目录
一、涉及到的相关知识
1.重载的方法
2.Convert.ToInt32(String)方法
3.判断字符串是否带有小数点
二、实例
1.示例
2.生成成果
一、涉及到的相关知识
1.重载的方法
重载方法就是方法名称相同,但是每个方法中参数的数据类型、个数或顺序不同的方法。如果一个类中存在两个以上的同名方法,并且方法的参数类型、个数或者顺序不同,当调用这样的方法时,编译器会根据传入的参数自动进行判断,决定调用哪个方法。
2.Convert.ToInt32(String)方法
将数字的指定字符串表示形式转换为等效的 32 位带符号整数。
public static int ToInt32 (string? value);
参数
value String
包含要转换的数字的字符串。
返回
Int32
一个与 value 中数字等效的 32 位带符号整数,如果 value 为 null,则为 0(零)。
例外
FormatException
value 不由一个可选符号后跟一系列数字 (0-9) 组成。
OverflowException
value 表示小于 Int32.MinValue 或大于 Int32.MaxValue 的数字。在C#中,Convert.ToInt32(string)方法用于将字符串转换为整数。如果字符串包含非数字字符,例如小数点,该方法将引发异常。例如,字符串是"123.456",包含非数字字符"."。因此,直接使用Convert.ToInt32(string)会引发异常。
为了避免异常,可以先使用Decimal.Parse(string)方法将字符串转换为小数,然后再使用Convert.ToInt32(decimal)方法将小数转换为整数。
string str = "123.456";
decimal decimalValue = Decimal.Parse(str);
int intValue = Convert.ToInt32(decimalValue);或者,使用string.Split()方法将字符串按指定的分隔符拆分为一个字符串数组。例如,可以使用小数点"."作为分隔符,然后取第一个元素作为整数部分。
string str = "123.456";
string[] parts = str.Split('.');
// 如果有小数点,取小数点前面的部分作为整数
// 如果没有小数点,整个字符串就是整数部分
string integerPart = parts.Length > 0 ? parts[0] : str;
int intValue = Convert.ToInt32(integerPart);3.判断字符串是否带有小数点
使用正则表达式@"^\d+\.\d+$"判断字符串是否含有“.”,然后执行相应操作。
二、实例
1.示例
//重载加法运算
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
namespace _111
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private GroupBox? groupBox1;
private GroupBox? groupBox2;
private RadioButton? radioButton3;
private RadioButton? radioButton2;
private RadioButton? radioButton1;
private TextBox? textBox1;
private Label? label2;
private Label? label1;
private TextBox? textBox2;
private TextBox? textBox3;
private Button? button1;
private Label? label3;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
Load += Form1_Load;
}
private void Form1_Load(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
//
// radioButton1
//
radioButton1 = new RadioButton
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(11, 17),
Name = "radioButton1",
Size = new Size(40, 21),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = true,
Text = "int",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
//
// radioButton2
//
radioButton2 = new RadioButton
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(11, 39),
Name = "radioButton2",
Size = new Size(90, 21),
TabIndex = 1,
TabStop = true,
Text = "int+double",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
//
// radioButton3
//
radioButton3 = new RadioButton
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(11, 61),
Name = "radioButton3",
Size = new Size(67, 21),
TabIndex = 2,
TabStop = true,
Text = "double",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
//
// label1
//
label1 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(6, 23),
Name = "label1",
Size = new Size(44, 17),
TabIndex = 0,
Text = "加数:"
};
//
// label2
//
label2 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(6, 53),
Name = "label2",
Size = new Size(56, 17),
TabIndex = 1,
Text = "被加数:"
};
//
// textBox1
//
textBox1 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(56, 17),
Name = "textBox1",
Size = new Size(91, 23),
TabIndex = 2
};
//
// textBox2
//
textBox2 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(56, 47),
Name = "textBox2",
Size = new Size(91, 23),
TabIndex = 3
};
//
// groupBox1
//
groupBox1 = new GroupBox
{
Location = new Point(12, 12),
Name = "groupBox1",
Size = new Size(153, 92),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = false,
Text = "数据运算"
};
groupBox1.Controls.Add(textBox2);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(textBox1);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(label2);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(label1);
groupBox1.SuspendLayout();
//
// groupBox2
//
groupBox2 = new GroupBox
{
Location = new Point(171, 12),
Name = "groupBox2",
Size = new Size(127, 92),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = false,
Text = "选择数据类型"
};
groupBox2.Controls.Add(radioButton3);
groupBox2.Controls.Add(radioButton2);
groupBox2.Controls.Add(radioButton1);
groupBox2.SuspendLayout();
//
// textBox3
//
textBox3 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(88, 107),
Name = "textBox3",
Size = new Size(100, 23),
TabIndex = 1
};
//
// button1
//
button1 = new Button
{
Location = new Point(223, 107),
Name = "button1",
Size = new Size(75, 23),
TabIndex = 2,
Text = "开始计算",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
button1.Click += Button1_Click;
//
// label3
//
label3 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(12, 113),
Name = "label3",
Size = new Size(68, 17),
TabIndex = 3,
Text = "运算结果:"
};
//
// Form1
//
AutoScaleDimensions = new SizeF(7F, 17F);
AutoScaleMode = AutoScaleMode.Font;
ClientSize = new Size(309, 136);
Controls.Add(label3);
Controls.Add(button1);
Controls.Add(textBox3);
Controls.Add(groupBox2);
Controls.Add(groupBox1);
Name = "Form1";
Text = "重载加法运算";
groupBox1.ResumeLayout(false);
groupBox1.PerformLayout();
groupBox2.ResumeLayout(false);
groupBox2.PerformLayout();
}
private void Button1_Click(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox3!.Text = "";
try
{
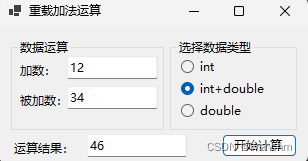
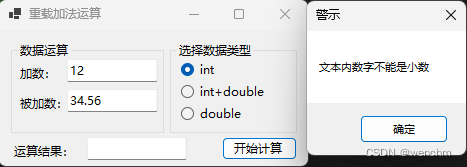
if (radioButton1!.Checked)
{
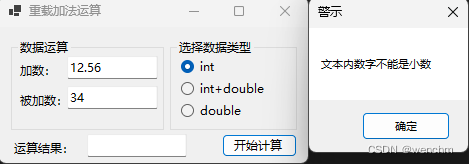
if (!IsDecimalNumber(textBox1!.Text) && !IsDecimalNumber(textBox2!.Text))
{
textBox3!.Text = Add(Convert.ToInt32(textBox1!.Text), Convert.ToInt32(textBox2!.Text)).ToString();
}
else
{
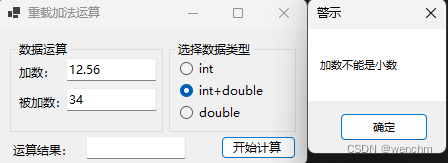
MessageBox.Show("文本内数字不能是小数","警示");
}
}
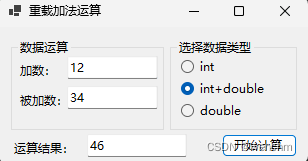
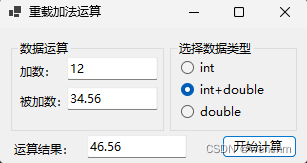
else if (radioButton2!.Checked)
{
if (!IsDecimalNumber(textBox1!.Text))
{
textBox3!.Text = Add(Convert.ToInt32(textBox1!.Text), Convert.ToDouble(textBox2!.Text)).ToString();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("加数不能是小数", "警示");
}
}
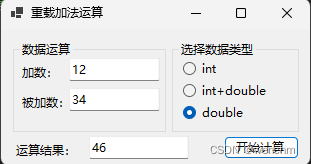
else if (radioButton3!.Checked)
{
textBox3!.Text = Add(Convert.ToDouble(textBox1!.Text) ,Convert.ToDouble(textBox2!.Text)).ToString();
}
}
catch { }
}
public static int Add(int x, int y)//定义一个静态方法Add,返回值为int类型,有两个int类型的参数
{
return x + y;
}
public static double Add(int x, double y)//重新定义方法Add,它与第一个方法的返回值类型及参数类型不同
{
return x + y;
}
public static double Add(double x, double y)//重新定义方法Add,它与第一个方法的返回值类型及参数类型不同
{
return x + y;
}
/// <summary>
/// 使用正则表达式判断字符串是否为带小数的数字
/// ^\d+\.\d+$ : ^ 表示字符串开始, \d+ 表示一个或多个数字,
/// \.? 表示可能存在的小数点, \d+ 表示小数点后面的一个或多个数字,
/// $ 表示字符串结束
/// </summary>
public static bool IsDecimalNumber(string str)
{
return MyRegex().IsMatch(str);
}
[GeneratedRegex(@"^\d+\.\d+$")]
private static partial Regex MyRegex();
}
}
2.生成成果