☘️过度的信息对一个过着充实生活的人来说,是一种不必要的负担☘️
文章目录
- 前言
- 工具类实现
- 文件实用工具类
- 代码实现
- Json实用工具类
- 代码实现
- 服务端
- 单例配置类
- 系统配置信息
- 单例配置类
- 数据管理类
- 数据信息
- 数据管理
- 热点管理类
- 业务处理类
- 客户端
- 数据管理类
- 文件备份类
- 总结
☘️项目源代码:云备份
☘️云备份专栏:云备份
前言
在云备份开篇的博客中介绍了云备份项目的总体实现方向,接下来就是对项目的逐步实现,然后对各部分进行组装。

工具类实现
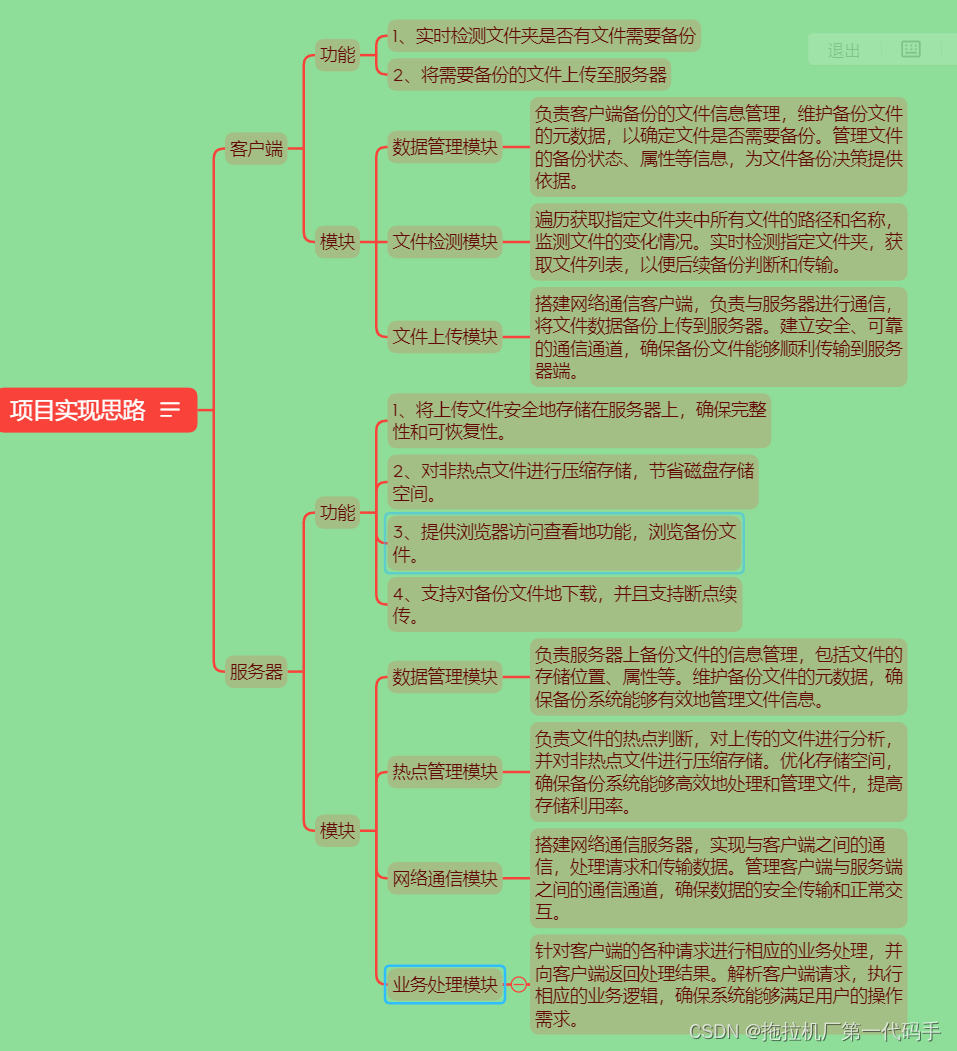
如上的模块功能划分图,我们知道无论是客户端还是服务端都涉及对文件的操作,例如客户端需要将备份的文件上传至服务器时,就需要打开文件读取文件的数据然后将其进行组织成一定格式,在发送给服务器。
而服务器在接收到数据后,则需要将组织后的数据进行反序列化成原始数据,然后存放进文件中。当用户需要将备份的文件进行还原时,服务器也需要读取对应文件的数据,将其组织后再发送给客户端,客户端在进行反序列化得到原始数据后在写进文件。
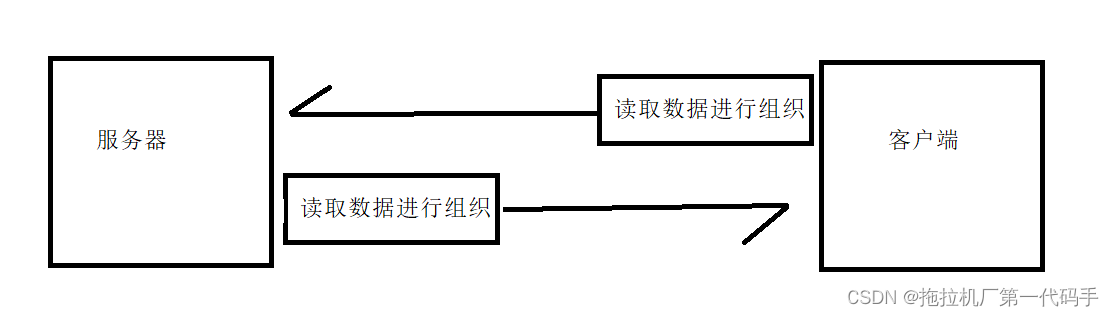
因此,我们的工具类就需要有对文件操作的类以及对数据进行组织的类,分别为文件实用工具类和Json实用工具类。
文件实用工具类
我们在实现文件实用工具类时,使用了C++17的<filesystem>库,<filesystem> 库是 C++17 新增的标准库之一,旨在提供对文件系统进行操作的接口,使得文件和目录的处理更加简单和可移植。这个库定义了一组类和函数,可以用来进行文件和目录的操作,如路径处理、文件检查、目录遍历、文件复制、移动和删除等。
如下是 <filesystem> 库的主要组成部分和功能:
-
命名空间和别名:
<filesystem>库的内容定义在std::filesystem命名空间中。通常为了方便使用,可以使用namespace fs = std::filesystem;这样的别名来简化调用。 -
路径处理:
<filesystem>提供了丰富的路径处理功能,包括构建路径、连接路径、获取路径的各种组成部分等。 -
文件和目录检查: 通过
<filesystem>可以方便地检查文件和目录的存在性、类型、权限等信息。 -
目录遍历: 提供了对目录进行遍历的功能,可以轻松地获取目录中的所有文件和子目录。
-
文件复制、移动和删除: 提供了对文件进行复制、移动和删除的接口,可以方便地进行文件操作。
-
文件大小和最后修改时间: 可以获取文件的大小和最后修改时间等属性信息。
-
文件权限: 可以设置和查询文件的权限,包括读、写和执行权限等。
-
异常处理:
<filesystem>提供了一些异常类,用于处理文件系统操作可能遇到的异常情况。
使用 <filesystem> 库可以简化很多文件和目录操作的代码,同时也提高了代码的可移植性,因为这个库提供的接口是标准化的,不会受到操作系统的影响。
在使用 <filesystem> 库时,需要确保编译器支持 C++17 标准,并在编译时指定相应的标准版本。例如,可以使用 -std=c++17 或 -std=c++20 等标志来编译支持 <filesystem> 库的代码。
更多详细信息可以直接跳转filesystem。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <experimental/filesystem>
#include "bundle.h"
namespace wzh
{
namespace fs = std::experimental::filesystem;
class FileUtil
{
public:
FileUtil(const std::string filename)
: _filename(filename) {}
int64_t fileSize() //获取文件大小
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(_filename.c_str(), &st) < 0)
{
std::cout << "get file size failed\n";
return -1;
}
return st.st_size;
}
time_t lastModTime() //获取文件最后一次修改时间
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(_filename.c_str(), &st) < 0)
{
std::cout << "get file lastModTime failed\n";
return -1;
}
return st.st_mtime;
}
time_t lastAccTime() //获取最后一次访问时间
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(_filename.c_str(), &st) < 0)
{
std::cout << "get file lastAccTime failed\n";
return -1;
}
return st.st_atime;
}
std::string fileName() //获取文件名称
{
size_t pos = _filename.find_last_of("/");
if(pos == std::string::npos)
{
return _filename;
}
return _filename.substr(pos + 1);
}
bool setContent(const std::string &body) //向文件写入数据
{
std::ofstream ofs;
ofs.open(_filename, std::ios::binary);
if(ofs.is_open() == false)
{
std::cout << "write open failed\n";
return false;
}
ofs.write(&body[0], body.size());
if(ofs.good() == false)
{
std::cout << "write file content failed\n";
ofs.close();
return false;
}
ofs.close();
return true;
}
bool getContent(std::string *body) //向文件读取数据
{
size_t fsize = fileSize();
return getPosLen(body, 0, fsize);
}
bool getPosLen(std::string *body, size_t pos, size_t len) //获取文件指定位置,指定长度的数据
{
std::ifstream ifs;
ifs.open(_filename, std::ios::binary);
if(ifs.is_open() == false)
{
std::cout << "read open file failed\n";
return false;
}
size_t fsize = fileSize();
if(pos + len > fsize)
{
std::cout << "get file len is error\n";
return false;
}
ifs.seekg(pos, std::ios::beg);
body->resize(len);
ifs.read(&(*body)[0], len);
if(ifs.good() == false)
{
std::cout << "get file content failed\n";
ifs.close();
return false;
}
ifs.close();
return true;
}
bool exits() // 判断(文件/目录)是否存在
{
return fs::exists(_filename);
}
bool scanDirectory(std::vector<std::string> *arry) //浏览目录中的所有文件
{
for(auto& p : fs::directory_iterator(_filename))
{
if(fs::is_directory(p) == true)
continue;
arry->push_back(fs::path(p).relative_path().string());
}
}
bool createDirectory() //创建目录
{
if(exits()) return true;
return fs::create_directories(_filename);
}
bool comPress(const std::string &packname) //压缩文件
{
std::string body;
if(getContent(&body) == false)
{
std::cout << "compress get file content failed\n";
return false;
}
std::string packed = bundle::pack(bundle::LZIP, body);
FileUtil fu(packname);
if(fu.setContent(packed) == false)
{
std::cout << "comPress write packed data failed\n";
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool unCompress(const std::string &filename) //解压文件
{
std::string body;
if(getContent(&body) == false)
{
std::cout << "unCompress get file content failed\n";
return false;
}
std::string unpacked = bundle::unpack(body);
FileUtil fu(filename);
if(fu.setContent(unpacked) == false)
{
std::cout << "unCompress set file ccontent failed\n";
return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
std::string _filename;
};
}
文件实用工具类 FileUtil,封装了一些常见的文件和目录操作功能。代码中定义了一个命名空间,用于组织代码。同时使用了别名定义,简化了文件系统命名空间的使用,使得可以使用 fs 来代替 std::experimental::filesystem。
成员函数中,构造函数接受文件名作为参数,并初始化私有成员 _filename。而 fileSize()、lastModTime()、lastAccTime() 通过调用 stat 函数获取文件的大小、最后修改时间和最后访问时间。fileName() 用于从文件路径中提取文件名。setContent()、getContent()、getPosLen() 用于向文件写入数据、读取数据,以及获取指定位置和长度的文件内容。exits() 用于判断文件是否存在。scanDirectory() 遍历目录中的所有文件,并将文件名存储在传入的字符串向量中。createDirectory() 用来创建目录,如果目录已存在,则直接返回成功。comPress() 读取文件内容并使用 bundle 命名空间的 pack 函数进行压缩,然后将压缩后的内容写入新文件。unCompress() 读取文件内容并使用 bundle 命名空间的 unpack 函数进行解压,然后将解压后的内容写入新文件。
请注意,由于使用了 <experimental/filesystem> 头文件,编译器需要开启 C++17 或更高的标准支持,并且在链接时需要链接 <stdc++fs> 库。
Json实用工具类
对数据进行组织的Json实用工具类我们借助 JsonCpp 库来实现数据的处理。
代码实现
class JsonUtil
{
public:
static bool serialize(const Json::Value &root, std::string *str)
{
Json::StreamWriterBuilder swb;
std::unique_ptr<Json::StreamWriter> sw(swb.newStreamWriter());
std::stringstream ss;
if(sw->write(root, &ss) != 0)
{
std::cout << "serialize write failed\n";
return false;
}
*str = ss.str();
return true;
}
static bool deSerialize(const std::string &str, Json::Value *root)
{
Json::CharReaderBuilder crb;
std::unique_ptr<Json::CharReader> cr(crb.newCharReader());
std::string err;
bool ret = cr->parse(str.c_str(), str.c_str() + str.size(), root, &err);
if(ret == false)
{
std::cout << "deSerialize parse error: " << err << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
JsonUtil 类中包含了两个静态方法,用于 JSON 数据的序列化和反序列化。serialize 方法接受一个 Json::Value 类型的参数 root,表示要序列化的 JSON 数据的根节点。还接受一个 std::string 指针参数 str,用于存储序列化后的 JSON 字符串。使用了 Json::StreamWriterBuilder 创建一个写入流构建器,然后创建一个唯一指针指向 Json::StreamWriter 对象。使用 sw->write 方法将 root 中的 JSON 数据写入一个 std::stringstream 中。如果写入失败,输出错误信息并返回 false,否则将 std::stringstream 中的内容赋值给传入的 str。
deSerialize 方法接受一个 std::string 类型的参数 str,表示要反序列化的 JSON 字符串。还接受一个 Json::Value 指针参数 root,用于存储反序列化后的 JSON 数据。使用 Json::CharReaderBuilder 创建一个字符读取流构建器,然后创建一个唯一指针指向 Json::CharReader 对象。 cr->parse 方法将 str 中的 JSON 字符串解析为 root 中的 JSON 数据。如果解析失败,输出错误信息和错误内容,并返回 false,否则返回 true 表示反序列化成功。
Json::StreamWriterBuilder和Json::CharReaderBuilder是 JsonCpp 提供的用于构建写入流和字符读取流的类。Json::StreamWriter和Json::CharReader则是实际的写入和读取 JSON 数据的类。
这个工具类简化了使用 JsonCpp 库进行 JSON 数据的序列化和反序列化的过程,提供了方便的接口,同时对错误进行了基本的处理。在使用时,需要确保 JsonCpp 库被正确引入,并在编译时链接相应的库。
服务端
单例配置类
单例配置类确保系统在第一次启动时获取系统的配置信息,如热点文件的判断时间,间隔多久时间的文件再没有被访问时定义为非热点文件,然后对其进行压缩存储。如上传的文件存放的目录路径,压缩后的文件存放路径等等。
系统配置信息
我们将系统的配置信息都写入到配置文件中,让程序第一次运行时由单例配置类进行对配置文件的加载,获取配置信息。将系统配置信息写入到配置文件进行运行时加载可以增强系统的鲁棒性和灵活性。
{
"hot_time" : 30,
"server_port" : 8080,
"server_ip" : "0.0.0.0",
"pack_suffix" : ".lz",
"pack_dir" : "./packdir/",
"back_dir" : "./backdir/",
"download_preffix" : "./download/",
"manager_file" : "./cloud.dat"
}
"hot_time" : 30:热更新时间为 30 秒。"server_port" : 8080:服务器端口号为 8080。"server_ip" : "0.0.0.0":服务器 IP 地址为 0.0.0.0,通常表示监听所有可用的网络接口。"pack_suffix" : ".lz":打包文件的后缀为.lz。"pack_dir" : "./packdir/":打包文件存储目录为当前目录下的packdir文件夹。"back_dir" : "./backdir/":备份文件存储目录为当前目录下的backdir文件夹。"download_preffix" : "./download/":下载文件的前缀为当前目录下的download文件夹。"backup_file" : "./cloud.dat":备份文件信息的路径为当前目录下的cloud.dat文件。
这些配置项可以用于配置系统的各种参数,如服务器端口号、IP 地址、文件存储路径等。通过解析这些配置项,可以使系统在运行时根据预定义的参数进行设置和运行。在实际应用中,可以根据需要动态地读取和修改这些配置项,以满足不同环境下的需求。
单例配置类
单例配置类在系统的第一次运行时对配置文件进行加载,获取各配置信息。
#ifndef __MY_CON__
#define __MY_CON__
#include <mutex>
#include "Util.hpp"
#define CONFIG_FILE "./cloud.conf"
namespace wzh
{
class config
{
public:
static config* getInstance()
{
if(_instance == NULL)
{
_mutex.lock();
if(_instance == NULL)
{
_instance = new config();
}
_mutex.unlock();
}
return _instance;
}
int getHotTime()
{
return _hot_time;
}
int getServerPort()
{
return _server_port;
}
std::string getServerIp()
{
return _server_ip;
}
std::string getDownloadPreffix()
{
return _download_preffix;
}
std::string getPackFileSuffix()
{
return _pack_suffix;
}
std::string getPackDir()
{
return _pack_dir;
}
std::string getBackDir()
{
return _back_dir;
}
std::string getBackupFile()
{
return _backup_file;
}
private:
config()
{
readConfigFile();
}
static config* _instance;
static std::mutex _mutex;
bool readConfigFile()
{
FileUtil fu(CONFIG_FILE);
std::string body;
if(fu.getContent(&body) == false)
{
std::cout << "readConfigFile failed\n";
return false;
}
Json::Value root;
if(JsonUtil::deSerialize(body, &root) == false)
{
std::cout << "parse config file failed\n";
return false;
}
_hot_time = root["hot_time"].asInt();
_server_ip = root["server_ip"].asString();
_server_port = root["server_port"].asInt();
_pack_dir = root["pack_dir"].asString();
_back_dir = root["back_dir"].asString();
_pack_suffix = root["pack_suffix"].asString();
_download_preffix = root["download_preffix"].asString();
_backup_file = root["backup_file"].asString();
return true;
}
private:
int _hot_time;
int _server_port;
std::string _server_ip;
std::string _pack_suffix;
std::string _pack_dir;
std::string _back_dir;
std::string _download_preffix;
std::string _backup_file;
};
config* config::_instance = NULL;
std::mutex config::_mutex;
}
#endif
代码中实现了单例模式类 config,用于读取系统配置信息并提供对外接口获取配置参数。单例模式实现使用了懒汉式单例模式,_instance 和 _mutex 是静态成员变量,用于存储单例对象和保证线程安全。getInstance() 方法返回单例对象的指针,确保只有一个实例存在。其中readConfigFile() 方法用于从配置文件中读取配置信息。使用 FileUtil 类读取配置文件内容,然后通过 JSON 序列化工具类 JsonUtil 解析配置信息。还提供了一系列公有方法用于获取各种配置参数,如热更新时间、服务器端口、服务器 IP 等。
数据管理类
数据管理类对备份文件的信息进行有效组织,并提供一系列接口供其他模块功能来获取文件信息进行利用。
数据信息
typedef struct BackupInfo
{
bool pack_flag;
size_t fsize;
time_t atime;
time_t mtime;
std::string real_path;
std::string pack_path;
std::string url;
void newBackupInfo(const std::string &realpath)
{
config *con = config::getInstance();
std::string packdir = con->getPackDir();
std::string packsuffix = con->getPackFileSuffix();
std::string download_preffix = con->getDownloadPreffix();
FileUtil fu(realpath);
pack_flag = false;
fsize = fu.fileSize();
mtime = fu.lastModTime();
atime = fu.lastAccTime();
real_path = realpath;
pack_path = packdir + fu.fileName() + packsuffix;
url = download_preffix + fu.fileName();
}
}BackupInfo;
-
bool pack_flag;:用于表示是否已经压缩的标志。 -
size_t fsize;:表示文件大小,存储文件的字节数。 -
time_t atime;:表示文件的最后访问时间。 -
time_t mtime;:表示文件的最后修改时间。 -
std::string real_path;:表示文件的实际路径,即文件在文件系统中的路径。 -
std::string pack_path;:表示文件的打包压缩路径,即文件在备份过程中打包压缩后存储的路径。 -
std::string url;:表示文件的下载 URL,即用户可以通过该 URL 下载文件。 -
void newBackupInfo(const std::string &realpath):这是一个成员函数,用于初始化备份信息。它接受一个realpath参数,即文件的实际路径。在该函数中,首先获取配置信息对象的实例,然后利用该实例获取备份相关的配置信息,包括打包目录、打包文件后缀和下载文件前缀。接着利用FileUtil类获取文件的大小、最后修改时间和最后访问时间,并设置其他字段的值。
数据管理
class DataManager
{
public:
DataManager()
{
_backup_file = config::getInstance()->getBackupFile();
pthread_rwlock_init(&_rwlock, NULL);
InitLoad();
}
~DataManager()
{
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&_rwlock);
}
bool inSert(const BackupInfo &info)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
_table[info.url] = info;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
storage();
return true;
}
bool upDate(const BackupInfo &info)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
_table[info.url] = info;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
storage();
return true;
}
bool getOneByURL(const std::string &url, BackupInfo *info)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
auto it = _table.find(url);
if(it == _table.end())
{
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return false;
}
*info = it->second;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return true;
}
bool getOneByRealPath(const std::string &realpath, BackupInfo *info)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
auto it = _table.begin();
for(; it != _table.end(); it++)
{
if(it->second.real_path == realpath)
{
*info = it->second;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return true;
}
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return false;
}
bool getAll(std::vector<BackupInfo> *arry)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
auto it = _table.begin();
for(; it != _table.end(); it++)
{
arry->push_back(it->second);
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return true;
}
bool storage()
{
std::vector<BackupInfo> arry;
getAll(&arry);
Json::Value root;
for(int i = 0; i < arry.size(); i++)
{
Json::Value item;
item["pack_flag"] = arry[i].pack_flag;
item["fsize"] = (Json::Int64)arry[i].fsize;
item["atime"] = (Json::Int64)arry[i].atime;
item["mtime"] = (Json::Int64)arry[i].mtime;
item["pack_path"] = arry[i].pack_path;
item["real_path"] = arry[i].real_path;
item["url"] = arry[i].url;
root.append(item);
}
std::string body;
JsonUtil::serialize(root, &body);
FileUtil fu(_backup_file);
fu.setContent(body);
return true;
}
bool InitLoad()
{
FileUtil fu(_backup_file);
if(fu.exits() == false) return true;
std::string body;
fu.getContent(&body);
Json::Value root;
JsonUtil::deSerialize(body, &root);
for(int i = 0; i < root.size(); i++)
{
BackupInfo info;
info.pack_flag = root[i]["pack_flag"].asBool();
info.fsize = root[i]["fsize"].asInt();
info.atime = root[i]["atime"].asInt64();
info.mtime = root[i]["mtime"].asInt64();
info.pack_path = root[i]["pack_path"].asString();
info.real_path = root[i]["real_path"].asString();
info.url = root[i]["url"].asString();
inSert(info);
}
return true;
}
private:
std::string _backup_file;
pthread_rwlock_t _rwlock;
std::unordered_map<std::string, BackupInfo> _table;
};
DataManager 数据管理类,主要用于管理备份信息的存储、更新和获取操作,并实现了从文件中加载和持久化备份信息的功能。
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
DataManager() | 初始化了备份文件路径、读写锁,并调用 InitLoad() 函数加载备份信息到内存中。 |
~DataManager() | 释放了读写锁。 |
inSert(const BackupInfo &info) | 向数据表中插入备份信息。 |
upDate(const BackupInfo &info) | 更新数据表中的备份信息。 |
getOneByURL(const std::string &url, BackupInfo *info) | 根据 URL 获取单个备份信息。 |
getOneByRealPath(const std::string &realpath, BackupInfo *info) | 根据实际路径获取单个备份信息。 |
getAll(std::vector<BackupInfo> *arry) | 获取所有备份信息。 |
storage() | 将备份信息持久化存储到文件中。 |
InitLoad() | 从备份文件中加载备份信息到内存中。 |
成员变量:
_backup_file:备份文件的路径。_rwlock:读写锁,用于保护数据表的并发访问。_table:使用无序映射存储备份信息,键为备份信息的 URL。
这个 DataManager 类的设计使得它能够方便地进行备份信息的存储、更新和获取,并且在对象构造时自动加载已有的备份信息,提高了代码的易用性和可维护性。
热点管理类
热点管理类用于遍历备份文件夹中的文件,对其中的文件进行判断是否为热点文件,对非热点文件进行压缩处理。
class HotManager
{
public:
HotManager()
{
config *con = config::getInstance();
_back_dir = con->getBackDir();
_pack_dir = con->getPackDir();
_pack_suffix = con->getPackFileSuffix();
_hot_time = con->getHotTime();
FileUtil tmp1(_back_dir);
FileUtil tmp2(_pack_dir);
tmp1.createDirectory();
tmp2.createDirectory();
}
bool RunModule()
{
while(1)
{
FileUtil fu(_back_dir);
std::vector<std::string> arry;
fu.scanDirectory(&arry);
for(auto &a : arry)
{
if(HotJudge(a) == true) continue;
BackupInfo bi;
if(_data->getOneByRealPath(a, &bi) == false)
{
bi.newBackupInfo(a);
}
FileUtil tmp(a);
tmp.comPress(bi.pack_path);
tmp.reMove();
bi.pack_flag = true;
_data->upDate(bi);
}
usleep(1000);
}
return true;
}
private:
bool HotJudge(const std::string &filename)
{
FileUtil fu(filename);
time_t last_atime = fu.lastAccTime();
time_t cur_time = time(NULL);
if(cur_time - last_atime <= _hot_time) return true;
return false;
}
private:
std::string _back_dir;
std::string _pack_dir;
int _hot_time;
std::string _pack_suffix;
};
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
HotManager() | 在对象创建时从配置文件中获取备份目录、打包目录、热文件时间阈值等参数,并且创建备份目录和打包目录。 |
RunModule() | 运行热备份模块的主循环。该函数通过不断扫描备份目录中的文件,判断是否为热文件。若文件不是热文件,则进行压缩备份操作,并更新备份信息。该循环会持续执行,通过 usleep(1000) 控制循环的执行频率。 |
HotJudge(const std::string &filename) | 判断文件是否为热文件。通过获取文件的最后访问时间,与当前时间进行比较判断文件是否为热文件。 |
成员变量:
_back_dir:备份目录的路径。_pack_dir:打包目录的路径。_hot_time:热文件时间阈值,用于判断文件是否为热文件。_pack_suffix:打包文件的后缀名。
这个 HotManager 类使得它能够周期性地监视备份目录中的文件,并根据热文件的判断条件执行相应的操作,从而实现了备份管理的自动化。
业务处理类
服务端提供提供了上传文件、列出文件列表和下载文件的功能,对客户端发送来的请求做出相应的处理后返回处理结果,并且下载支持断点续传功能。
class server
{
public:
server()
{
config *con = config::getInstance();
_server_port = con->getServerPort();
_server_ip = con->getServerIp();
_download_preffix = con->getDownloadPreffix();
}
bool RunModule()
{
_server.Post("/upload", UpLoad);
_server.Get("/listshow", ListShow);
_server.Get("/", ListShow);
std::string download_url = _download_preffix + "(.*)";
_server.Get(download_url, DownLoad); // (.*)匹配任意字符任意次
_server.listen(_server_ip.c_str(), _server_port);
return true;
}
private:
static void UpLoad(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &res)
{
auto ret = req.has_file("file");
if(ret == false)
{
res.status = 400;
return;
}
const auto &file = req.get_file_value("file");
std::string back_dir = config::getInstance()->getBackDir();
std::string realpath = back_dir + FileUtil(file.filename).fileName();
if(FileUtil(back_dir).exits() == false) FileUtil(back_dir).createDirectory();
FileUtil fu(realpath);
fu.setContent(file.content);
BackupInfo info;
info.newBackupInfo(realpath);
_data->inSert(info);
}
static std::string timetoStr(time_t t)
{
std::string tmp = std::ctime(&t);
return tmp;
}
static void ListShow(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &res)
{
std::vector<BackupInfo> arry;
_data->getAll(&arry);
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "<html><head><title>Download</title></head>";
ss << "<body><h1>Download</h1><table>";
for(auto &a :arry)
{
ss << "<tr>";
std::string filename = FileUtil(a.real_path).fileName();
ss << "<td><a href='" << a.url << "'>" << filename << "</a></td>";
ss << "<td align='right'>" << timetoStr(a.mtime) << "</td>";
ss << "<td align='right'>" << a.fsize / 1024 << "k</td>";
ss << "</tr>";
}
ss << "</table></body></html>";
res.body = ss.str();
res.set_header("Content-Type", "text/html");
res.status = 200;
}
static std::string getETag(const BackupInfo &info)
{
FileUtil fu(info.real_path);
std::string etag = fu.fileName();
etag += "-";
etag += std::to_string(info.fsize);
etag += "-";
etag += std::to_string(info.mtime);
return etag;
}
static void DownLoad(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &res)
{
BackupInfo info;
_data->getOneByURL(req.path, &info);
if(info.pack_flag == true)
{
FileUtil fu(info.pack_path);
fu.unCompress(info.real_path);
fu.reMove();
info.pack_flag = false;
_data->upDate(info);
}
bool retrans = false;
std::string old_etag;
if(req.has_header("If-Range"))
{
old_etag = req.get_header_value("If-Range");
if(old_etag == getETag(info)) retrans = true;
}
FileUtil fu(info.real_path);
fu.getContent(&res.body);
res.set_header("Accept-Ranges", "bytes");
res.set_header("ETag", getETag(info));
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream");
if(retrans == false) res.status = 200;
else res.status = 206;
}
private:
int _server_port;
std::string _server_ip;
std::string _download_preffix;
httplib::Server _server;
};
-
在
DownLoad函数中检查了If-Range头部,以确定是否需要重新传输文件。这是实现断点续传的一种方式。如果客户端在请求中提供了上次请求时服务器返回的 ETag(文件标识),并且与当前文件的 ETag 相匹配,那么可以断定客户端已经具有相应的部分文件。在这种情况下,你可以返回状态码 206 Partial Content,表示只返回文件的一部分内容。否则,返回状态码 200 OK,表示返回整个文件内容。 -
在
DownLoad函数中将文件内容设置到响应体中,并设置了Accept-Ranges和ETag头部。Accept-Ranges: bytes表示服务器支持字节范围请求,这是断点续传所需的。ETag是文件的标识,用于判断文件是否发生了变化。 -
在
UpLoad函数中处理了文件上传的逻辑。首先,检查请求中是否包含文件,然后获取文件内容并保存到指定目录中。接着,创建一个BackupInfo对象并插入到数据管理模块中。
客户端
客户端的开发在Windows上,使用的工具为vs2017及以上版本。
注意:需要支持C++17.
数据管理类
数据管理类对文件进行描述组织,并提供增加修改浏览等功能,能够进行持久化存储。
class dataManager
{
public:
dataManager(const std::string& backupfile)
:_backup_file(backupfile)
{
InitLoad();
}
void splitStr(const std::string& str, const std::string& sep, std::vector<std::string>* arry)
{
size_t cur = 0, pos = 0;
while (cur < str.size())
{
pos = str.find(sep, cur);
if (pos == std::string::npos) break;
std::string tmp = str.substr(cur, pos - cur);
arry->push_back(tmp);
cur = pos + sep.size();
}
if (cur < str.size())
{
std::string tmp = str.substr(cur);
arry->push_back(tmp);
}
}
bool InitLoad()
{
FileUtil fu(_backup_file);
std::string body;
fu.getContent(&body);
std::vector<std::string> arry;
splitStr(body, "\n", &arry);
for (auto& str : arry)
{
std::vector<std::string> tmp;
splitStr(str, " : ", &tmp);
if (tmp.size() != 2) continue;
_table[tmp[0]] = tmp[1];
}
return true;
}
bool inSert(const std::string& key, const std::string& val)
{
_table[key] = val;
storage();
return true;
}
bool upData(const std::string& key, const std::string& val)
{
_table[key] = val;
storage();
return true;
}
bool getOneByKey(const std::string& key, std::string* val)
{
auto it = _table.find(key);
if (it == _table.end()) return false;
*val = it->second;
return true;
}
protected:
bool storage()
{
std::stringstream ss;
for (auto it = _table.begin(); it != _table.end(); it++)
{
ss << it->first << " : " << it->second << "\n";
}
FileUtil fu(_backup_file);
fu.setContent(ss.str());
return true;
}
private:
std::string _backup_file;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _table;
};
dataManager类用于管理键值对数据,其中键和值都是字符串类型。- 构造函数
dataManager(const std::string& backupfile)接受一个参数backupfile,表示备份文件的路径,用于存储数据。 storage()方法将当前内存中的数据持久化到备份文件中。它将所有键值对拼接成一个字符串,并将其写入备份文件。splitStr()方法用于将字符串按照指定的分隔符拆分成字符串数组。InitLoad()方法用于从备份文件中加载数据到内存中。它读取备份文件的内容,按行分割,然后将键值对存储到内存中的哈希表中。inSert()方法用于向数据管理类中插入新的键值对,并将数据持久化到备份文件中。upData()方法用于更新指定键对应的值,并将更新后的数据持久化到备份文件中。getOneByKey()方法用于根据给定的键获取对应的值,并将值通过参数返回。
文件备份类
文件备份类实现的功能是定期扫描指定目录下的文件,并将需要上传的文件发送到服务器。
class Backup
{
public:
Backup(const std::string &backdir, const std::string &backfile)
:_back_dir(backdir)
{
_data = new dataManager(backfile);
FileUtil(_back_dir).createDirectory();
}
std::string getFileIdentifier(const std::string& filename)
{
FileUtil fu(filename);
std::stringstream ss;
ss << fu.fileName() << "-" << fu.fileSize() << "-" << fu.lastModTime();
return ss.str();
}
bool runModue()
{
while (1)
{
FileUtil fu(_back_dir);
std::vector<std::string> arry;
fu.scanDirectory(&arry);
for (auto& a : arry)
{
if (isNeedUpload(a))
{
if (upLoad(a))
{
_data->inSert(a, getFileIdentifier(a));
std::cout << "upload successful!\n";
}
}
}
Sleep(1);
}
return true;
}
protected:
bool isNeedUpload(const std::string& filename)
{
std::string id;
if (_data->getOneByKey(filename, &id))
{
std::string new_id = getFileIdentifier(filename);
if (new_id == id) return false;
}
FileUtil fu(filename);
if (time(NULL) - fu.lastModTime() < 5) return false;
std::cout << filename << " need upload!\n";
return true;
}
bool upLoad(const std::string& filename)
{
FileUtil fu(filename);
std::string body;
fu.getContent(&body);
httplib::Client cli(SERVER_IP, SERVER_PORT);
httplib::MultipartFormData item;
item.content = body;
item.filename = fu.fileName();
item.name = "file";
item.content_type = "application/octet-stream";
httplib::MultipartFormDataItems items;
items.push_back(item);
auto res = cli.Post("/upload", items);
if (!res || res->status != 200)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
std::string _back_dir;
dataManager* _data;
};
- 构造函数
Backup接收备份目录和备份文件名作为参数,初始化备份客户端对象。 getFileIdentifier函数用于生成文件标识符,它基于文件名、文件大小和最后修改时间生成一个字符串。runModule函数是备份客户端的主要执行逻辑。它循环扫描备份目录下的文件,如果发现需要上传的文件,则调用upLoad函数上传文件,并将文件信息记录到备份数据中。isNeedUpload函数用于检查文件是否需要上传。它检查备份数据中是否已存在相同文件,并比较文件最后修改时间,以决定是否需要上传文件。upLoad函数负责上传文件到服务器。它使用 httplib 库创建一个客户端,将文件内容以 multipart/form-data 格式发送到指定的上传端点/upload。如果上传成功(返回状态码 200),则返回 true,否则返回 false。
总结
开发云备份项目涉及多个技术领域,包括文件操作、网络通信、并发处理等。需要解决各种技术挑战,例如如何有效地上传和下载大文件、处理网络请求超时、处理并发上传等。
而且在开发云备份项目可能涉及学习新的库、框架或技术。这可能包括学习使用第三方库来处理HTTP请求、学习文件压缩和解压缩技术、学习关于网络安全的最佳实践等。开发云备份项目也是一个持续学习和改进的过程,会不断遇到新的挑战和问题,需要持续学习并改进解决方案。
总的来说,开发云备份项目是一个充满挑战和机会的过程,通过这个项目可以提高技术能力、团队协作能力和项目管理能力。同时,也会从中获得成就感和满足感,因为付出的努力将会变成一个实实在在的产品或服务。
最后,云备份专栏持续更新中,对项目周边知识点以及项目难点进行清扫,以及项目的更新迭代,欢迎佬们提出自己的问题观点想法,加入对代码的更新迭代队伍中。



![[BUUCTF]-PWN:ciscn_2019_final_3解析](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/07e9c756be8b476498e9fb408f18d917.png)



![[office] excel2016怎么求最大值和最小值 #职场发展#知识分享](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b2e30ad30245887ba39845b64fdd2c67.jpeg)