💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
💥1 概述
摘要非侵入式负载监测(NILM)是智能电网和智能家居中的一个重要课题。已经提出了许多能量分解算法来从一个聚集的信号观测中检测各种单独的设备。
然而,由于电动汽车在家充电是最近才出现的,因此很少有研究在住宅环境中对插电式电动汽车(EV)充电进行能量分解的工作。最近的研究表明,电动汽车充电对智能电网有很大影响,尤其是在夏季。因此,电动汽车充电监测已成为能源分解中一个更为重要和紧迫的缺失部分。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的方法来从聚集的实际功率信号中分解EV充电信号。所提出的方法可以有效地减轻来自空调(AC)的干扰,在存在AC电力信号的情况下实现准确的EV充电检测和能量估计。此外,所提出的算法不需要训练,需要较轻的计算负载,提供较高的估计精度,并且适用于以1/60 Hz的低采样率记录的数据。当该算法在大约一整年(总共125个月的数据)内对11所房屋记录的真实世界数据进行测试时,估计电动汽车充电能耗的平均误差为15.7 kwh/月(而电动汽车充电的真实平均能耗为208.5 kwh/),分解电动汽车充电负载信号的平均归一化均方误差为0.19。
文献来源:

📚2 运行结果
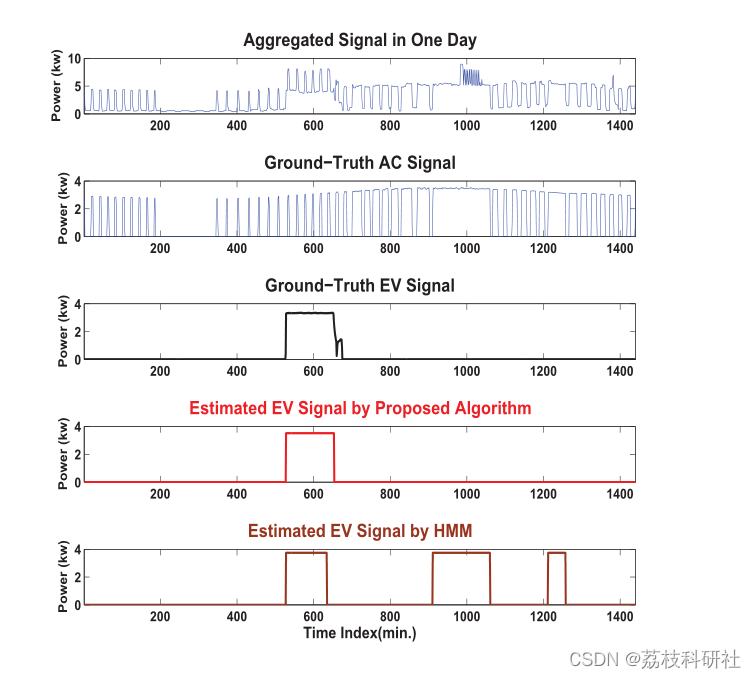

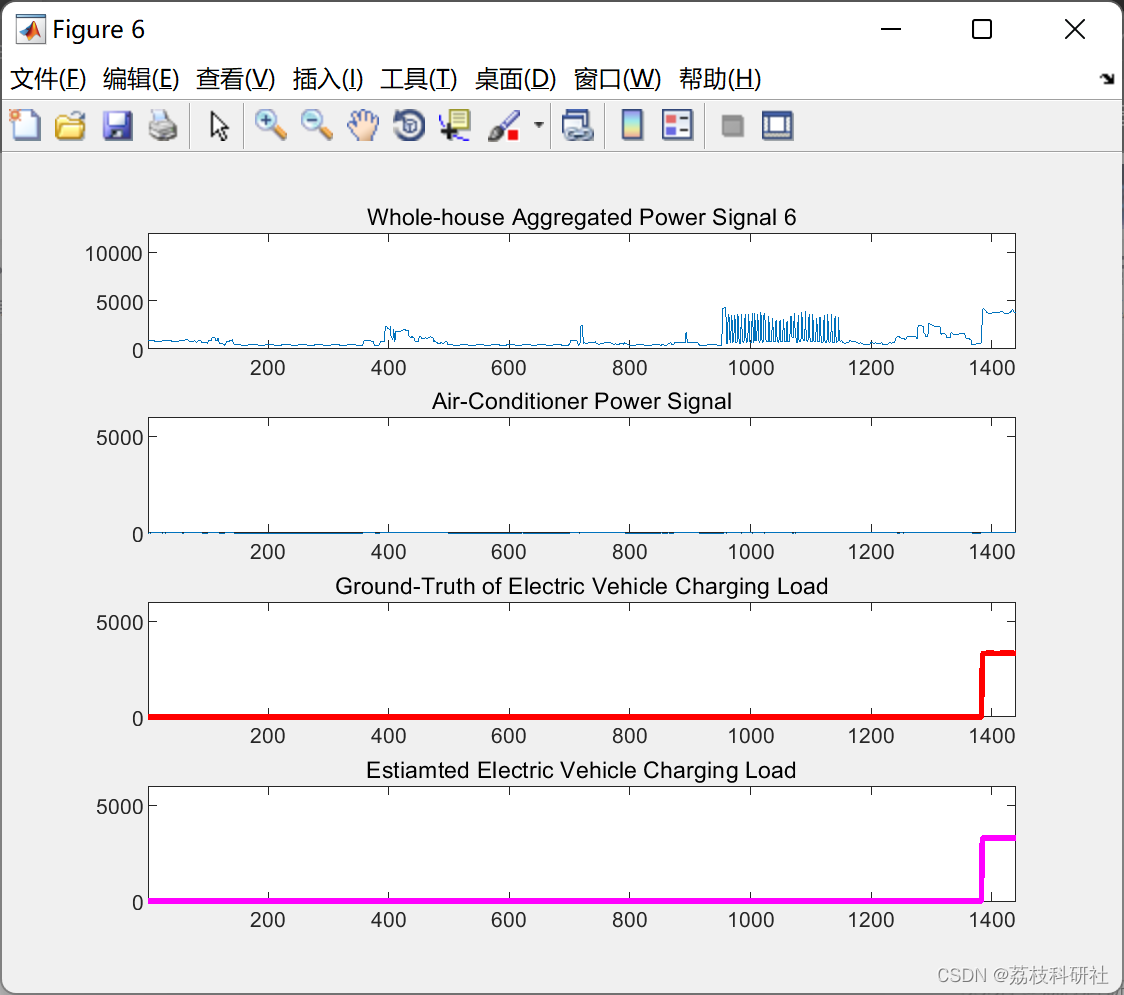
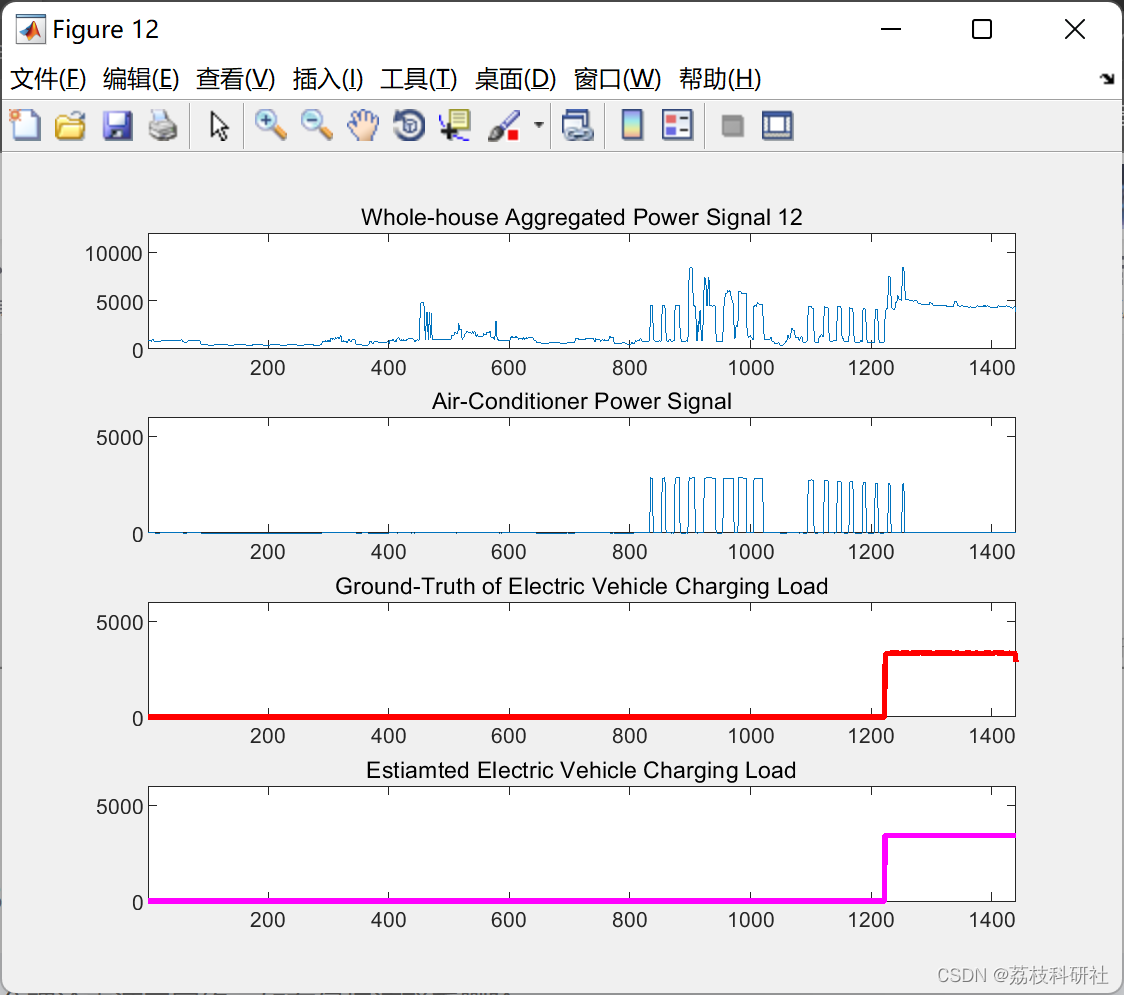
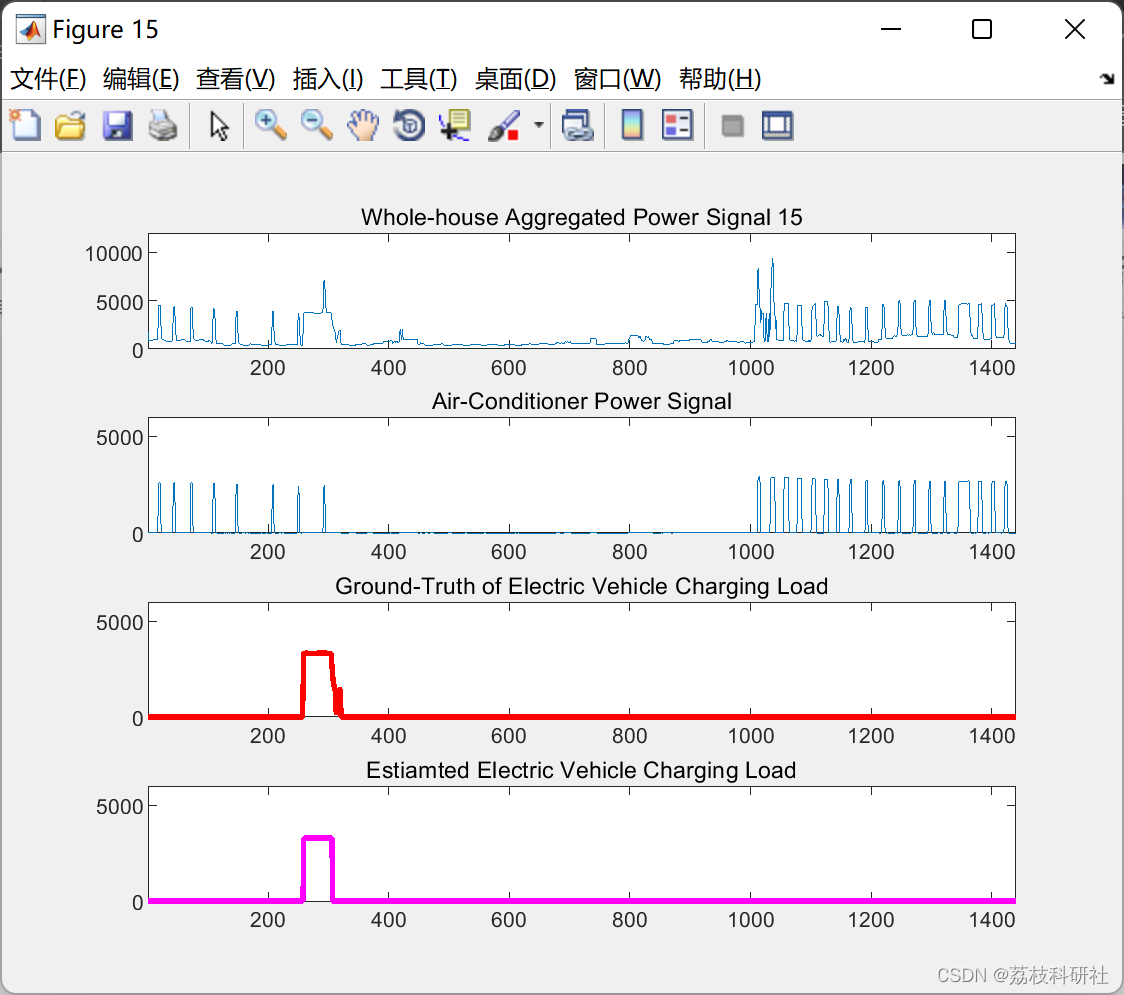
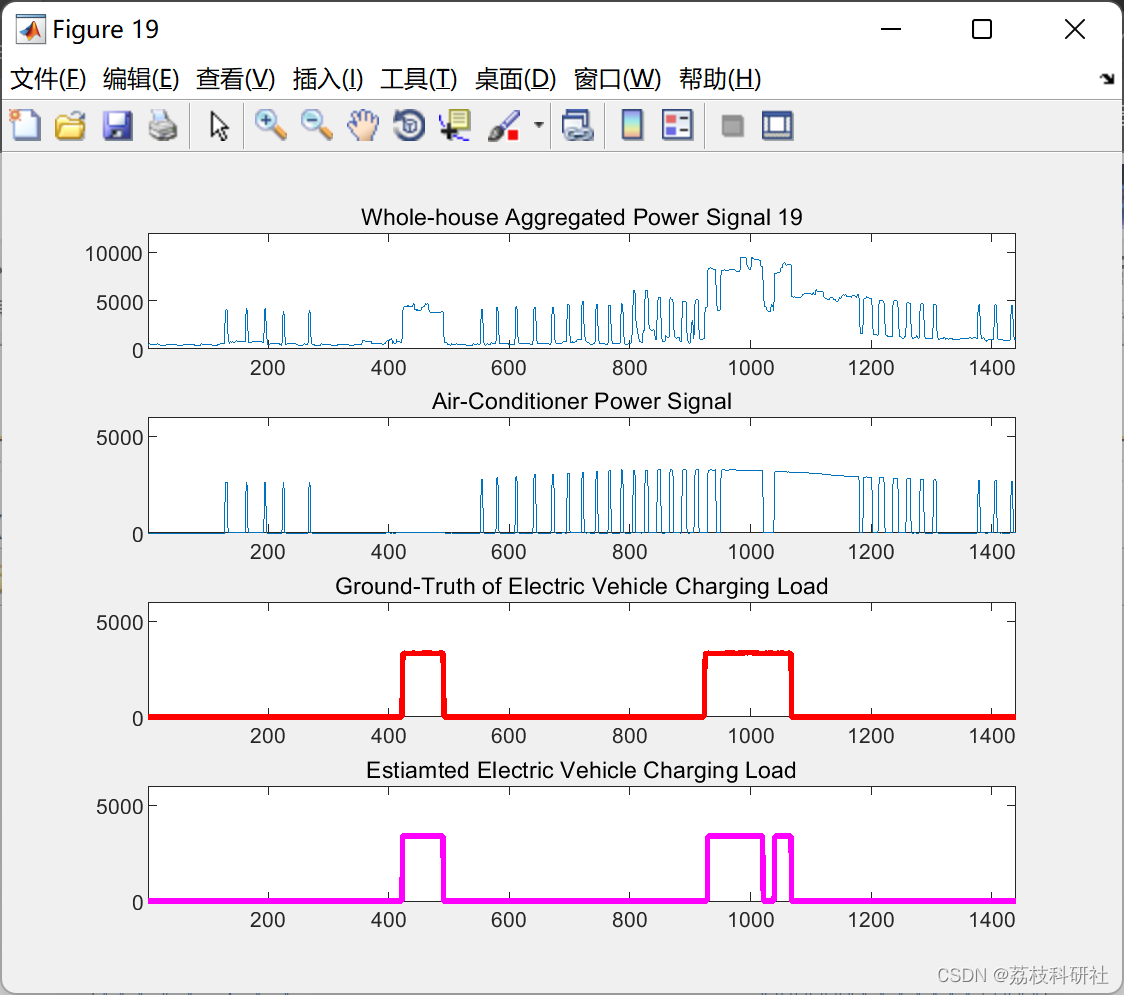
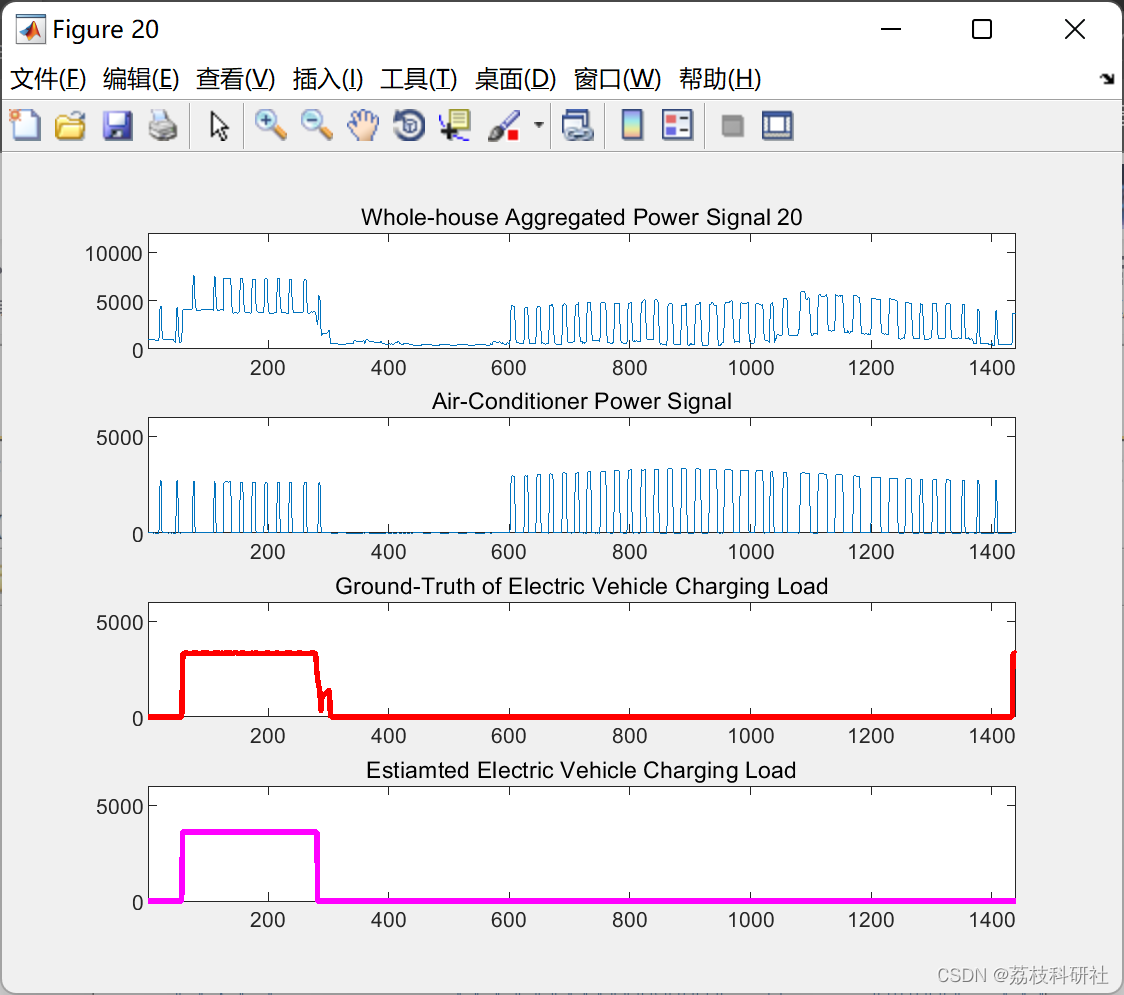
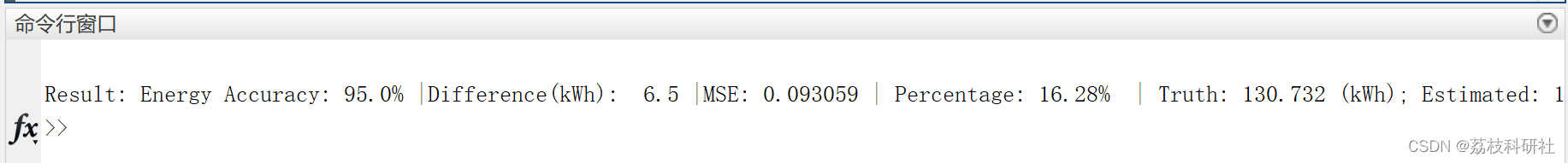
部分代码:
% Reference:
% Zhilin Zhang, Jae Hyun Son, Ying Li, Mark Trayer, Zhouyue Pi,
% Dong Yoon Hwang, Joong Ki Moon, Training-Free Non-Intrusive Load
% Monitoring of Electric Vehicle Charging with Low Sampling Rate,
% The 40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society
% (IECON 2014), Oct.29-Nov.1, 2014, Dallas, TX
if iscolumn(orgAgg), orgAgg = orgAgg'; end;
EVest = zeros(size(orgAgg));
if isempty(contextInfo.EVamplitude),
EVAMP = 3000;
else
EVAMP = contextInfo.EVamplitude;
end
% Although one day has 1440 samples, we may want to estimate current day
% plus the early morning of the next day (because EV signal can happen
% around mid-night). So, orgAgg can be a vector including samples from
% current day and the early morning of the next day. Thus DAYLEN may be
% larger than 1440. However, in this simulation, we only focus on exactly
% one day. So, the length of orgAgg is 1440.
DAYLEN = length(orgAgg);
%=====================================================================
% 1. Remove baseline noise
% This can enhance the robustness (Sometimes the baseline noise is
% very large, thus making the pre-set threshold value is not suitable).
% The baseline noise will be further removed at the end of this
% algorithm.
%=====================================================================
res = min(orgAgg);
ts = orgAgg - res;
if verbose, fprintf('\nStep 1: Removed residual noise (%f) \n',res); end;
%=====================================================================
% 2. Thresholding
%=====================================================================
% Set threshold value
% We could set 3000, since EV always has amplitude >3000 W. However, this
% value will remove many context information (such as AC spikes and lumps),
% which is useful to remove ambiguility.
THRESHOLD = 2500;
if verbose, fprintf('Step 2: Calculate threshold value: %f\n',THRESHOLD); end;
% Thresholding
EVsignal = ts;
EVsignal(EVsignal<THRESHOLD) = 0;
% Record the thresholded signal
EV_step2 = EVsignal;
% =========================================================================
% 3. Use bumpTrainFilter to remove AC spike trains
% =========================================================================
% Obtain segments with amplitude > THRESHOLD
[segment, ~] = getSegment(EVsignal);
if isempty(segment), EVest = zeros(size(ts)); return; end;
% Remove segments with short duration (basically from AC, dryer/oven, etc)
min_shrtDuration = 20;
max_duration = 90;
incrPercentage = 1;
segment_lowthr_info = bumpTrainFilter(segment, min_shrtDuration, max_duration, incrPercentage);
% Reconstruct the signal after filtering bump trains
EV_step3 = getSignal(segment_lowthr_info,EVsignal);
if isempty(EV_step3), EVest = zeros(size(ts)); return; end;
if verbose, fprintf('Step 3: Running bumpTrainFilter. \n'); end;
% =========================================================================
% 4. Fill the very short gaps between two successive segments
% =========================================================================
gapDistanceMax = 10;
[EV_step4, segment_lowthr_pit] = pitFilter(EVsignal,segment_lowthr_info,gapDistanceMax);
if verbose, fprintf('Step 4: Running pitFilter. \n'); end;
if verbose,
set(0, 'DefaultFigurePosition', [300 10 600 700]);
figure;
subplot(411); plot(ts); title('Aggregated Signal After Removal Residual');
subplot(412); plot(EV_step2); title(['Signal After Low Thresholding:',num2str(THRESHOLD)]);
subplot(413); plot(EV_step3); title('Signal After BumpTrainFilter');
subplot(414); plot(EV_step4); title('Signal After PitFilter');
end
%=====================================================================
% 5. Determine the type of each segment
%=====================================================================
newSegmentNum = size(segment_lowthr_pit,1);
heightResolution = 2;
differentiateRange = 200;
type = [];
for k = 1 : newSegmentNum
segment_study = EV_step4(segment_lowthr_pit(k,1):segment_lowthr_pit(k,2));
[type(k), temp] = findType(segment_study, heightResolution, differentiateRange);
changeAmplitude{k} = temp;
end
if verbose, fprintf('Step 5: Classify Segment Type. Type of Each Segment: \n'); disp(type); end;
%=====================================================================
% 6. Energy disaggregation
%=====================================================================
finalSegmentInfo = []; % Variable storing information of the EV segments.
% The (i,1)-th entry records the beginning
% location of the i-th segment. The (i,2)-th entry
% records the ending location of the i-th segment.
% The (i,3)-th entry records the height of the
% segment.
finalSegmentNb = 0;
for k = 1 : newSegmentNum
if verbose, fprintf('Check No.%d Segment\n',k); end;
curSegment = orgAgg(segment_lowthr_pit(k,1):segment_lowthr_pit(k,2));
% Height of curSegment including residual noise
rawHeight = getHeight(curSegment);
% Remove approximate local residual noise
avgNoiseAmplitude = localNoiseAmplitude([segment_lowthr_pit(k,1),segment_lowthr_pit(k,2)], orgAgg);
curHeight = rawHeight - avgNoiseAmplitude;
if type(k) == 0
% For this type, it is probably the dryer/oven waveforms, which has
% no sharp drop-off in signal points at some amplitude. However, we
% need to consider one rare situation, i.e. the almost completely
% overlapping of EV and dryer/oven waveforms.
if length(curSegment)<30 | length(curSegment)>300
% jump to the next segment, thus automatically remove curSegment
else
if curHeight > 5500,
% construct a square wave with height given
% by 3500 (or taking from other EV waveforms)
finalSegmentNb = finalSegmentNb + 1;
finalSegmentInfo(finalSegmentNb,:) = [segment_lowthr_pit(k,1),segment_lowthr_pit(k,2),EVAMP,type(k)];
else
% jump to the next segment, thus automatically removing curSegment
end
end
elseif type(k) == 1
% For this type, it could be a single EV waveform (with residual
% noise), an EV waveform overlapping with a narrow dryer/oven
% waveform or with one or two bumps of AC
%
if length(curSegment) > 300 | curHeight < max(EVAMP - 300, 3000)
% jump to the next segment, thus automatically removing curSegment
else
% Flag to indicate whether curSegment is EV
curSegmentEV = 1;
% If curSegmentEV locates between 12pm-10pm (720 - 1320)
curSegmentLoc1 = segment_lowthr_pit(k,1);
curSegmentLoc2 = segment_lowthr_pit(k,2);
if 1 <= curSegmentLoc1 & curSegmentLoc2 <= DAYLEN
% if surrounding segments are AC spikes, and the top layer
% of curSegment has no AC spikes (note it should be
% classified as Type 2, but sometimes when the AC spike
% number is one or two, and it may be classified as Type 1)
% Remove dryer/oven waveform around the curSegment (2 hours
% before and after curSegment)
studyArea = EVsignal( [max(1,segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)-120) : max(1,segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)-1), ...
min(DAYLEN,segment_lowthr_pit(k,2)+1): min(DAYLEN,segment_lowthr_pit(k,2)+120)] );
[studyArea_filtdryer, ~] = dryerFilter(studyArea);
[ACseg,~] = getSegment(studyArea_filtdryer);
% Remove AC spike train
min_shrtDuration_sur = 25;
max_duration_sur = min(90,max(min_shrtDuration_sur,length(curSegment)*0.6));
incrPercentage_sur = 1;
[~, rmvBumpInfo, removeFlag] = bumpTrainFilter(ACseg, min_shrtDuration_sur, max_duration_sur, incrPercentage_sur);
if removeFlag & size(rmvBumpInfo,1)> 4
% Check if the top layer of curSegment has AC spikes;
% if so, then curSegment is EV; otherwise, not EV
% get the segment information of the top layer
curSegment_topLayer = curSegment;
curSegment_topLayer(curSegment_topLayer < getHeight(curSegment)+ 1000) = 0;
% -----------------------------------------------------
% Decide if the top layer has AC spikes using autocorrelation
[ACindicator] = ACdetector(curSegment_topLayer);
if ~ACindicator
curSegmentEV = 0;
end
else
% Check if nearby segments have similar width as
% curSegment. If so, curSegment is not EV
% Find the left segment closest to curSegment
leading_loc2 = max( segment(find(segment(:,2) < segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)),2) );
if ~isempty(leading_loc2) % if leading_loc2 is empty, then curSegment is at the beginning of this day
leading_loc1 = max( segment(find(segment(:,1) < leading_loc2),1) );
leading_flag = 1;
else
leading_flag = 0;
end
% Find the right segment closest to curSegment
following_loc1 = min( segment( find(segment_lowthr_pit(k,2) < segment(:,1)),1) );
if ~isempty(following_loc1) % if following_loc1 is empty, then curSegment is at the end of this day
following_loc2 = min( segment( find( following_loc1 < segment(:,2)),2) );
following_flag = 1;
else
following_flag = 0;
end
if leading_flag & following_flag
if length(curSegment)/length(leading_loc1:leading_loc2) < 3 & (segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)-leading_loc2 <= 30) | ...
length(curSegment)/length(following_loc1:following_loc2)< 3 & (following_loc1 - segment_lowthr_pit(k,2) <= 30)
% if surrounding segments have similar width and close gaps
curSegmentEV = 0;
end
elseif leading_flag
if length(curSegment)/length(leading_loc1:leading_loc2) < 3 & (segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)-leading_loc2 <= 30)
curSegmentEV = 0;
end
elseif following_flag
if length(curSegment)/length(following_loc1:following_loc2)< 3 & (following_loc1 - segment_lowthr_pit(k,2) <= 30)
curSegmentEV = 0;
end
end
end
end
if curSegmentEV,
% construct the EV signal
finalSegmentNb = finalSegmentNb + 1;
finalSegmentInfo(finalSegmentNb,:) = [segment_lowthr_pit(k,1),segment_lowthr_pit(k,2),curHeight,type(k)];
end
end
elseif type(k) >= 2
% For this type, it could be an overlap with EV and AC (with other
% appliances). We need to determine whether the upper part
% or the bottom part is an EV waveform
% determine the up-bound and the bottom-bound of the threshold
upBound = max(curSegment)-200;
bottomBound = max( changeAmplitude{k}(1)+200, getHeight(curSegment) );
highThreshold = max(5000, changeAmplitude{k}(1)*0.4 + changeAmplitude{k}(2)*0.6);
if highThreshold <bottomBound | highThreshold > upBound
highThreshold = (bottomBound + upBound)/2;
end
topSegment = curSegment;
topSegment(topSegment<highThreshold) = 0;
[topSegmentInfo, topSegNum] = getSegment(topSegment);
% Filling pits in topSegment with very short duration
[topSegment2, topSegmentInfo2] = pitFilter(topSegment,topSegmentInfo,10);
topSegNum2 = size(topSegmentInfo2,1);
%figure(1);subplot(515); plot(topSegment2); title('Top Part After Filling Pits');
topSegmentWidthList = diff(topSegmentInfo2');
if length(curSegment) > 300
% In this situation, the bottom one is AC part, and thus the top one is EV
for tsn = 1 : topSegNum2
% If each segment of the top part is long enough, then it
% is an EV waveform
if topSegmentWidthList(tsn) > 20
% obtain current top segment associated with curSegment
segmentStudy = curSegment(topSegmentInfo2(tsn,1):topSegmentInfo2(tsn,2));
% check if it is a dryer waveform
windowLen = length(segmentStudy); % window length (used to slide the aggregated signal)
thr_crossRate = 5*windowLen/30; % thresholding for level-crossing counting (a dryer should have larger counting than this value)
incremental = 200; % value to increase the level for level-crossing counting
[dryerFlag,~] = detectDryer(segmentStudy, windowLen, thr_crossRate, incremental); % detect whether dryer exists
if ~dryerFlag % if not dryer, then reconstruct a square signal by using its width and the height
% location of beginning and the ending of the top bump in the whole aggregated signal
globalLocation = [topSegmentInfo2(tsn,1) + segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)-1, ...
topSegmentInfo2(tsn,2) + segment_lowthr_pit(k,1)-1];
% calculate the height of the bump
topHeight = getHeight( curSegment(topSegmentInfo2(tsn,1):topSegmentInfo2(tsn,2)));
% calculate the height of the bottom bump
bottomHeight = getHeight(curSegment);
% height
curHeight = topHeight - bottomHeight;
% determine if there is random flunctuation
if max(ts(globalLocation)) > 6000
if curHeight < 3500,
curHeight = 3500;
end
% record the information of the bump
finalSegmentNb = finalSegmentNb + 1;
finalSegmentInfo(finalSegmentNb,:) = [globalLocation, curHeight, type(k)];
end
end
end
end
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]Zhilin Zhang, Jae Hyun Son, Ying Li, Mark Trayer, Zhouyue Pi, Dong Yoon Hwang, Joong Ki Moon, Training-Free Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring of Electric Vehicle Charging with Low Sampling Rate, The 40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2014), Oct.29-Nov.1, 2014, Dallas, TX