文章目录
- YOLOv5代码解读[02] models/yolov5l.yaml文件解析
- yolov5l.yaml文件
- 检测头1--->耦合头
- 检测头2--->解耦头
- 检测头3--->ASFF检测头
- Model类解析
- parse_model函数
YOLOv5代码解读[02] models/yolov5l.yaml文件解析
yolov5l.yaml文件
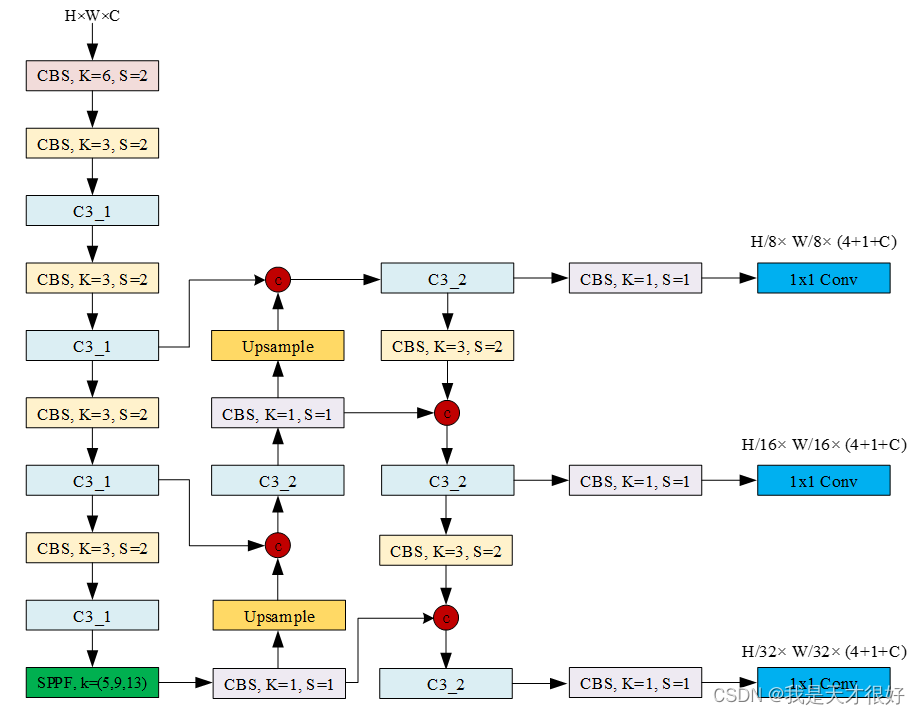
nc: 27
depth_multiple: 1.0
width_multiple: 1.0
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23]
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119]
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326]
backbone:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]],
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]],
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]],
]
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]],
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]],
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]],
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]],
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]],
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors, False]],
]
检测头1—>耦合头
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None
onnx_dynamic = False
export = False
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), Decoupled=False, ch=(), inplace=True):
super().__init__()
self.decoupled = Decoupled
self.nc = nc
self.no = nc + 5
self.nl = len(anchors)
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2))
if self.decoupled:
self.m = nn.ModuleList(DecoupledHead(x, self.nc, anchors) for x in ch)
else:
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no*self.na, 1) for x in ch)
self.inplace = inplace
def forward(self, x):
z = []
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i])
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training:
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i]
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i]
else:
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i]
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i]
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1),) if self.export else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
def _make_grid(self, nx=20, ny=20, i=0, torch_1_10=check_version(torch.__version__, '1.10.0')):
d = self.anchors[i].device
t = self.anchors[i].dtype
y, x = torch.arange(ny, device=d, dtype=t), torch.arange(nx, device=d, dtype=t)
if torch_1_10:
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid(y, x, indexing='ij')
else:
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid(y, x)
grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).expand((1, self.na, ny, nx, 2))
anchor_grid = (self.anchors[i].clone() * self.stride[i]).view((1, self.na, 1, 1, 2)).expand((1, self.na, ny, nx, 2))
return grid, anchor_grid
检测头2—>解耦头
class DecoupledHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ch=256, nc=80, anchors=()):
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc
self.nl = len(anchors)
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2
self.merge = Conv(ch, 128 , 1, 1)
self.cls_convs1 = Conv(128, 64, 3, 1, 1)
self.cls_convs2 = Conv(64, 64, 3, 1, 1)
self.reg_convs1 = Conv(128, 64, 3, 1, 1)
self.reg_convs2 = Conv(64, 64, 3, 1, 1)
self.cls_preds = nn.Conv2d(64 , self.nc*self.na, 1)
self.reg_preds = nn.Conv2d(64 , 4*self.na, 1)
self.obj_preds = nn.Conv2d(64 , 1*self.na, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.merge(x)
x1 = self.cls_convs1(x)
x1 = self.cls_convs2(x1)
x1 = self.cls_preds(x1)
x2 = self.reg_convs1(x)
x2 = self.reg_convs2(x2)
x21 = self.reg_preds(x2)
x22 = self.obj_preds(x2)
out = torch.cat([x21, x22, x1], 1)
return out
检测头3—>ASFF检测头
class ASFF_Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None
onnx_dynamic = False
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), multiplier=0.5, rfb=False, inplace=True):
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc
self.no = nc + 5
self.nl = len(anchors)
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2))
self.l0_fusion = ASFFV5(level=0, multiplier=multiplier, rfb=rfb)
self.l1_fusion = ASFFV5(level=1, multiplier=multiplier, rfb=rfb)
self.l2_fusion = ASFFV5(level=2, multiplier=multiplier, rfb=rfb)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch)
self.inplace = inplace
def forward(self, x):
z = []
result = []
result.append(self.l2_fusion(x))
result.append(self.l1_fusion(x))
result.append(self.l0_fusion(x))
x = result
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i])
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training:
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i]
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i]
else:
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i]
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i]
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
def _make_grid(self, nx=20, ny=20, i=0):
d = self.anchors[i].device
if check_version(torch.__version__, '1.10.0'):
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(ny, device=d), torch.arange(nx, device=d)], indexing='ij')
else:
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(ny, device=d), torch.arange(nx, device=d)])
grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).expand((1, self.na, ny, nx, 2)).float()
anchor_grid = (self.anchors[i].clone() * self.stride[i]).view((1, self.na, 1, 1, 2)).expand((1, self.na, ny, nx, 2)).float()
return grid, anchor_grid
Model类解析
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, anchors=None):
super().__init__()
if isinstance(cfg, dict):
self.yaml = cfg
else:
self.yaml_file = Path(cfg).name
with open(cfg, encoding='ascii', errors='ignore') as f:
self.yaml = yaml.safe_load(f)
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch)
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc
if anchors:
LOGGER.info(f'Overriding model.yaml anchors with anchors={anchors}')
self.yaml['anchors'] = round(anchors)
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=[ch])
self.names = [str(i) for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])]
self.inplace = self.yaml.get('inplace', True)
m = self.model[-1]
if isinstance(m, Detect) or isinstance(m, ASFF_Detect):
s = 256
m.inplace = self.inplace
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in self.forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))])
m.anchors /= m.stride.view(-1, 1, 1)
check_anchor_order(m)
self.stride = m.stride
if m.decoupled:
LOGGER.info('decoupled done')
pass
else:
self._initialize_biases()
initialize_weights(self)
self.info()
LOGGER.info('')
def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):
if augment:
return self._forward_augment(x)
return self._forward_once(x, profile, visualize)
def _forward_augment(self, x):
img_size = x.shape[-2:]
s = [1, 0.83, 0.67]
f = [None, 3, None]
y = []
for si, fi in zip(s, f):
xi = scale_img(x.flip(fi) if fi else x, si, gs=int(self.stride.max()))
yi = self._forward_once(xi)[0]
yi = self._descale_pred(yi, fi, si, img_size)
y.append(yi)
y = self._clip_augmented(y)
return torch.cat(y, 1), None
def _forward_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
y, dt = [], []
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1:
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f]
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
x = m(x)
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None)
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x
def _descale_pred(self, p, flips, scale, img_size):
if self.inplace:
p[..., :4] /= scale
if flips == 2:
p[..., 1] = img_size[0] - p[..., 1]
elif flips == 3:
p[..., 0] = img_size[1] - p[..., 0]
else:
x, y, wh = p[..., 0:1] / scale, p[..., 1:2] / scale, p[..., 2:4] / scale
if flips == 2:
y = img_size[0] - y
elif flips == 3:
x = img_size[1] - x
p = torch.cat((x, y, wh, p[..., 4:]), -1)
return p
def _clip_augmented(self, y):
nl = self.model[-1].nl
g = sum(4 ** x for x in range(nl))
e = 1
i = (y[0].shape[1] // g) * sum(4 ** x for x in range(e))
y[0] = y[0][:, :-i]
i = (y[-1].shape[1] // g) * sum(4 ** (nl - 1 - x) for x in range(e))
y[-1] = y[-1][:, i:]
return y
def _profile_one_layer(self, m, x, dt):
c = isinstance(m, Detect) or isinstance(m, ASFF_Detect)
o = thop.profile(m, inputs=(x.copy() if c else x,), verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0
t = time_sync()
for _ in range(10):
m(x.copy() if c else x)
dt.append((time_sync() - t) * 100)
if m == self.model[0]:
LOGGER.info(f"{'time (ms)':>10s} {'GFLOPs':>10s} {'params':>10s} {'module'}")
LOGGER.info(f'{dt[-1]:10.2f} {o:10.2f} {m.np:10.0f} {m.type}')
if c:
LOGGER.info(f"{sum(dt):10.2f} {'-':>10s} {'-':>10s} Total")
def _initialize_biases(self, cf=None):
m = self.model[-1]
for mi, s in zip(m.m, m.stride):
b = mi.bias.view(m.na, -1)
b.data[:, 4] += math.log(8 / (640 / s) ** 2)
b.data[:, 5:] += math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.999999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum())
mi.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(b.view(-1), requires_grad=True)
def _print_biases(self):
m = self.model[-1]
for mi in m.m:
b = mi.bias.detach().view(m.na, -1).T
LOGGER.info(('%6g Conv2d.bias:' + '%10.3g' * 6) % (mi.weight.shape[1], *b[:5].mean(1).tolist(), b[5:].mean()))
def _print_weights(self):
for m in self.model.modules():
if type(m) is Bottleneck:
LOGGER.info('%10.3g' % (m.w.detach().sigmoid() * 2))
def fuse(self):
LOGGER.info('Fusing layers... ')
for m in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(m, (Conv, DWConv)) and hasattr(m, 'bn'):
m.conv = fuse_conv_and_bn(m.conv, m.bn)
delattr(m, 'bn')
m.forward = m.forward_fuse
self.info()
return self
def info(self, verbose=False, img_size=640):
model_info(self, verbose, img_size)
def _apply(self, fn):
self = super()._apply(fn)
m = self.model[-1]
if isinstance(m, Detect) or isinstance(m, ASFF_Detect) or isinstance(m, Decoupled_Detect):
m.stride = fn(m.stride)
m.grid = list(map(fn, m.grid))
if isinstance(m.anchor_grid, list):
m.anchor_grid = list(map(fn, m.anchor_grid))
return self
parse_model函数
def parse_model(d, ch):
LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>18}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<40}{'arguments':<30}")
anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors
no = na * (nc + 5)
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1]
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']):
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m
for j, a in enumerate(args):
try:
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a
except NameError:
pass
n = n_ = max(round(n*gd), 1) if n > 1 else n
if m in [Conv, DWConv, CrossConv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck,
BottleneckCSP, MobileBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, MixConv2d, Focus,
InvertedResidual, ConvBNReLU, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost, CoordAtt,
CoordAttv2, OSA_Stage]:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2*gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost]:
args.insert(2, n)
n = 1
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
elif m is Detect:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int):
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
elif m is ASFF_Detect :
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int):
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
elif m is ConvNeXt_Block:
c2 = args[0]
args = args[1:]
else:
c2 = ch[f]
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args)
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '')
np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters())
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>18}{n_:>3}{np:10.0f} {t:<40}{str(args):<30}')
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1)
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)