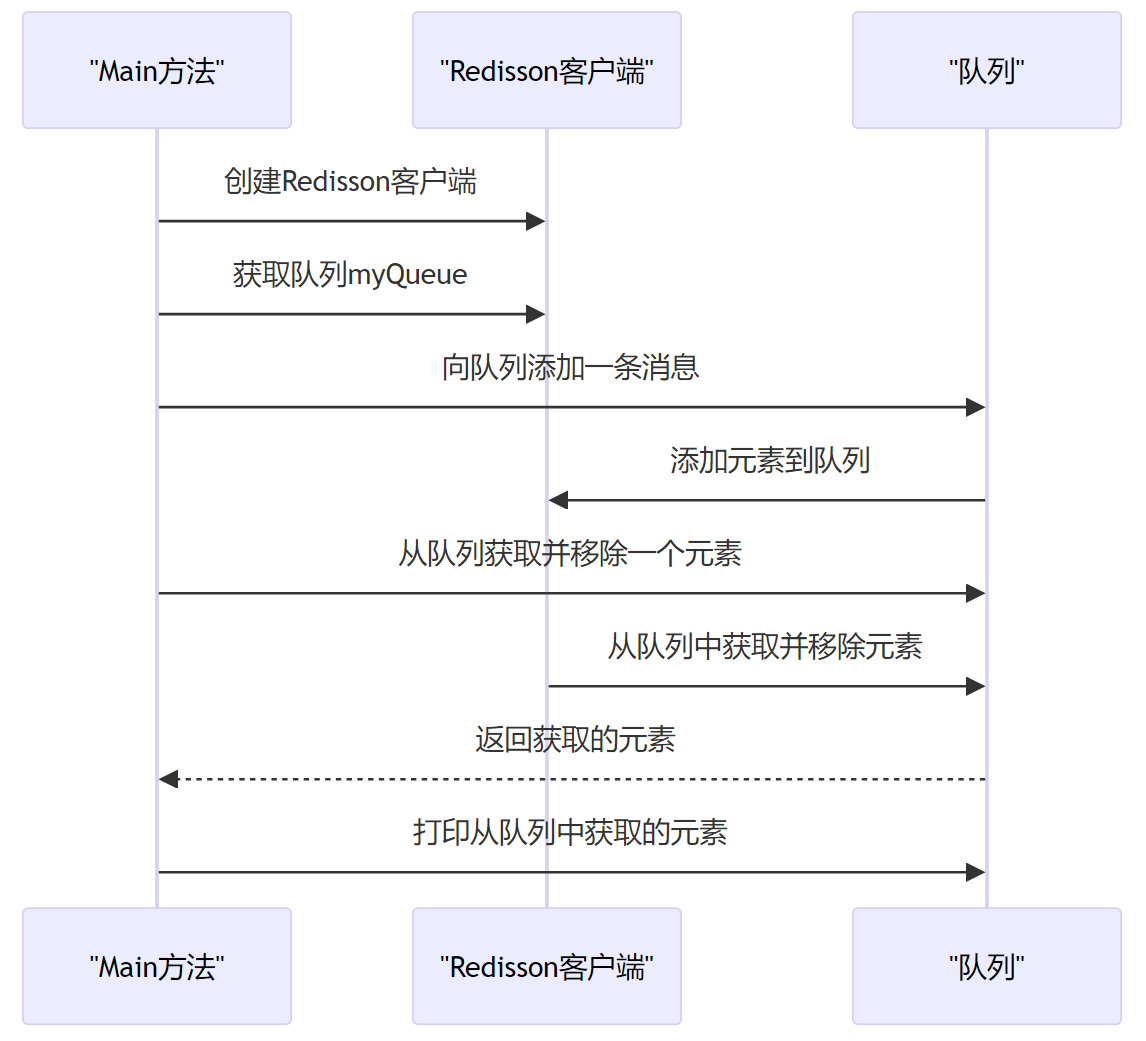
1: 定义 Use Cases 和 约束
Use cases
作用域内的Use Case
- Service 通过目录计算过去一周内最受欢迎的产品
- User 通过目录去View过去周内最受欢迎的产品
- Service 有高可用
作用域外
- 整个电商网站
- 设计组件(只是计算销售排名)
约束和假设
- Traffic 不是平均分布的
- 类目会被存进多个不同目录
- 类目不能改变目录
- 没有子目录,比如:
foo/bar/baz - 结果会被定时更新
- 更受换一个的产品或许需要更频繁的更新
- 1000 万产品
- 1000 目录
- 10 亿交易 / 月
- 1000 亿 请求 / 月
- 100:1读写比率
计算使用量
-
每个 trasnaction 的 Size
created_at- 5 bytesproduct_id- 8 bytescategory_id- 4 bytesseller_id- 8 bytesbuyer_id- 8 bytesquantity- 4 bytestotal_price- 5 bytes- Total: ~40 bytes
-
每个月有 40 GB 的新 trasnaction 内容
- 40 字节 / transaction * 10 亿 transaction / 月
- 1.44 TB 新 transaction 内容 / 3 年
- 假设大部分是新的交易,而不是更新已经存在的
- 平均 400 transaction / s
- 平均 40000 读请求 / s
便利转换指南:
- 每个月有250万秒
- 1 request / s = 250 万 请求 / 月
- 40 request / s = 1 亿请求每月
- 400 request / s = 10 亿请求每月
2:创建一个High Level设计
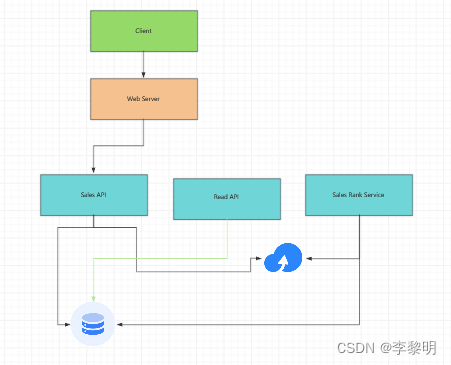
3: 设计核心组件
Use case: Service 通过category计算过去周内最受欢迎的产品
我们可以我们可以存储二进制 Sales API server的 log 文件进受管理的独享存储,比如 Amazon S3, 而不是管理我们自己的分布式文件系统
我们将假设这是一个简单的 log entry, tab delimited:
timestamp product_id category_id qty total_price seller_id buyer_id
t1 product1 category1 2 20.00 1 1
t2 product1 category2 2 20.00 2 2
t2 product1 category2 1 10.00 2 3
t3 product2 category1 3 7.00 3 4
t4 product3 category2 7 2.00 4 5
t5 product4 category1 1 5.00 5 6
Sales Rank Service 会使用 MapReduce, 使用这个 Sales API Sever的 log 文件作为输入,而且结果会被写进聚合表 sales_rank. 我们应该讨论数据库是选用SQL 还是NoSQL.
我们将使用多步骤的 MapReduce:
- Step1: 转移数据到 `(category, produce_id), sum(quantity)
- Step2: 执行分布式排序
class SalesRanker(MRJob):
def within_past_week(self, timestamp):
"""Return True if timestamp is within past week, False otherwise."""
...
def mapper(self, _ line):
"""Parse each log line, extract and transform relevant lines.
Emit key value pairs of the form:
(category1, product1), 2
(category2, product1), 2
(category2, product1), 1
(category1, product2), 3
(category2, product3), 7
(category1, product4), 1
"""
timestamp, product_id, category_id, quantity, total_price, seller_id, \
buyer_id = line.split('\t')
if self.within_past_week(timestamp):
yield (category_id, product_id), quantity
def reducer(self, key, value):
"""Sum values for each key.
(category1, product1), 2
(category2, product1), 3
(category1, product2), 3
(category2, product3), 7
(category1, product4), 1
"""
yield key, sum(values)
def mapper_sort(self, key, value):
"""Construct key to ensure proper sorting.
Transform key and value to the form:
(category1, 2), product1
(category2, 3), product1
(category1, 3), product2
(category2, 7), product3
(category1, 1), product4
The shuffle/sort step of MapReduce will then do a
distributed sort on the keys, resulting in:
(category1, 1), product4
(category1, 2), product1
(category1, 3), product2
(category2, 3), product1
(category2, 7), product3
"""
category_id, product_id = key
quantity = value
yield (category_id, quantity), product_id
def reducer_identity(self, key, value):
yield key, value
def steps(self):
"""Run the map and reduce steps."""
return [
self.mr(mapper=self.mapper,
reducer=self.reducer),
self.mr(mapper=self.mapper_sort,
reducer=self.reducer_identity),
]
这个结果将变成下面的 sorted list, 我们可以插入 sales_rank 表中:
(category1, 1), product4
(category1, 2), product1
(category1, 3), product2
(category2, 3), product1
(category2, 7), product3
sales_rank table 会有如下的结构:
id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT
category_id int NOT NULL
total_sold int NOT NULL
product_id int NOT NULL
PRIMARY KEY(id)
FOREIGN KEY(category_id) REFERENCES Categories(id)
FOREIGN KEY(product_id) REFERENCES Products(id)
我们将创建一个index在id, category_id, and product_id 上去加速查询(log 时间而不是扫描整张表)
,而且放进数据去内存。从内存中序列化的读取数据需要250微妙,当从SSD读取需要4倍,从磁盘读取需要80倍。
Use Case: User 通过目录查看过去一周内最受欢迎的产品
- Client 发送请求到Web Server
- Web Server 转发请求到 Read API server
- Read API server 从数据库表
sales_rank重读取数据
我们可以使用如下Rest API:
$ curl https://amazon.com/api/v1/popular?category_id=1234
Response:
{
"id": "100",
"category_id": "1234",
"total_sold": "100000",
"product_id": "50",
},
{
"id": "53",
"category_id": "1234",
"total_sold": "90000",
"product_id": "200",
},
{
"id": "75",
"category_id": "1234",
"total_sold": "80000",
"product_id": "3",
}
4: 扩展设计
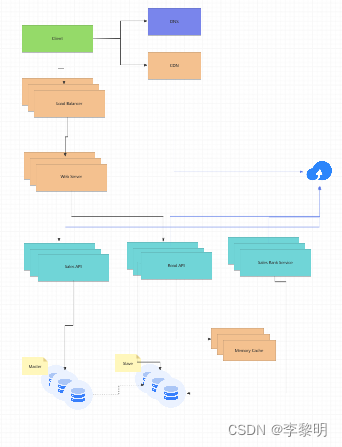
分析数据库可以使用数据仓库解决方案,如Amazon Redshift或Google BigQuery。
我们可能只想在数据库中存储有限时间段的数据,而将剩余数据存储在数据仓库或对象存储中。像亚马逊S3这样的对象存储可以轻松应对每月40 GB新内容的限制。
为了解决每秒 40,000 个平均读取请求(峰值更高),流行内容(及其销售排名)的流量应由内存缓存而不是数据库处理。内存缓存对于处理分布不均的流量和流量尖峰也很有效。由于读取量很大,SQL 读取副本可能无法处理缓存缺失。我们可能需要采用额外的 SQL 扩展模式。
对于单个SQL写主从架构来说,每秒400次平均写入(峰值更高)可能很困难,这也表明需要额外的扩展技术。