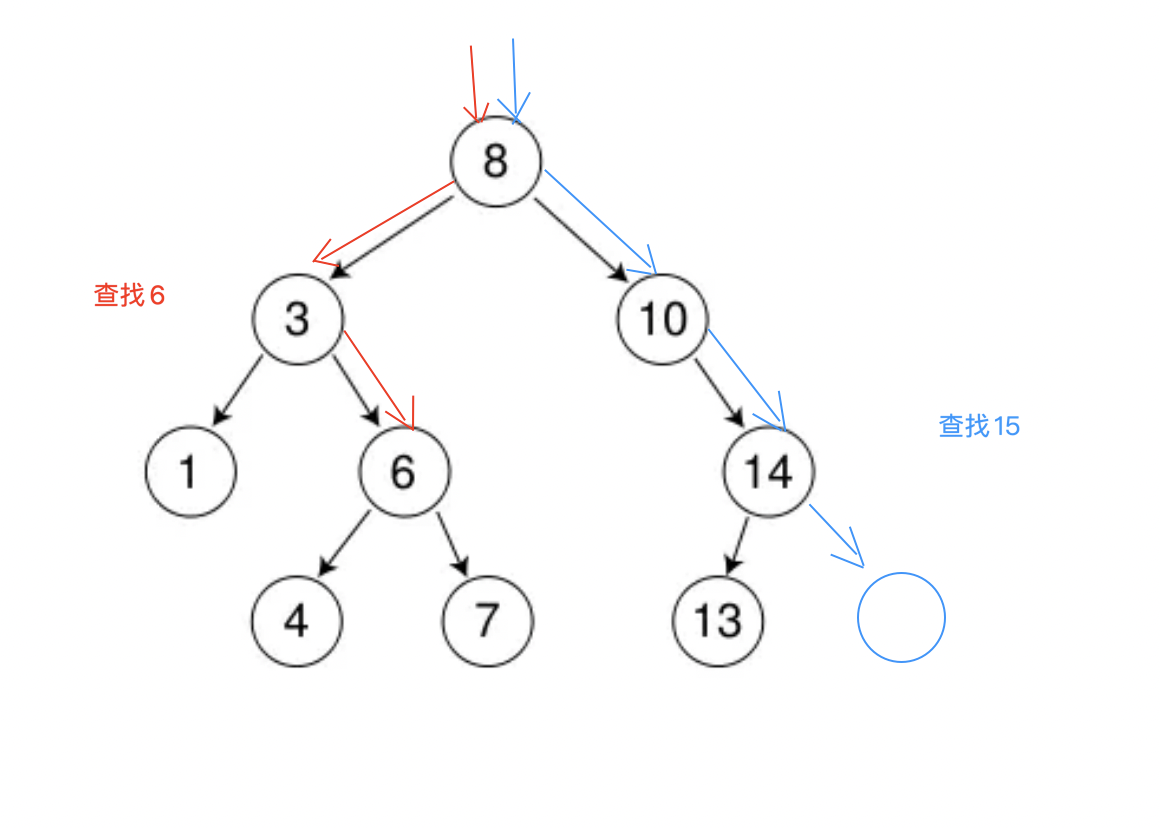
- 从根开始比较,比根小的去根的左子树中查找,比根大的去根的右子树中查找
- 一直查找直到找到,没找到的话则走到了空。
template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { //typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; BSTreeNode<K> *_left; BSTreeNode<K> *_right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K &key) : _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BinarySearchTree { public: typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; bool Find(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; if (cur == nullptr) return false; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return true; } } return false; } private: Node *_root = nullptr; };
2.2、二叉搜索树的插入
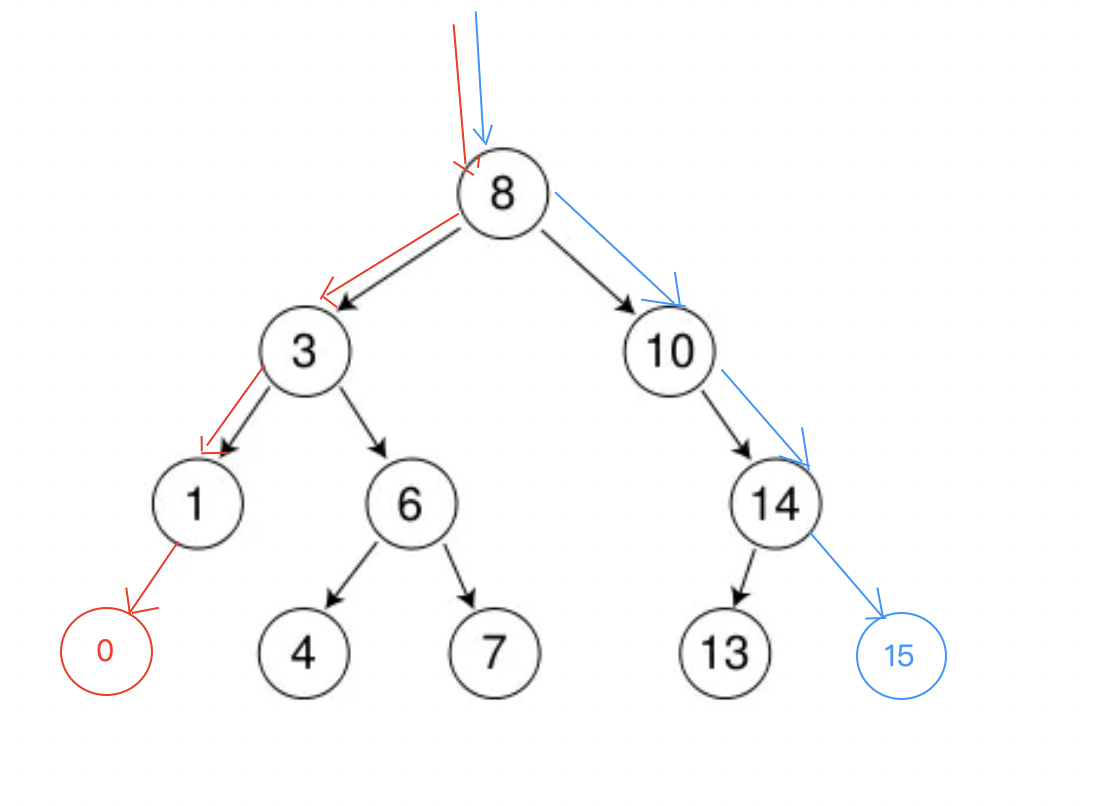
- 若树为空则直接插入
- 若树不为空,按查找的性质去找查找位置
template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { //typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; BSTreeNode<K> *_left; BSTreeNode<K> *_right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K &key) : _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BinarySearchTree { public: typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; bool Insert(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; Node *parent = nullptr; if (cur == nullptr) { Node *newNode = new Node(key); _root = newNode; return true; } while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; } } // cur == nullptr Node *newNode = new Node(key); if (parent->_key < key) parent->_right = newNode; else if (parent->_key > key) parent->_left = newNode; return true; } private: Node *_root = nullptr; };
2.2、二叉树的删除
首先查找要查找的值是否在该树中,如果不存在,则返回。否则要删除的结点分下面四种情况:
- 要删除的结点无孩子
- 要删除的结点无左孩子,只有右孩子
- 要删除的结点无右孩子,只有左孩子
- 要删除的结点有左右孩子
上面1,2,3其实可以结合起来,即将要删除的结点无孩子直接归类为无左孩子(2)或者无右孩子(3)。如下:
- 若要删除的结点是其双亲结点的左孩子,则让其双亲的左指针指向要删除的结点的右孩子,若要删除的结点是其双亲结点的右孩子,则让其双亲的右指针指向要删除的结点的右孩子。
- 若要删除的结点是其双亲结点的左孩子,则让其双亲的左指针指向要删除的结点的左孩子,若要删除的结点是其双亲结点的右孩子,则让其双亲的右指针指向要删除的结点的左孩子。
- 找当前要删除结点的左子树中的最大值(或者右子树最小值)来替换当前结点(非递归直接赋值,递归直接交换值,仅交换值,不是交换结点)
template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { //typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; BSTreeNode<K> *_left; BSTreeNode<K> *_right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K &key) : _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BinarySearchTree { public: typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; bool Erase(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; Node *parent = nullptr; if (cur == nullptr) return false; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { //找到要删的结点 // 当前要删的结点有一个孩子或者没有孩子 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { // 判断跟结点是否只有一颗子树 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_right; } else { if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_right; else parent->_right = cur->_right; } delete cur; return true; } else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { // 判断跟结点是否只有一颗子树 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_left; } else { if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_left; else parent->_right = cur->_left; } delete cur; return true; } else { // 当前要删的结点有两个孩子 // 找个替代的值去删 -- 找左子树的最右结点,即左子树最大的结点 Node *LeftMax = cur->_left; Node *LeftMaxParent = cur; while (LeftMax->_right) { LeftMaxParent = LeftMax; LeftMax = LeftMax->_right; } cur->_key = LeftMax->_key; if (LeftMaxParent->_left == LeftMax) LeftMaxParent->_left = LeftMax->_left; else LeftMaxParent->_right = LeftMax->_left; delete LeftMax; return true; } } } return false; } private: Node *_root = nullptr; };
3、二叉搜索树的实现(含递归版本)
template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { //typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; BSTreeNode<K> *_left; BSTreeNode<K> *_right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K &key) : _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BinarySearchTree { public: typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; BinarySearchTree() = default; BinarySearchTree(const BinarySearchTree<K> &b) { _root = Copy(b._root); } Node *Copy(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return nullptr; Node *newNode = new Node(root->_key); newNode->_left = Copy(root->_left); newNode->_right = Copy(root->_right); return newNode; } BinarySearchTree<K> &operator=(BinarySearchTree<K> b) { swap(b._root, _root); return *this; } ~BinarySearchTree() { Destroy(_root); } void Destroy(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return; Destroy(root->_left); Destroy(root->_right); delete root; } bool Erase(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; Node *parent = nullptr; if (cur == nullptr) return false; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { //找到要删的结点 // 当前要删的结点有一个孩子或者没有孩子 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { // 判断跟结点是否只有一颗子树 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_right; } else { if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_right; else parent->_right = cur->_right; } delete cur; return true; } else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { // 判断跟结点是否只有一颗子树 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_left; } else { if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_left; else parent->_right = cur->_left; } delete cur; return true; } else { // 当前要删的结点有两个孩子 // 找个替代的值去删 -- 找左子树的最右结点,即左子树最大的结点 Node *LeftMax = cur->_left; Node *LeftMaxParent = cur; while (LeftMax->_right) { LeftMaxParent = LeftMax; LeftMax = LeftMax->_right; } cur->_key = LeftMax->_key; if (LeftMaxParent->_left == LeftMax) LeftMaxParent->_left = LeftMax->_left; else LeftMaxParent->_right = LeftMax->_left; delete LeftMax; return true; } } } return false; } bool Insert(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; Node *parent = nullptr; if (cur == nullptr) { Node *newNode = new Node(key); _root = newNode; return true; } while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; } } // cur == nullptr Node *newNode = new Node(key); if (parent->_key < key) parent->_right = newNode; else if (parent->_key > key) parent->_left = newNode; return true; } bool Find(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; if (cur == nullptr) return false; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return true; } } return false; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } bool FindR(const K &key) { return _FindR(_root, key); } bool InsertR(const K &key) { return _InsertR(_root, key); } bool EraseR(const K &key) { return _EraseR(_root, key); } private: bool _EraseR(Node *root, const K &key) { if (root == nullptr) return false; if (root->_key < key) { return _EraseR(root->_right, key); } else if (root->_key > key) { return _EraseR(root->_left, key); } else { Node *del = root; if (root->_right == nullptr) root = root->_left; else if (root->_left == nullptr) root = root->_right; else { // 将当前要删的结点的值和当前结点的左子树最大值的结点交换 Node *LeftMax = root->_left; while (LeftMax->_right) { LeftMax = LeftMax->_right; } swap(LeftMax->_key, root->_key); return _EraseR(root, key); } delete del; return true; } } bool _InsertR(Node *&root, const K &key) { if (root == nullptr) { root = new Node(key); return true; } if (root->_key < key) { return _InsertR(root->_right, key); } else if (root->_key > key) { return _InsertR(root->_left, key); } else { return false; } } bool _FindR(Node *root, const K &key) { if (root == nullptr) return false; if (root->_key < key) { return _FindR(root->_right, key); } else if (root->_key > key) { return _FindR(root->_left, key); } else { return true; } } void _InOrder(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return; if (root->_left) _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; if (root->_right) _InOrder(root->_right); } Node *_root = nullptr; };
4、二叉搜索树的应用
4.1、K模型
K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
比如:上述实现的就是,比如存的就是整型值,看该树中是否有要查找的值。或者给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确。
4.2、KV模型
KV模型即每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值value,即<key, value>的键值对。
比如:英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word,chinese>就构成一种键值对。
- 对K模型的二叉搜索树进行小改造就可以得到KV模型的二叉搜索树
template<class K, class V> struct BSTreeNode { //typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; BSTreeNode<K, V> *_left; BSTreeNode<K, V> *_right; K _key; V _val; BSTreeNode(const K &key,const K &val) : _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key),_val(val) {} }; template<class K, class V> class BinarySearchTree { public: typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node; BinarySearchTree() = default; BinarySearchTree(const BinarySearchTree<K, V> &b) { _root = Copy(b._root); } Node *Copy(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return nullptr; Node *newNode = new Node(root->_key); newNode->_left = Copy(root->_left); newNode->_right = Copy(root->_right); return newNode; } BinarySearchTree<K, V> &operator=(BinarySearchTree<K, V> b) { swap(b._root, _root); return *this; } ~BinarySearchTree() { Destroy(_root); } void Destroy(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return; Destroy(root->_left); Destroy(root->_right); delete root; } bool Erase(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; Node *parent = nullptr; if (cur == nullptr) return false; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { //找到要删的结点 // 当前要删的结点有一个孩子或者没有孩子 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { // 判断跟结点是否只有一颗子树 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_right; } else { if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_right; else parent->_right = cur->_right; } delete cur; return true; } else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { // 判断跟结点是否只有一颗子树 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_left; } else { if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_left; else parent->_right = cur->_left; } delete cur; return true; } else { // 当前要删的结点有两个孩子 // 找个替代的值去删 -- 找左子树的最右结点,即左子树最大的结点 Node *LeftMax = cur->_left; Node *LeftMaxParent = cur; while (LeftMax->_right) { LeftMaxParent = LeftMax; LeftMax = LeftMax->_right; } cur->_key = LeftMax->_key; if (LeftMaxParent->_left == LeftMax) LeftMaxParent->_left = LeftMax->_left; else LeftMaxParent->_right = LeftMax->_left; delete LeftMax; return true; } } } return false; } bool Insert(const K &key,const K &val) { Node *cur = _root; Node *parent = nullptr; if (cur == nullptr) { Node *newNode = new Node(key,val); _root = newNode; return true; } while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; } } // cur == nullptr Node *newNode = new Node(key,val); if (parent->_key < key) parent->_right = newNode; else if (parent->_key > key) parent->_left = newNode; return true; } Node *Find(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; if (cur == nullptr) return nullptr; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return cur; } } return nullptr; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return; if (root->_left) _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; if (root->_right) _InOrder(root->_right); } Node *_root = nullptr; }; void test_BST_KV() { BinarySearchTree<string, string> bstkv; bstkv.Insert("hello", "你好"); bstkv.Insert("xp", "徐鹏"); bstkv.Insert("zl", "紫玲"); bstkv.Insert("search", "搜索"); string s; while (cin >> s) { auto ret = bstkv.Find(s); if (ret) cout << ret->_val << endl; else cout << "没有这个" << endl; } }
5、二叉搜索树的性能分析
由于二叉搜索树的插入和删除都用到了查找,所以查找效率代表了二叉搜索树的各操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二叉搜索树的深度的函数,深度越深,查找中比较的次数越多。
但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树。
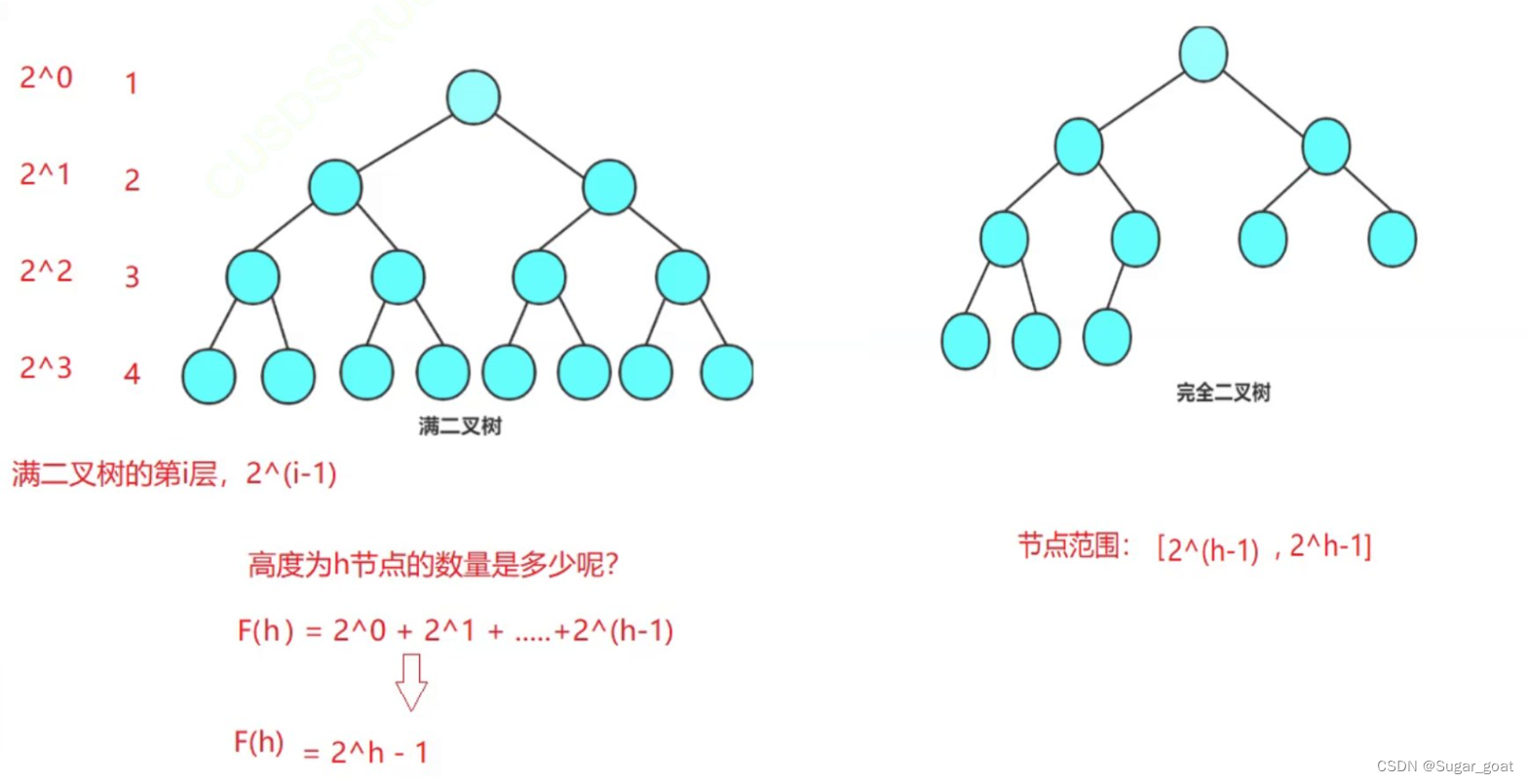
时间复杂度:
- 在最优的情况下,二叉搜索树接近为完全二叉树,其平均比较次数为:nlogn
- 在最坏的情况下,二叉搜索树接近为单边二叉树,其平均比较次数为:n^2
如果退化为单边树,那么二叉搜索树的优势就失去了,怎么解决?后面学了AVL(平衡二叉树)和红黑树就可以解决这个问题。
6、二叉树进阶面试题
1、606. 根据二叉树创建字符串
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 606. 根据二叉树创建字符串 class Solution { public: string tree2str(TreeNode *root) { if (root == nullptr) return ""; string str = to_string(root->val); // 要加括号:1、当前结点的左不空,左为空右不空也要加 // 2、当前结点的右不空 // 往左子树找 if (root->left || root->right) { str += '('; str += tree2str(root->left); str += ')'; } // 往右子树找 if (root->right) { str += '('; str += tree2str(root->right); str += ')'; } return str; } };2、102. 二叉树的层序遍历
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 class Solution { public: vector <vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode *root) { vector <vector<int>> vv; if (root == nullptr) return vv; queue < TreeNode * > q; q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { vector<int> v; // 用来每次尾插vv int size = q.size();// 当前层的元素个数 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { TreeNode *cur = q.front(); v.push_back(cur->val); q.pop(); if (cur->left) q.push(cur->left); if (cur->right) q.push(cur->right); } vv.push_back(v); } return vv; } };3、107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II class Solution { public: vector <vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode *root) { vector <vector<int>> vv; if (root == nullptr) return vv; queue < TreeNode * > q; q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { vector<int> v; // 用来每次尾插vv int size = q.size();// 当前层的元素个数 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { TreeNode *cur = q.front(); v.push_back(cur->val); q.pop(); if (cur->left) q.push(cur->left); if (cur->right) q.push(cur->right); } vv.push_back(v); } reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end()); return vv; } };4、236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 解法一:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool IsInTree(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *cur) { if (root == nullptr) return false; return root == cur || IsInTree(root->left, cur) || IsInTree(root->right, cur); } TreeNode *lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *p, TreeNode *q) { if (root == nullptr) return nullptr; if (p == root || q == root) return root; bool pInLeft, pInRight, qInLeft, qInRight; pInLeft = IsInTree(root->left, p); pInRight = !pInLeft; // p肯定在左右子树中的一个 qInLeft = IsInTree(root->left, q); qInRight = !qInLeft; // q肯定在左右子树中的一个 if ((pInLeft && qInRight) || (pInRight && qInLeft)) { // 左右子树各一个,那么当前结点就是公共结点 return root; } else if ((pInLeft && qInLeft)) { return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);// 去左子树找 } else return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);// 去右子树找 } };
- 解法二:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ // 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 class Solution { public: bool GetPath(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *cur, stack<TreeNode *> &v) { if (root == nullptr) return false; v.push(root); if (cur == root) return true; // 去左边找 if (GetPath(root->left, cur, v)) return true; // 去右边找 if (GetPath(root->right, cur, v)) return true; // 左右都没找到 v.pop(); return false; } TreeNode *lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *p, TreeNode *q) { stack < TreeNode * > sp; stack < TreeNode * > sq; GetPath(root, p, sp); GetPath(root, q, sq); // 两个路径找交点 while (sp.size() != sq.size()) { if (sp.size() > sq.size()) sp.pop(); else sq.pop(); } while (sp.top() != sq.top()) { sp.pop(); sq.pop(); } return sp.top(); } };5、JZ36 二叉搜索树与双向链表
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ // JZ36 二叉搜索树与双向链表 class Solution { public: void InOrderConvert(TreeNode *cur, TreeNode *&pre) { if (cur == nullptr) return; InOrderConvert(cur->left, pre); // 关键 cur->left = pre; if (pre) pre->right = cur; pre = cur; InOrderConvert(cur->right, pre); } TreeNode *Convert(TreeNode *pRootOfTree) { if (!pRootOfTree) return nullptr; TreeNode *pre = nullptr; InOrderConvert(pRootOfTree, pre); TreeNode *head = pRootOfTree; while (head->left) { head = head->left; } return head; } };6、105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 class Solution { public: TreeNode *_buildTree(vector<int> &preorder, vector<int> &inorder, int &prei, int inbegin, int inend) { // 中序左右区间不对 if (inbegin > inend) return nullptr; // 先创建结点 ,再构建它的左右子树 TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(preorder[prei++]); // 中序序列划分左右区间 int rooti = inbegin; while (rooti <= inend) { if (inorder[rooti] != root->val) rooti++; else break; } // 再构建左右子树 // [inbegin,rooti-1] [rooti+1,inend] root->left = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, inbegin, rooti - 1); root->right = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, rooti + 1, inend); return root; } TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &preorder, vector<int> &inorder) { int prei = 0; return _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, 0, inorder.size() - 1); } };7、106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 class Solution { public: TreeNode *_buildTree(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder, int &posti, int inbegin, int inend) { // 中序左右区间不对 if (inbegin > inend) return nullptr; // 先创建结点 ,再构建它的左右子树 TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(postorder[posti--]); // 中序序列划分左右区间 先构建右子树 int rooti = inend; while (rooti >= inbegin) { if (inorder[rooti] != root->val) rooti--; else break; } // 再构建右左子树 // [inbegin,rooti-1] [rooti+1,inend] root->right = _buildTree(inorder, postorder, posti, rooti + 1, inend); root->left = _buildTree(inorder, postorder, posti, inbegin, rooti - 1); return root; } TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder) { int posti = postorder.size() - 1; return _buildTree(inorder, postorder, posti, 0, inorder.size() - 1); } };8、144. 二叉树的前序遍历
- 用非递归方法:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 144. 二叉树的前序遍历 class Solution { public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) { stack < TreeNode * > s; vector<int> v; TreeNode *cur = root; while (cur || !s.empty()) { while (cur) { v.push_back(cur->val); s.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } // 左子树已经走完 TreeNode *top = s.top(); s.pop(); // 现在走右子树 cur = top->right; } return v; } };9、94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 用非递归方法:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 94. 二叉树的中序遍历 class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) { stack < TreeNode * > s; vector<int> v; TreeNode *cur = root; while (cur || !s.empty()) { while (cur) { s.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } // 左子树已经走完 TreeNode *top = s.top(); s.pop(); // 出栈的时候访问 v.push_back(top->val); // 现在走右子树 cur = top->right; } return v; } };10、145. 二叉树的后序遍历
- 用非递归方法:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ // 145. 二叉树的后序遍历 class Solution { public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) { stack < TreeNode * > s; vector<int> v; TreeNode *cur = root; TreeNode *pre = nullptr; while (cur || !s.empty()) { while (cur) { s.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } // 左子树已经走完 TreeNode *top = s.top(); // 当前结点的右子树为空,可以访问当前结点 // 或者右子树不空,但是已经访问过,也可以访问当前结点 // 否则去右子树继续访问 if (top->right == nullptr || top->right == pre) { v.push_back(top->val); s.pop(); // top被pop掉了说明top就变成上一个被访问的结点 pre = top; } else { // 现在走右子树 cur = top->right; } } return v; } };
OKOK,二叉排序树的讲解就到这里。如果你对Linux和C++也感兴趣的话,可以看看我的主页哦。下面是我的github主页,里面记录了我的学习代码和leetcode的一些题的题解,有兴趣的可以看看。
Xpccccc的github主页