JavaScript 简单类型与复杂类型
目录
- JavaScript 简单类型与复杂类型
- 1. 简单类型与复杂类型
- 2. 堆和栈
- 3. 简单类型的内存分配
- 4.复杂类型的内存分配
- 5. 简单类型传参
- 6. 复杂类型传参
- 7.下面是代码
- 1、Math对象最大值
- 2. 封装自己的数学对象
- 3. Math绝对值和三个取整方法
- 4.Math对象获取随机数的方法
- 5.Date日期对象
- 6. 格式化日期年月日和时分秒
- 7.获得Date总的毫秒数
- 8. 倒计时效果
- 9.检查是否为数组的方法
- 10.添加删除数组元素的方法
- 11. 筛选数组,排序数组
- 12. 获取数组元素索引的方法
- 13.数组去重
- 14.数组转换成为字符转
- 15.基本包装类型
- 16,根据字符返回字符串的位置
- 17.查找某个字符转出现的次数
- 18.根据字符串位置返回字符串
- 19.统计出现次数最多的字符和出现次数
- 20.字符串操作方法
学习目标:
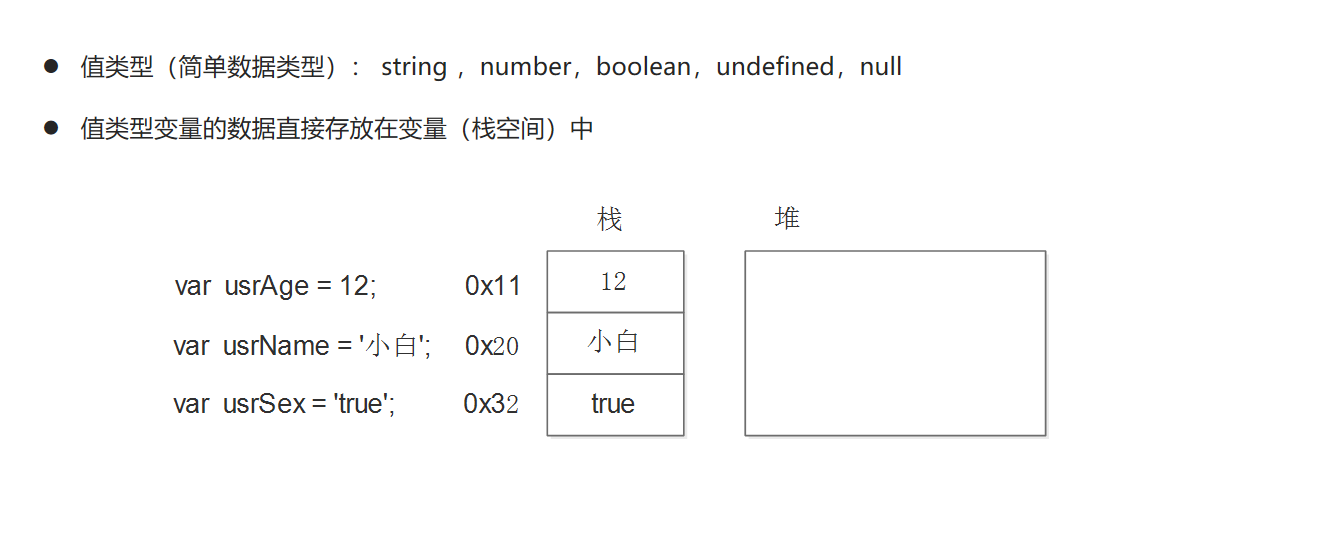
简单类型与复杂类型
堆和栈
简单类型的内存分配
复杂类型的内存分配
简单类型传参
复杂类型传参1. 简单类型与复杂类型

2. 堆和栈

3. 简单类型的内存分配
4.复杂类型的内存分配
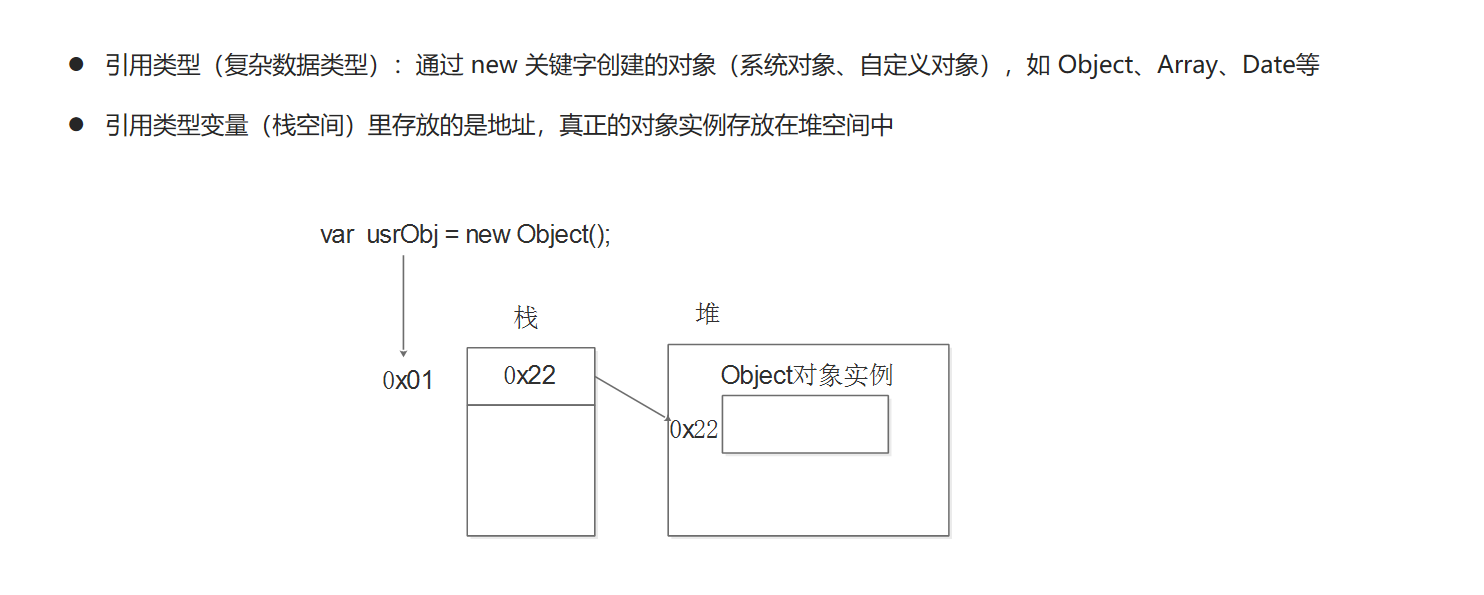
5. 简单类型传参
函数的形参也可以看做是一个变量,当我们把一个值类型变量作为参数传给函数的形参时,其实是把变量在栈空间里的值复制了一份给形参,那么在方法内部对形参做任何修改,都不会影响到的外部变量。

6. 复杂类型传参
函数的形参也可以看做是一个变量,当我们把引用类型变量传给形参时,其实是把变量在栈空间里保存的堆地址复制给了形参,形参和实参其实保存的是同一个堆地址,所以操作的是同一个对象。

7.下面是代码
1、Math对象最大值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// Math数学对象 不是一个构造函数 ,所以我们不需要new 来调用 而是直接使用里面的属性和方法即可
console.log(Math.PI); // 一个属性 圆周率
console.log(Math.max(1, 99, 3)); // 99
console.log(Math.max(-1, -10)); // -1
console.log(Math.max(1, 99, 'pink老师')); // NaN
console.log(Math.max()); // -Infinity
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>2. 封装自己的数学对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 利用对象封装自己的数学对象 里面有 PI 最大值和最小值
var myMath = {
PI: 3.141592653,
max: function() {
var max = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] > max) {
max = arguments[i];
}
}
return max;
},
min: function() {
var min = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] < min) {
min = arguments[i];
}
}
return min;
}
}
console.log(myMath.PI);
console.log(myMath.max(1, 5, 9));
console.log(myMath.min(1, 5, 9));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>3. Math绝对值和三个取整方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 1.绝对值方法
console.log(Math.abs(1)); // 1
console.log(Math.abs(-1)); // 1
console.log(Math.abs('-1')); // 隐式转换 会把字符串型 -1 转换为数字型
console.log(Math.abs('pink')); // NaN
// 2.三个取整方法
// (1) Math.floor() 地板 向下取整 往最小了取值
console.log(Math.floor(1.1)); // 1
console.log(Math.floor(1.9)); // 1
// (2) Math.ceil() ceil 天花板 向上取整 往最大了取值
console.log(Math.ceil(1.1)); // 2
console.log(Math.ceil(1.9)); // 2
// (3) Math.round() 四舍五入 其他数字都是四舍五入,但是 .5 特殊 它往大了取
console.log(Math.round(1.1)); // 1
console.log(Math.round(1.5)); // 2
console.log(Math.round(1.9)); // 2
console.log(Math.round(-1.1)); // -1
console.log(Math.round(-1.5)); // 这个结果是 -1
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>4.Math对象获取随机数的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 1.Math对象随机数方法 random() 返回一个随机的小数 0 =< x < 1
// 2. 这个方法里面不跟参数
// 3. 代码验证
console.log(Math.random());
// 4. 我们想要得到两个数之间的随机整数 并且 包含这2个整数
// Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
console.log(getRandom(1, 10));
// 5. 随机点名
var arr = ['张三', '张三丰', '张三疯子', '李四', '李思思', 'pink老师'];
// console.log(arr[0]);
console.log(arr[getRandom(0, arr.length - 1)]);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>5.Date日期对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// Date() 日期对象 是一个构造函数 必须使用new 来调用创建我们的日期对象
var arr = new Array(); // 创建一个数组对象
var obj = new Object(); // 创建了一个对象实例
// 1. 使用Date 如果没有参数 返回当前系统的当前时间
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
// 2. 参数常用的写法 数字型 2019, 10, 01 或者是 字符串型 '2019-10-1 8:8:8'
var date1 = new Date(2019, 10, 1);
console.log(date1); // 返回的是 11月 不是 10月
var date2 = new Date('2019-10-1 8:8:8');
console.log(date2);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>6. 格式化日期年月日和时分秒
/*年月日*/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 格式化日期 年月日
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.getFullYear()); // 返回当前日期的年 2019
console.log(date.getMonth() + 1); // 月份 返回的月份小1个月 记得月份+1 呦
console.log(date.getDate()); // 返回的是 几号
console.log(date.getDay()); // 3 周一返回的是 1 周六返回的是 6 但是 周日返回的是 0
// 我们写一个 2019年 5月 1日 星期三
var year = date.getFullYear();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var dates = date.getDate();
var arr = ['星期日', '星期一', '星期二', '星期三', '星期四', '星期五', '星期六'];
var day = date.getDay();
console.log('今天是:' + year + '年' + month + '月' + dates + '日 ' + arr[day]);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
/*时分秒*/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 格式化日期 时分秒
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.getHours()); // 时
console.log(date.getMinutes()); // 分
console.log(date.getSeconds()); // 秒
// 要求封装一个函数返回当前的时分秒 格式 08:08:08
function getTimer() {
var time = new Date();
var h = time.getHours();
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h;
var m = time.getMinutes();
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m;
var s = time.getSeconds();
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s;
return h + ':' + m + ':' + s;
}
console.log(getTimer());
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>7.获得Date总的毫秒数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 获得Date总的毫秒数(时间戳) 不是当前时间的毫秒数 而是距离1970年1月1号过了多少毫秒数
// 1. 通过 valueOf() getTime()
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.valueOf()); // 就是 我们现在时间 距离1970.1.1 总的毫秒数
console.log(date.getTime());
// 2. 简单的写法 (最常用的写法)
var date1 = +new Date(); // +new Date() 返回的就是总的毫秒数
console.log(date1);
// 3. H5 新增的 获得总的毫秒数
console.log(Date.now());
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>8. 倒计时效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 倒计时效果
// 1.核心算法:输入的时间减去现在的时间就是剩余的时间,即倒计时 ,但是不能拿着时分秒相减,比如 05 分减去25分,结果会是负数的。
// 2.用时间戳来做。用户输入时间总的毫秒数减去现在时间的总的毫秒数,得到的就是剩余时间的毫秒数。
// 3.把剩余时间总的毫秒数转换为天、时、分、秒 (时间戳转换为时分秒)
// 转换公式如下:
// d = parseInt(总秒数/ 60/60 /24); // 计算天数
// h = parseInt(总秒数/ 60/60 %24) // 计算小时
// m = parseInt(总秒数 /60 %60 ); // 计算分数
// s = parseInt(总秒数%60); // 计算当前秒数
function countDown(time) {
var nowTime = +new Date(); // 返回的是当前时间总的毫秒数
var inputTime = +new Date(time); // 返回的是用户输入时间总的毫秒数
var times = (inputTime - nowTime) / 1000; // times是剩余时间总的秒数
var d = parseInt(times / 60 / 60 / 24); // 天
d = d < 10 ? '0' + d : d;
var h = parseInt(times / 60 / 60 % 24); //时
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h;
var m = parseInt(times / 60 % 60); // 分
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m;
var s = parseInt(times % 60); // 当前的秒
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s;
return d + '天' + h + '时' + m + '分' + s + '秒';
}
console.log(countDown('2019-5-1 18:00:00'));
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>9.检查是否为数组的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 翻转数组
function reverse(arr) {
// if (arr instanceof Array) {
if (Array.isArray(arr)) {
var newArr = [];
for (var i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newArr[newArr.length] = arr[i];
}
return newArr;
} else {
return 'error 这个参数要求必须是数组格式 [1,2,3]'
}
}
console.log(reverse([1, 2, 3]));
console.log(reverse(1, 2, 3));
// 检测是否为数组
// (1) instanceof 运算符 它可以用来检测是否为数组
var arr = [];
var obj = {};
console.log(arr instanceof Array);
console.log(obj instanceof Array);
// (2) Array.isArray(参数); H5新增的方法 ie9以上版本支持
console.log(Array.isArray(arr));
console.log(Array.isArray(obj));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>10.添加删除数组元素的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 添加删除数组元素方法
// 1. push() 在我们数组的末尾 添加一个或者多个数组元素 push 推
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
// arr.push(4, 'pink');
console.log(arr.push(4, 'pink'));
console.log(arr);
// (1) push 是可以给数组追加新的元素
// (2) push() 参数直接写 数组元素就可以了
// (3) push完毕之后,返回的结果是 新数组的长度
// (4) 原数组也会发生变化
// 2. unshift 在我们数组的开头 添加一个或者多个数组元素
console.log(arr.unshift('red', 'purple'));
console.log(arr);
// (1) unshift是可以给数组前面追加新的元素
// (2) unshift() 参数直接写 数组元素就可以了
// (3) unshift完毕之后,返回的结果是 新数组的长度
// (4) 原数组也会发生变化
// 3. pop() 它可以删除数组的最后一个元素
console.log(arr.pop());
console.log(arr);
// (1) pop是可以删除数组的最后一个元素 记住一次只能删除一个元素
// (2) pop() 没有参数
// (3) pop完毕之后,返回的结果是 删除的那个元素
// (4) 原数组也会发生变化
// 4. shift() 它可以删除数组的第一个元素
console.log(arr.shift());
console.log(arr);
// (1) shift是可以删除数组的第一个元素 记住一次只能删除一个元素
// (2) shift() 没有参数
// (3) shift完毕之后,返回的结果是 删除的那个元素
// (4) 原数组也会发生变化
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>11. 筛选数组,排序数组
筛选
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 有一个包含工资的数组[1500, 1200, 2000, 2100, 1800],要求把数组中工资超过2000的删除,剩余的放到新数组里面
var arr = [1500, 1200, 2000, 2100, 1800];
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < 2000) {
// newArr[newArr.length] = arr[i];
newArr.push(arr[i]);
}
}
console.log(newArr);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
排序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 数组排序
// 1. 翻转数组
var arr = ['pink', 'red', 'blue'];
arr.reverse();
console.log(arr);
// 2. 数组排序(冒泡排序)
var arr1 = [13, 4, 77, 1, 7];
arr1.sort(function(a, b) {
// return a - b; 升序的顺序排列
return b - a; // 降序的顺序排列
});
console.log(arr1);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>12. 获取数组元素索引的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 返回数组元素索引号方法 indexOf(数组元素) 作用就是返回该数组元素的索引号 从前面开始查找
// 它只返回第一个满足条件的索引号
// 它如果在该数组里面找不到元素,则返回的是 -1
// var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink', 'blue'];
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'pink'];
console.log(arr.indexOf('blue'));
// 返回数组元素索引号方法 lastIndexOf(数组元素) 作用就是返回该数组元素的索引号 从后面开始查找
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink', 'blue'];
console.log(arr.lastIndexOf('blue')); // 4
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>13.数组去重
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 数组去重 ['c', 'a', 'z', 'a', 'x', 'a', 'x', 'c', 'b'] 要求去除数组中重复的元素。
// 1.目标: 把旧数组里面不重复的元素选取出来放到新数组中, 重复的元素只保留一个, 放到新数组中去重。
// 2.核心算法: 我们遍历旧数组, 然后拿着旧数组元素去查询新数组, 如果该元素在新数组里面没有出现过, 我们就添加, 否则不添加。
// 3.我们怎么知道该元素没有存在? 利用 新数组.indexOf(数组元素) 如果返回时 - 1 就说明 新数组里面没有改元素
// 封装一个 去重的函数 unique 独一无二的
function unique(arr) {
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (newArr.indexOf(arr[i]) === -1) {
newArr.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return newArr;
}
// var demo = unique(['c', 'a', 'z', 'a', 'x', 'a', 'x', 'c', 'b'])
var demo = unique(['blue', 'green', 'blue'])
console.log(demo);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>14.数组转换成为字符转
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 数组转换为字符串
// 1. toString() 将我们的数组转换为字符串
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(arr.toString()); // 1,2,3
// 2. join(分隔符)
var arr1 = ['green', 'blue', 'pink'];
console.log(arr1.join()); // green,blue,pink
console.log(arr1.join('-')); // green-blue-pink
console.log(arr1.join('&')); // green&blue&pink
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>15.基本包装类型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 基本包装类型
var str = 'andy';
console.log(str.length);
// 对象 才有 属性和方法 复杂数据类型才有 属性和方法
// 简单数据类型为什么会有length 属性呢?
// 基本包装类型: 就是把简单数据类型 包装成为了 复杂数据类型
// (1) 把简单数据类型包装为复杂数据类型
var temp = new String('andy');
// (2) 把临时变量的值 给 str
str = temp;
// (3) 销毁这个临时变量
temp = null;
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>16,根据字符返回字符串的位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 字符串对象 根据字符返回位置 str.indexOf('要查找的字符', [起始的位置])
var str = '改革春风吹满地,春天来了';
console.log(str.indexOf('春'));
console.log(str.indexOf('春', 3)); // 从索引号是 3的位置开始往后查找
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>17.查找某个字符转出现的次数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 查找字符串"abcoefoxyozzopp"中所有o出现的位置以及次数
// 核心算法:先查找第一个o出现的位置
// 然后 只要indexOf 返回的结果不是 -1 就继续往后查找
// 因为indexOf 只能查找到第一个,所以后面的查找,一定是当前索引加1,从而继续查找
var str = "oabcoefoxyozzopp";
var index = str.indexOf('o');
var num = 0;
// console.log(index);
while (index !== -1) {
console.log(index);
num++;
index = str.indexOf('o', index + 1);
}
console.log('o出现的次数是: ' + num);
// 课后作业 ['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'pink','red'], 求 red 出现的位置和次数
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>18.根据字符串位置返回字符串
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 根据位置返回字符
// 1. charAt(index) 根据位置返回字符
var str = 'andy';
console.log(str.charAt(3));
// 遍历所有的字符
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
console.log(str.charAt(i));
}
// 2. charCodeAt(index) 返回相应索引号的字符ASCII值 目的: 判断用户按下了那个键
console.log(str.charCodeAt(0)); // 97
// 3. str[index] H5 新增的
console.log(str[0]); // a
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>19.统计出现次数最多的字符和出现次数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 有一个对象 来判断是否有该属性 对象['属性名']
var o = {
age: 18
}
if (o['sex']) {
console.log('里面有该属性');
} else {
console.log('没有该属性');
}
// 判断一个字符串 'abcoefoxyozzopp' 中出现次数最多的字符,并统计其次数。
// o.a = 1
// o.b = 1
// o.c = 1
// o.o = 4
// 核心算法:利用 charAt() 遍历这个字符串
// 把每个字符都存储给对象, 如果对象没有该属性,就为1,如果存在了就 +1
// 遍历对象,得到最大值和该字符
var str = 'abcoefoxyozzopp';
var o = {};
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
var chars = str.charAt(i); // chars 是 字符串的每一个字符
if (o[chars]) { // o[chars] 得到的是属性值
o[chars]++;
} else {
o[chars] = 1;
}
}
console.log(o);
// 2. 遍历对象
var max = 0;
var ch = '';
for (var k in o) {
// k 得到是 属性名
// o[k] 得到的是属性值
if (o[k] > max) {
max = o[k];
ch = k;
}
}
console.log(max);
console.log('最多的字符是' + ch);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>20.字符串操作方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 字符串操作方法
// 1. concat('字符串1','字符串2'....)
var str = 'andy';
console.log(str.concat('red'));
// 2. substr('截取的起始位置', '截取几个字符');
var str1 = '改革春风吹满地';
console.log(str1.substr(2, 2)); // 第一个2 是索引号的2 从第几个开始 第二个2 是取几个字符
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
其他方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// 1. 替换字符 replace('被替换的字符', '替换为的字符') 它只会替换第一个字符
var str = 'andyandy';
console.log(str.replace('a', 'b'));
// 有一个字符串 'abcoefoxyozzopp' 要求把里面所有的 o 替换为 *
var str1 = 'abcoefoxyozzopp';
while (str1.indexOf('o') !== -1) {
str1 = str1.replace('o', '*');
}
console.log(str1);
// 2. 字符转换为数组 split('分隔符') 前面我们学过 join 把数组转换为字符串
var str2 = 'red, pink, blue';
console.log(str2.split(','));
var str3 = 'red&pink&blue';
console.log(str3.split('&'));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>