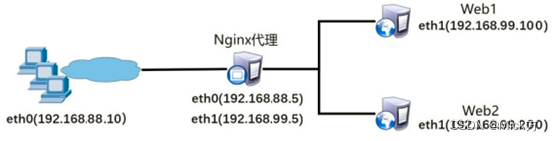
协议:一组规则
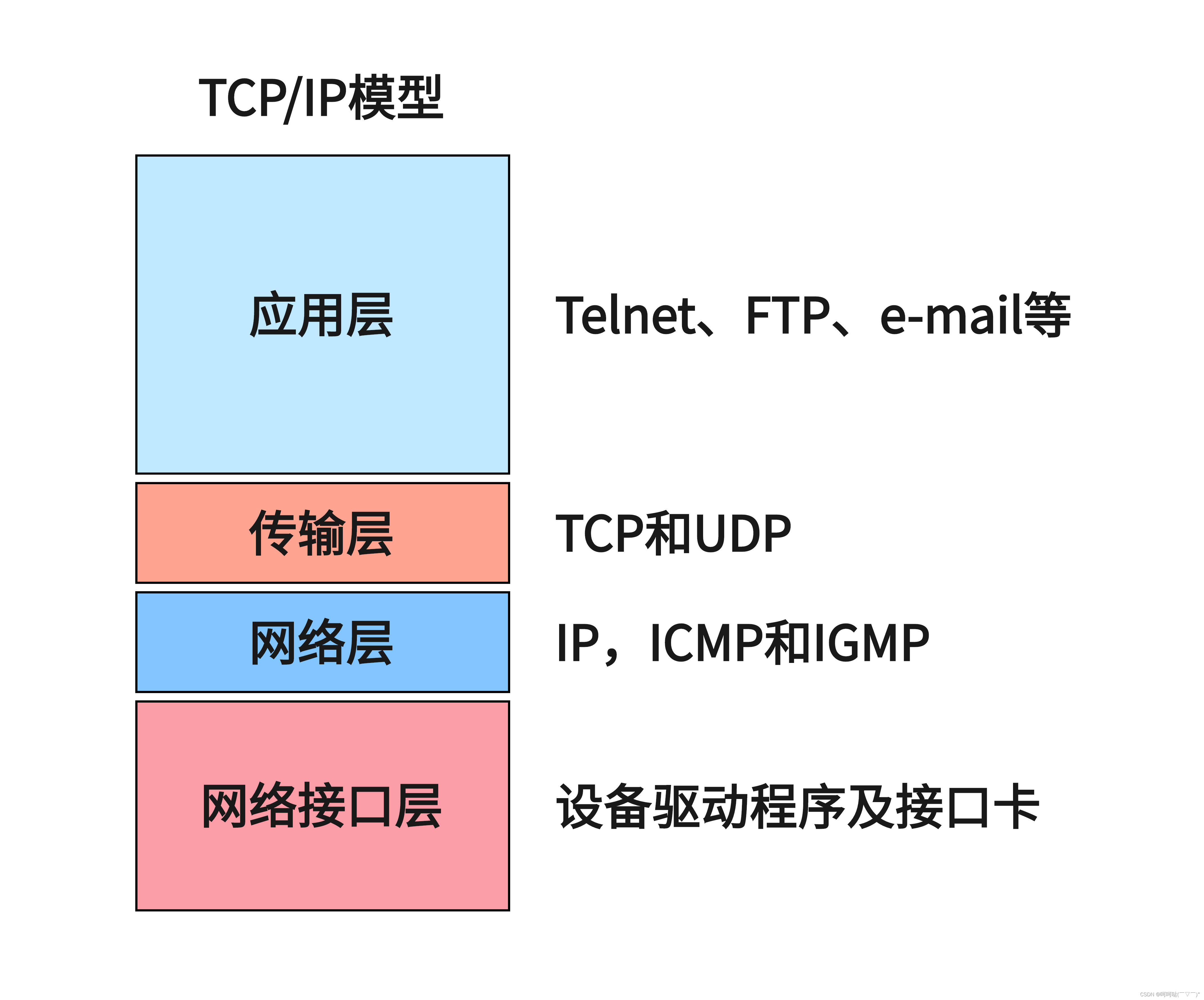
分层模型结构:
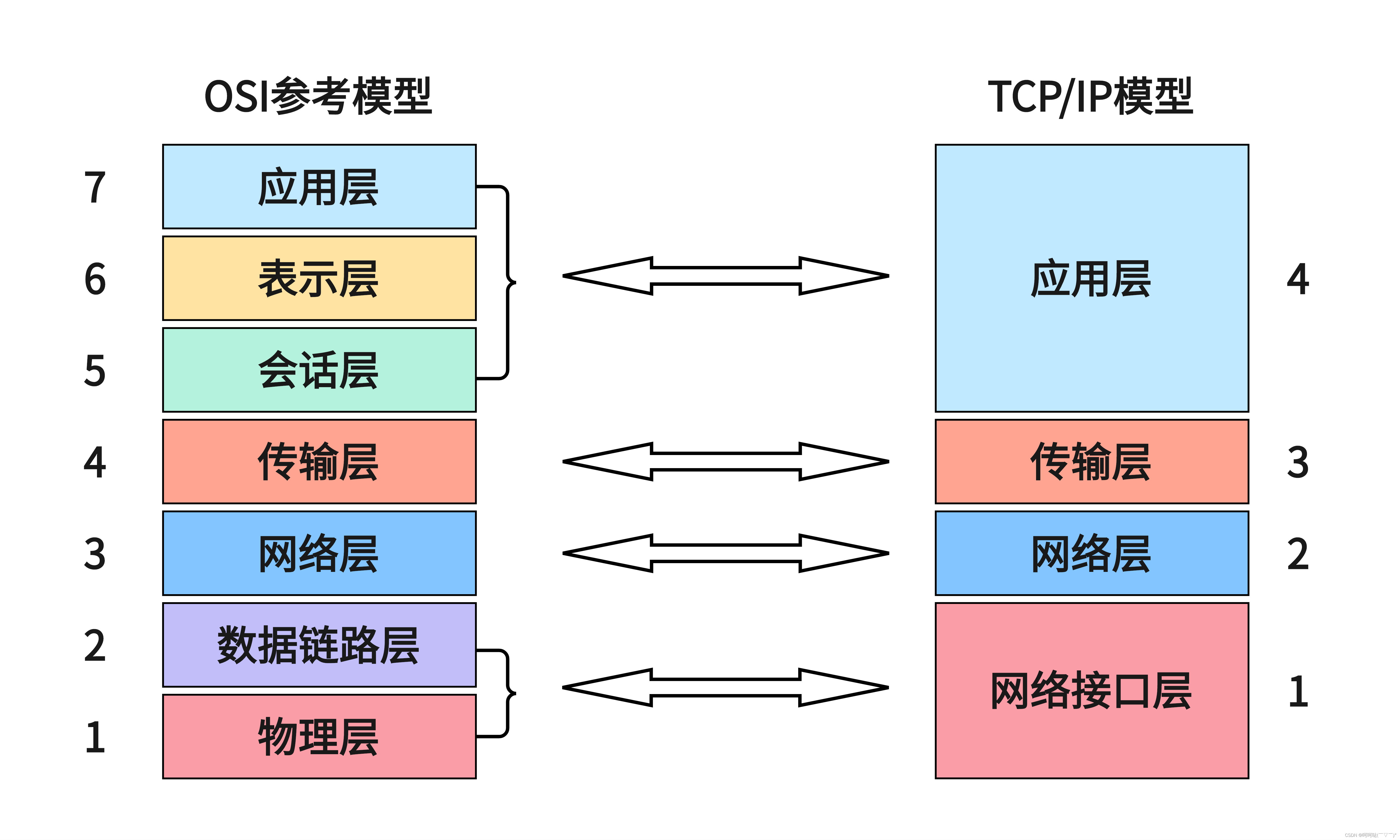
- OSI七层模型:物理层、数据链路层、网络层、传输层、会话层、表示层、应用层
- TCP/IP 4层模型:链路层/网络接口层、网络层、传输层、应用层
- 应用层:http、ftp、nfs、ssh、telnet、
- 传输层:TCP、UDP
- 网络层:IP、ICMP、IGMP
- 链路层:以太网帧协议、ARP
C/S模型和B/S模型
- C/S模型:client-server
- B/S模型:browser-server
网络传输流程:
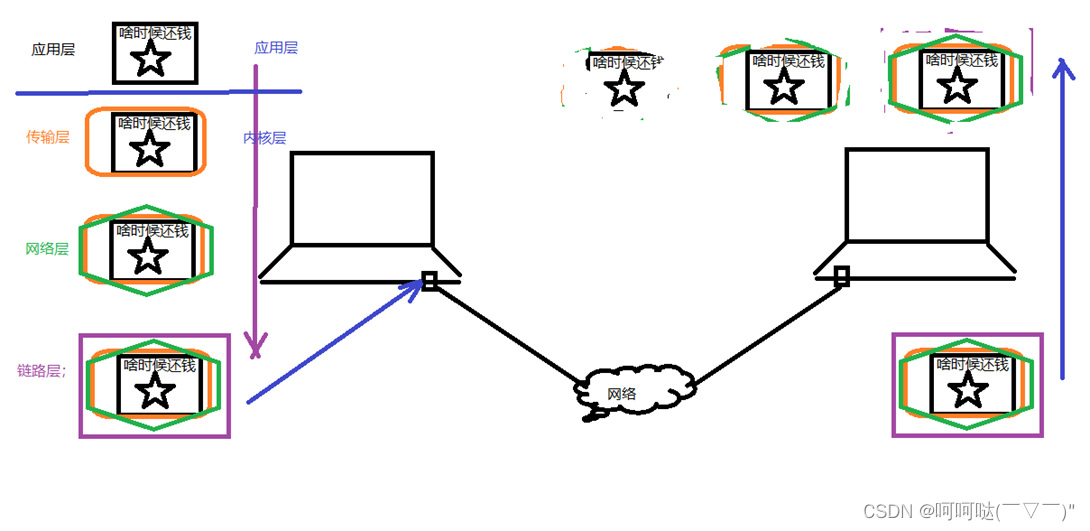
- 数据没有封装之前,是不能在网络中传递
- 数据-》应用层-》传输层-》网络层-》链路层 --- 网络环境
以太网帧协议:
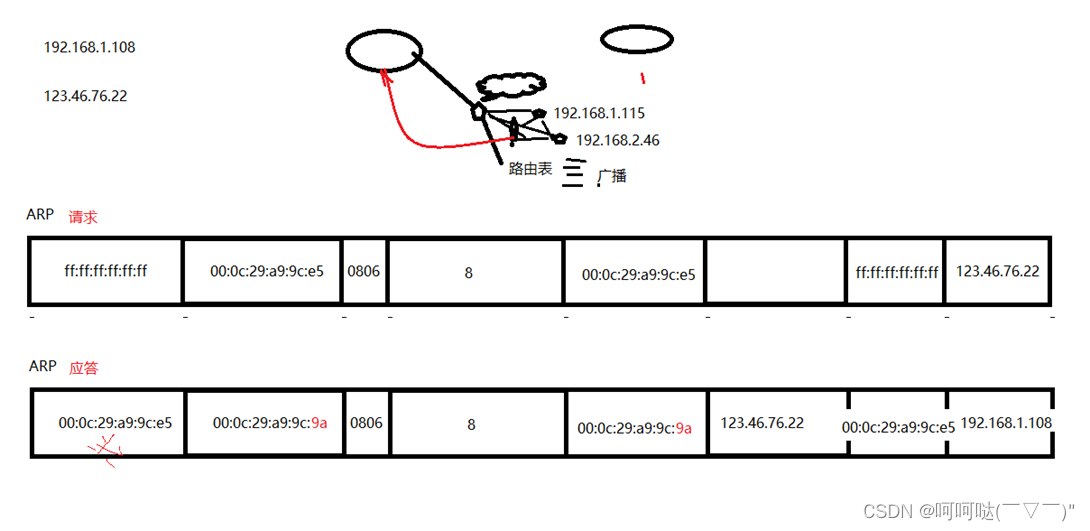
- ARP协议:根据IP地址获取mac地址
- 以太网帧协议:根据mac地址,完成数据包传输
IP协议:
- 版本: IPv4、IPv6 -- 4位
- TTL:time to live (设置数据包在路由节点中的跳转上限,每经过一个路由节点,该值-1, 减为0的路由,有义务将该数据包丢弃)
- 源IP:32位 -- 4字节
192.168.1.108 --- 点分十进制 IP地址(string)- 目的IP:32位--- 4字节
IP地址:可以在网络环境中,唯一标识一台主机
端口号:可以进行网络通信的一台主机上,唯一标识一个进程
IP地址+端口号:可以在网络环境中,唯一标识一个进程
UDP协议
16位:源端口号 2^16 = 65536
16位:目的端口号
TCP协议
16位:源端口号 2^16 = 65536
16位:目的端口号
32序号
32确认序号
6个标志位
16位窗口大小 2^16 = 65536网络套接字:socket
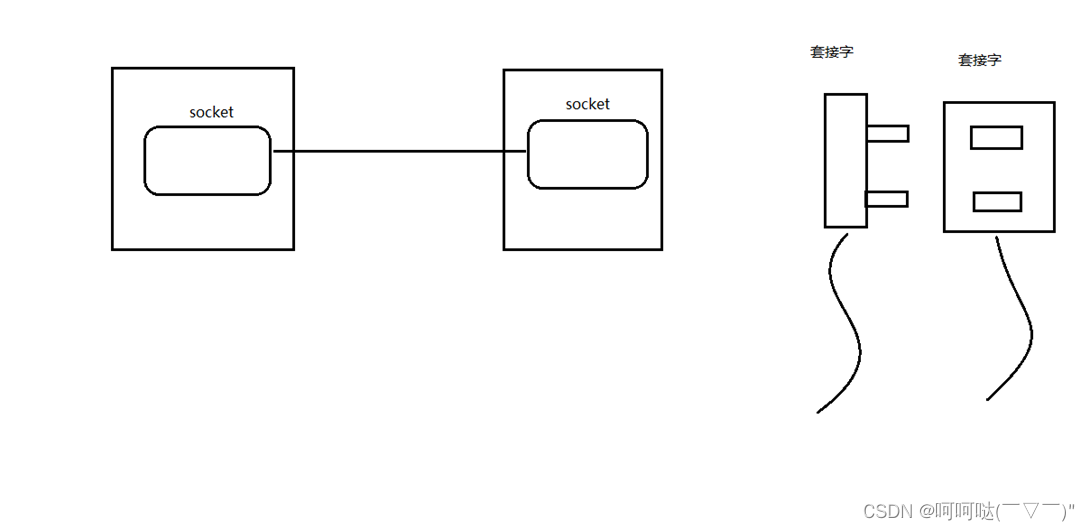
- 一个文件描述符指向一个套接字(该套接字内部由内核借助两个缓冲区实现)
- 在通信过程中,套接字一定是成对出现的
网络字节序:
- 小端法:(pc本地存储) 高位存高地址,低位存低地址 int a = 0x12345678
- 大端法:(网络存储) 高位存低地址,低位存高地址
htonl --> 本地--》网络 (IP) 192.168.1.11 --> string --> atoi --> int --> htonl --> 网络字节序
htons --> 本地--》网络 (port)
ntohl --> 网络--》 本地(IP)
ntohs --> 网络--》 本地(Port)注意:htonl --> 本地 --> 网络(IP)
192.168.1.11 --> string --> atoi --> int --> htonl --> 网络字节序
IP地址转换函数
- inet_pton
- inet_ntop
- 本地字节序(string IP) ---> 网络字节序
// 本地字节序(string IP) ---> 网络字节序
int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
af: AF_INET,AF_INET6
src:传入,IP地址(点分十进制)
dst:传出转换后的 网络字节序的 IP地址
返回值:
成功: 1
异常: 0,说明src指向的不是一个有效的ip地址
失败: -1NAME
inet_pton - convert IPv4 and IPv6 addresses from text to binary form
SYNOPSIS
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
DESCRIPTION
This function converts the character string src into a network address
structure in the af address family, then copies the network address
structure to dst. The af argument must be either AF_INET or AF_INET6.
dst is written in network byte order.- 网络字节序 ---> 本地字节序(string IP)
// 网络字节序 ---> 本地字节序(string IP)
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src,char *dst, socklen_t size);
af: AF_INET,AF_INET6
src: 网络字节序IP地址
dst: 本地字节序(string IP)
size: dst的大小
返回值:
成功: dst
失败: NULLNAME
inet_ntop - convert IPv4 and IPv6 addresses from binary to text form
SYNOPSIS
#include <arpa/inet.h>
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src,
char *dst, socklen_t size);
DESCRIPTION
This function converts the network address structure src in the af
address family into a character string. The resulting string is copied
to the buffer pointed to by dst, which must be a non-null pointer. The
caller specifies the number of bytes available in this buffer in the
argument size.- sockaddr地址结构: IP + Port --> 在网络环境中唯一标识一个进程
sockaddr地址结构: IP + Port --> 在网络环境中唯一标识一个进程
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_port = htons(8080);
#if 0
int dst;
inet_pton(AF_INET,"192.168.1.100",(void*)dst);
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = dst;
#else
// 取出系统中有效的任意IP地址(二进制类型)
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
bind(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&addr,sizeof(addr));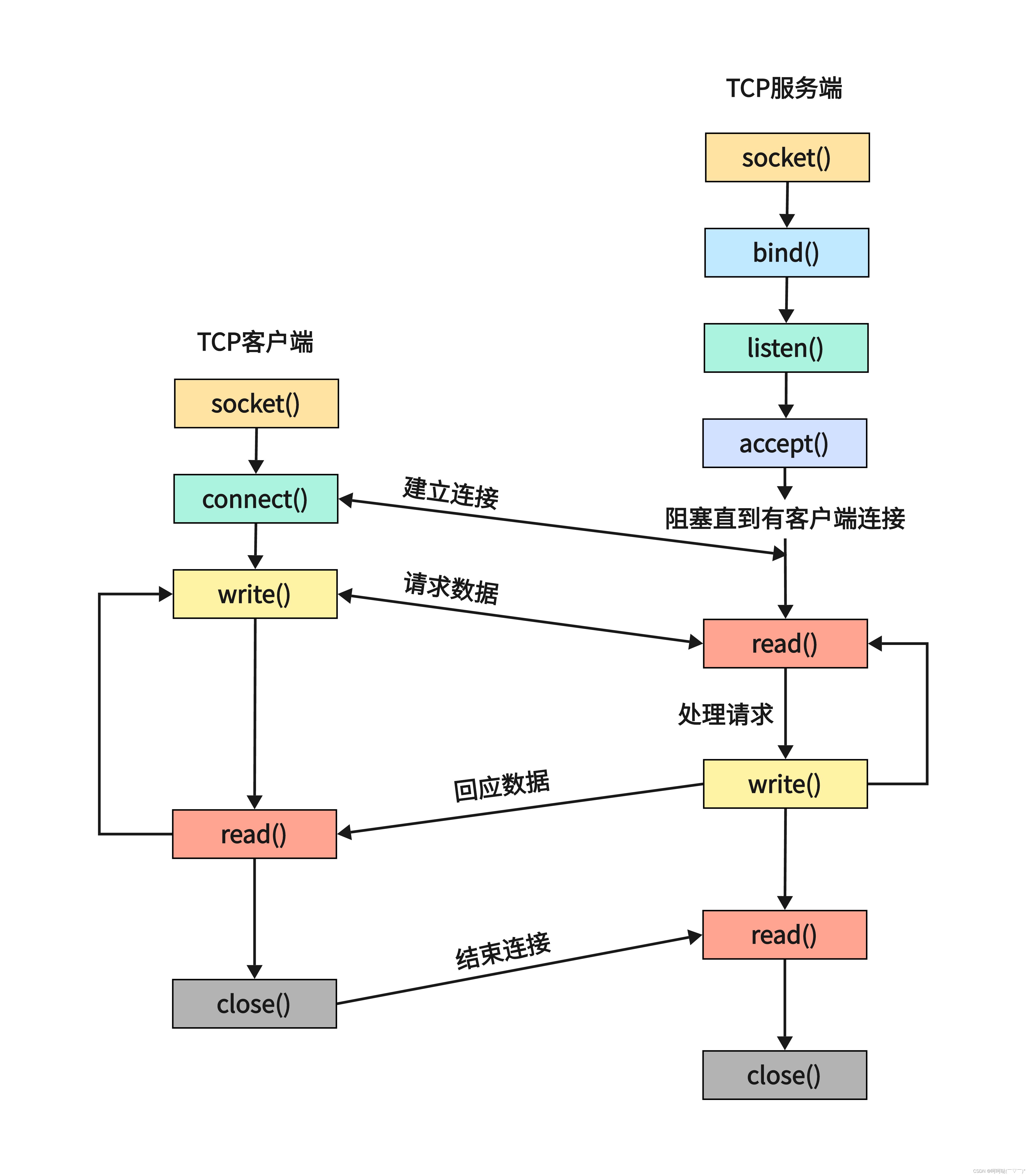
- socket函数,创建一个套接字
socket函数
#include <sys/socket.h>
// 创建一个套接字
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
domain: AF_INET,AF_INET6
type: SOCK_STREAM,SOCK_DGRAM
protocol: 0
返回值:
成功: 新套接字所对应文件描述符
失败: -1 errnoNAME
socket - create an endpoint for communication
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
DESCRIPTION
socket() creates an endpoint for communication and returns a file
descriptor that refers to that endpoint. The file descriptor returned
by a successful call will be the lowest-numbered file descriptor not
currently open for the process.- bind函数
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
sockfd: socket 函数返回值
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_port = htons(8080);
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
addr:传入参数(struct sockaddr*)&addr
addrlen:sizeof(addr) 地址结构的大小
返回值:
成功: 0
失败: -1 errnoNAME
bind - bind a name to a socket
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr,
socklen_t addrlen);
DESCRIPTION
When a socket is created with socket(2), it exists in a name space
(address family) but has no address assigned to it. bind() assigns the
address specified by addr to the socket referred to by the file descrip‐
tor sockfd. addrlen specifies the size, in bytes, of the address struc‐
ture pointed to by addr. Traditionally, this operation is called
“assigning a name to a socket”.
It is normally necessary to assign a local address using bind() before a
SOCK_STREAM socket may receive connections (see accept(2)).- listen函数,设置同时与服务器建立连接的上限数(同时进行3次握手的客户端数量)
// 设置同时与服务器建立连接的上限数(同时进行3次握手的客户端数量)
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
sockfd: socket 函数返回值
backlog: 上限数值,最大值为128
返回值:
成功: 0
失败: -1 errnoNAME
listen - listen for connections on a socket
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
DESCRIPTION
listen() marks the socket referred to by sockfd as a passive socket,
that is, as a socket that will be used to accept incoming connection
requests using accept(2).
The sockfd argument is a file descriptor that refers to a socket of type
SOCK_STREAM or SOCK_SEQPACKET.
The backlog argument defines the maximum length to which the queue of
pending connections for sockfd may grow. If a connection request
arrives when the queue is full, the client may receive an error with an
indication of ECONNREFUSED or, if the underlying protocol supports
retransmission, the request may be ignored so that a later reattempt at
connection succeeds.- accept函数,阻塞等待客户端建立连接,成功的话,返回一个与客户端成功连接的socket文件描述符
// 阻塞等待客户端建立连接,成功的话,返回一个与客户端成功连接的socket文件描述符
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
sockfd:socket 函数返回值
addr:传出参数,成功与服务器建立连接的那个客户端的地址结构(IP+port)
socklen_t client_addr_len = sizeof(addr);
addrlen:传入传出 &client_addr_len
入:addr的大小
出:客户端addr实际大小
返回值:
成功:能与客户端进行数据通信的 socket 对应的文件描述
失败:-1,errnoNAME
accept, accept4 - accept a connection on a socket
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int accept4(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr,
socklen_t *addrlen, int flags);
DESCRIPTION
The accept() system call is used with connection-based socket types (SOCK_STREAM, SOCK_SEQPACKET). It extracts
the first connection request on the queue of pending connections for the listening socket, sockfd, creates a new
connected socket, and returns a new file descriptor referring to that socket. The newly created socket is not in
the listening state. The original socket sockfd is unaffected by this call.- connect函数
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
sockfd: socket 函数返回值
struct sockaddr_in server_addr; // 服务器地址结构
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(8080);
inet_pton(AF_INET, "服务器IP地址", &server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
addr:传入参数,服务器的地址结构
addrlen:服务器的地址结构的大小
返回值:
成功: 0
失败: -1,errno
如果不使用bind绑定客户端地址结构,采用"隐式绑定".NAME
connect - initiate a connection on a socket
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr,
socklen_t addrlen);
DESCRIPTION
The connect() system call connects the socket referred to by the file
descriptor sockfd to the address specified by addr. The addrlen argu‐
ment specifies the size of addr. The format of the address in addr is
determined by the address space of the socket sockfd; see socket(2) for
further details.
If the socket sockfd is of type SOCK_DGRAM, then addr is the address to
which datagrams are sent by default, and the only address from which
datagrams are received. If the socket is of type SOCK_STREAM or
SOCK_SEQPACKET, this call attempts to make a connection to the socket
that is bound to the address specified by addr.
Generally, connection-based protocol sockets may successfully connect()
only once; connectionless protocol sockets may use connect() multiple
times to change their association. Connectionless sockets may dissolve
the association by connecting to an address with the sa_family member of
sockaddr set to AF_UNSPEC (supported on Linux since kernel 2.2).TCP 通信流程分析:
TCP 通信流程分析:
Server:
1.socket() 创建socket
2.bind() 绑定服务器地址结构
3.listen() 设置同时与服务器建立连接的上限数(监听上限)
4.accept() 阻塞监听客户端连接
5.read(fd) 读socket获取客户端数据
6.小 -- 大写 toupper()
7.write(fd)
8.close()
Client:
1.socket() 创建socket
2.connect() 与服务器建立连接
3.write() 写数据到socket
4.read() 读转换后的数据
5.显示读取结果
6.close()未完待续~