前言
mongodb:为了在node应用中与MongoDB交互,开发者需要使用MongoDB的驱动程序,所以安装的mongodb就是其驱动程序;
mongoose: 是一个用于 MongoDB 的对象建模工具,提供了一个丰富的查询语言和许多其他功能,以帮助开发者更方便地使用 MongoDB,可以理解为MongoDB插件/工具。
一般来说,对于大多数 MongoDB 的操作,使用 mongoose 已经足够了
服务端工程目录示例:
--server // 根目录
--model
--main.js // 数据对象模型model
--routes
--user.js // 路由(接口)文件
--db.js // 连接 MongoDB 数据库
--server.js // 入口文件,连接数据库,启动服务,挂载路由如何在中创建一个用户“表”(集合),并且实现添加和查询
在MongoDB中,术语“表”对应的是集合(Collection)。创建一个集合并不需要显式操作,因为当你向一个不存在的集合中插入文档时,MongoDB会自动创建这个集合。
1.连接服务器
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 连接数据库函数
async function connect() {
try {
await mongoose.connect('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/mydatabase', {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
});
console.log('Connected to MongoDB');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error connecting to MongoDB:', error);
throw error; // 抛出错误以便在调用处被捕获
}
}
module.exports = { connect };2.创建一个Mongoose Schema对象
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
// 用户Schema
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true },
email: { type: String, unique: true, required: true },
password: { type: String, required: true },
});
// 创建User Model
const User = mongoose.model("User", userSchema);
module.exports = { User };
上面的代码:创建一个Mongoose Schema对象,它是对MongoDB集合中存储的文档结构的一种描述或模式定义。参数传入一个对象来定义文档的结构。
在这个例子中:
- name、email 和 password 是我们定义的字段(或键),它们代表了文档可能具有的属性。
- 对于每个字段,我们指定了其类型,如 String、Number、Date 等。这里 name 和 password 都被指定为 String 类型。
- 对于 email 字段,我们不仅指定了类型为 String,还添加了一个选项 unique: true,这意味着MongoDB会确保该集合中的所有文档的 email 字段值都是唯一的,即不会有重复的电子邮件地址。
通过定义这样一个Schema,Mongoose会在插入、更新文档时自动进行数据类型检查和约束验证,以保证数据库中数据的一致性和完整性。后续通过 mongoose.model('User', userSchema) 可以基于此Schema创建Model,进而执行查询、插入、更新和删除等数据库操作。
3.user相关接口编写
// usersRoutes.js
const express = require("express");
const { User } = require("../model/main"); // 确保路径正确指向db.js文件
const router = express.Router();
// 用户保存接口
router.post("/", async (req, res) => {
try {
const newUser = new User(req.body);
await newUser.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "User created!", user: newUser });
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error creating user:", error);
res
.status(500)
.json({ error: "An error occurred while creating the user." });
}
});
// 查询单个用户或所有用户接口
router.get("/:id?", async (req, res) => {
try {
if (req.params.id) {
const userId = req.params.id;
const user = await User.findById(userId);
if (!user) {
return res.status(404).json({ message: "User not found." });
}
res.json(user);
} else {
const users = await User.find();
res.json(users);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching user(s):", error);
res
.status(500)
.json({ error: "An error occurred while fetching the user(s)." });
}
});
module.exports = router;
4.编写服务启动文件, 并挂在用户路由
// server.js
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const cors = require('cors');
const { connect } = require('./db'); // 确保路径正确指向db.js文件
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use(bodyParser.json());
// 在服务器启动前先连接数据库
async function startServer() {
try {
await connect();
console.log('Connected to MongoDB');
// 挂载用户路由到 /api/users
const usersRoutes = require('./routes/user');
app.use('/api/users', usersRoutes);
// 启动服务器
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error connecting to MongoDB:', error);
}
}
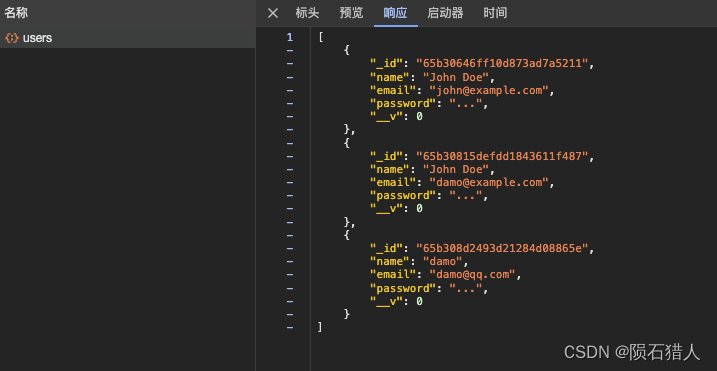
startServer();5.启动服务,在前端工程中调用接口,获取到用户数据
在服务端工程的终端下:启动服务:node server.js
前端工程调用查询: