文章目录
- 前言
- 一、使用 stb_image 库加载纹理图片
-
- 1. 获取 stb_image.h 头文件
- 2. 使用 stb_image.h 中的相关接口加载纹理图片
- 3. 纹理图片——cordeBouee4.jpg
- 二、渲染使用纹理贴图的旋转 3D 立方体
-
- 1. egl_wayland_texture_cube.c
- 2. Matrix.h 和 Matrix.c
- 3. xdg-shell-client-protocol.h 和 xdg-shell-protocol.c
- 4. 编译
- 5. 运行
- 三、不使用外部图片的纹理贴图的旋转3d 立方体
-
- 1. egl_wayland_texture_cube3_0.c
- 2. Matrix.h 和 Matrix.c
- 3. xdg-shell-client-protocol.h 和 xdg-shell-protocol.c
- 4. 编译
- 5. 运行
- 总结
- 参考资料
前言
本文主要介绍如果使用 wayland(xdg_wm_base) + egl + opengles3.0 绘制一个使用纹理贴图的绕Y轴旋转的正方体,涉及纹理图片加载(stb_image.h)等相关知识
软硬件环境:
硬件:PC
软件:ubuntu22.04 egl1.4 opengles3.0 weston9.0
一、使用 stb_image 库加载纹理图片
stb_image 是一个非常轻量级的图像加载库,由 Sean Barrett 创建并维护。这个库以单个头文件的形式存在,可以直接包含到你的项目中,无需额外的编译和链接过程。
通过包含对应的头文件,可以使用 stb_image 来加载各种常见的图片格式,例如 JPEG、PNG 等
1. 获取 stb_image.h 头文件
可以在 stb_image 库github 仓库地址 找到该库的源代码和详细信息
对于本文只需要获取 stb_image.h 这个头文件即可,将stb_image.h 头文件放到自己的工程代码目录下,如下图所示
2. 使用 stb_image.h 中的相关接口加载纹理图片
在代码中添加 STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION 宏定义和 #include “stb_image.h”,然后使用 stbi_load() 函数接口加载 JPG图片,加载完成后就会得到图片的分辨率以及像素格式信息,在使用 glTexImage2D() 加载到纹理后,然后使用 stb_image_free() 释放相关的资源,如下代码所示
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
GLuint createTexture(void)
{
GLuint textureId;
int width, height, nrChannels;
/* Generate a texture object. */
glGenTextures(1, &textureId);
unsigned char* data = stbi_load("./cordeBouee4.jpg", &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data) {
printf("width = %d, height = %d, nrChannels = %d\n", width, height, nrChannels);
GLenum format;
if (nrChannels == 1)
format = GL_RED;
else if (nrChannels == 3)
format = GL_RGB;
else if (nrChannels == 4)
format = GL_RGBA;
/* Activate a texture. */
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
/* Bind the texture object. */
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureId);
/* Load the texture. */
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
/* Set the filtering mode. */
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
stbi_image_free(data);
} else {
printf("stbi_load picture failed\n");
}
return textureId;
}
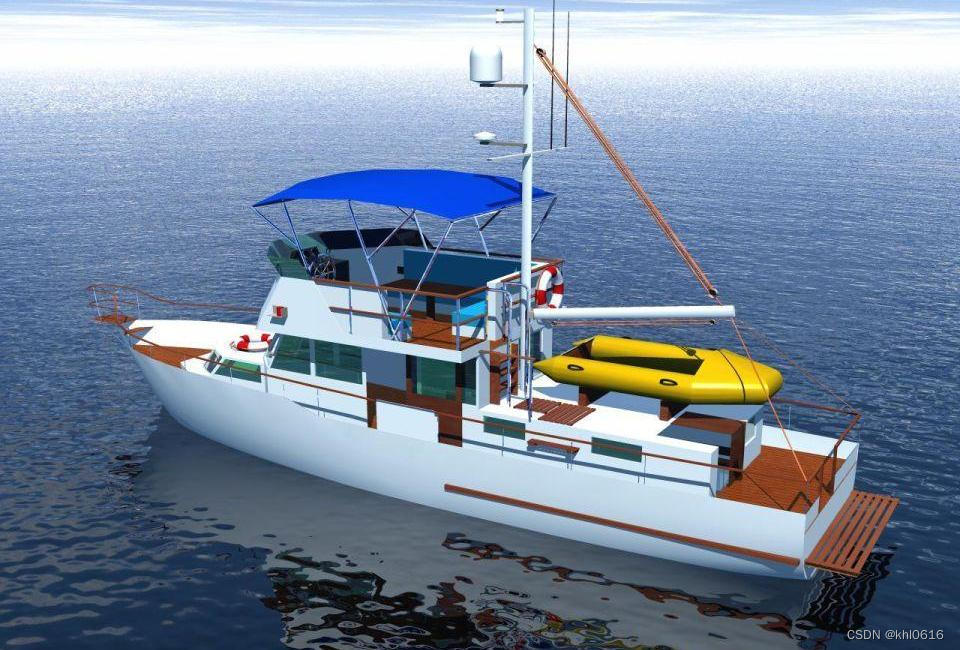
3. 纹理图片——cordeBouee4.jpg
如下图片就是本文使用的纹理图片——cordeBouee4.jpg

二、渲染使用纹理贴图的旋转 3D 立方体
使用 opengles3.0 渲染一个使用纹理贴图的旋转3D立方体,代码如 egl_wayland_texture_cube.c 所示
1. egl_wayland_texture_cube.c
#include <wayland-client.h>
#include <wayland-server.h>
#include <wayland-egl.h>
#include <EGL/egl.h>
#include <GLES3/gl3.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "xdg-shell-client-protocol.h"
#include "Matrix.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#define WIDTH 800
#define HEIGHT 600
struct wl_display *display = NULL;
struct wl_compositor *compositor = NULL;
struct xdg_wm_base *wm_base = NULL;
struct wl_registry *registry = NULL;
//opengles global var
GLuint projectionLocation;
GLuint modelLocation;
GLuint viewLocation;
GLuint simpleCubeProgram;
GLuint samplerLocation;
GLuint textureId;
float projectionMatrix[16];
float modelMatrix[16];
float viewMatrix[16];
float angleX = 30.0f;
float angleY = 0.0f;
float angleZ = 0.0f;
struct window {
struct wl_surface *surface;
struct xdg_surface *xdg_surface;
struct xdg_toplevel *xdg_toplevel;
struct wl_egl_window *egl_window;
};
static void
xdg_wm_base_ping(void *data, struct xdg_wm_base *shell, uint32_t serial)
{
xdg_wm_base_pong(shell, serial);
}
/*for xdg_wm_base listener*/
static const struct xdg_wm_base_listener wm_base_listener = {
xdg_wm_base_ping,
};
/*for registry listener*/
static void registry_add_object(void *data, struct wl_registry *registry, uint32_t name, const char *interface, uint32_t version)
{
if (!strcmp(interface, "wl_compositor")) {
compositor = wl_registry_bind(registry, name, &wl_compositor_interface, 1);
} else if (strcmp(interface, "xdg_wm_base") == 0) {
wm_base = wl_registry_bind(registry, name,
&xdg_wm_base_interface, 1);
xdg_wm_base_add_listener(wm_base, &wm_base_listener, NULL);
}
}
void registry_remove_object(void *data, struct wl_registry *registry, uint32_t name)
{
}
static struct wl_registry_listener registry_listener = {
registry_add_object, registry_remove_object};
static void
handle_surface_configure(void *data, struct xdg_surface *surface,
uint32_t serial)
{
//struct window *window = data;
xdg_surface_ack_configure(surface, serial);
//window->wait_for_configure = false;
}
static const struct xdg_surface_listener xdg_surface_listener = {
handle_surface_configure
};
static void
handle_toplevel_configure(void *data, struct xdg_toplevel *toplevel,
int32_t width, int32_t height,
struct wl_array *states)
{
}
static void
handle_toplevel_close(void *data, struct xdg_toplevel *xdg_toplevel)
{
}
static const struct xdg_toplevel_listener xdg_toplevel_listener = {
handle_toplevel_configure,
handle_toplevel_close,
};
bool initWaylandConnection()
{
if ((display = wl_display_connect(NULL)) == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to connect to Wayland display!\n");
return false;
}
if ((registry = wl_display_get_registry(display)) == NULL)
{
printf("Faield to get Wayland registry!\n");
return false;
}
wl_registry_add_listener(registry, ®istry_listener, NULL);
wl_display_dispatch(display);
if (!compositor)
{
printf("Could not bind Wayland protocols!\n");
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool initializeWindow(struct window *window)
{
initWaylandConnection();
window->surface = wl_compositor_create_surface (compositor);
window->xdg_surface = xdg_wm_base_get_xdg_surface(wm_base, window->surface);
if (window->xdg_surface == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to get Wayland xdg surface\n");
return false;
} else {
xdg_surface_add_listener(window->xdg_surface, &xdg_surface_listener, window);
window->xdg_toplevel =
xdg_surface_get_toplevel(window->xdg_surface);
xdg_toplevel_add_listener(window->xdg_toplevel,
&xdg_toplevel_listener, window);
xdg_toplevel_set_title(window->xdg_toplevel, "egl_wayland_texture");
}
return true;
}
void releaseWaylandConnection(struct window *window)
{
if(window->xdg_toplevel)
xdg_toplevel_destroy(window->xdg_toplevel);
if(window->xdg_surface)
xdg_surface_destroy(window->xdg_surface);
wl_surface_destroy(window->surface);
xdg_wm_base_destroy(wm_base);
wl_compositor_destroy(compositor);
wl_registry_destroy(registry);
wl_display_disconnect(display);
}
bool createEGLSurface(EGLDisplay eglDisplay, EGLConfig eglConfig, EGLSurface *eglSurface, struct window *window)
{
window->egl_window = wl_egl_window_create(window->surface, WIDTH, HEIGHT);
if (window->egl_window == EGL_NO_SURFACE) {
printf("Can't create egl window\n");
return false;
} else {
printf("Created wl egl window\n");
}
*eglSurface = eglCreateWindowSurface(eglDisplay, eglConfig, window->egl_window, NULL);
return true;
}
void deInitializeGLState(GLuint shaderProgram)
{
// Frees the OpenGL handles for the program
glDeleteProgram(shaderProgram);
}
void releaseEGLState(EGLDisplay eglDisplay)
{
if (eglDisplay != NULL)
{
// To release the resources in the context, first the context has to be released from its binding with the current thread.
eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
// Terminate the display, and any resources associated with it (including the EGLContext)
eglTerminate(eglDisplay);
}
}
//" gl_Position = projection * modelView * vec4(vertexPosition, 1.0);\n"
static const char glVertexShader[] 
![【洛谷 P8602】[蓝桥杯 2013 省 A] 大臣的旅费 题解(图论+深度优先搜索+树的直径+链式前向星)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/62b79a590cbf4d4cb03e4929ea10aeb3.png)