文章目录
- 前言
- 一、根据call *sys_call_table来获取
- 二、使用dump_stack
- 三、根据MSR_LSTAR寄存器
- 四、使用sys_close
- 参考资料
前言
Linux 3.10.0 – x86_64
最简单获取sys_call_table符号的方法:
# cat /proc/kallsyms | grep sys_call_table
ffffffff816beee0 R sys_call_table
内核模块使用 kallsyms_lookup_name(推荐) 或者 kprobe:
unsigned long * __sys_call_table = (unsigned long *)kallsyms_lookup_name("sys_call_table");
下面举例说明一下x86_64平台下其他获取sys_call_table的方案。
一、根据call *sys_call_table来获取
(1)
// linux-3.10/arch/x86/kernel/entry_64.S
/*
* Register setup:
* rax system call number
* rdi arg0
* rcx return address for syscall/sysret, C arg3
* rsi arg1
* rdx arg2
* r10 arg3 (--> moved to rcx for C)
* r8 arg4
* r9 arg5
* r11 eflags for syscall/sysret, temporary for C
* r12-r15,rbp,rbx saved by C code, not touched.
*
* Interrupts are off on entry.
* Only called from user space.
*
* XXX if we had a free scratch register we could save the RSP into the stack frame
* and report it properly in ps. Unfortunately we haven't.
*
* When user can change the frames always force IRET. That is because
* it deals with uncanonical addresses better. SYSRET has trouble
* with them due to bugs in both AMD and Intel CPUs.
*/
ENTRY(system_call)
......
system_call_fastpath:
......
movq %r10,%rcx
call *sys_call_table(,%rax,8) # XXX: rip relative
movq %rax,RAX-ARGOFFSET(%rsp)
......
在进入system_call时,中断被禁用。system_call仅从用户空间调用。系统调用通过指令syscall来执行。
在x86_64架构的用户空间下进行系统调用时,常用的寄存器如下:
rax:系统调用号(syscall number)放置在rax寄存器中,用于指定要调用的特定系统调用。
rdi:第一个参数(arg0)。在系统调用期间,用户提供的第一个参数通常存储在rdi寄存器中。
rsi:第二个参数(arg1)。用户提供的第二个参数通常存储在rsi寄存器中。
rdx:第三个参数(arg2)。用户提供的第三个参数通常存储在rdx寄存器中。
r10、r8、r9:第四、五、六个参数(arg3、arg4、arg5)。用户提供的第四、五、六个参数通常存储在r10、r8和r9寄存器中。
rcx:系统调用的返回地址。在进行系统调用时,将返回地址存储在rcx寄存器中,以便在系统调用完成后返回到正确的位置。
r11:用于存储eflags寄存器的值。在进行系统调用前,将当前eflags寄存器的值保存在r11寄存器中,以便在系统调用完成后恢复它。
用户空间函数调用:
rax:返回值 参数传递:rdi,rsi,rdx,rcx,r8,r9
用户空间系统调用:
rax:系统调用号 参数传递:rdi,rsi,rdx,r10、r8、r9 (rcx -> r10)
(2)
在x86_64架构中,调用sys_call_table的机器码操作是通过间接调用(indirect call)指令来实现的。具体的操作码是ff 14 c5,其表示的汇编指令是callq *%rax。
这条指令的作用是从rax寄存器中获取一个指针地址,然后跳转到该地址执行代码。在这种情况下,我们假设rax寄存器中存储了sys_call_table的地址,以便通过间接调用来调用相应的系统调用函数。
我们通过crash调试便可以获取到sys_call_table的地址:
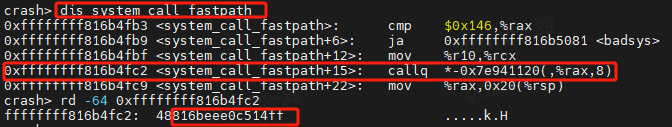
由上面的汇编代码:
system_call
-->system_call_fastpath
-->call *sys_call_table(,%rax,8)
我们反汇编system_call_fastpath:
crash> dis system_call_fastpath
0xffffffff816b4fb3 <system_call_fastpath>: cmp $0x146,%rax
0xffffffff816b4fb9 <system_call_fastpath+6>: ja 0xffffffff816b5081 <badsys>
0xffffffff816b4fbf <system_call_fastpath+12>: mov %r10,%rcx
0xffffffff816b4fc2 <system_call_fastpath+15>: callq *-0x7e941120(,%rax,8)
0xffffffff816b4fc9 <system_call_fastpath+22>: mov %rax,0x20(%rsp)
可以看到在地址0xffffffff816b4fc2,调用call *sys_call_table(,%rax,8),然后读取内存地址0xffffffff816b4fc2的值:
crash> rd -64 0xffffffff816b4fc2
ffffffff816b4fc2: 48816beee0c514ff .....k.H
call的操作码是0xff14c5,后面就是sys_call_table的地址0x816beee0
因此sys_call_table的地址是0xffffffff816beee0。
备注:第三节使用了rdmsr来获取 system_call 符号的值。
(3)
我们也可以借助vmlinux来objdump来获取其地址:
# ./extract-vmlinux vmlinuz-3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 > vmlinux
# objdump -d vmlinux > vmlinux.txt
# vim vmlinux.txt
我们根据 ff 14 c5 指令码来搜索,上一条指令且是movq %r10,%rcx:
movq %r10,%rcx
call *sys_call_table(,%rax,8) # XXX: rip relative
ffffffff816b4fbf: 4c 89 d1 mov %r10,%rcx
ffffffff816b4fc2: ff 14 c5 e0 ee 6b 81 callq *-0x7e941120(,%rax,8)
可以看到 ff 14 c5 机器码后面的地址就是sys_call_table的地址0x816beee0(x86_64是小端机器)。
因此sys_call_table的地址是0xffffffff816beee0。
二、使用dump_stack
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
static int __init lkm_init(void)
{
dump_stack();
return 0;
}
static void __exit lkm_exit(void)
{
}
module_init(lkm_init);
module_exit(lkm_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
[ 7666.386756] Call Trace:
[ 7666.386761] [<ffffffff816a3d91>] dump_stack+0x19/0x1b
[ 7666.386762] [<ffffffffc01f3009>] lkm_init+0x9/0x1000 [sys_call_table]
[ 7666.386764] [<ffffffff810020e8>] do_one_initcall+0xb8/0x230
[ 7666.386766] [<ffffffff81100734>] load_module+0x1f64/0x29e0
[ 7666.386769] [<ffffffff8134bbf0>] ? ddebug_proc_write+0xf0/0xf0
[ 7666.386770] [<ffffffff810fcdd3>] ? copy_module_from_fd.isra.42+0x53/0x150
[ 7666.386772] [<ffffffff81101366>] SyS_finit_module+0xa6/0xd0
[ 7666.386774] [<ffffffff816b4fc9>] system_call_fastpath+0x16/0x1b
我们就可以看到 system_call_fastpath+0x16 的地址是0xffffffff816b4fc9,因此system_call_fastpath的地址是:
0xffffffff816b4fc9 - 0x16 = 0xffffffff816b4fb3
我们可以从/proc/kallsyms验证:
# cat /proc/kallsyms | grep system_call_fastpath
ffffffff816b4fb3 t system_call_fastpath
system_call_fastpath:
#if __SYSCALL_MASK == ~0
cmpq $__NR_syscall_max,%rax
#else
andl $__SYSCALL_MASK,%eax
cmpl $__NR_syscall_max,%eax
#endif
ja badsys
movq %r10,%rcx
call *sys_call_table(,%rax,8) # XXX: rip relative
这里我们简单点,从上面的crash可以看到:
crash> dis system_call_fastpath
0xffffffff816b4fb3 <system_call_fastpath>: cmp $0x146,%rax
0xffffffff816b4fb9 <system_call_fastpath+6>: ja 0xffffffff816b5081 <badsys>
0xffffffff816b4fbf <system_call_fastpath+12>: mov %r10,%rcx
0xffffffff816b4fc2 <system_call_fastpath+15>: callq *-0x7e941120(,%rax,8)
call *sys_call_table 在 system_call_fastpath 的 0xf(15)处。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
static int __init lkm_init(void)
{
int i;
unsigned char *ptr;
ptr = (unsigned char *)(0xffffffff816b4fc9 - 0x16 + 0xf);
for (i = 0; i < 8; i ++) {
//printk("%02x ", (unsigned char)ptr[i]);
printk("%02x ", (unsigned char)*(ptr + i));
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit lkm_exit(void)
{
}
module_init(lkm_init);
module_exit(lkm_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
(unsigned char)ptr[i]) = (unsigned char)*(ptr + i))
# insmod sys_call_table.ko
[# dmesg -c
[ 8416.858466] ff 14 c5 e0 ee 6b 81 48
可以看到 ff 14 c5 机器码后面的地址就是sys_call_table的地址0x816beee0(x86_64是小端机器)。
因此sys_call_table的地址是0xffffffff816beee0。
或者直接搜索:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
static int __init lkm_init(void)
{
int i, j;
unsigned char *ptr;
ptr = (unsigned char *)(0xffffffff816b4fc9 - 0x16 + 0xf);
for (i = 0; i < 20; i ++) {
if( ((unsigned char)ptr[i] == 0xff) && ((unsigned char)ptr[i + 1] == 0x14) && ((unsigned char)ptr[i +2] == 0xc5) ){
printk("0x%x ", *(unsigned int *)(ptr+i+3));
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit lkm_exit(void)
{
}
module_init(lkm_init);
module_exit(lkm_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
# insmod sys_call_table.ko
# dmesg -c
[ 280.502659] 0x816beee0
因此sys_call_table的地址是0xffffffff816beee0。
三、根据MSR_LSTAR寄存器
我们来看一下内核的启动过程:
start_kernel()
-->trap_init()
-->cpu_init()
-->syscall_init()
#define MSR_STAR 0xc0000081 /* legacy mode SYSCALL target */
#define MSR_LSTAR 0xc0000082 /* long mode SYSCALL target */
#define MSR_CSTAR 0xc0000083 /* compat mode SYSCALL target */
| Register
| Address | Architectural MSR Name / Bit Fields (Former MSR Name) | MSR/Bit Description |
|---|---|---|
| C000_0081H | IA32_STAR | System Call Target Address (R/W) |
| C000_0082H | IA32_LSTAR | IA-32e Mode System Call Target Address (R/W) Target RIP for the called procedure when SYSCALL is executed in 64-bit mode. |
| C000_0083H | IA32_CSTAR | IA-32e Mode System Call Target Address (R/W) Not used, as the SYSCALL instruction is not recognized in compatibility mode. |
我们主要看MSR_LSTAR寄存器:
IA32_LSTAR 是 IA-32e 模式下的系统调用目标地址寄存器,用于存储在 64 位模式下执行 SYSCALL 指令时被调用过程的目标 RIP(指令指针)。
当在 64 位模式下执行 SYSCALL 指令时,系统将从 IA32_LSTAR 寄存器中加载 RIP 的值,以跳转至相应的系统调用处理程序。
为了使内核接收传入的系统调用,它必须通过将其地址写入IA32_LSTAR MSR寄存器 来注册将在发生系统调用时执行的代码的地址。
/* May not be marked __init: used by software suspend */
void syscall_init(void)
{
/*
* LSTAR and STAR live in a bit strange symbiosis.
* They both write to the same internal register. STAR allows to
* set CS/DS but only a 32bit target. LSTAR sets the 64bit rip.
*/
wrmsrl(MSR_STAR, ((u64)__USER32_CS)<<48 | ((u64)__KERNEL_CS)<<32);
wrmsrl(MSR_LSTAR, system_call);
wrmsrl(MSR_CSTAR, ignore_sysret);
......
/* Flags to clear on syscall */
wrmsrl(MSR_SYSCALL_MASK,
X86_EFLAGS_TF|X86_EFLAGS_DF|X86_EFLAGS_IF|
X86_EFLAGS_IOPL|X86_EFLAGS_AC);
}
这行代码把system_call入口地址存入到MSR_LSTAR寄存器。syscall指令会把该地址加载到到%rip寄存器,从该地址开始执行。
syscall指令:
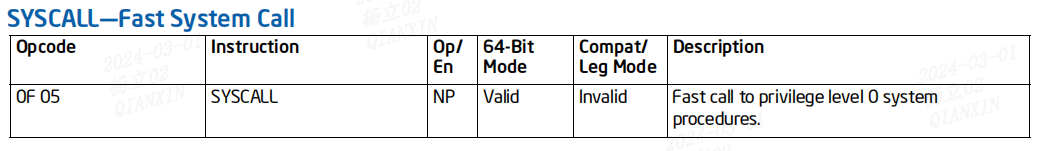
SYSCALL 指令用于在特权级别 0(内核模式)下调用操作系统的系统调用处理程序。它通过从 IA32_LSTAR MSR 寄存器加载 RIP(同时将 SYSCALL 指令后面的指令地址保存在 RCX 中)来实现这一功能。IA32_LSTAR MSR 寄存器的值是一个规范地址(canonical address),通过 WRMSR 指令确保其始终包含一个规范地址。
SYSCALL 指令:RIP = IA32_LSTAR MSR 寄存器 = system_call
过程如下:

特别说明一下,因为初始化时,掩码中包含中断标志位X86_EFLAGS_IF,所以syscall指令执行时,中断是禁止的。
我们可以看到在syscall_init中将 system_call 的地址写入了 MSR_LSTAR 寄存器:
wrmsrl(MSR_LSTAR, system_call);
那么我们读取MSR_LSTAR寄存器就可以获取到system_call的地址,进入获取到sys_call_table的地址。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
static int __init lkm_init(void)
{
unsigned long msr_lstar;
rdmsrl(MSR_LSTAR, msr_lstar);
printk("MSR_LSTAR = %lx\n", msr_lstar);
return 0;
}
static void __exit lkm_exit(void)
{
}
module_init(lkm_init);
module_exit(lkm_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
]# cat /proc/kallsyms | grep '\<system_call\>'
ffffffff816b4f50 T system_call
# insmod get_msr.ko
# dmesg -c
[ 1474.209016] MSR_LSTAR = ffffffff816b4f50
获取到了system_call的地址那么解析其后面的字节便可以找到sys_call_table的地址。
完整代码:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
void *memmem(const void *haystack, size_t haystack_size, const void *needle, size_t needle_size )
{
char *p;
for (p = (char *)haystack; p <= ((char *)haystack - needle_size + haystack_size); p++ )
if (memcmp(p, needle, needle_size) == 0 )
return (void *)p;
return NULL;
}
unsigned long *find_sys_call_table ( void )
{
char **p;
unsigned long sct_off = 0;
unsigned char code[512];
rdmsrl(MSR_LSTAR, sct_off);
memcpy(code, (void *)sct_off, sizeof(code));
p = (char **)memmem(code, sizeof(code), "\xff\x14\xc5", 3);
if (p)
{
unsigned long *sct = *(unsigned long **)((char *)p + 3);
// Stupid compiler doesn't want to do bitwise math on pointers
sct = (unsigned long *)(((unsigned long)sct & 0xffffffff) | 0xffffffff00000000);
return sct;
}
else
return NULL;
}
static int __init lkm_init(void)
{
unsigned long *sys_call_table = find_sys_call_table();
printk("The sys_call_table address is:%lx\n",(unsigned long)sys_call_table);
return 0;
}
static void __exit lkm_exit(void)
{
}
module_init(init_get_sys_call_table);
module_exit(exit_get_sys_call_table);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
# cat /proc/kallsyms | grep '\<sys_call_table\>'
ffffffff816beee0 R sys_call_table
# insmod sys_call_table.ko
# dmesg -c
[ 2363.360239] The sys_call_table address is:0xffffffff816beee0
四、使用sys_close
// linux-3.10/fs/open.c
/*
* Careful here! We test whether the file pointer is NULL before
* releasing the fd. This ensures that one clone task can't release
* an fd while another clone is opening it.
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(close, unsigned int, fd)
{
int retval = __close_fd(current->files, fd);
/* can't restart close syscall because file table entry was cleared */
if (unlikely(retval == -ERESTARTSYS ||
retval == -ERESTARTNOINTR ||
retval == -ERESTARTNOHAND ||
retval == -ERESTART_RESTARTBLOCK))
retval = -EINTR;
return retval;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sys_close);
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sys_close);
系统调用函数(sys_close)在内核中是导出的,因此可以直接获取其地址。
// linux-3.10/arch/x86/include/asm/page_64_types.h
/*
* Set __PAGE_OFFSET to the most negative possible address +
* PGDIR_SIZE*16 (pgd slot 272). The gap is to allow a space for a
* hypervisor to fit. Choosing 16 slots here is arbitrary, but it's
* what Xen requires.
*/
#define __PAGE_OFFSET _AC(0xffff880000000000, UL)
// linux-3.10/arch/x86/include/asm/page_types.h
#define PAGE_OFFSET ((unsigned long)__PAGE_OFFSET)
__PAGE_OFFSET是一个常量,用于表示内核虚拟地址空间的起始地址。
PAGE_OFFSET 是内核内存空间的起始地址。 因为 sys_close 是导出函数 (需要指出的是, sys_open 、 sys_read 等并不是导出的), 我们可以直接得到他的地址;因为系统调用号 (也就是 sys_call_table 这个一维数组的索引) 在同一 ABI (x86 跟 x64 不是同一 ABI)上具有高度的后向兼容性, 更重要的是,我们可以直接使用这个索引(代码中的 __NR_close )!
从内核内存的起始地址开始, 逐一尝试每一个指针大小的内存:把它当成是 sys_call_table 的地址, 用某个系统调用的编号(也就是索引)访问数组中的成员, 如果访问得到的值刚好是是这个系统调用号所对应的系统调用的地址, 那么我们就认为当前尝试的这块指针大小的内存就是我们要找的 sys_call_table 的地址。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/syscalls.h> //__NR_close
unsigned long **get_sys_call_table(void)
{
//内核内存空间的起始地址(PAGE_OFFSET)是已知的,因为它是内核的固定位置。
unsigned long **entry = (unsigned long **)PAGE_OFFSET;
for ( ; (unsigned long)entry < ULONG_MAX; entry += 1) {
if (entry[__NR_close] == (unsigned long *)sys_close) {
return entry;
}
}
return NULL;
}
static int __init lkm_init(void)
{
unsigned long **real_sys_call_table = get_sys_call_table();
printk("PAGE_OFFSET = %lx\n", (unsigned long)PAGE_OFFSET);
printk("sys_call_table = %lx\n", (unsigned long)real_sys_call_table);
return 0;
}
static void __exit lkm_exit(void)
{
}
module_init(lkm_init);
module_exit(lkm_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
# insmod sys_call_table.ko
# dmesg -c
[ 7405.938954] PAGE_OFFSET = ffff880000000000
[ 7405.938956] sys_call_table = ffff8800016beee0
从内核内存的起始地址(PAGE_OFFSET)开始,逐一尝试不同大小的内存块。这是因为sys_call_table通常被存储在一块连续的内存区域中。
对于每个尝试的内存地址,使用__NR_close作为索引来访问sys_call_table数组中的成员。
检查返回的值是否与sys_close函数的地址匹配。如果匹配成功,那么当前尝试的内存地址就被认为是sys_call_table的地址。
参考资料
Linux 3.10.0
https://blog.csdn.net/whatday/article/details/100513427
https://juejin.cn/post/7203681024236355639
https://docs-conquer-the-universe.readthedocs.io/zh-cn/latest/linux_rootkit/sys_call_table.html



![[linux]shell脚本语言:变量、测试、控制语句以及函数的全面详解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/76b6806d36ed47b2a145cb9bf9e78dc9.png)