目录
- 0. 背景
- 1. 创建虚拟环境
- 2. pyinstaller打包
- 2.1. 生成并修改spec文件
- 2.2. 重新生成二进制文件
- 3. 测试
- 4. 加密打包
- 4.1. 创建入口函数main.py
- 4.2. 修改detect.py
- 4.3. 加密生成main.spec文件
- 4.4. 修改main.spec文件
- 4.5. 生成二进制文件
- 4.6. 测试
0. 背景
最近需要在ubuntu 18.04上将自己写的一些基于yolov5的项目代码打包成二进制文件,方便部署的同时也尽量减少暴露源码。
参考网上的很多教程,绝大多数是在win上做的,好像没有在ubuntu 18.04上的详细打包步骤。
1. 创建虚拟环境
这里选用anaconda创建一个干净的Python环境,我这里的python版本为3.8,其他python版本影响应该不大。后面用pyinstaller打包的就是这个环境里面的依赖。
后面的操作会用到一些库,如果执行命令时报错,就自己装库。
首先,下载yolov5-v4.0,这里选择v4.0没有特殊意思,仅仅是我自己用的就是v4.0,其他版本应该也行
git clone https://gitee.com/monkeycc/yolov5.git -b v4.0
其次,创建虚拟环境,这里,需要确认下你的显卡型号、cuda版本是否和pytorch版本适配(可以去Pytorch官网查看),如果不适配后面可能会报错。我这里cuda版本是11.1,我这里选择pytorch 1.10.0。
千万不要直接pip install -r requirements.txt,会损坏你其他虚拟环境的torch!
conda create -n pyinstaller python=3.8
conda activate pyinstaller
pip install torch==1.10.0+cu111 torchvision==0.11.0+cu111 torchaudio==0.10.0 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
pip install pyyaml numpy opencv-python matplotlib scipy tqdm pandas seaborn -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install pyinstaller -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
cd yolov5
最后,下载weights(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1uVa5eylGETYN0tUB2adjcQ
提取码:ruwf),这里我将yolov5s.pt下载到./yolov5/weights。自己将一张图片test.png放到项目地址./yolov5中,然后执行以下命令测试下,一般是没问题的
python detect.py --source test.png --weights weights/yolov5s.pt
2. pyinstaller打包
pyinstaller命令需要在目标python代码detect.py所在目录./yolov5中执行。这里,我们分为两步,第一步为生成spec文件,第二步为修改spec文件参数,重新生成二进制文件。
2.1. 生成并修改spec文件
执行如下命令
cd yolov5
pyinstaller -D detect.py
生成的spec文件detect.spec位于目录yolov5中,下一步对detect.spec进行修改,主要是指定外部库、指定外部资源。
这里spec文件参数含义可以参考博客《【python第三方库】pyinstaller使用教程及spec资源文件介绍》以及博客《pyinstaller spec文件详解》,这里我对我们需要修改的参数进行介绍。
-
Analysis里面的
scripts参数,如下图

这里的scripts参数为.py文件列表,默认是目标python代码detect.py。由于我这里只需要执行detect.py,所以不需要写多余的python代码。如果除了detect.py外,还想单独执行其他python代码,可以将该python代码加入到列表中。 -
Analysis里面的
pathex参数,如下图

这里的pathex参数为文件夹列表,当空的时候,默认为目标python代码detect.py所在的目录./yolov5的绝对地址;这里通常添加自定义库所在目录地址。因为yolov5项目所需要的自定义库utils位于./yolov5中,所以这里pathex参数默认即可。 -
Analysis里面的
datas参数,如下图

这里的datas参数为资源目录/资源的列表,当有非python代码之外的其他资源时,如图片/图片目录、数据库/数据库目录、配置/配置目录、权重文件/权重文件目录等,需要在这里写明。比如权重文件yolov5s.pt,存放于./yolov5/weights目录下,这里的根目录为./yolov5;实际二进制文件运行的根目录为./yolov5/dist/detect,因此需要在该根目录下复制weights。 -
Analysis里面的
hiddenimports参数,如下图

这里的hiddenimports参数为第三方库名称列表。当报错ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'xxx',即第三方库无法import时,将module名增加到列表中。
最后完整的detect.spec文件如下,
# -*- mode: python ; coding: utf-8 -*-
block_cipher = None
a = Analysis(
['detect.py'],
pathex=[],
binaries=[],
datas=[('models','./models'), ('weights', './weights'), ('data', './data')],
hiddenimports=['utils', 'utils.autoanchor'],
hookspath=[],
hooksconfig={},
runtime_hooks=[],
excludes=[],
win_no_prefer_redirects=False,
win_private_assemblies=False,
cipher=block_cipher,
noarchive=False,
)
pyz = PYZ(a.pure, a.zipped_data, cipher=block_cipher)
exe = EXE(
pyz,
a.scripts,
[],
exclude_binaries=True,
name='detect',
debug=False,
bootloader_ignore_signals=False,
strip=False,
upx=True,
console=True,
disable_windowed_traceback=False,
argv_emulation=False,
target_arch=None,
codesign_identity=None,
entitlements_file=None,
)
coll = COLLECT(
exe,
a.binaries,
a.zipfiles,
a.datas,
strip=False,
upx=True,
upx_exclude=[],
name='detect',
)
2.2. 重新生成二进制文件
修改好detect.spec后,重新生成二进制文件,如下
pyinstaller detect.spec
生成过程中会提示是和删除原有./yolov5/dist/detect目录下的所有文件,直接输入y即可,如下图
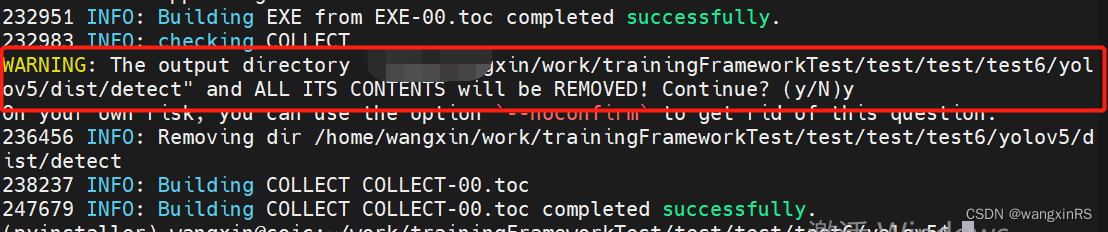
如无意外,很快可以看到成功完成。
生成的二进制文件所在目录为yolov5/dist/detect。
3. 测试
这里,退出python环境,然后执行二进制文件,如下
conda deactivate pyinstaller
cd dist/detect
./detect --source ../../test.png --weights weights/yolov5s.pt
这里,测试结果位于yolov5/dist/detect/runs中。
4. 加密打包
加密编译,防止被反编译。
安装pycrypto第三方库。
pip install pycrypto -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install tinyaes -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
加密打包按照如下步骤进行
- 创建入口函数main.py,该函数将其他python代码(detect.py)作为第三方库进行调用;
- 修改detect.py,方便入口函数main.py进行调用;
- 使用命令行
pyinstaller -D main.py生成main.spec文件; - 修改
main.spec文件,重新生成二进制文件
4.1. 创建入口函数main.py
之所以创建入口函数,主要是为了不暴露任何业务代码,将业务代码作为第三方库引入;同时,加密过程主要针对第三方库的业务代码,可以确保业务代码不可反编译。
# coding=utf8
from mydetect import detect
import argparse
import torch
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default='yolov5s.pt', help='model.pt path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default='data/images', help='source') # file/folder, 0 for webcam
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='inference size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='object confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='IOU threshold for NMS')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--view-img', action='store_true', help='display results')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all models')
parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
with torch.no_grad():
weights = opt.weights
source = opt.source
img_size = opt.img_size
conf_thres = opt.conf_thres
iou_thres = opt.iou_thres
device = opt.device
view_img = opt.view_img
save_txt = opt.save_txt
save_conf = opt.save_conf
classes = opt.classes
agnostic_nms = opt.agnostic_nms
augment = opt.augment
update = opt.update
project = opt.project
name = opt.name
exist_ok = opt.exist_ok
detect(weights, source, img_size, conf_thres, iou_thres, device, view_img, save_txt, save_conf, classes, agnostic_nms, augment, update, project, name, exist_ok)
4.2. 修改detect.py
将detect.py复制为mydetect.py,修改mydetect.py,如下
# coding=utf8
import argparse
import time
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
from numpy import random
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.datasets import LoadStreams, LoadImages
from utils.general import check_img_size, non_max_suppression, apply_classifier, scale_coords, xyxy2xywh, \
strip_optimizer, set_logging, increment_path
from utils.plots import plot_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, load_classifier, time_synchronized
# 这里主要将detect()的参数修改下
def detect(weights, source, img_size, conf_thres, iou_thres, device, view_img, save_txt, save_conf, classes, agnostic_nms, augment, update, project, name, exist_ok, save_img=False):
#source, weights, view_img, save_txt, imgsz = opt.source, opt.weights, opt.view_img, opt.save_txt, opt.img_size
imgsz = img_size
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.txt') or source.lower().startswith(
('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://'))
# Directories
save_dir = Path(increment_path(Path(project) / name, exist_ok=exist_ok)) # increment run
(save_dir / 'labels' if save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# Initialize
set_logging()
device = select_device(device)
half = device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA
# Load model
model = attempt_load(weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 model
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=model.stride.max()) # check img_size
if half:
model.half() # to FP16
# Second-stage classifier
classify = False
if classify:
modelc = load_classifier(name='resnet101', n=2) # initialize
modelc.load_state_dict(torch.load('weights/resnet101.pt', map_location=device)['model']).to(device).eval()
# Set Dataloader
vid_path, vid_writer = None, None
if webcam:
view_img = True
cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz)
else:
save_img = True
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz)
# Get names and colors
names = model.module.names if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.names
colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in names]
# Run inference
t0 = time.time()
img = torch.zeros((1, 3, imgsz, imgsz), device=device) # init img
_ = model(img.half() if half else img) if device.type != 'cpu' else None # run once
for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
# Inference
t1 = time_synchronized()
pred = model(img, augment=augment)[0]
# Apply NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes=classes, agnostic=agnostic_nms)
t2 = time_synchronized()
# Apply Classifier
if classify:
pred = apply_classifier(pred, modelc, img, im0s)
# Process detections
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per image
if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
p, s, im0, frame = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i].copy(), dataset.count
else:
p, s, im0, frame = path, '', im0s, getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)
p = Path(p) # to Path
save_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # img.jpg
txt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # img.txt
s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print string
gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results
for c in det[:, -1].unique():
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
s += f'{n} {names[int(c)]}s, ' # add to string
# Write results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
line = (cls, *xywh, conf) if opt.save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label format
with open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')
if save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to image
label = f'{names[int(cls)]} {conf:.2f}'
plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=3)
# Print time (inference + NMS)
print(f'{s}Done. ({t2 - t1:.3f}s)')
# Stream results
if view_img:
cv2.imshow(str(p), im0)
# Save results (image with detections)
if save_img:
if dataset.mode == 'image':
cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)
else: # 'video'
if vid_path != save_path: # new video
vid_path = save_path
if isinstance(vid_writer, cv2.VideoWriter):
vid_writer.release() # release previous video writer
fourcc = 'mp4v' # output video codec
fps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*fourcc), fps, (w, h))
vid_writer.write(im0)
if save_txt or save_img:
s = f"\n{len(list(save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt')))} labels saved to {save_dir / 'labels'}" if save_txt else ''
print(f"Results saved to {save_dir}{s}")
print(f'Done. ({time.time() - t0:.3f}s)')
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("运行mydetect.py!")
4.3. 加密生成main.spec文件
注意,pyinstaller命令需要在python环境中运行。
pyinstaller -D main.py
生成的main.spec文件位于./yolov5目录下。
4.4. 修改main.spec文件
相较于不加密的情况,这里将block_cipher = pyi_crypto.PyiBlockCipher(key='123456'),总体main.spec文件如下
# -*- mode: python ; coding: utf-8 -*-
block_cipher = pyi_crypto.PyiBlockCipher(key='123456')
a = Analysis(
['main.py'],
pathex=[],
binaries=[],
datas=[('models','./models'), ('weights', './weights'), ('data', './data')],
hiddenimports=['utils', 'utils.autoanchor'],
hookspath=[],
hooksconfig={},
runtime_hooks=[],
excludes=[],
win_no_prefer_redirects=False,
win_private_assemblies=False,
cipher=block_cipher,
noarchive=False,
)
pyz = PYZ(a.pure, a.zipped_data, cipher=block_cipher)
exe = EXE(
pyz,
a.scripts,
[],
exclude_binaries=True,
name='main',
debug=False,
bootloader_ignore_signals=False,
strip=False,
upx=True,
console=True,
disable_windowed_traceback=False,
argv_emulation=False,
target_arch=None,
codesign_identity=None,
entitlements_file=None,
)
coll = COLLECT(
exe,
a.binaries,
a.zipfiles,
a.datas,
strip=False,
upx=True,
upx_exclude=[],
name='detect',
)
4.5. 生成二进制文件
pyinstaller main.spec
4.6. 测试
进入yolov5/dist/main,可以看到
./main --source ../../test.png --weights weights/yolov5s.pt
如果没有问题的话,可以在./yolov5/dist/main/runs中找到推理结果。