文章目录
- 一、什么是策略模式
- 二、策略模式结构
- 三、使用场景+案例分析
- 1、使用场景
- 2、案例分析
- (1)消除条件分支
一、什么是策略模式
策略模式是一种行为型设计模式,它允许定义一组算法,并将每个算法封装在独立的类中,使它们可以互相替换。策略模式通过将算法的使用与算法的实现分离,使得算法可以独立于客户端而变化。
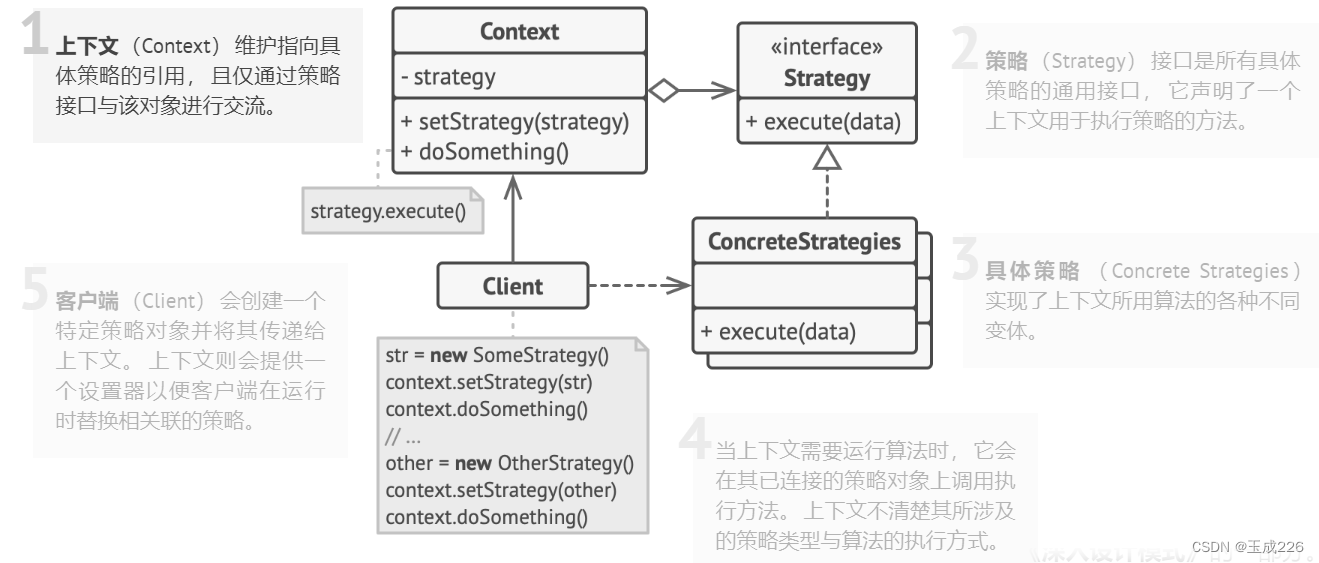
- 在策略模式中,通常会有一个上下文(Context)类,该类包含一个策略接口(Strategy),以及具体的策略类(Concrete Strategies)。上下文类将具体的任务委托给策略接口,在运行时可以根据需要切换不同的策略类,从而达到动态改变算法行为的目的。
- 策略模式的核心思想是面向接口编程,而不是面向实现编程。这种设计模式提供了一种灵活的方式来管理和复用算法,同时使得算法的扩展变得更加容易。它适用于需要根据不同情况选择不同算法的场景,例如排序、搜索、计算等问题。
总结起来,策略模式通过将算法封装成独立的类,使得可以在运行时动态地选择和切换算法,从而提高代码的可维护性、扩展性和复用性。
二、策略模式结构
三、使用场景+案例分析
1、使用场景
策略模式通常适用于以下场景:
-
多算法选择:当需要在运行时根据情况选择不同的算法时,可以使用策略模式。例如,对于排序算法,根据数据量的不同可能选择快速排序、冒泡排序或插入排序等。
-
消除条件分支:当代码中存在大量的条件分支语句,并且这些条件分支都是根据相同的输入来选择不同的行为时,可以考虑使用策略模式来消除这些条件分支。
-
算法的封装和复用:当系统中存在多个类似的算法,但它们的实现细节不同,可以将这些算法封装成独立的策略类,以便复用和维护。
-
可扩展性:当需要为系统提供一种灵活、可拓展的方式来添加新的算法或行为时,策略模式可以帮助实现这一点,而无需修改现有的代码。
-
单一职责原则:当需要遵循单一职责原则,即每个类应该只负责一种功能时,策略模式可以将不同的算法分离到单独的策略类中,使得每个类都专注于一种算法。
总的来说,策略模式适用于需要动态地切换算法、消除条件分支、提高可维护性和可扩展性的场景。通过策略模式,可以更好地管理和组织算法,使系统更加灵活和易于维护。
2、案例分析
(1)消除条件分支
在元数据管理系统中有可视化建表的功能,在向底层建表的过程中不同类型的数据源有不同的分区形式,原有代码的处理形式是使用if语句判断数据源类型使用对应的方式对分区进行处理。每次新接进来的数据源如果有分区的特性需要需要if语句进行处理,这样的处理方式并不符合开闭原则(对扩展开放,对修改关闭)。现在我们基于BeanPostProcessor+注解+注册管理器形式的策略模式来取消条件分支。
- 策略(strategy)
public interface IConvertPartition {
void processPartition(ProcessParam param);
void partitionParams(PartitionParam param);
}
- 具体策略(concrete strategy)
不同的数据源有不同的实现形式,仅仅举例一个数据源的具体策略:
@ConvertPartition(tableType = TableType.KINGBASE_ES, dataType = DataType.KINGBASE_ES)
@Slf4j
public class KingbaseConverPartition implements IConvertPartition {
@Override
public void processPartition(ProcessParam param) {
//具体的分区处理逻辑
}
@Override
public void partitionParams(PartitionParam param){
//具体的分区处理逻辑
}
}
- 上下文(context)
import com.alibaba.excel.util.CollectionUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.*;
@Slf4j
public class ConvertDraftPartitionUtilsContext {
/**
* partition转换 处理器
*/
private static final Map<TableType, IConvertPartition> CONVERT_DRAFT_UTILS_MAP = new HashMap<>();
private static final Map<DataType, IConvertPartition> TABLE_PUBLISH_DATATYPE_MAP = new HashMap<>();
public static <T> void register(T dataType, IConvertPartition convertPartition) {
if (dataType instanceof TableType) {
CONVERT_DRAFT_UTILS_MAP.putIfAbsent((TableType)dataType, convertDraftPartition);
} else if (dataType instanceof DataType) {
TABLE_PUBLISH_DATATYPE_MAP.put((DataType) dataType, convertDraftPartition);
}
}
public static IConvertPartition getIConvertPartition(TableType dataType) {
return CONVERT_DRAFT_UTILS_MAP.get(dataType);
}
public static Set<TableType> getTableTypes() {
Set<TableType> tableTypes = CONVERT_DRAFT_UTILS_MAP.keySet();
log.info("convert draft partition table type list: {}", tableTypes);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(tableTypes)) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
return tableTypes;
}
public static void processPartition(TableType dataType, ProcessParam param) {
IConvertPartition iConvertPartition = getIConvertPartition(dataType);
if (!Objects.isNull(iConvertPartition)) {
log.info("{} start process partition", dataType.getCode());
iConvertPartition.processPartition(param);
}
}
public static void processParam(DataType dataType, PartitionParam param) {
IConvertPartition iConvertPartition = TABLE_PUBLISH_DATATYPE_MAP.get(dataType);
if (!Objects.isNull(iConvertPartition)) {
log.info("{} start process partition params", dataType.getDataTypeName());
iConvertPartition.partitionParams(param);
}
}
public static Set<TableType> getTableTypeWithPartitions() {
log.info("The type of a table with partitions: {}", CONVERT_DRAFT_UTILS_MAP.keySet());
return CONVERT_DRAFT_UTILS_MAP.keySet();
}
}
- 注解
@Component
@Inherited
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ConvertPartition {
DataType dataType();
TableType tableType();
}
- BeanPostProcessor
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Objects;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ConvertPartitionRegisterProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof IConvertPartition) {
Class<?> aClass = bean.getClass();
log.info("the convertDraftPartition of [ {} ] begin to register", aClass.getSimpleName());
ConvertPartition annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(ConvertPartition.class);
if (Objects.isNull(annotation)) {
return bean;
}
DataType dataType = annotation.dataType();
TableType tableType = annotation.tableType();
registerHandler(aClass, bean, dataType, tableType);
}
return bean;
}
private void registerHandler(Class<?> aClass, Object bean, Object... dataTypes){
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(dataTypes)) {
for (Object dataType : dataTypes) {
if (!Objects.isNull(dataType)) {
ConvertPartitionUtilsContext.register(dataType, (IConvertPartition)bean);
log.info("the [ {} ] register success", aClass.getSimpleName());
}
}
}
}
}

![给定长度为n(n<=20)的数组a,-20<=ai<=20, 每次操作选择i,j,使a[i] += a[j], 在31次操作内使a不递减,输出每次操作的i,j](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/b7958c1f23bb46e79983ccc4e11940f6.png)






![[HTML]Web前端开发技术28(HTML5、CSS3、JavaScript )JavaScript基础——喵喵画网页](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1b9dece61d314044a355d452d141db77.png)