package Test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static int N = 110,hh = 0,tt = -1,n,m;
static int[][] g = new int[N][N]; //用来存储迷宫
static int[][] d = new int[N][N]; //用来存储d[i][j]到远点的距离
static PII[] q = new PII[N * N];
static int[] dx = {-1,0,1,0};
static int[] dy = {0,1,0,-1};
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static int bfs(){
d[0][0] = 0; //初始化头节点距离为0
//bfs模板
//先把头节点放入队列中
q[++tt] = new PII(0,0);
//扩展放入队列的点
while (hh<=tt){
PII t = q[hh++]; //把头节点拿出来,然后再把头节点周围满足条件的点放入
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = t.first + dx[i]; //行
int y = t.second + dy[i]; //列
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1){
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
//把扩展的点加入队列
q[++tt] = new PII(x,y);
}
}
}
//下标从0开始
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] init = in.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(init[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(init[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
init = in.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
g[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(init[j]);
d[i][j] = -1;
}
}
System.out.println(bfs());
in.close();
}
}
class PII{
int first;
int second;
public PII(int first, int second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
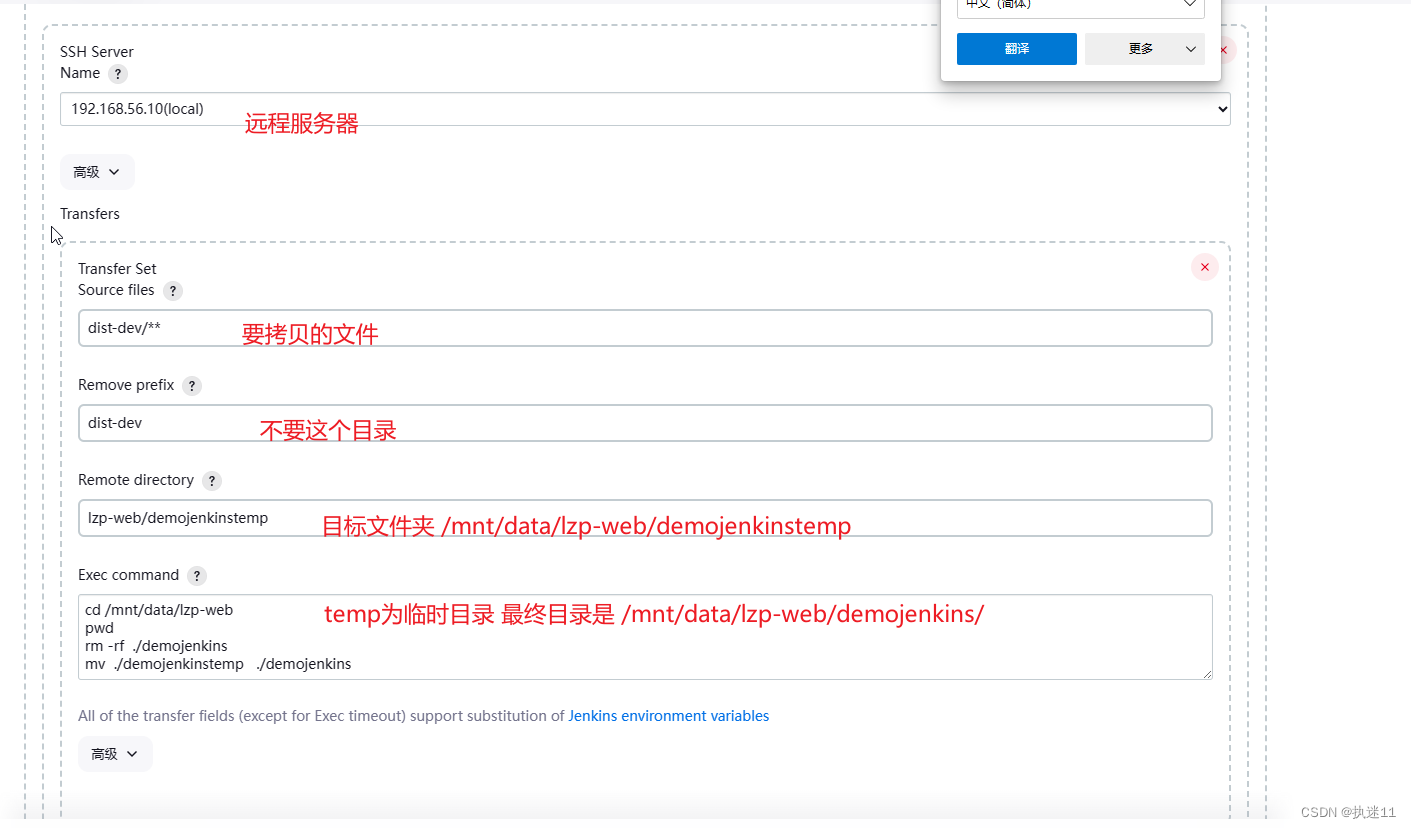
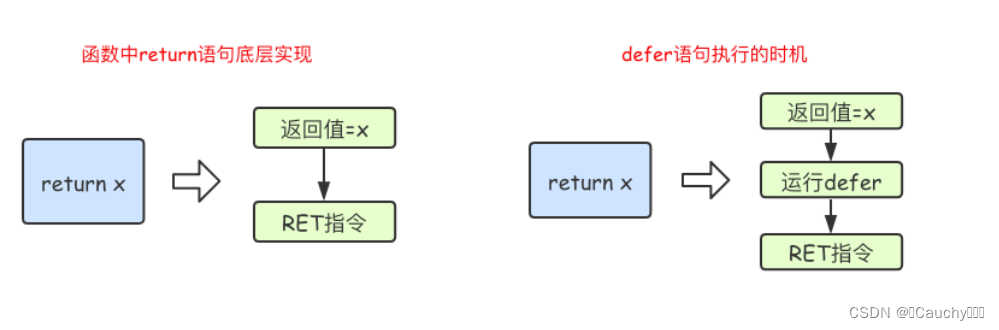


![[AI]文心一言爆火的同时,ChatGPT带来了这么多的开源项目你了解吗](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1ceb3fd255254ceeaa91ded1c5c1ddba.png)