Problem: 773. 滑动谜题
文章目录
- 题目描述
- 思路
- 解题方法
- 复杂度
- Code
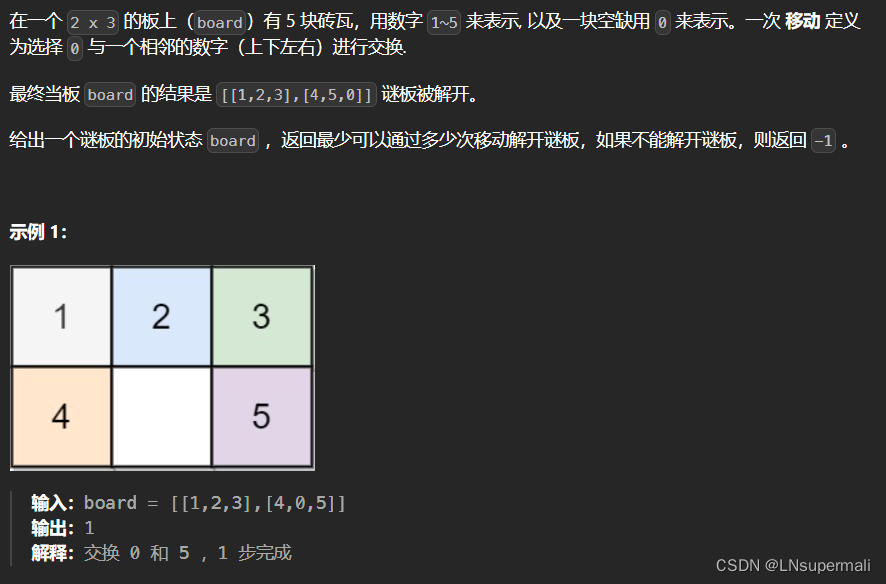
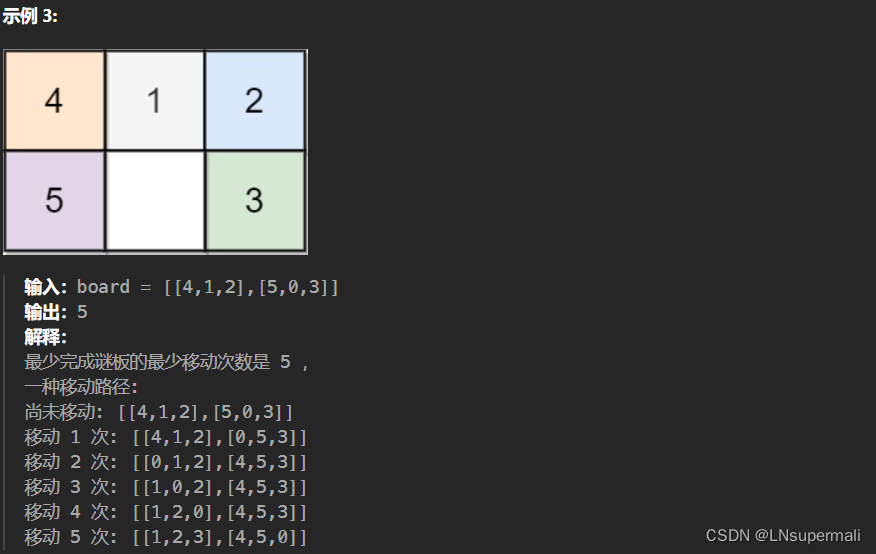
题目描述
思路
由于题目提到最小步数,则可以使用BFS来穷举出最小的结果
1.转换为BFS问题:由于0代表空着的可以移动的位置,所以我们只需要从当前位置和0的相邻位置移动从而转换出其它的可能的状态(这样也在逻辑上构成了一棵多叉树)
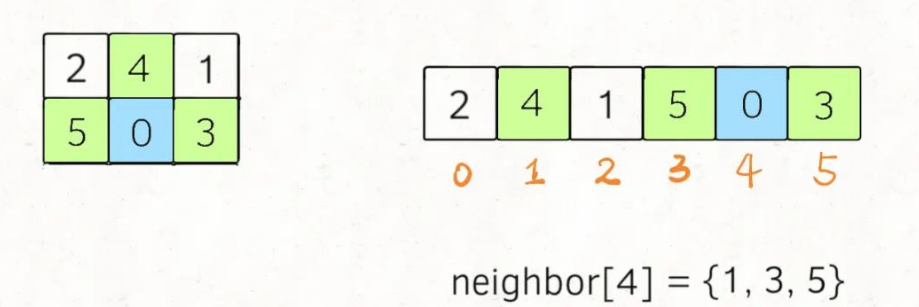
2.压缩二维数组,并标记出相邻索引:我们可以将二维数组board压缩,当在BFS遍历查找时找到一种状态等于压缩后的情况时,我们则立即返回此时的步数;但是我们为了解决相邻索引的问题,需要直接将这个映射写出来:在一维字符串中,索引i在二维数组中的的相邻索引为neighbor[i];
解题方法
1.将题目所给的初始board压缩为字符串;
2.记录一维字符串的相邻索引(如下代码;按顺势针);
3.BFS框架书写:3.1.用一个无序表记录已经走过的状态(防止重复甚至出现死循环);
3.2每次取出当前的状态,并匹配是否和目标target一致,一致则返回所需的步数(步数用一个变量step记录);
3.3.每次找到当前数字0的索引并与其相邻的数字交换位置,同时要在无序表中判断是否已经存在;
复杂度
时间复杂度:
O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
空间复杂度:
O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
Code
class Solution {
public:
/**
* BFS
*
* @param board Given array
* @return int
*/
int slidingPuzzle(vector<vector<int>> &board) {
int row = 2;
int col = 3;
string start = "";
string target = "123450";
// Converts the 2x3 array to a string
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
start.push_back(board[i][j] + '0');
}
}
// Records the adjacent index of a one-dimensional string
vector<vector<int>> neighbor = {
{1, 3},
{0, 4, 2},
{1, 5},
{0, 4},
{3, 1, 5},
{4, 2}
};
//BFS
queue <string> q;
unordered_set<string> visited;
q.push(start);
visited.insert(start);
int step = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
string cur = q.front();
q.pop();
// Determine whether the target situation has been reached
if (target == cur) {
return step;
}
// Find the index of the number 0
int index = 0;
for (; cur[index] != '0'; ++index);
// Switch the position of the digit 0 or any adjacent digit
for (int adj: neighbor[index]) {
string new_board = cur;
swap(new_board[adj], new_board[index]);
// Prevent backtracking
if (!visited.count(new_board)) {
q.push(new_board);
visited.insert(new_board);
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
};