【解法一】双栈思路梳理
【解法二】利用逆波兰表达式求解(中缀转后缀)
这个有俩种方法,一是直接根据条件进行各种情况的推导直接由中缀表达式求解,
二就是将中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式,利用更容易的逆波兰表达式求解方法
描述
请写一个整数计算器,支持加减乘三种运算和括号。
数据范围:0≤∣s∣≤1000≤∣s∣≤100,保证计算结果始终在整型范围内
【解法一】双栈思路梳理
最基本的就是遍历字符串给出一个访问遍历i=0;使用num栈来存放数字,使用ops栈来存放运算符
从各种情况慢慢演练:
① 当遍历为数字,那么直接入栈 也不能简单的直接将s[i]入栈,当然要连带它后面的数字进行判断,将一整个数字比如135入栈,下面源码的toInt函数哩就展示的这一功能,唯一注意点,就是需要给i取个引用,使之能通过形参的修改改变到实参。
② 当遍历为+-* 运算符时,如果ops栈为空 入ops栈(这个容易理解就不举例子了)
我当前遍历符号的优先级大于栈顶元素优先级,那么直接入栈
当遍历符号优先级小于栈顶元素优先级,取出2个操作数和一个操作符运算


③ 当为左括号 直接入ops栈
④ 当为右括号时,停在这个位置,把当前栈中的所有可操作运算进行执行
直到遇到之前放入的左括号为止 然后把这个左括号弹出,i也继续访问下一个元素

⑤ 当字符串s访问结束之后,还会剩余一些同级别操作符,把他们取出来依次计算即可如下:
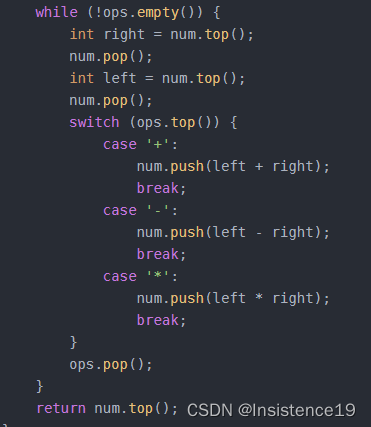
源码:
class Solution {
public:
int toInt(string s, int& i) {
int count = 0;
int j = i;
while (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9') {
i++;
count++;
}
string temp = (s.substr(j, count));
return atoi(temp.c_str());
}
int solve(string s) {
// write code here
map<char, int> mp;
mp['-'] = 1;
mp['+'] = 1;
mp['*'] = 2;
mp['('] = 0;
stack<int> num;
// num.push(0);
stack<char> ops;
int i = 0;
while (i < s.size()) {
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '*') {
if (ops.empty() || mp[s[i]] > mp[ops.top()])
ops.push(s[i++]);
else {
int right = num.top();
num.pop();
int left = num.top();
num.pop();
switch (ops.top()) {
case '+':
num.push(left + right);
break;
case '-':
num.push(left - right);
break;
case '*':
num.push(left * right);
break;
}
ops.pop();
ops.push(s[i++]);
}
} else if (s[i] == '(') {
ops.push(s[i++]);
} else if (s[i] == ')') {
while (ops.top() != '(') {
int right = num.top();
num.pop();
int left = num.top();
num.pop();
switch (ops.top()) {
case '+':
num.push(left + right);
break;
case '-':
num.push(left - right);
break;
case '*':
num.push(left * right);
break;
}
ops.pop();
}
ops.pop();
i++;
} else {
num.push(toInt(s, i));
}
}
while (!ops.empty()) {
int right = num.top();
num.pop();
int left = num.top();
num.pop();
switch (ops.top()) {
case '+':
num.push(left + right);
break;
case '-':
num.push(left - right);
break;
case '*':
num.push(left * right);
break;
}
ops.pop();
}
return num.top();
}
};【解法二】利用逆波兰表达式求解(中缀转后缀)
逼站2分钟视频【逆波兰 - 上(中缀表达式 转 后缀表达式)】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xp4y1r7rc/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=fc7e83e7f96712b431615535fe32fb1b
(1)若取出的字符是操作数 (eg, 6, 3, 7 ),则分析出完整的运算数,该操作数直接送入res。
(2)若取出的字符是运算符 (eg: ( * / - )),则将该运算符与S1栈栈顶元素比较,如果该运算符(不包括括号运算符)优先级高于S1栈栈顶运算符(包括左括号)优先级,则将该运算符进S1栈,否则,将S1栈的栈顶运算符弹出,送入res中,直至S1栈栈顶运算符(包括左括号)低于(不包括等于)该运算符优先级时停止弹出运算符,最后将该运算符送入S1栈。
(3)若取出的字符是“(”,则直接送入S1栈顶。
(4)若取出的字符是“)”,则将距离S1栈栈顶最近的“(”之间的运算符,逐个出栈,依次送入S2栈,此时抛弃“(”。
(5)重复上面的1~4步,直至处理完所有的输入字符。
(6)若取出的字符是“#”,则将S1栈内所有运算符(不包括“#”),逐个出栈,依次送入S2栈。
如果表达式结束,但栈中还有元素,将所有元素出栈,添加到后缀表达式中
源码:
#include<map>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
class solution
{
// 中缀转后缀
public:
string toInt(string s, int& i) {
int count = 0;
int j = i;
while (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9') {
i++;
count++;
}
return string(s.substr(j, count));
}
string solve(string s)
{
map<char, int> mp;
mp['('] = 0;
mp['+'] = 1;
mp['-'] = 1;
mp['*'] = 2;
mp['/'] = 2;
stack<char> ops;
string res;
int i = 0;
while (i < s.size())
{
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '/')
{
if (ops.empty() || mp[s[i]] > mp[ops.top()])
ops.push(s[i++]);
else
{
while (!ops.empty() && mp[s[i]] < mp[ops.top()])
{
res += ops.top();
ops.pop();
}
i++;
}
}
else if(s[i] == '(')
ops.push(s[i++]);
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
while (ops.top()!= '(')
{
res += ops.top();
ops.pop();
}
i++;
ops.pop();
}
else
{
res += toInt(s, i);
}
}
while (!ops.empty())
{
res += ops.top();
ops.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
solution ss;
cout << "请输入中缀表达式" << endl;
string s;
cin >> s;
cout << "中缀表达式为:";
fflush(stdout);
cout<<ss.solve(s);
return 0;
}














![[C语言]运用函数指针数组构建一个简单计算器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1ff809385ca84fb2a52569cdfb81d221.png)